Forums
- Forums
- Duggy's Reference Hangar
- USAAF / USN Library
- 332nd Fighter Group
332nd Fighter Group
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
-
9 years agoSun Mar 26 2023, 10:21amDuggy
 Main AdminThe Mustang pilot spotted the string of Bf-109's heading toward the crippled B-24. The pilot, a Lt. Weathers, dropped his wing tanks, and turned into the German formation. He gave the leader a burst with his .50 calibers and it nosed up, smoking, and soon went hurtling down to the ground. The pilot radioed the others in his flight and heard "I'm right behind you."
Main AdminThe Mustang pilot spotted the string of Bf-109's heading toward the crippled B-24. The pilot, a Lt. Weathers, dropped his wing tanks, and turned into the German formation. He gave the leader a burst with his .50 calibers and it nosed up, smoking, and soon went hurtling down to the ground. The pilot radioed the others in his flight and heard "I'm right behind you."
But when Weathers looked back for himself, all he could see was the nose cannon of another Bf-109, pointing right at him. He dropped flaps and chopped throttle, instantly slowing his Mustang, and the Bf-109 overran him. A few bursts, and Lt. Weathers had his second kill of the day. Two more e/a were still in view and seemed like easy pickings, but the voice of the Group CO echoed in the pilot's mind, "Your job is to protect the bombers and not chase enemy aircraft for personal glory." Weathers returned to the bomber.
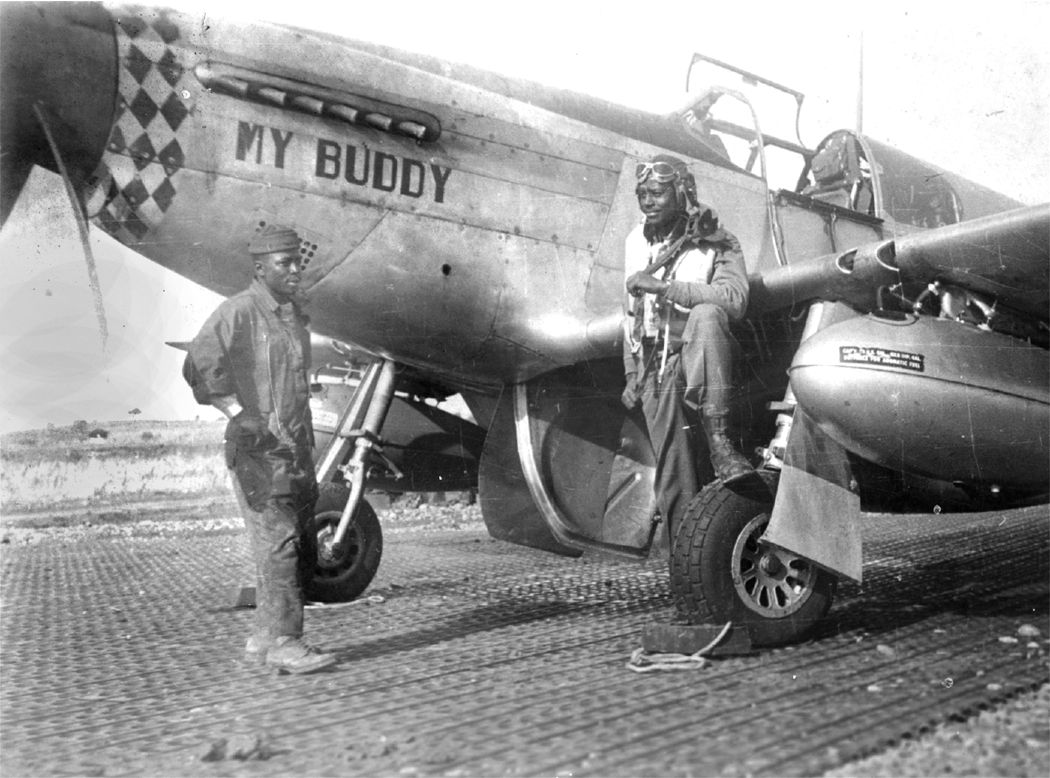
Two things were unusual about this American fighter pilot. First, he had foregone a sure kill. Second, he was Black. He flew with the 332nd Fighter Group, "The Redtails," the famous all-Black outfit that fought both American prejudice and Nazi militarism. Under the leadership and iron discipline of Col. Benjamin O. Davis, the Redtails had learned that their mission in life was to protect the bombers.
Prior to World War Two, the U.S. Army Air Corps did not employ Negroes (the respectful term in that era) in any role, a policy which found its justification in a racist and inaccurate report written in the 1920s. However in 1940, President Franklin D. Roosevelt ordered the Air Corps to build an all-Negro flying unit. The presidential order caused the Army to create the 99th Pursuit Squadron. To develop the Negro pilots needed for the new squadron, the Air Corps opened a new training base in central Alabama, at the Tuskegee Institute.
The Tuskegee Airmen is the popular name of a group of African-American military pilots (fighter and bomber) who fought in World War II. Officially, they formed the 332nd Fighter Group and the 477th Bombardment Group of the United States Army Air Forces. The name also applies to the navigators, bombardiers, mechanics, instructors, crew chiefs, nurses, cooks and other support personnel for the pilots.
The Tuskegee Airmen were the first African-American military aviators in the United States Armed Forces. During World War II, black Americans in many U.S. states were still subject to the Jim Crow laws and the American military was racially segregated, as was much of the federal government. The Tuskegee Airmen were subjected to discrimination, both within and outside the army. All black military pilots who trained in the United States trained at Moton Field, the Tuskegee Army Air Field, and were educated at Tuskegee University, located near Tuskegee, Alabama; the group included five Haitians from the Haitian Air Force (Alix Pasquet, Raymond Cassagnol, Pelissier Nicolas, Ludovic Audant, and Eberle Guilbaud). There was also one pilot from Port of Spain, Trinidad, Eugene Theodore.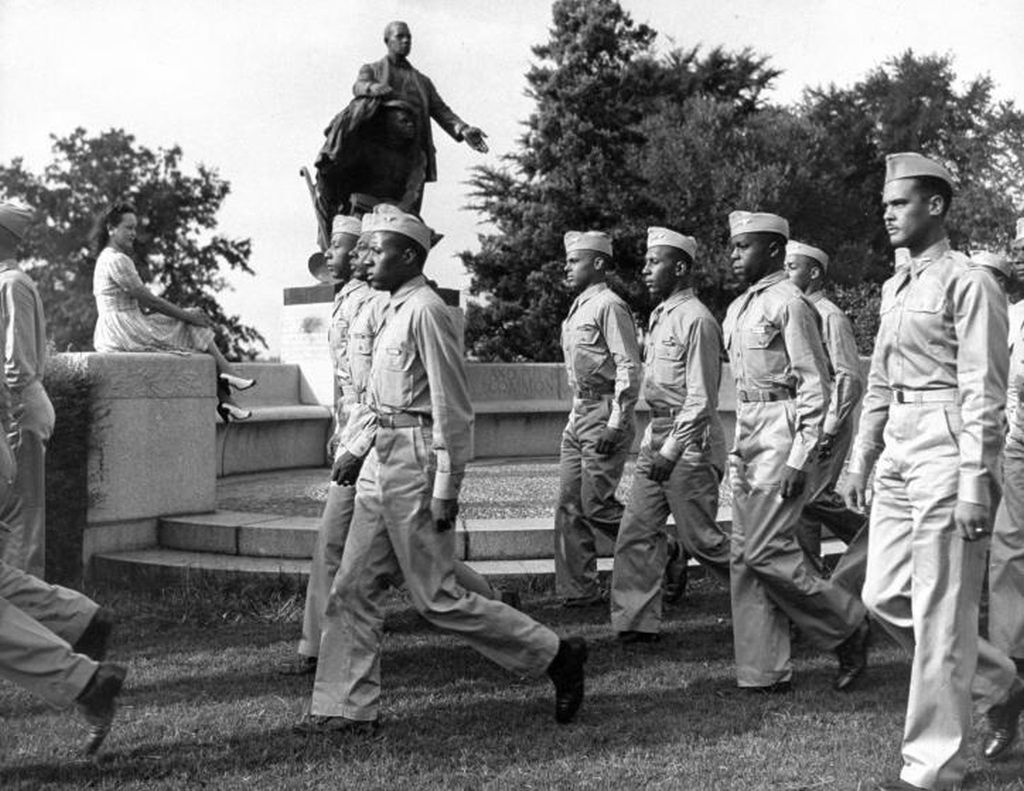
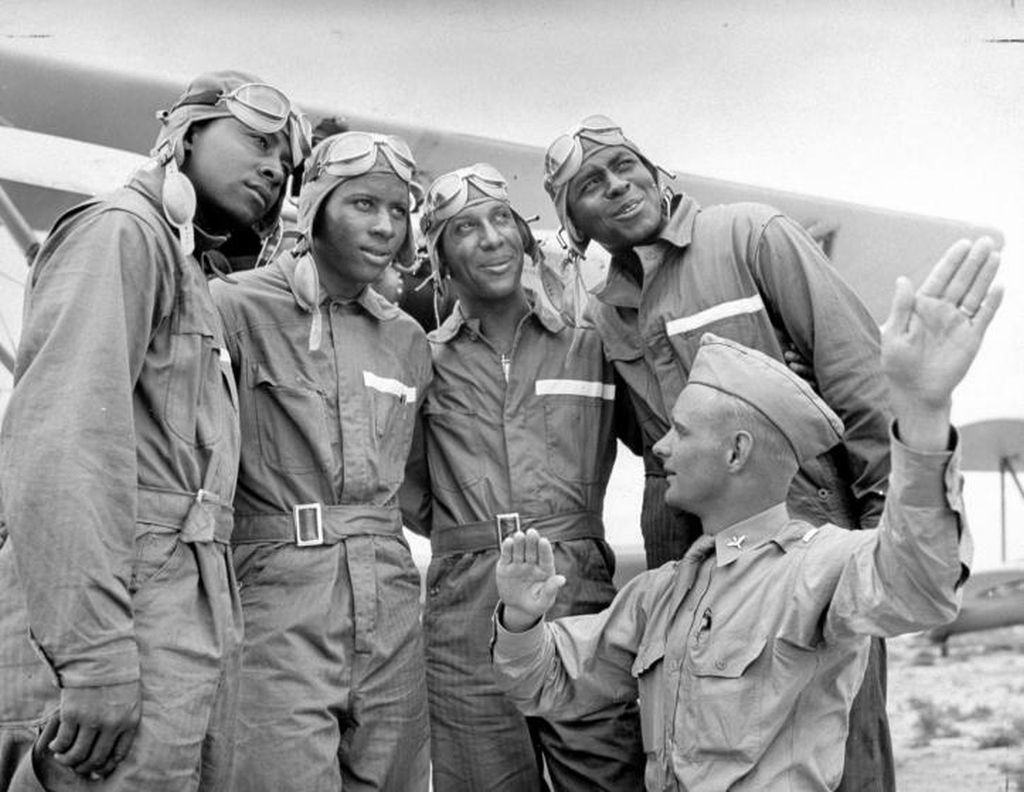
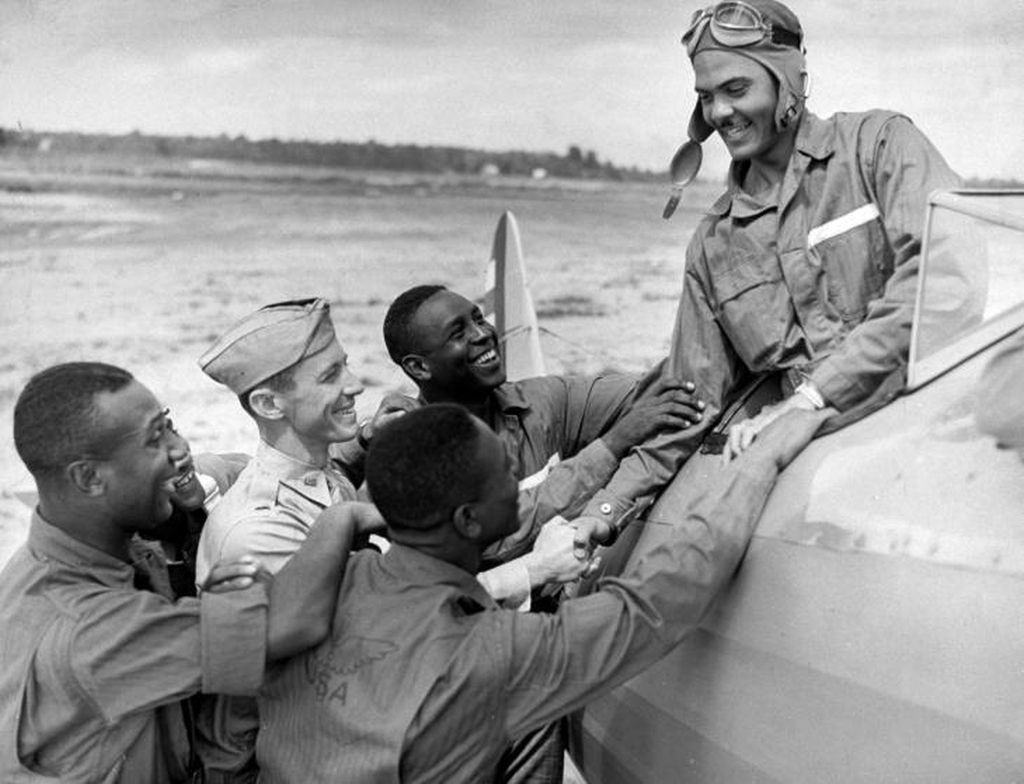
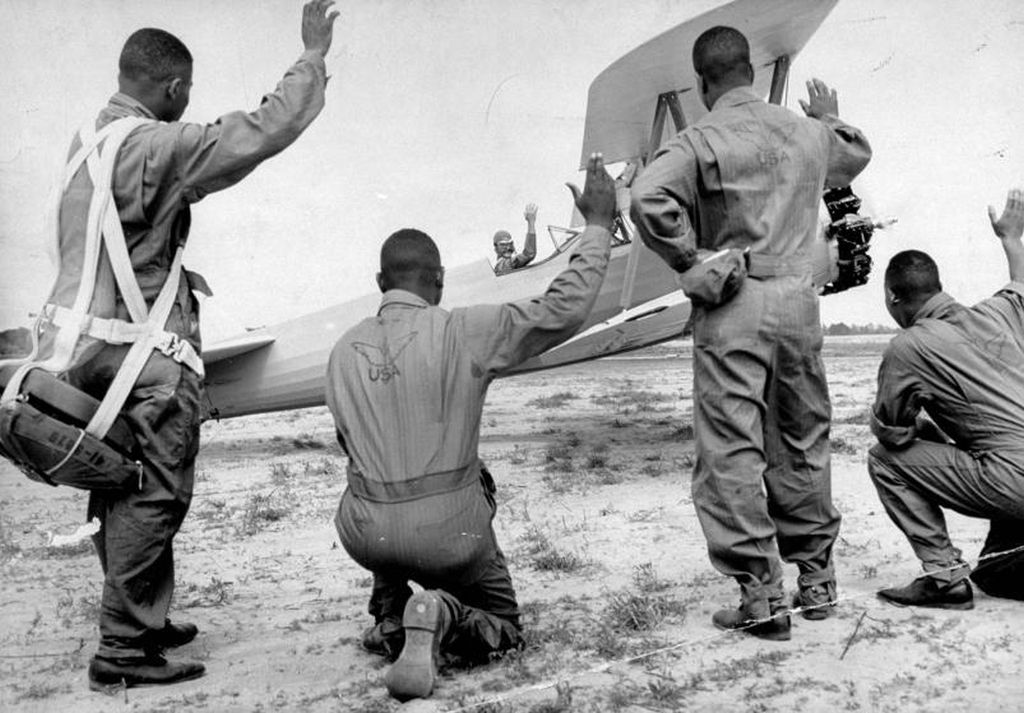
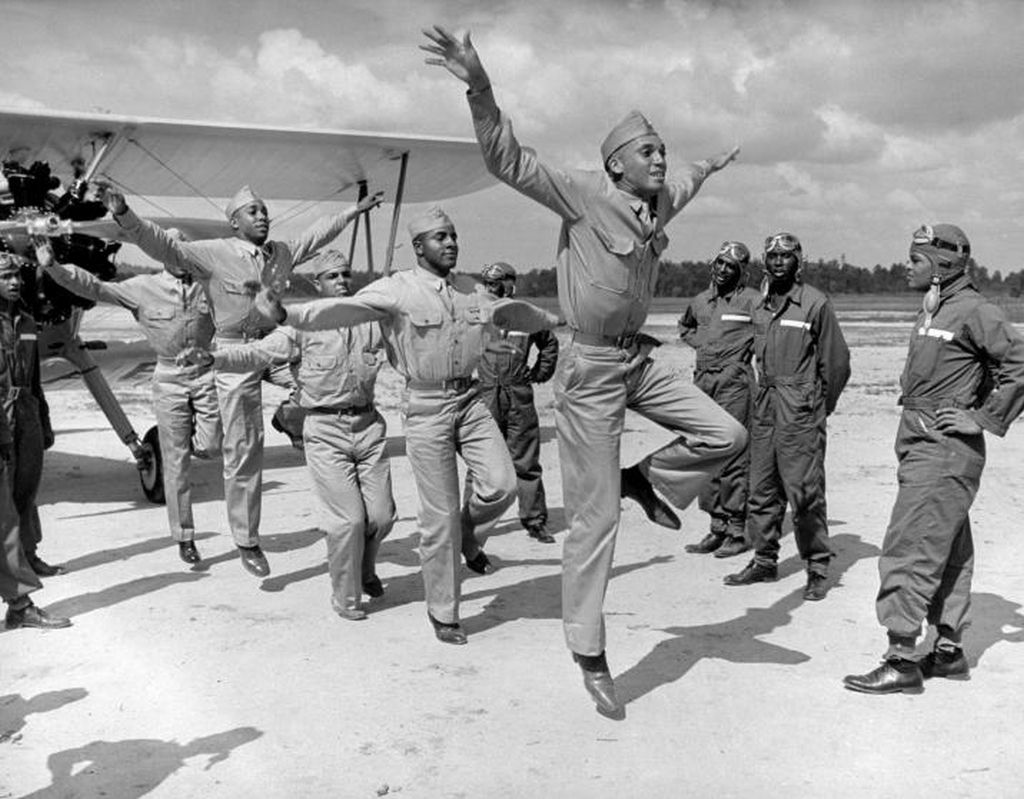
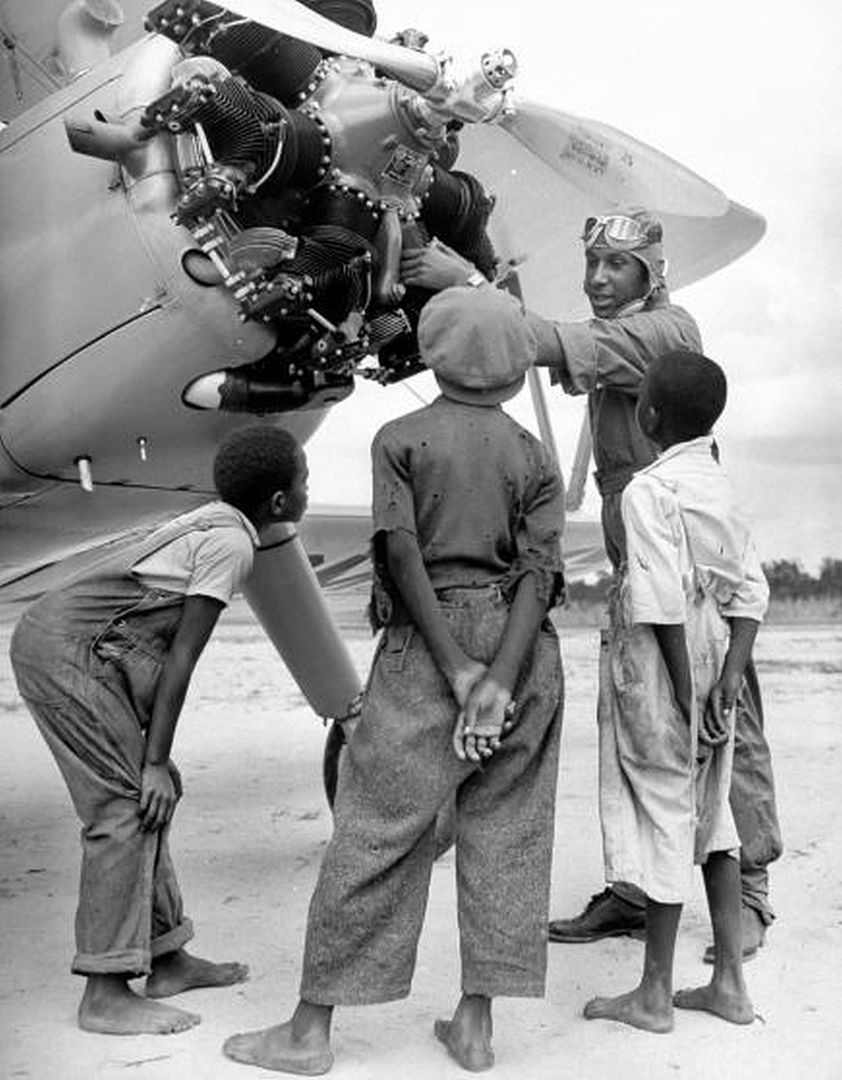
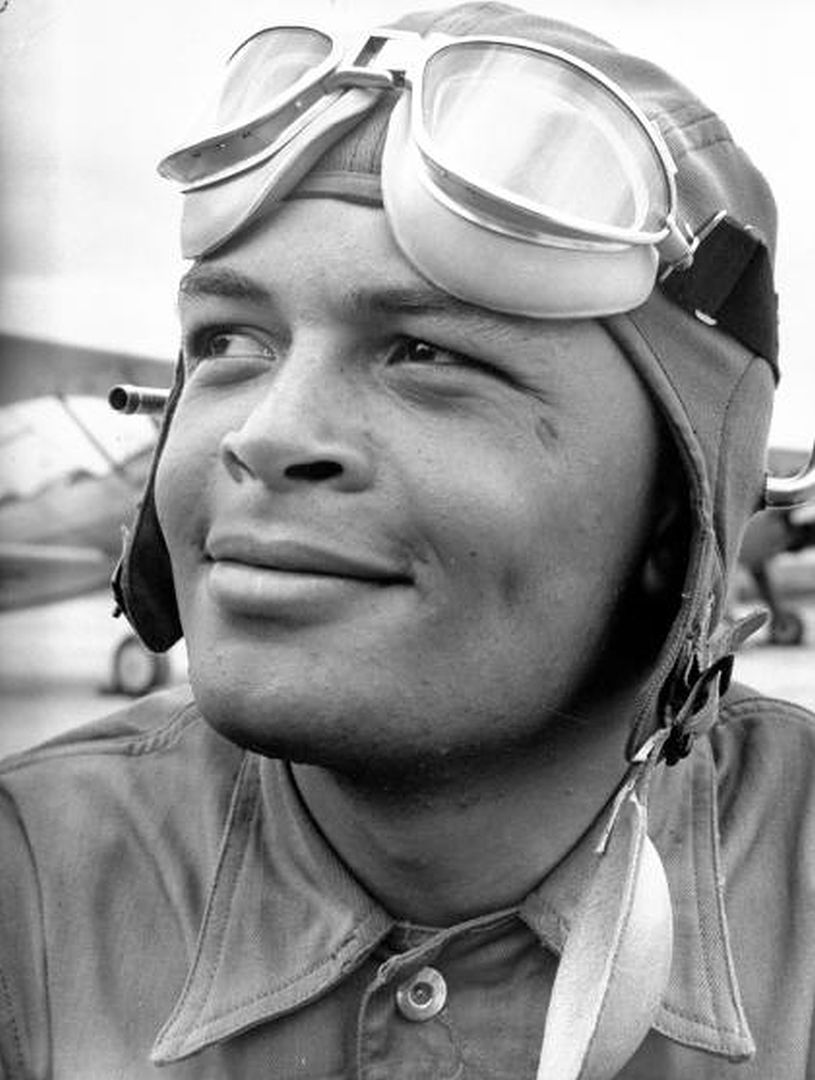
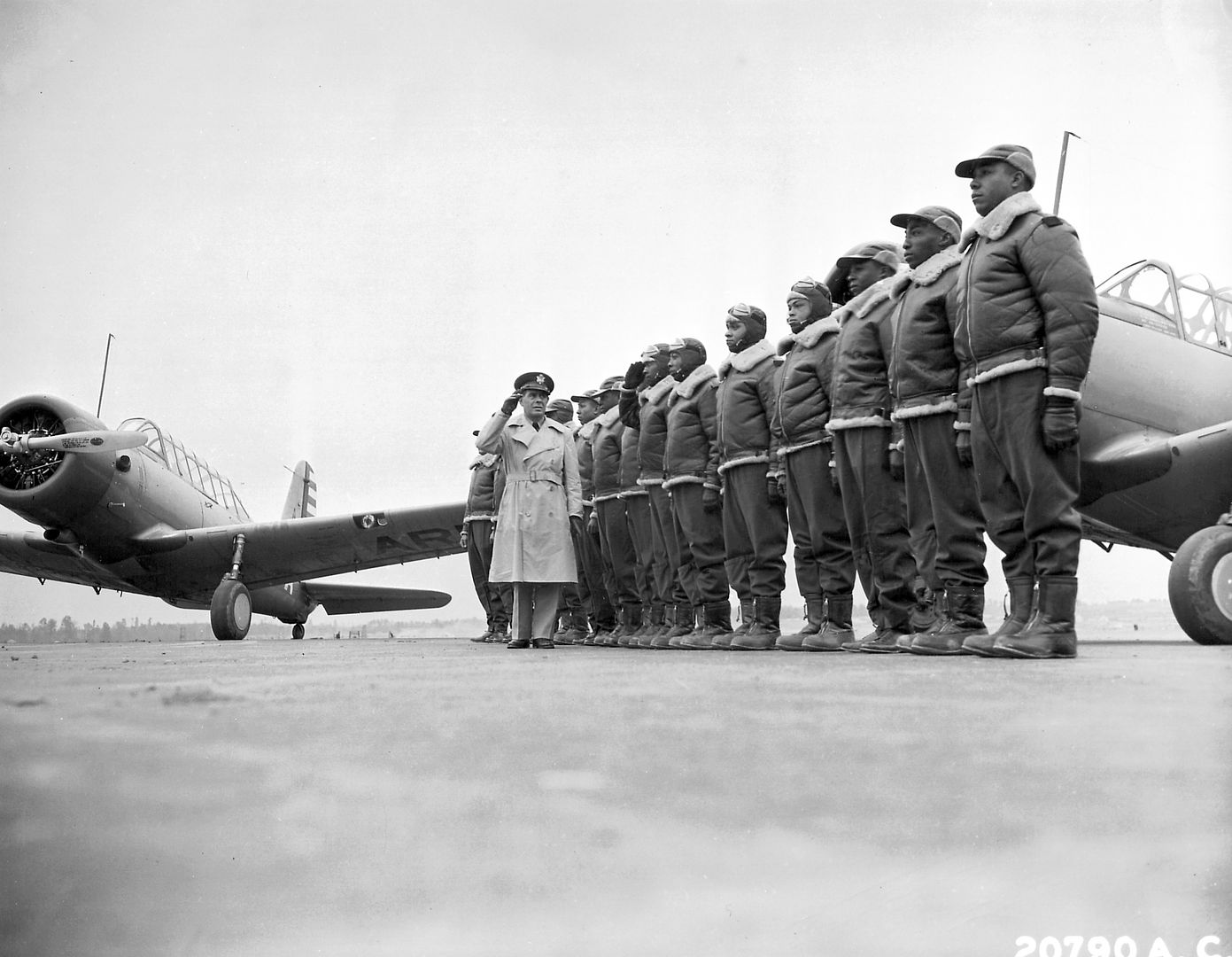
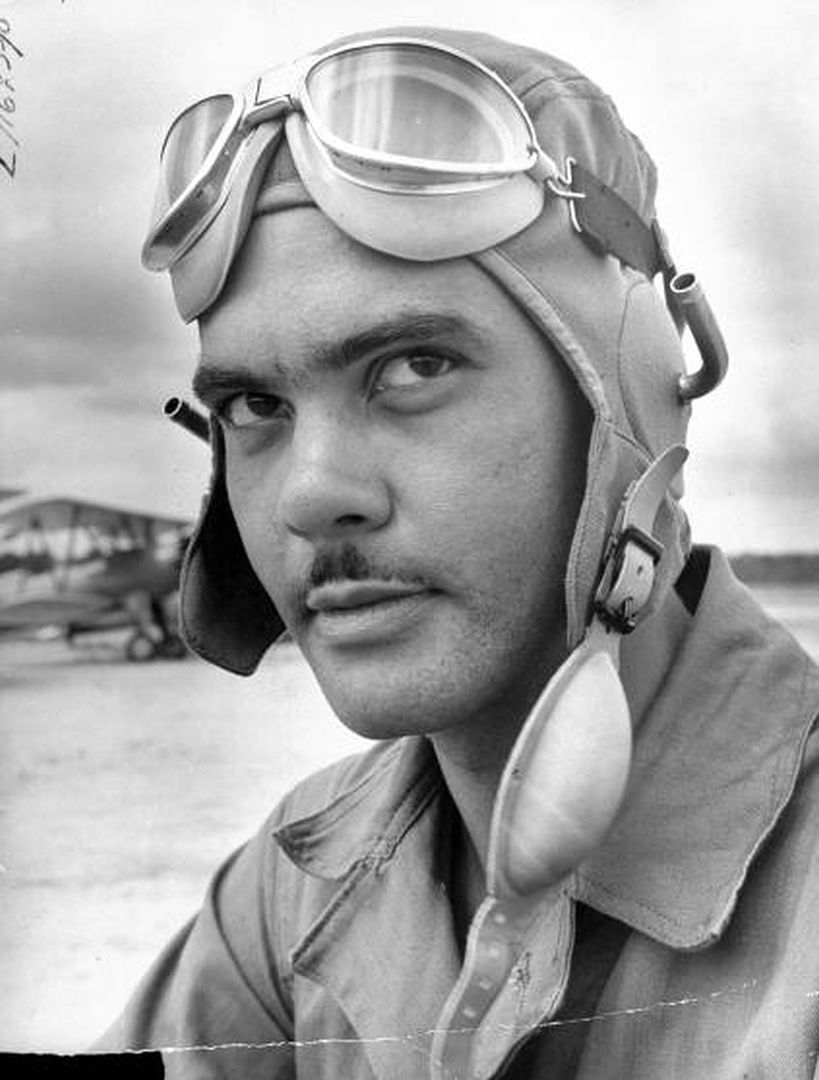
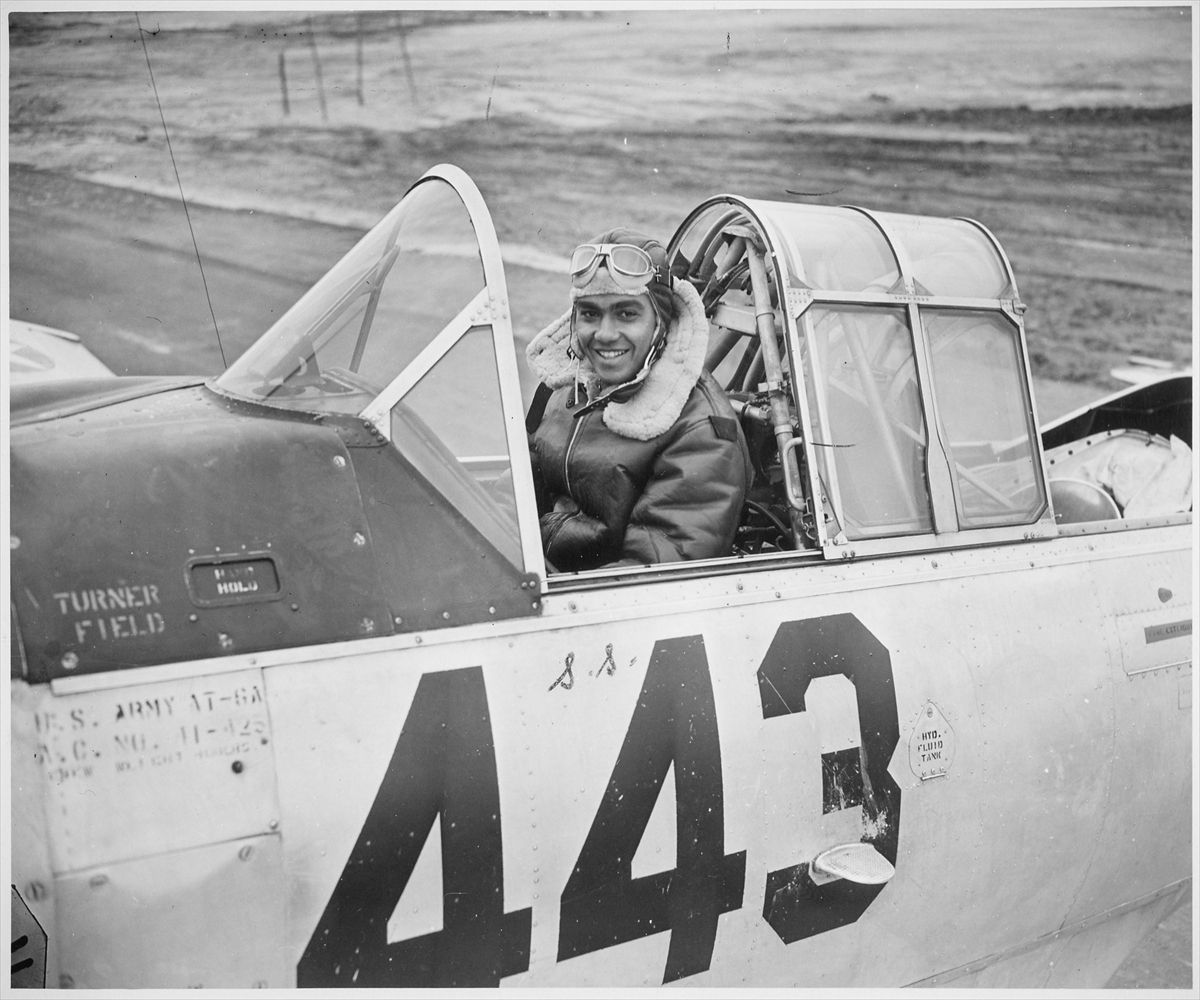
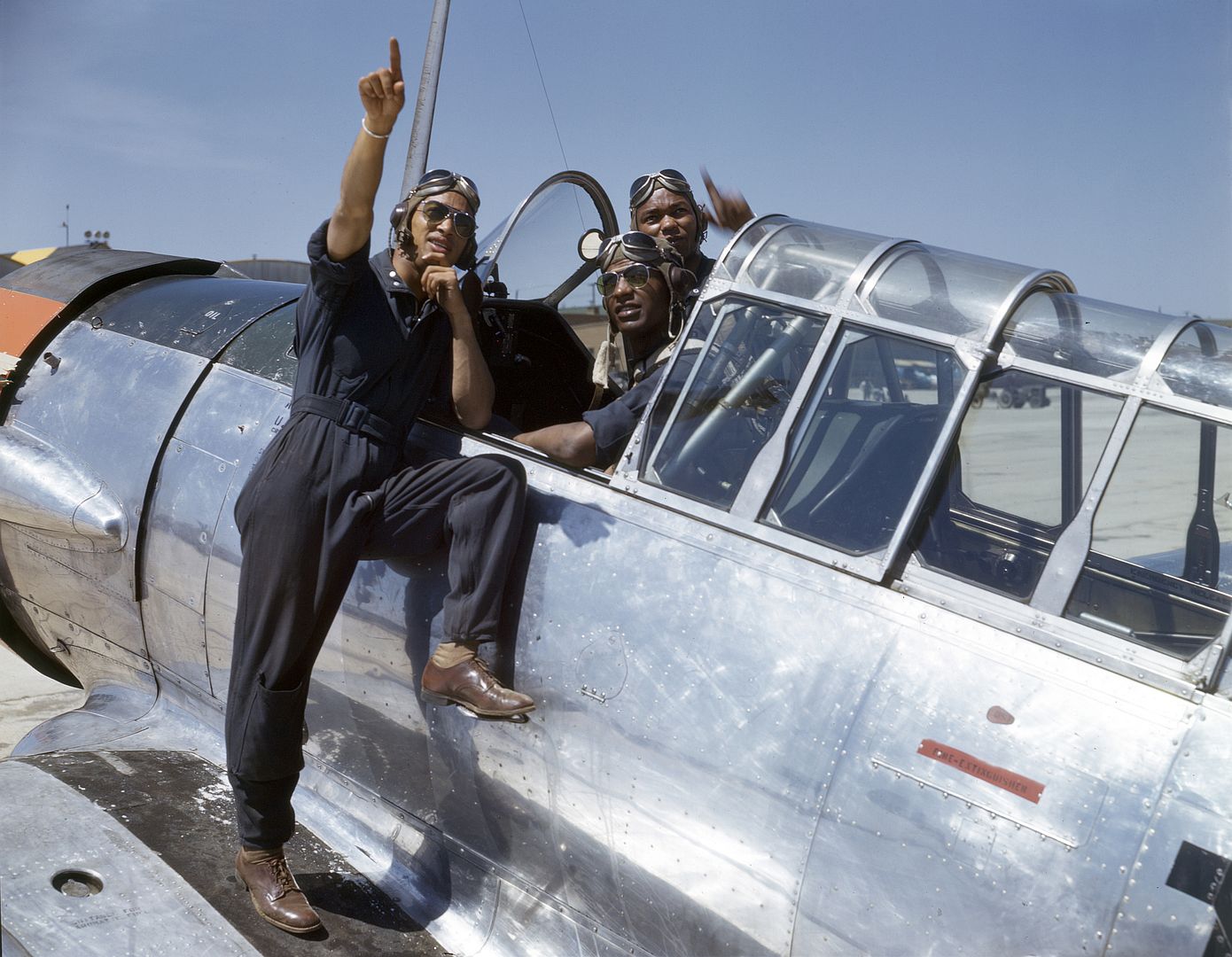











Mrs. Roosevelt Goes for a Ride
March 29, 1941 - Mrs. Eleanor Roosevelt visited Tuskegee and met Charles "Chief" Anderson, the head of the program, Mrs. Roosevelt asked, "Can Negroes really fly airplanes?" He replied: "Certainly we can; as a matter of fact, would you like to take an airplane ride?" Over the objections of her Secret Service agents, Mrs. Roosevelt accepted. The agent called President Roosevelt, who replied, "Well, if she wants to do it, there's nothing we can do to stop her."
With Mrs. Roosevelt in the back seat of his Piper J-3 Cub, Chief Anderson took off and flew her around for half an hour. Upon landing, Mrs. Roosevelt turned to the Chief and said, "I guess Negroes can fly," and they posed together for an historic photo. Not long after Mrs. Roosevelt's return to Washington, it was announced that the first Negro Air Corps pilots would be trained at Tuskegee Institute.
Some sources report the date of Mrs. Roosevelt's flight as April 19. But the 29 March date is based on Alabama newspaper microfilm from that period and correspondence with an archivist (Bob Clark) at the FDR presidential library in Hyde Park, NY.
Stories in two Alabama newspapers -- the Montgomery Advertiser and the Birmingham News -- place Mrs. Roosevelt in Tuskegee, Alabama, on Friday/Saturday, 28-29 March 1941, where she attended a trustee's meeting of the Julius Rosenwald Fund. A newspaper column written by Mrs. Roosevelt, dated 1 April 1941, refers to the previous Saturday (29 March) and her impromptu flight.
Oddly enough, Mrs. Roosevelt's now famous flight did not generate much notice at the time. Most big papers, including the New York Times and the Atlanta Constitution made no mention of her flight in March and April of 1941. The Montgomery Advertiser is the closest daily to Tuskegee, and it did not report the flight, but it did have a couple of stories about Mrs. Roosevelt being in Tuskegee.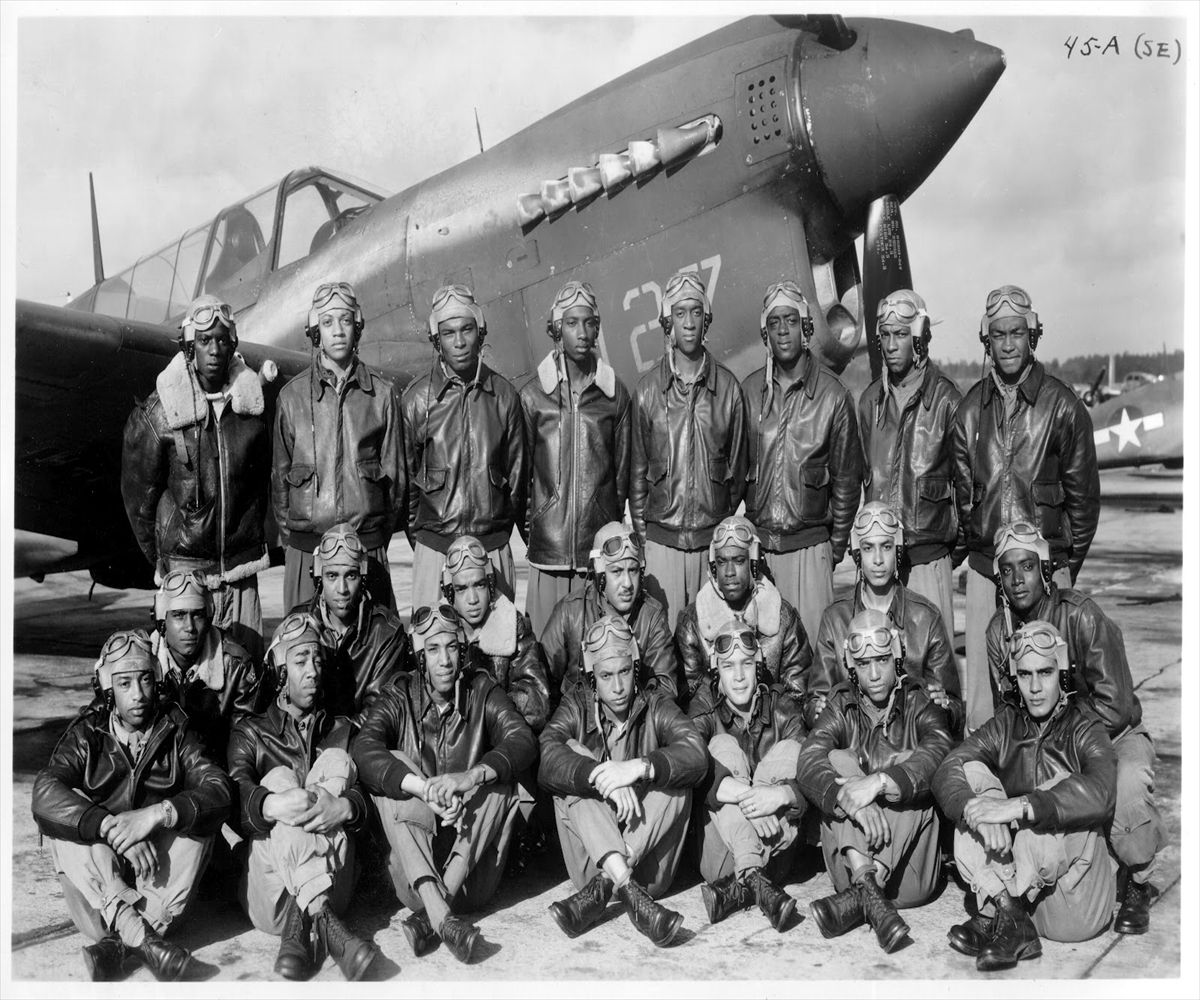
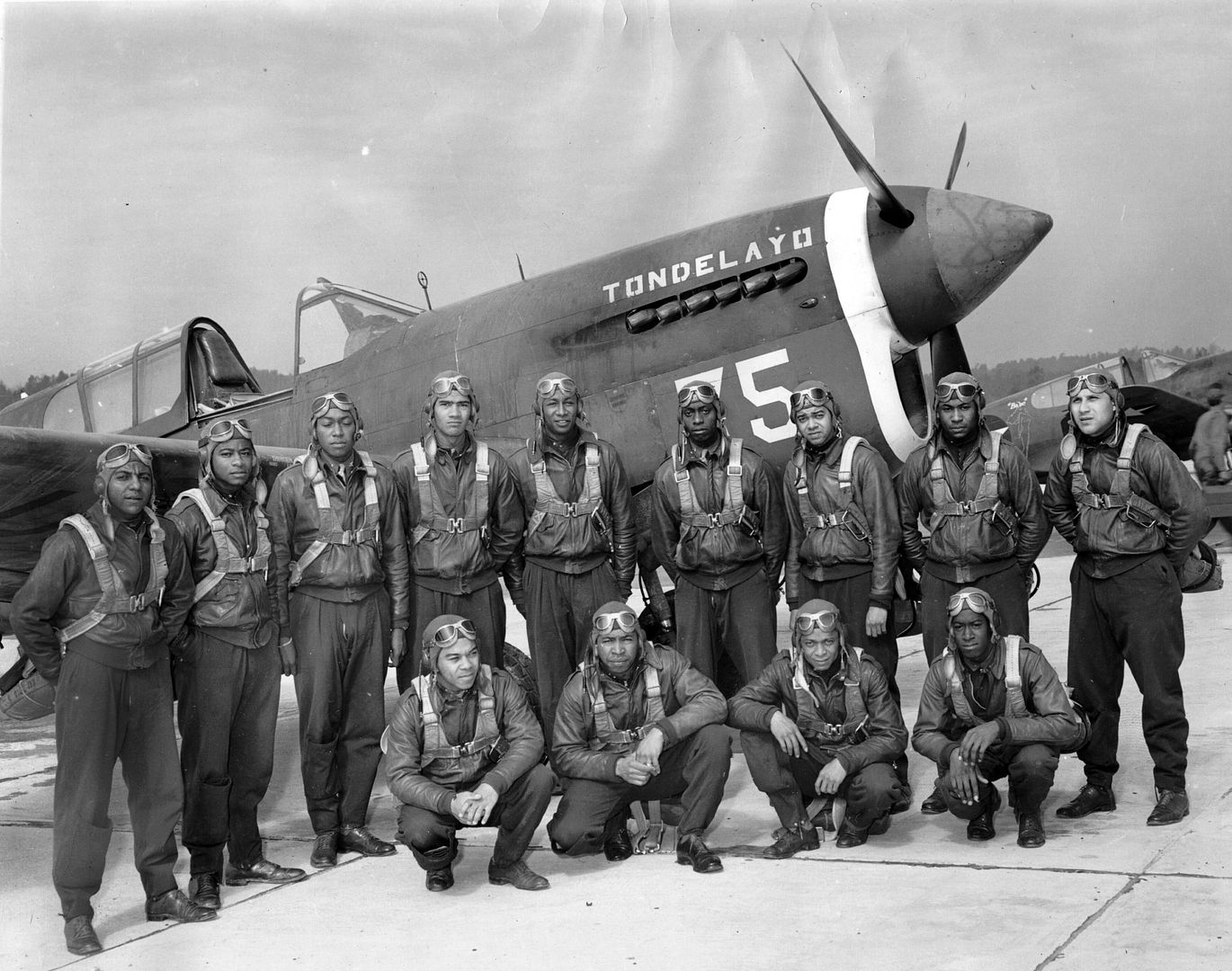
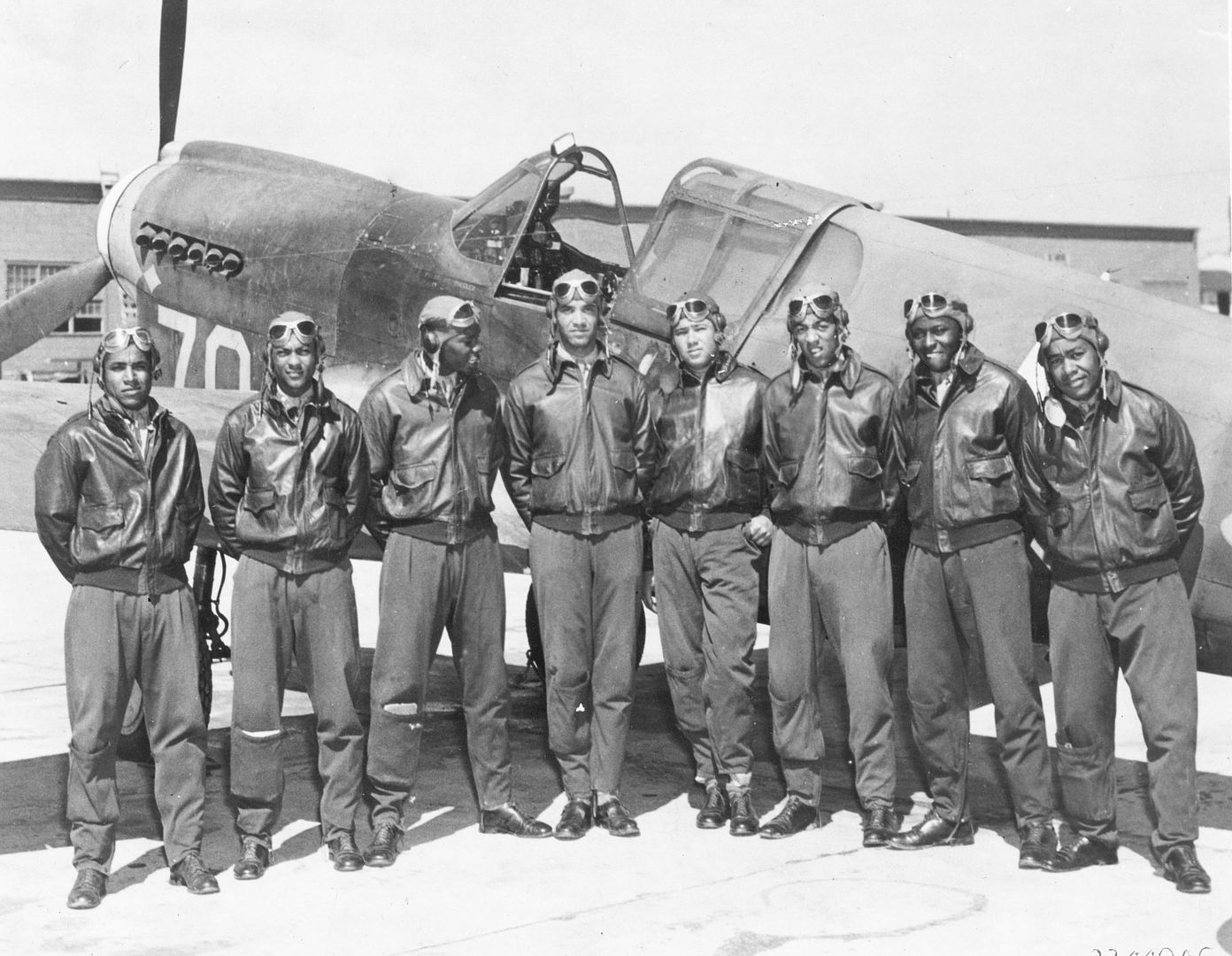
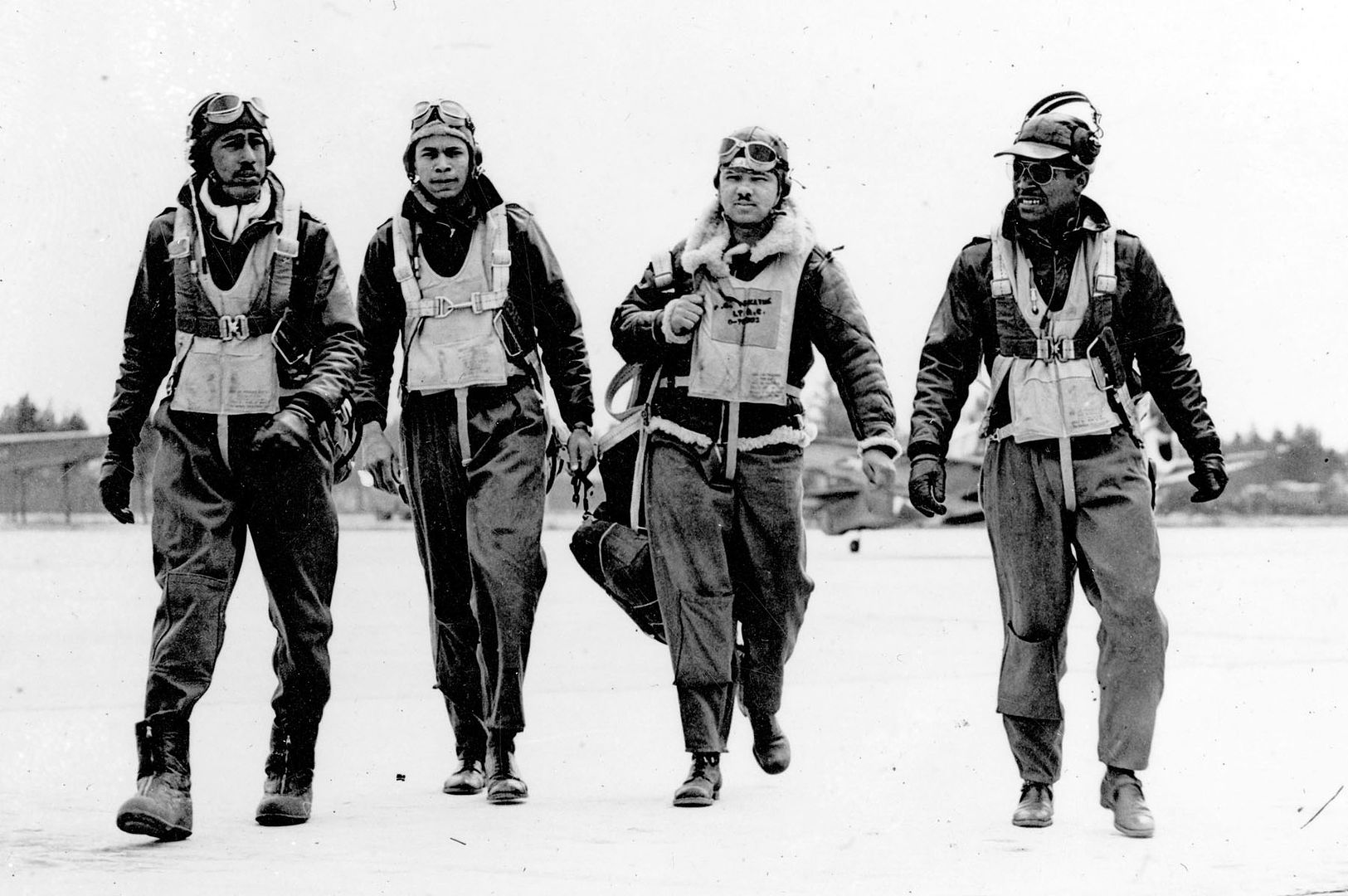
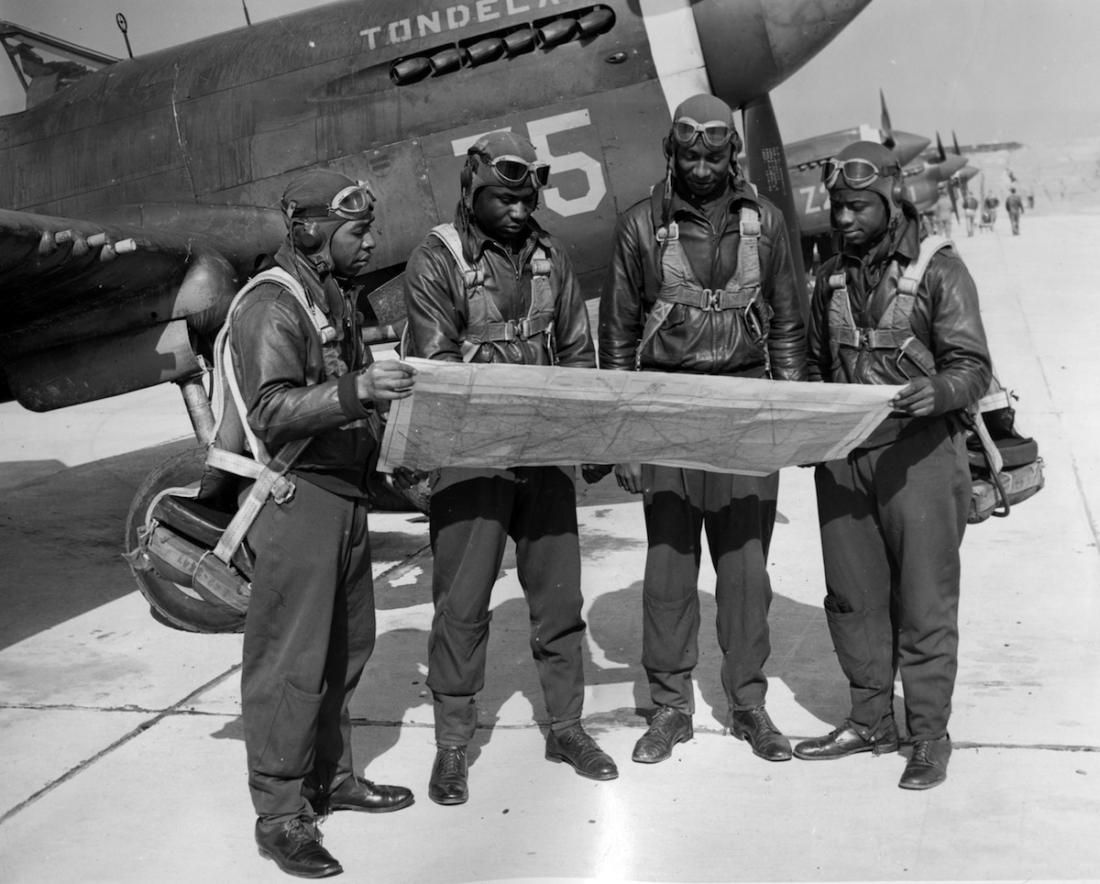




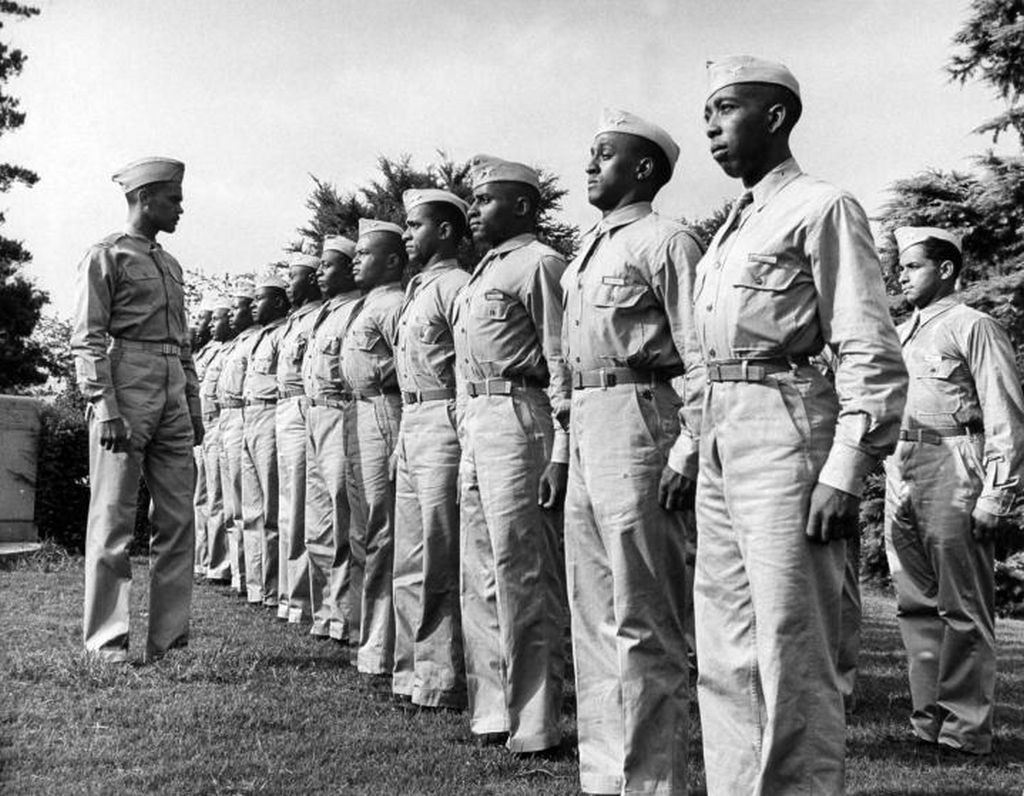
In the spring of 1941, the first African-American enlisted men began training to become maintainers and the first thirteen pilot candidates entered training. Progress was slow; it was not until September 2, that Captain Benjamin O. Davis, Jr., became the first Negro to solo an aircraft as a U.S. Army Air Corps officer. On March 7, 1942, young black pilots stood at attention on Tuskegee's airstrip, for induction into the U.S. Army Air Corps. Eight days later the 100th Fighter Squadron was established as a part of the 332nd Fighter Group.
The 99th Gets Started
May 31, 1943: the 99th Fighter Squadron arrived at Farjouna in Tunisia, attached to the 33rd Fighter Group, flying P-40s. Three days later, Lt. William A. Campbell, Charles B. Hall, Clarence C. Jamison and James R. Wiley, flew the squadron's first mission, a 'milk run' over Pantelleria. On June 9, six pilots of the 99th FS became the first U.S. Negro pilots to engage in aerial combat. Led by Lt. Charles Dryden, Lt. Willie Ashley, Sidney P. Brooks, Lee Rayford, Leon Roberts and Spann Watson, exchanged fire with German fighter planes, with no losses to either side. The Italian garrison on Pantelleria surrendered on June 11, 1943, in large part due to the powerful air attacks it had been subjected to. The 99th was a key part of the air assault.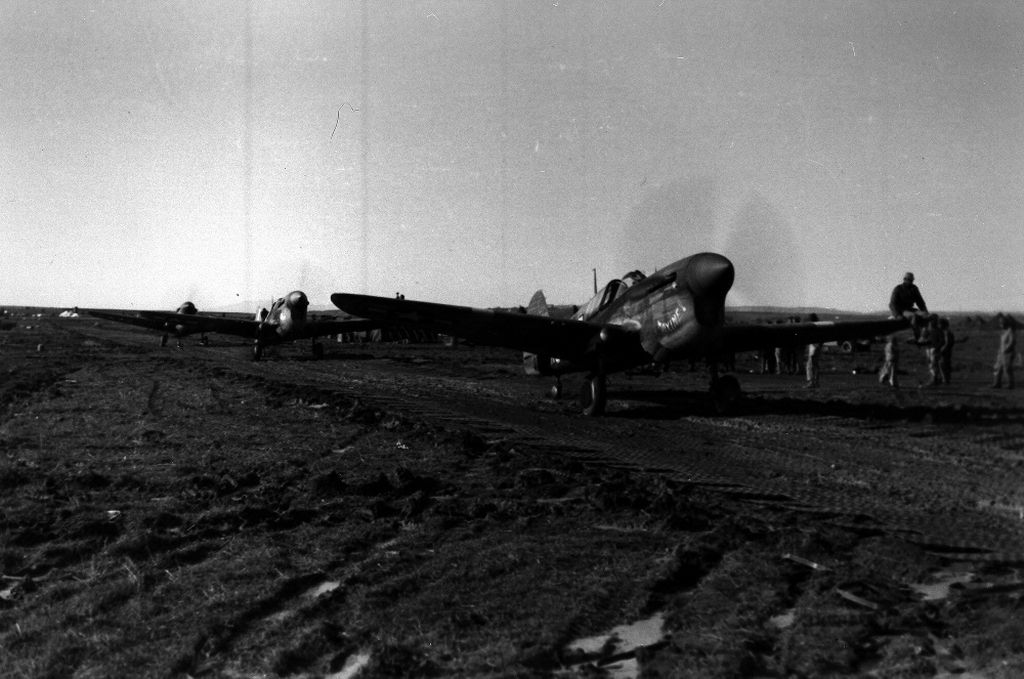
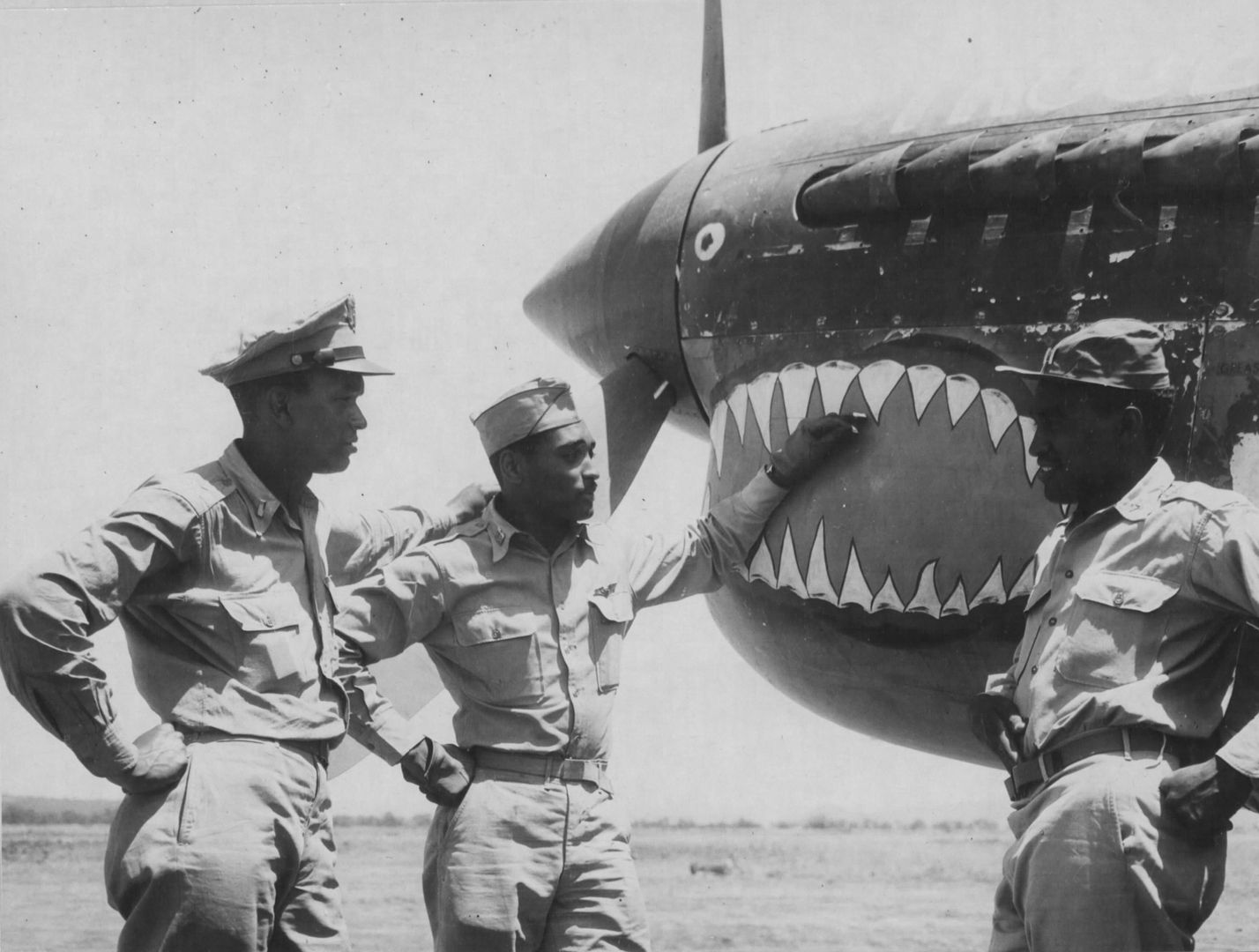
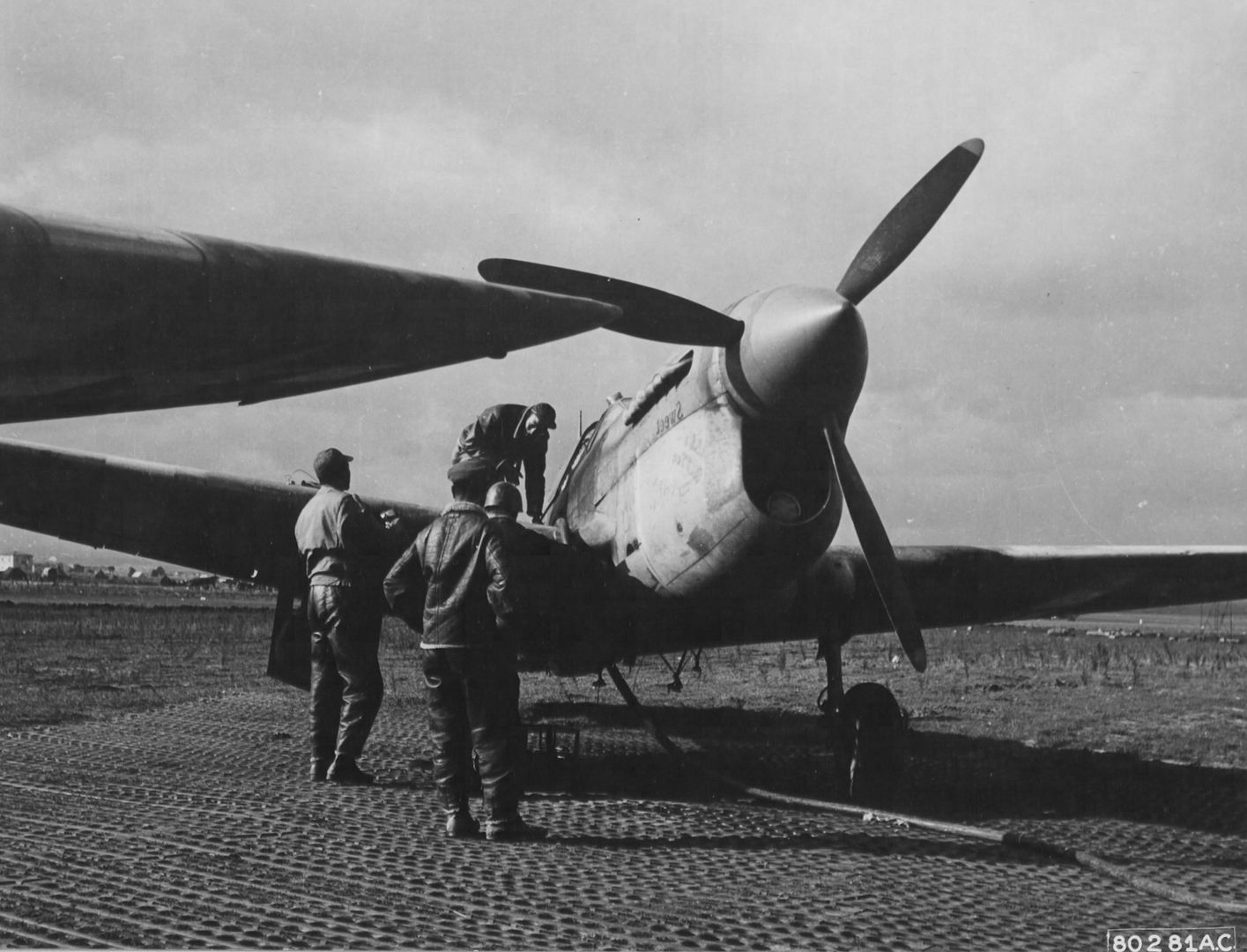
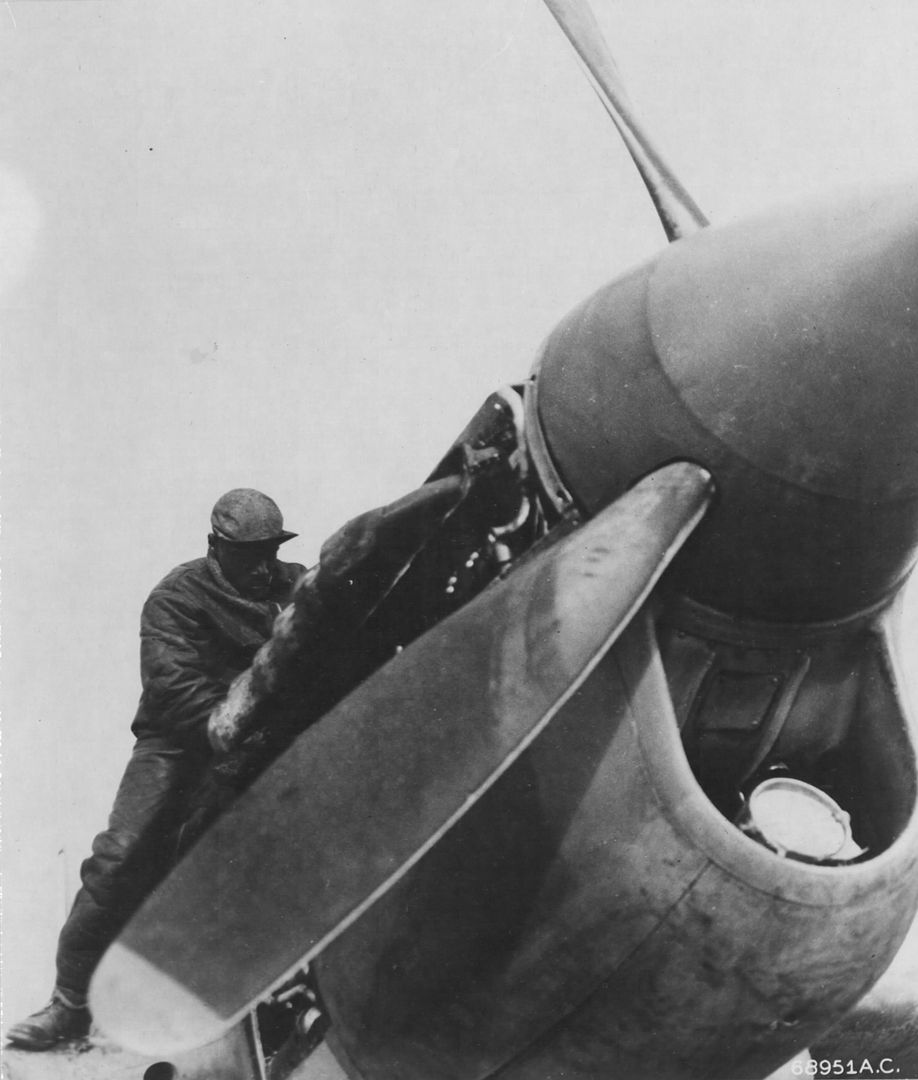
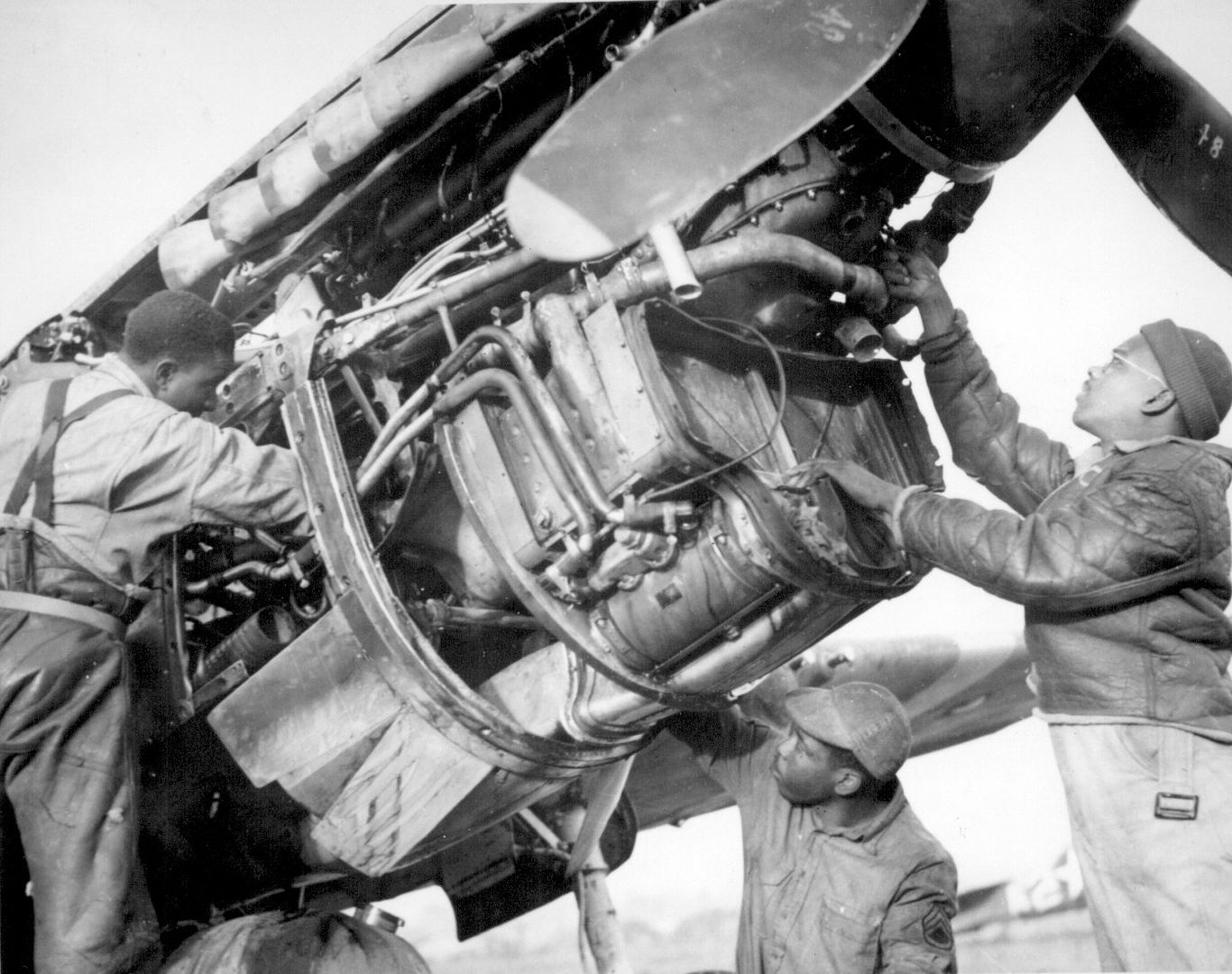
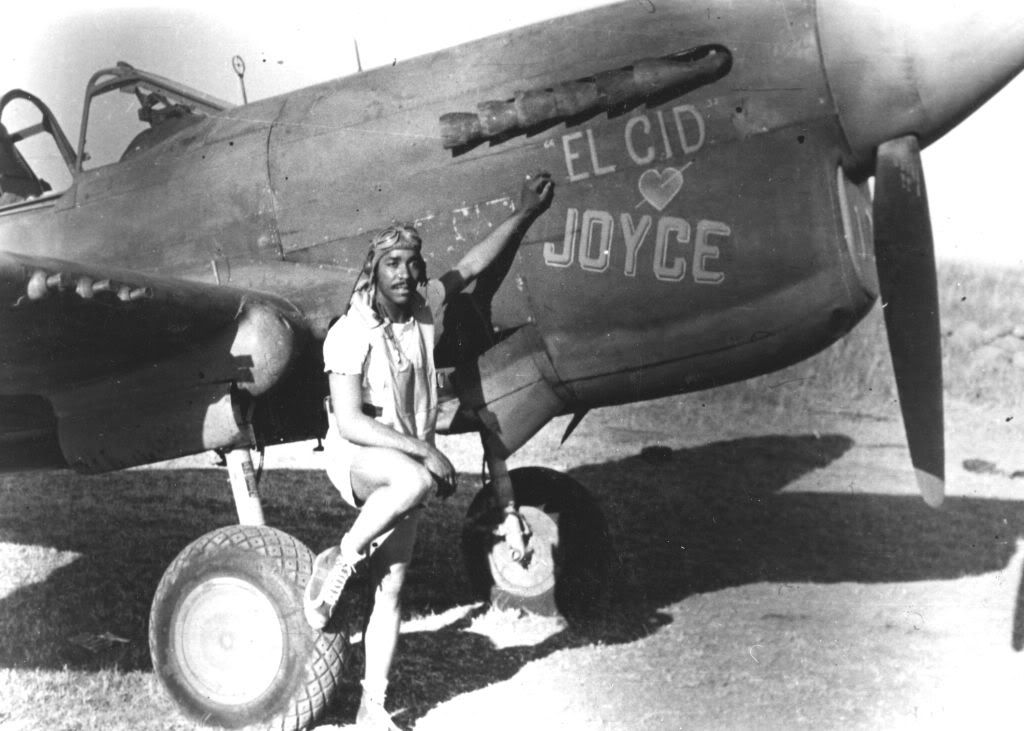
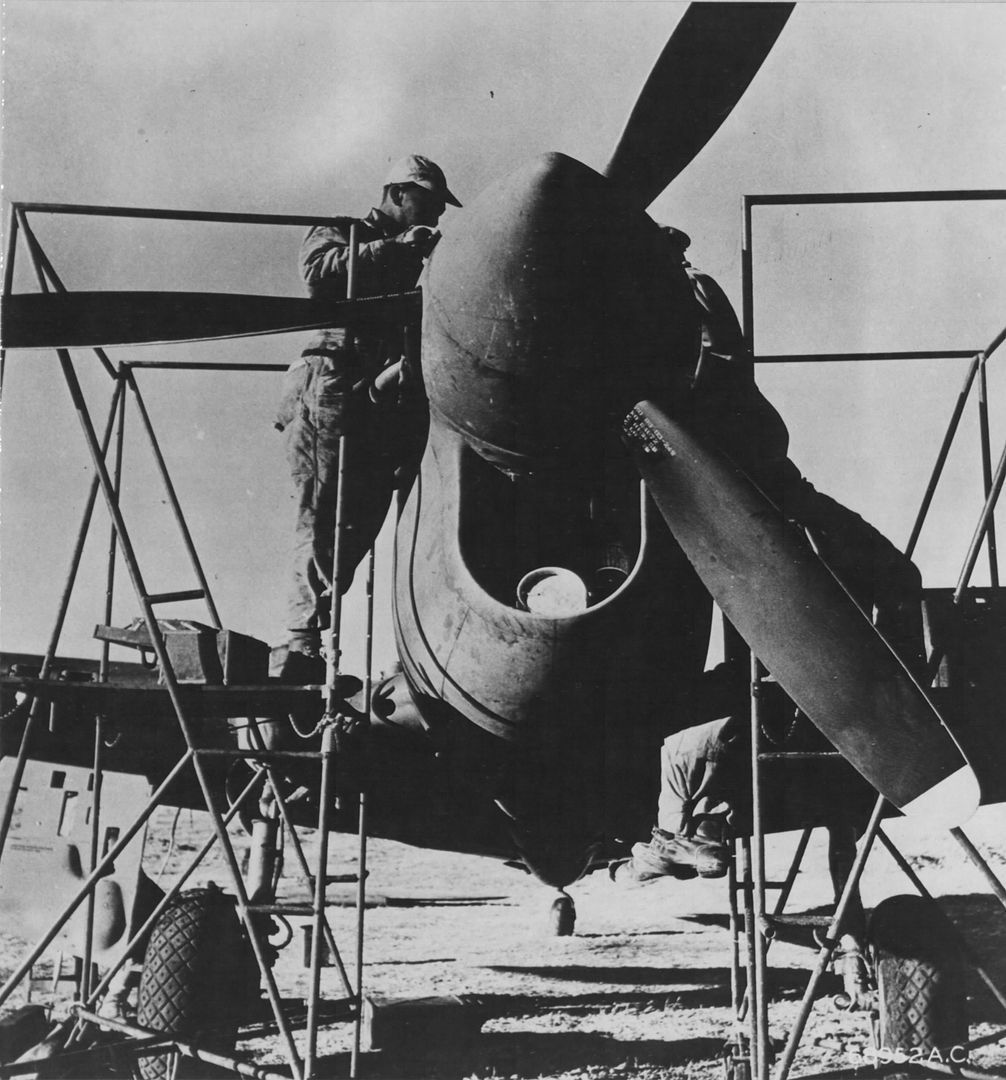
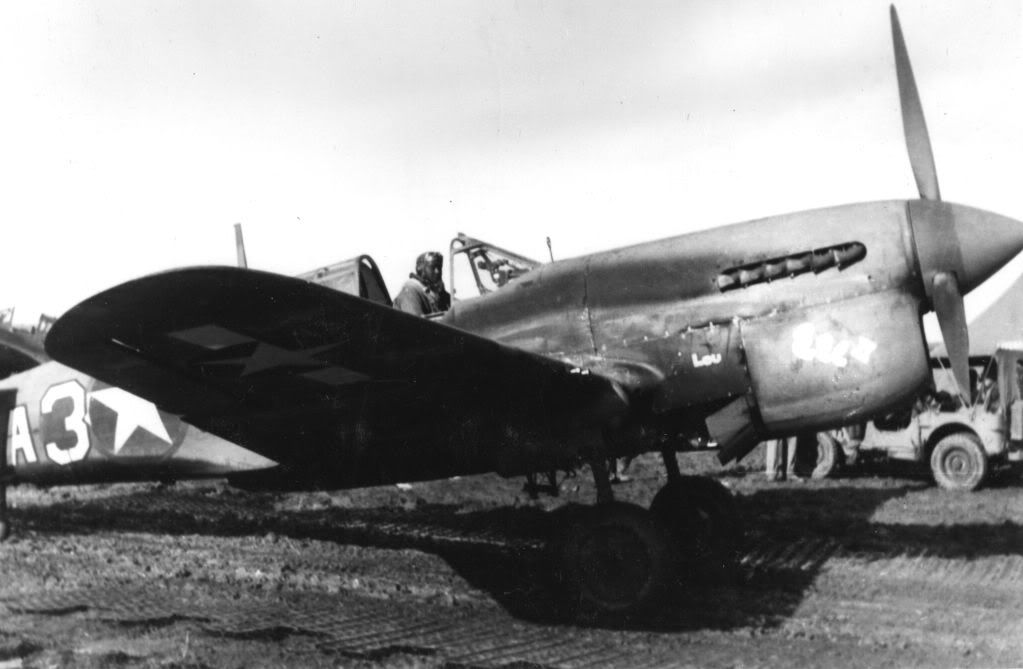







The 99th joined the 324th Fighter Group in El Haouria on June 29, 1943. At first they flew escort missions over the Sicilian coast. Within a few days, Lt Charles B. Hall got the 99th on the scoreboard when he downed an Fw-190. Sadly, this triumphant occasion was marred by the death of Lieutenants White and McCullin, victims of an operational accident.
Escort missions over Sicily continued through the summer of 1943. One Tuskegee Airman, Lt. Richard Bolling, was forced to bail out and floated in the Mediterranean for a full day before he was recovered. On July 19, the 99th moved over to Licata, on the coast.
The Critic
Despite their achievements and accomplishments, the 99th found continued resistance and prejudice here in the Mediterranean. The CO of the 33rd Fighter Group, Col. William Momyer, complained about the performance of the 99th FS, compared their combat record to White squadrons, alluded to lack of air discipline, and hinted at a lack of aggressiveness.
His comparisons overlooked the fact that the 99th did not operate at the front, but was stationed hundreds of miles to the rear. Nor did he mention his exclusion of 99th FS pilots from briefing sessions. But in those days, Blacks were easy targets, and in September of 1943, TIME magazine ran an article that repeated Momyer's accusations. About all the pilots could do was perform their jobs perfectly, and answer their critics with deeds, not words.
Italy
The 99th was scheduled to provide air support for the September 9 invasion of Salerno on the Italian peninsula. After the German counter-attack forced an Allied retreat, members of the 99th flew into Paestum, an airfield near Salerno, to provide air cover for the beachhead. In early October, the 99th started flying with the 79th Fighter Group based at Foggia, commanded by Col. Earl Bates, who fully involved the men of the 99th in combat missions. As the Germans retreated northward, the fliers of the 79th and 99th flew fighter-bomber missions on railroad, bridges, and communciation centers to hamper their mobility. These were grinding, demanding missions; pilots often flew more than 5 sorties a day. This activity continued through January, 1944, culminating in a large multi-Group strike on Naples' Capodichino Airdrome. But so far, the 99th only had the one aerial victory to their credit, while the 79th has destroyed or damaged almost 20 German aircraft.
But on January 24, 1944, the Negro pilots broke out in a big way, downing five German planes in a morning mission led by Capt. Clarence Jamison, and three more that afternoon when Lt. Wiley's flight mixed it up with the enemy. And the next day, the 99th continued its combat success, claiming four e/a destroyed. On February 5, Lt. Driver got another. On the 7th, they got three more; they also received an official commendation from General Hap Arnold at this time.
In April, the 99th was transferred from its partnership with the 79th FG to work with the 324th FG. As part of this Group, thay participated in Operation Strangle, the aerial campaign in May, 1944 to isolate the German garrison at Monte Cassino. Operation Strangle marked the end of the 99th Fighter Squadron's independent existence.
The 332nd
On July 4, 1944, the 99th was joined with three other Squadrons: the 100th, 301st and the 302nd to form the 332nd Fighter Group. These were all-Negro squadrons, all trained at Tuskegee. The veterans of the 99th resented the newcomers somewhat, but those issues soon worked themselves out. The Group transitioned to Mustangs at this time, decorating them with bright red spinners and tails, thus earning their nickname, 'Redtails'.
A week later the 332nd escorted bombers on a mission against railyards, and Capt. Joseph Elsberry shot down three Fw-190s, the first black pilot to achieve this feat. The next day, July 13, the Group flew its first mission to Ploesti. On the 16th, they met some Italian Macchis (from Mussolini's short-lived, rump state in the North, the Italian Social Republic), and downed two of them. Two days later, July 18, Lt. Clarence 'Lucky' Lester destroyed three German airplanes, and earned a DFC for himself in recognition. This was a big day for the Group, as they claimed 11 e/a destroyed.
Throughout July, and through October of 1944, the Redtails flew countless missions, usually bomber escorts. Sometimes they shot down German aircraft, and began to build a respectable Group tally. Less often, they lost one of their own.!!!!
On 24 March 1945, during the war, the Chicago Defender said that no bomber escorted by the Tuskegee Airmen had ever been lost to enemy fire, under the headline: "332nd Flies Its 200th Mission Without Loss"; the article was based on information supplied by the 15th Air Force.
This statement was repeated for many years, and not publicly challenged, partly because the mission reports were classified for a number of years after the war. In 2004, William Holton, who was serving as the historian of the Tuskegee Airmen Incorporated, conducted research into wartime action reports. Alan Gropman, a professor at the National Defense University, disputed the initial refutations of the no-loss myth, and said he researched more than 200 Tuskegee Airmen mission reports and found no bombers were lost to enemy fighters. Dr. Daniel Haulman of the Air Force Historical Research Agency conducted a reassessment of the history of the unit in 2006 and early 2007. His subsequent report, based on after-mission reports filed by both the bomber units and Tuskegee fighter groups, as well as missing air crew records and witness testimony, documented 25 bombers shot down by enemy fighter aircraft while being escorted by the Tuskegee Airmen.
"At least 25 bombers being escorted by the Tuskegee Airmen over Europe during World War II were shot down by enemy aircraft, according to a new Air Force report. The report contradicts the legend that the famed black aviators never lost a plane to fire from enemy aircraft. But historian William Holton said the discovery of lost bombers doesn't tarnish the unit's record.
"It's impossible not to lose bombers," said Holton, national historian for Tuskegee Airmen Inc. The report released March 28, 2007 was based on after-mission reports filed by both the bomber units and Tuskegee fighter groups, as well as missing air crew records and witness testimony, said Daniel Haulman, a historian at the Air Force Historical Research Agency at Maxwell Air Force Base in Montgomery. The tally includes only cases where planes were shot down by enemy aircraft, Haulman said. No one disputed the airmen lost some planes to anti-aircraft guns and other fire from the ground. "
The bomber pilots began to appreciate the Redtails. In Mustang Aces of the 9th and 15th Air Forces, one B-24 pilot recalled
"The P-38s always stayed too far out. Some of the Mustang group stayed in too close ... Other groups, we got the feeling that they just wanted to go and shoot down 109s ... The Red Tails were always out there where we wanted them to be ... We had no idea they were Black; it was the Army's best kept secret."
Luke Weathers' escort mission described above provided the group's only aerial victories for the month of November. They flew 22 missions in December, running the group tally to 62 confirmed air-to-air victories by year's end. Bad weather in January limited them to 11 missions, picking up to 39 in February, but without many aerial victories. On March 24, 1945, Col. Davis led the Group on the longest escort mission ever flown by the Fifteenth Air Force, a 1600-mile round trip to the Daimler-Benz tank works in Berlin. On this mission, Roscoe C. Brown, Jr., Charles Brantly and Earl Lane, each shot down a German Me-262 jet fighter aircraft. The Group received a Distinguished Unit Citation for their achievements this day.
The Tuskegee Airmen continued flying and fighting, killing and dying, until the end of the war in Europe in May, 1945.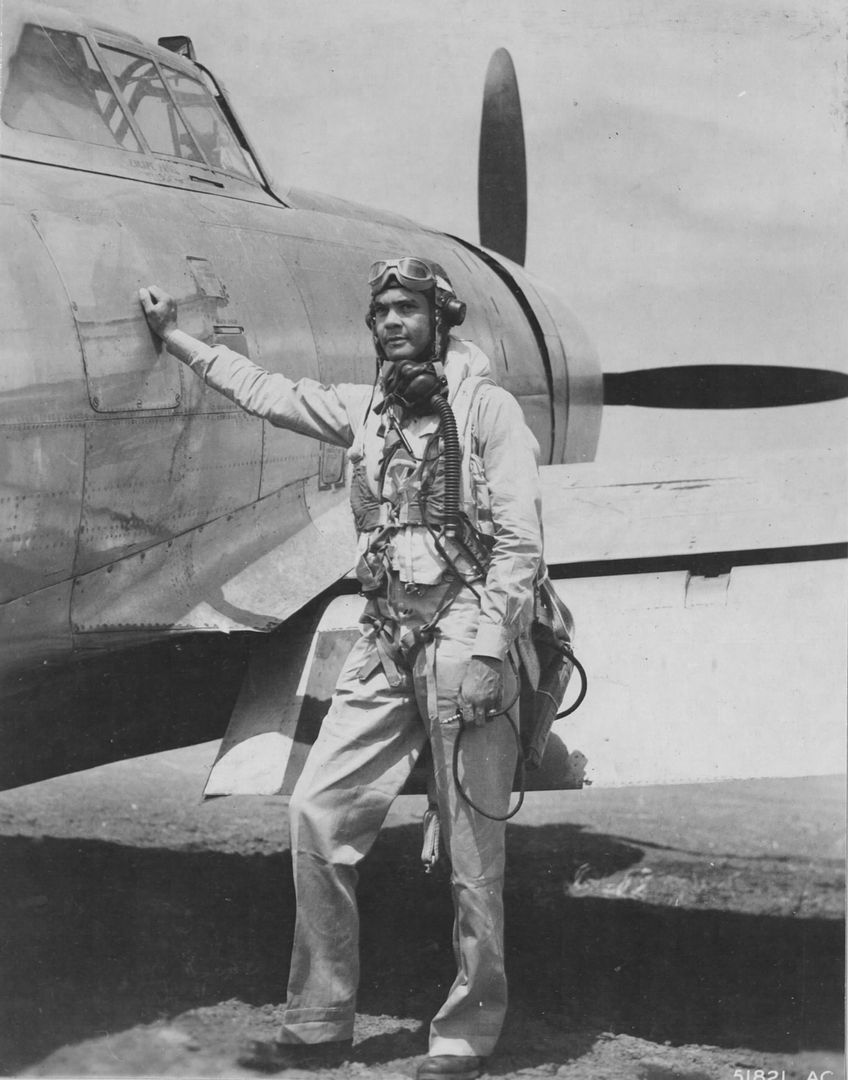
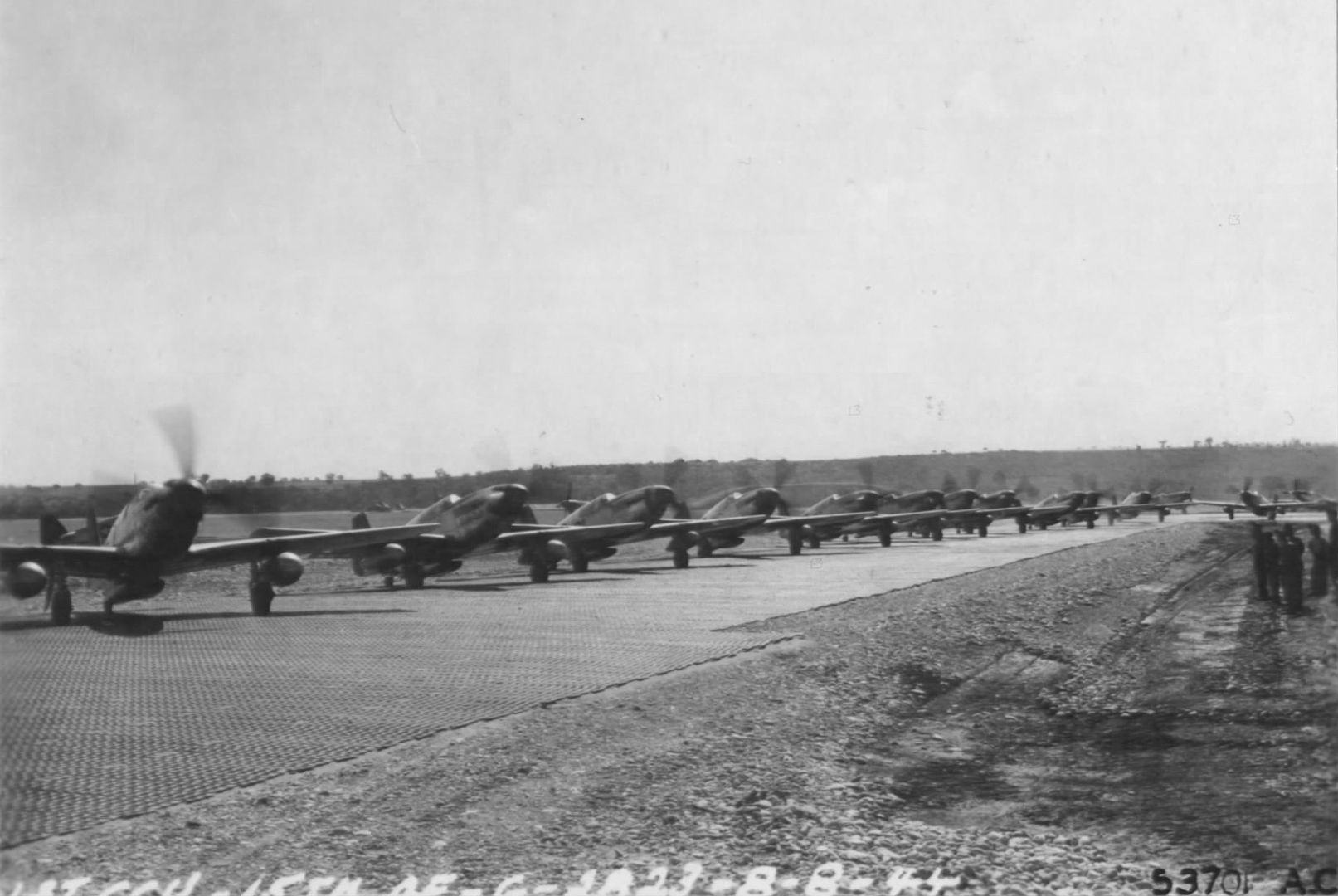
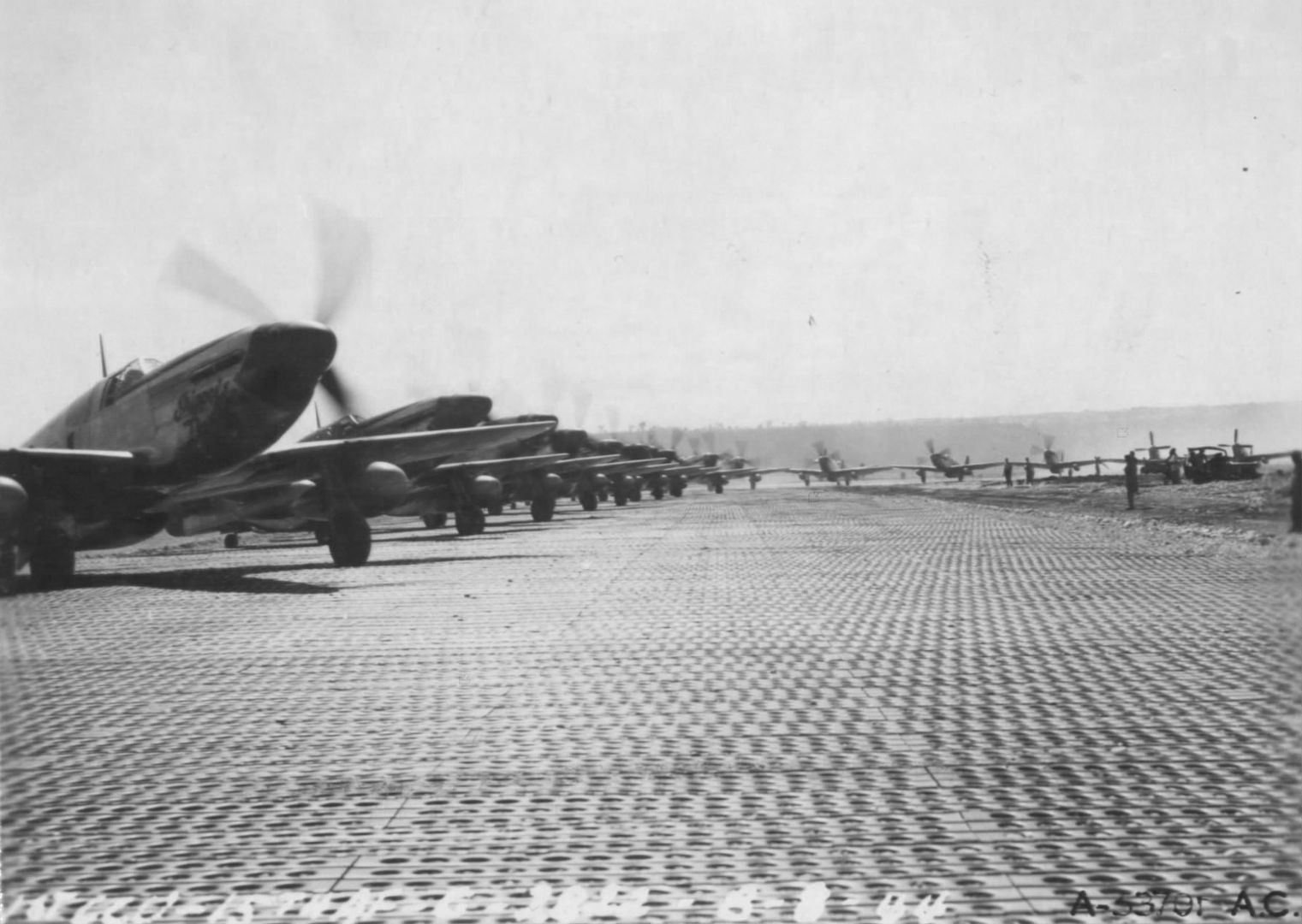



During World War II, long and dangerous missions often meant that fighters returned to their bases with only enough fuel in their airplanes to fly three minutes. Pilots of the 15th Army Air Force Squadron formed "The Three Minute Egg Club." Membership was limited to pilots who landed within these narrow margins.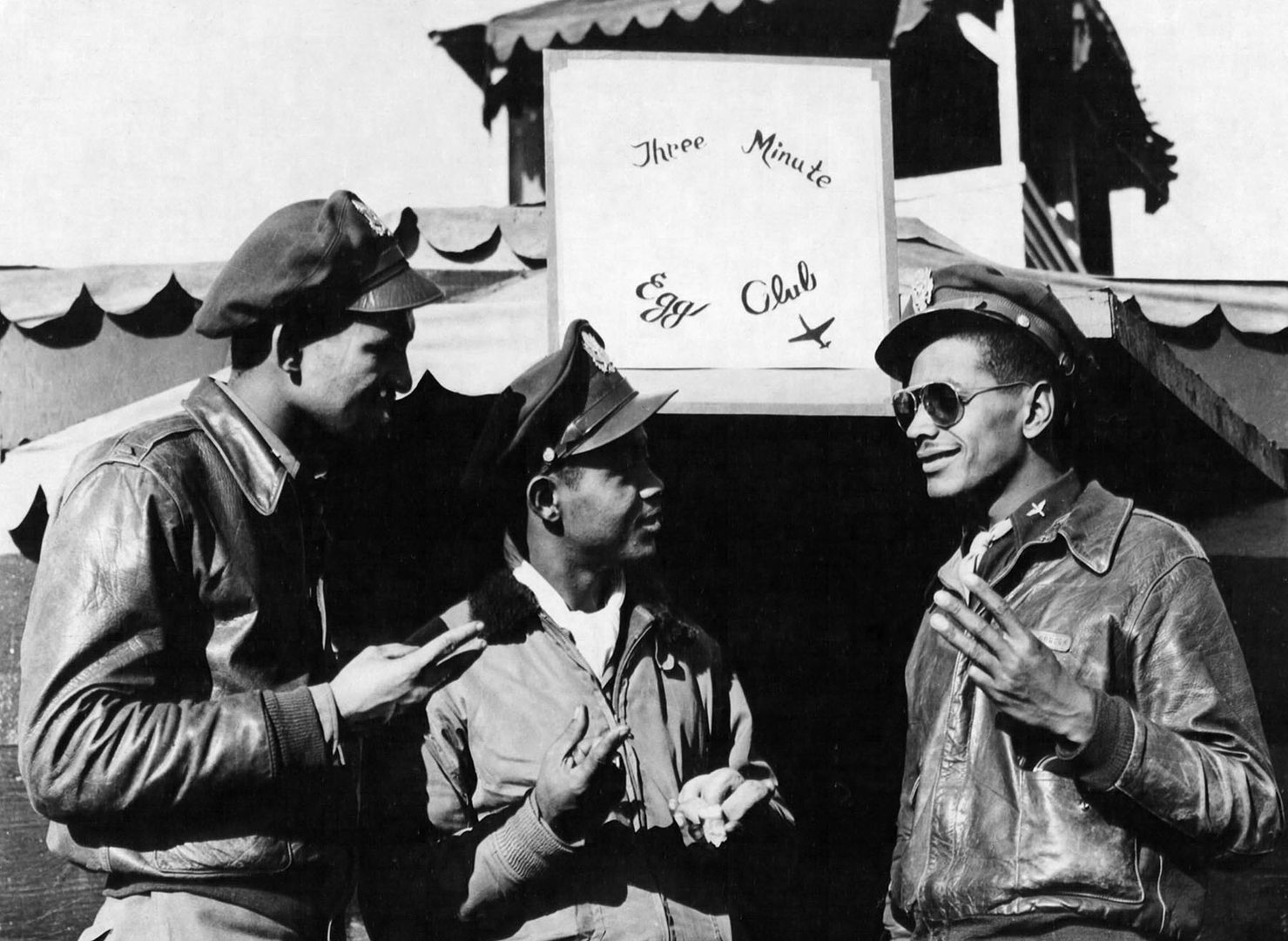
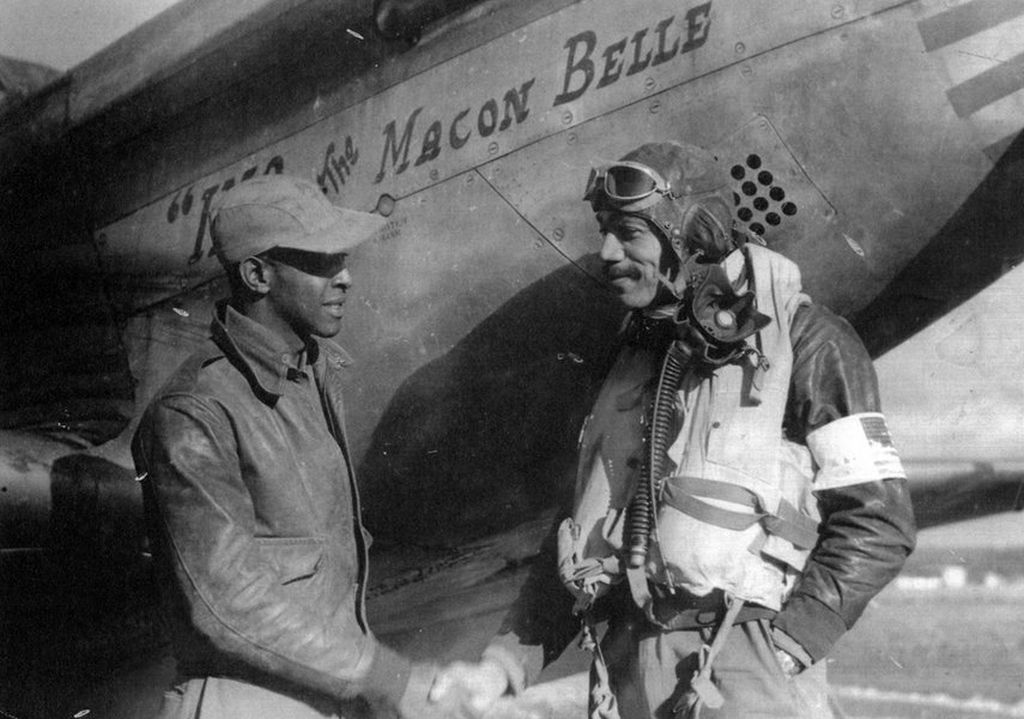
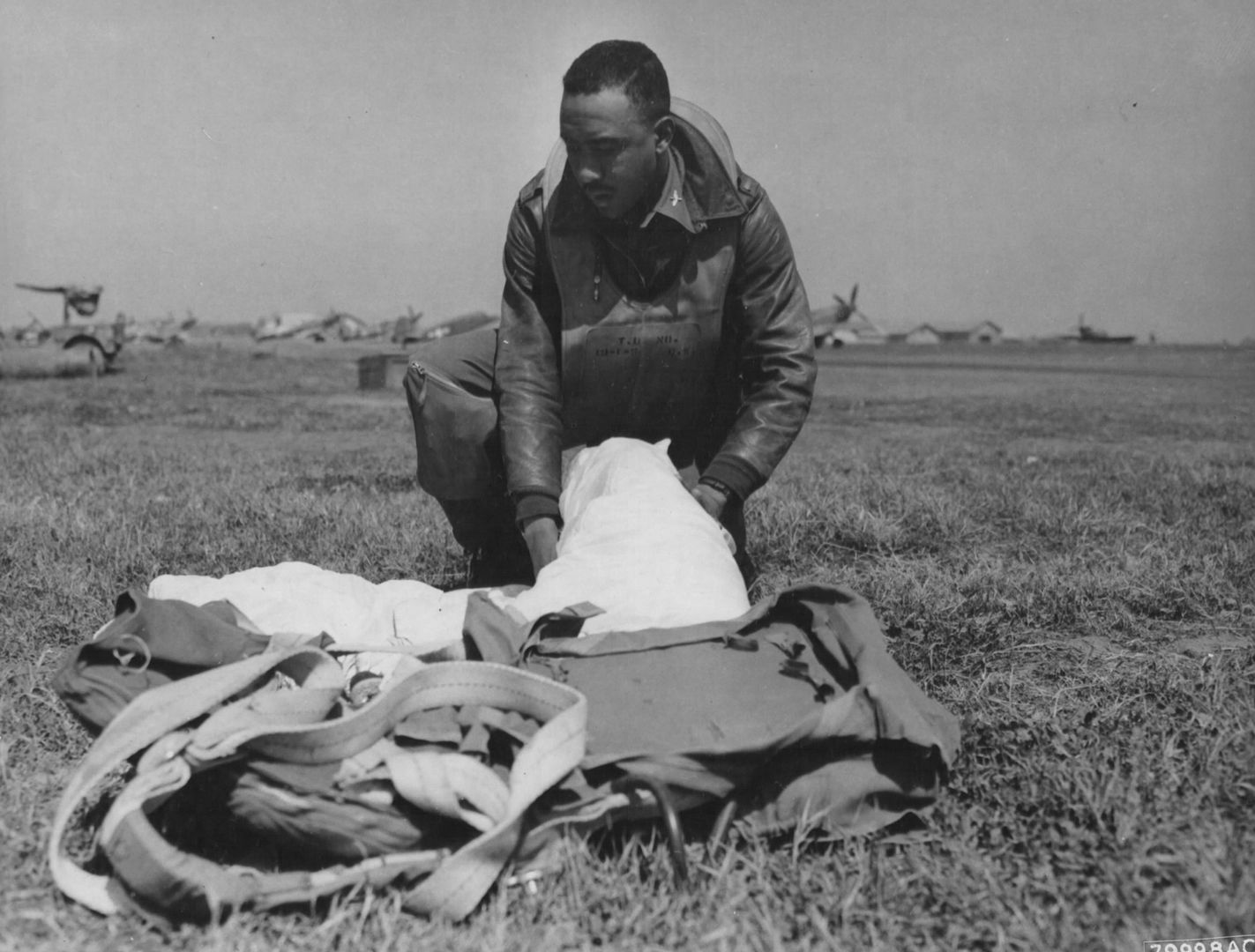
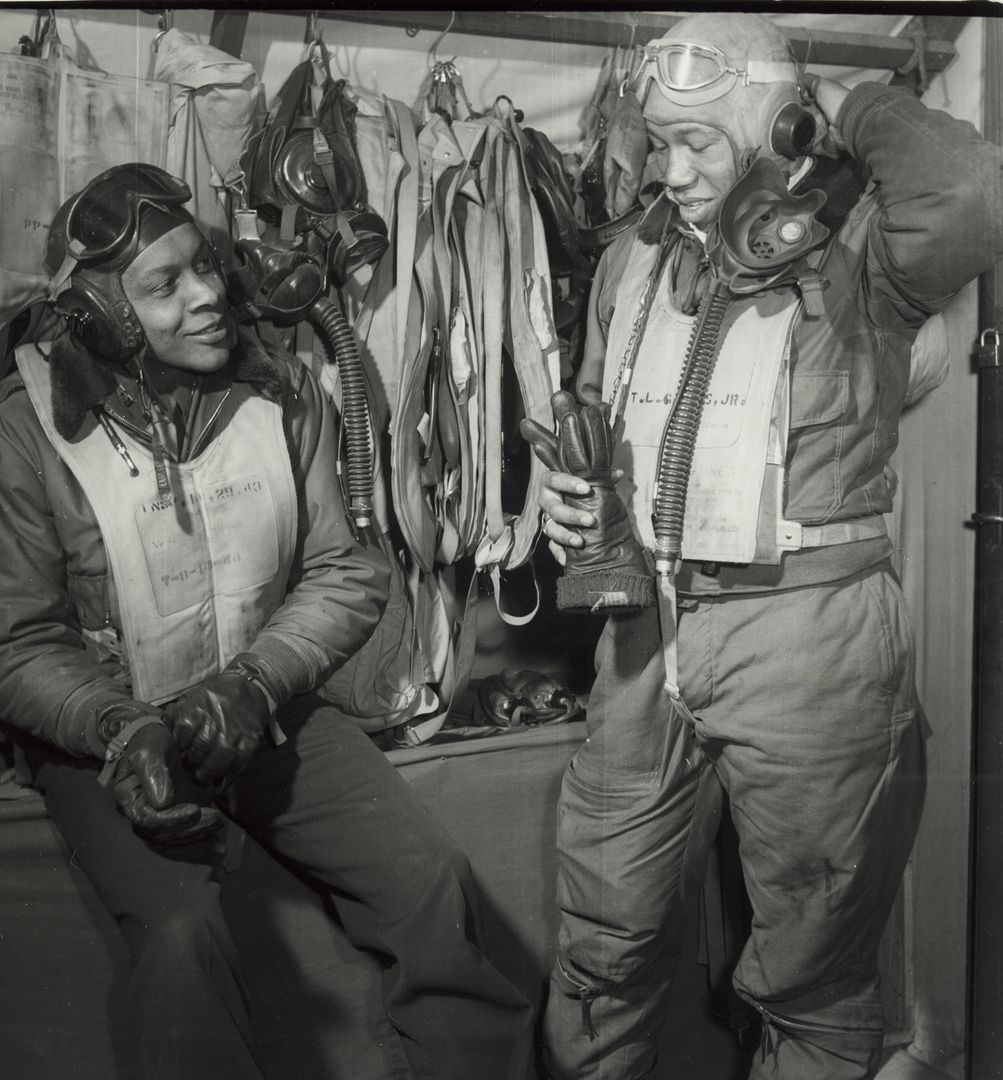
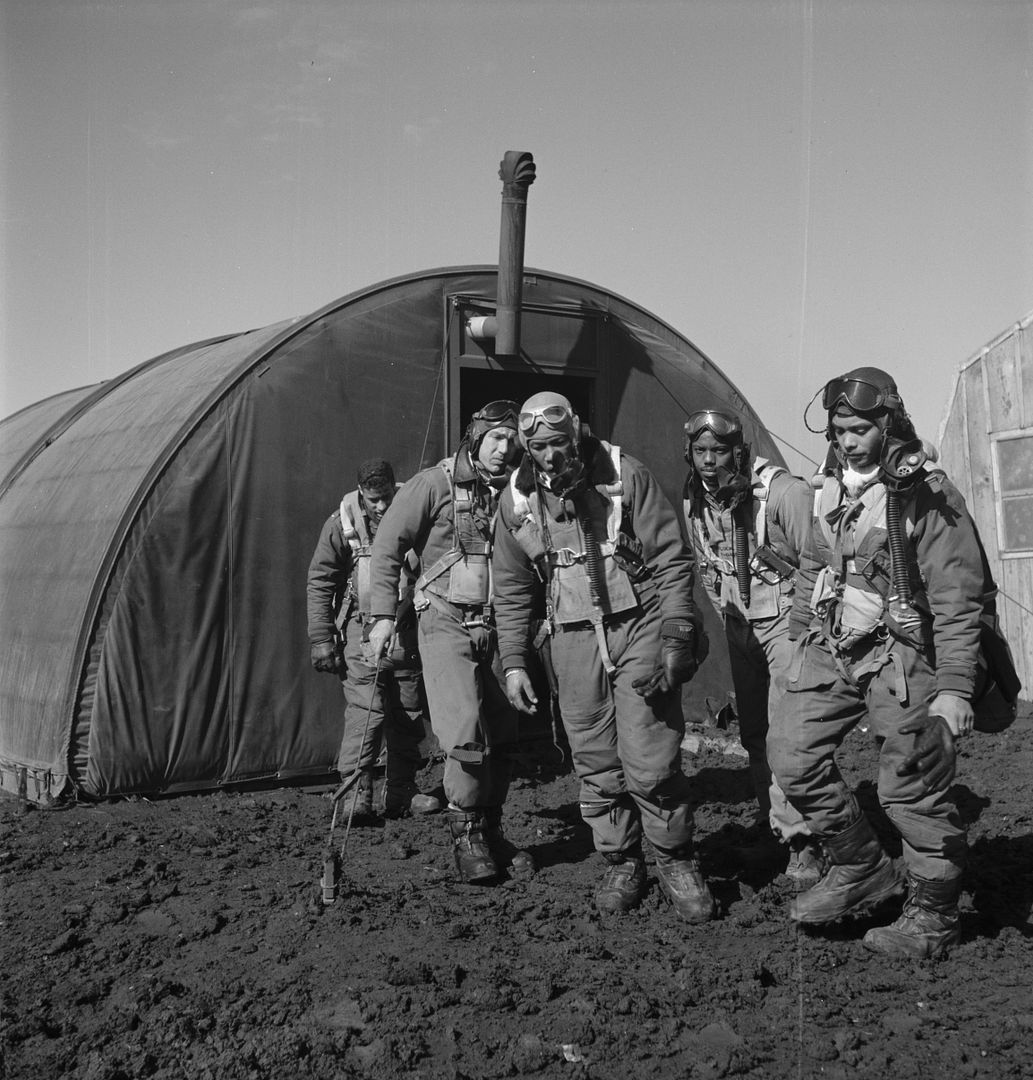
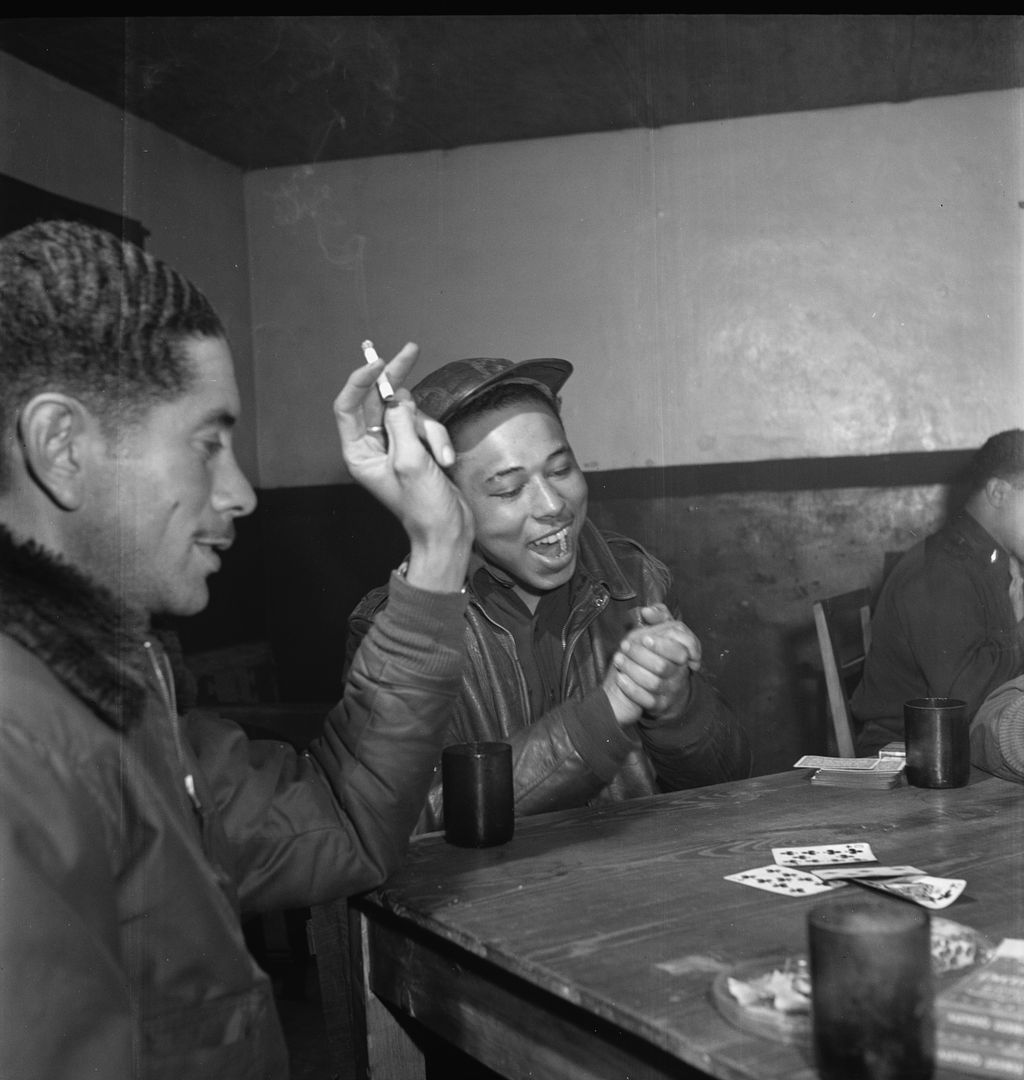
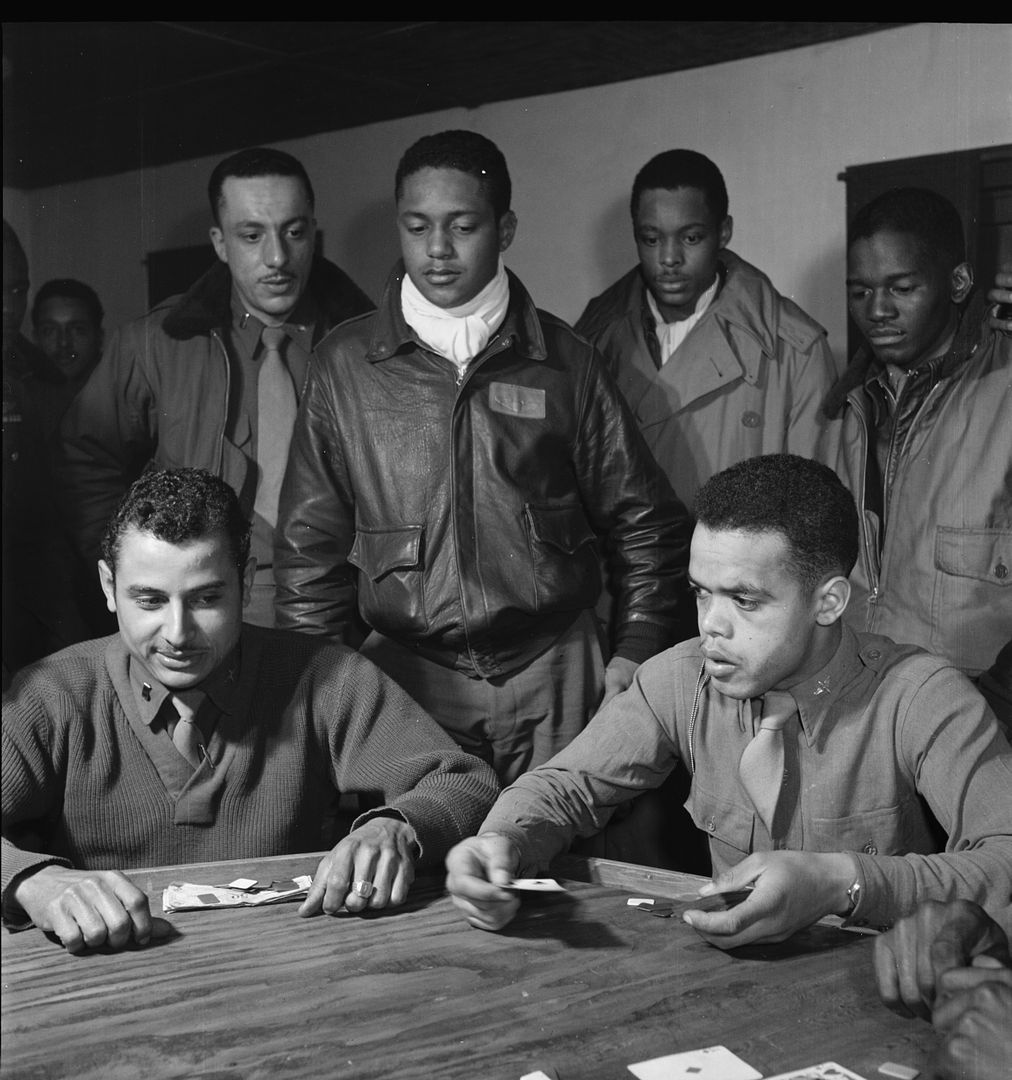
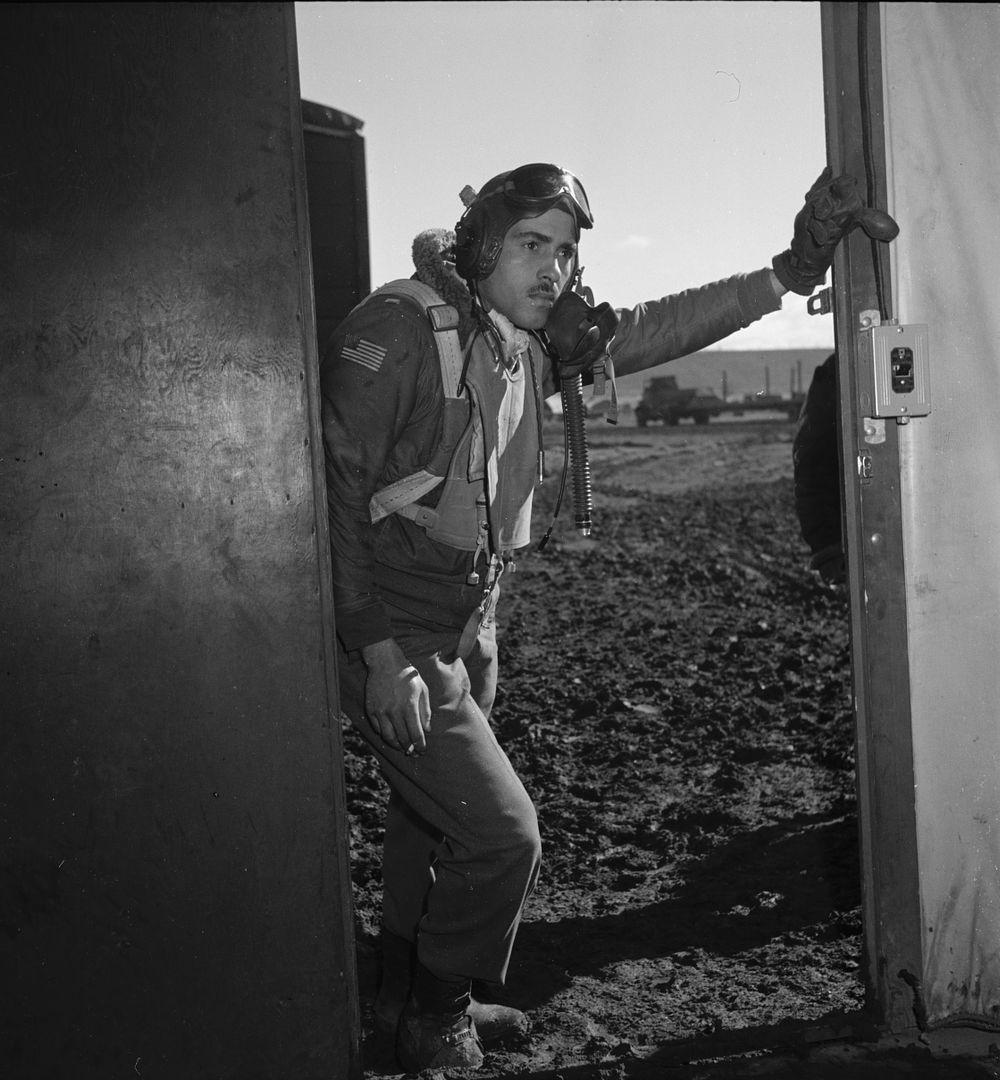
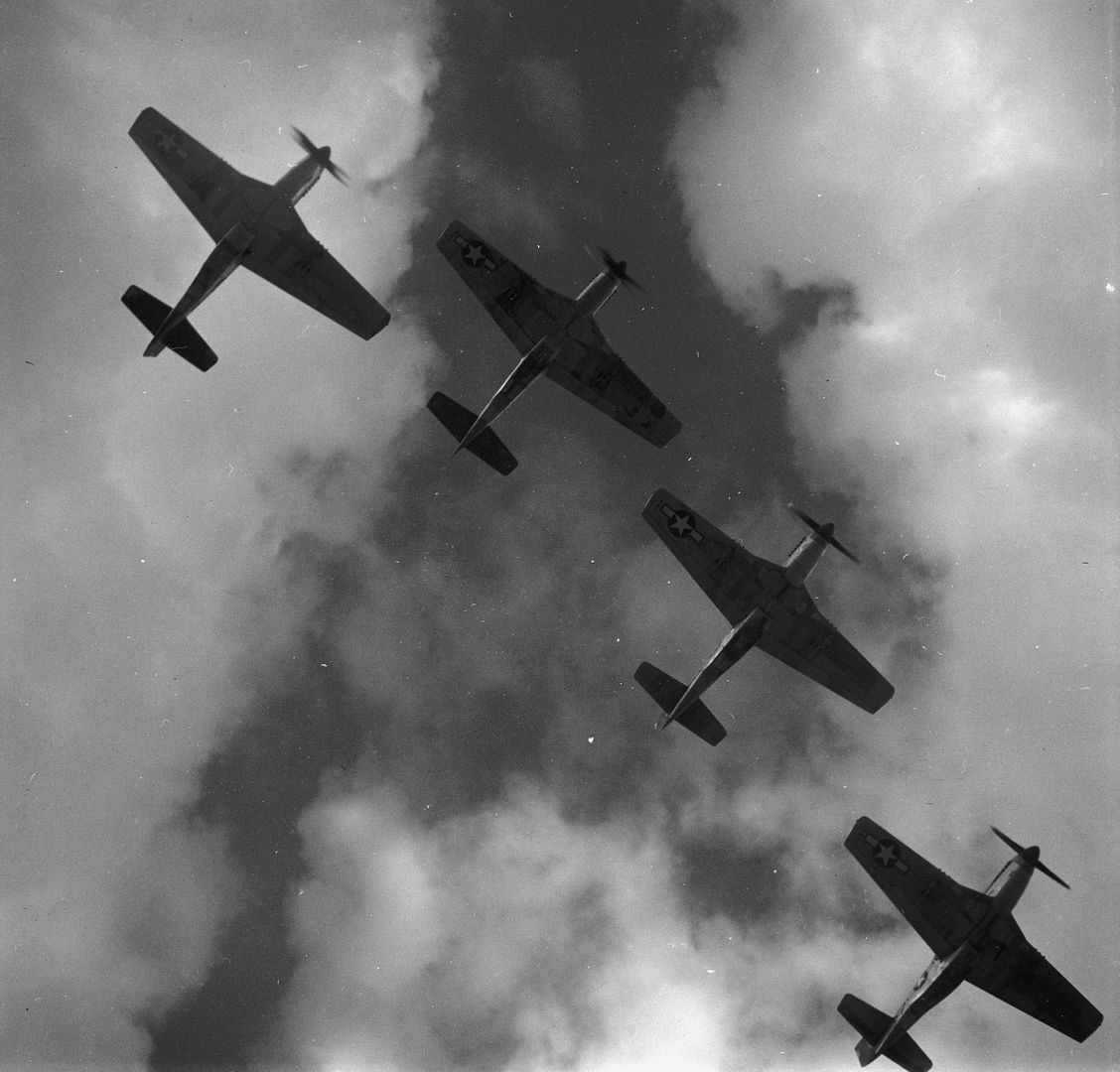
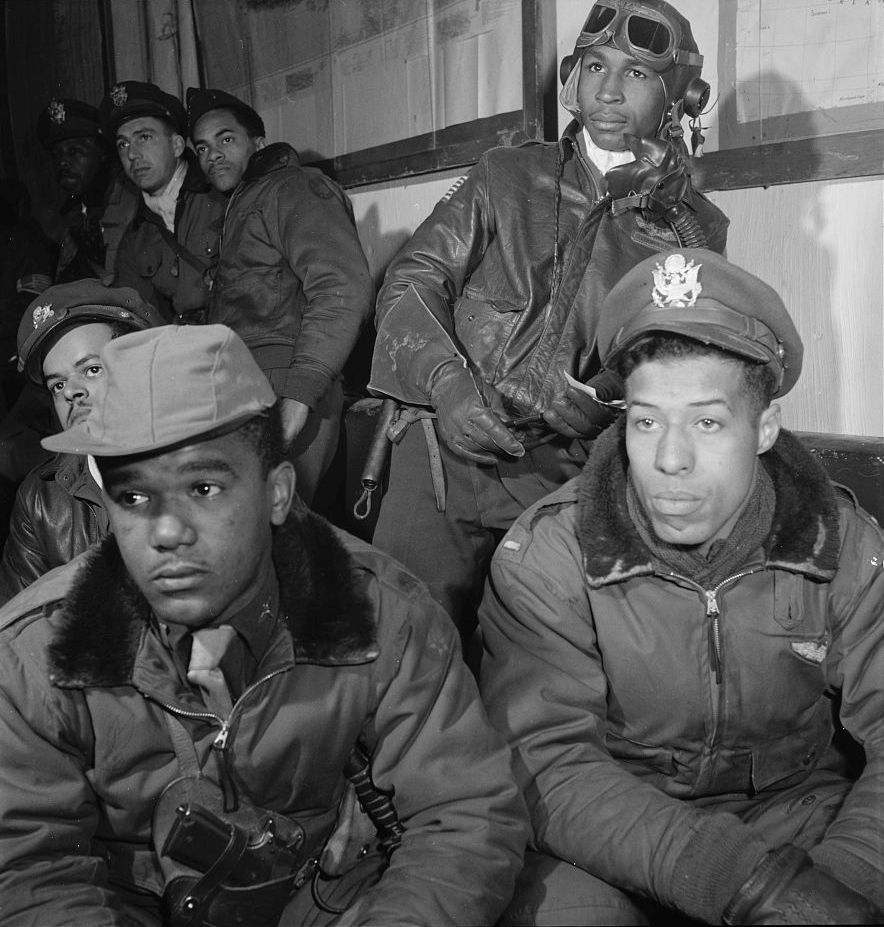
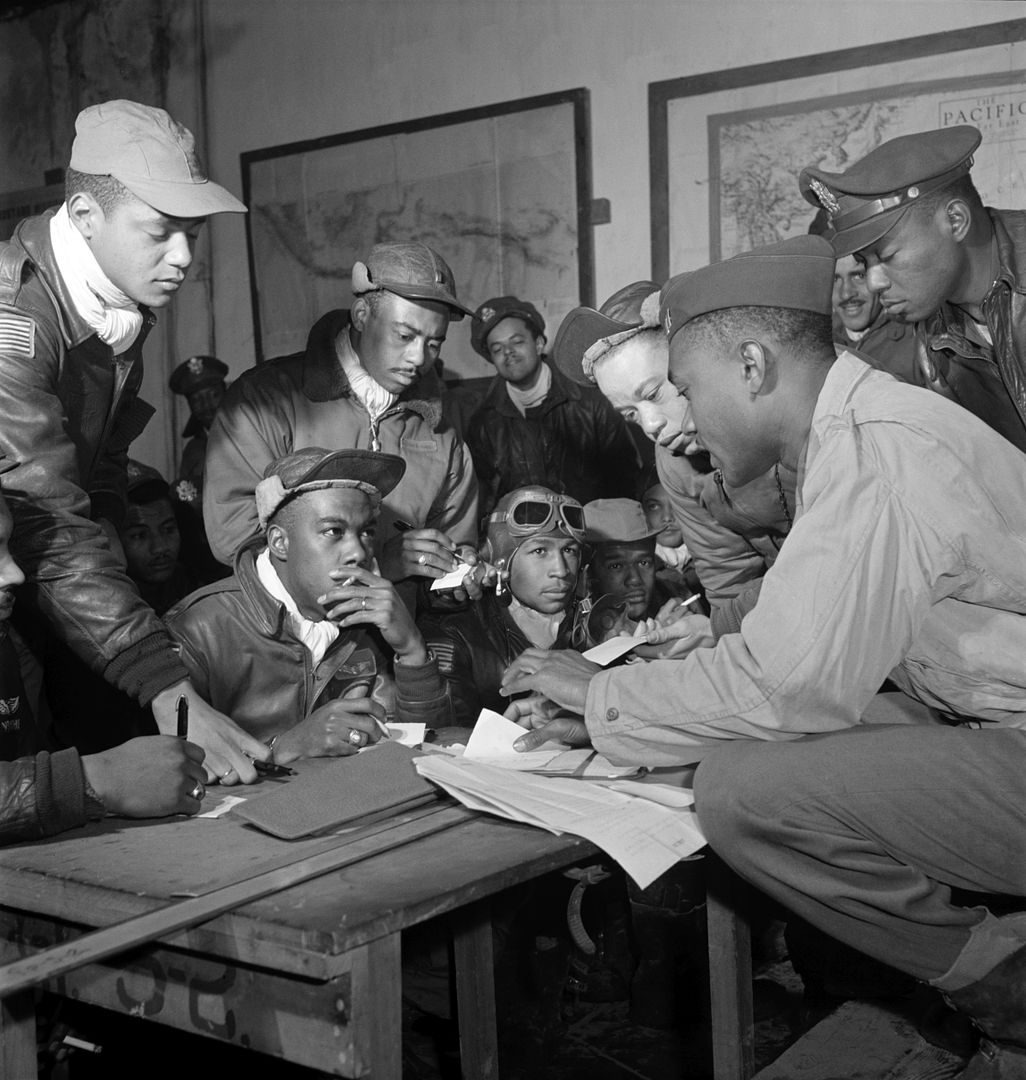
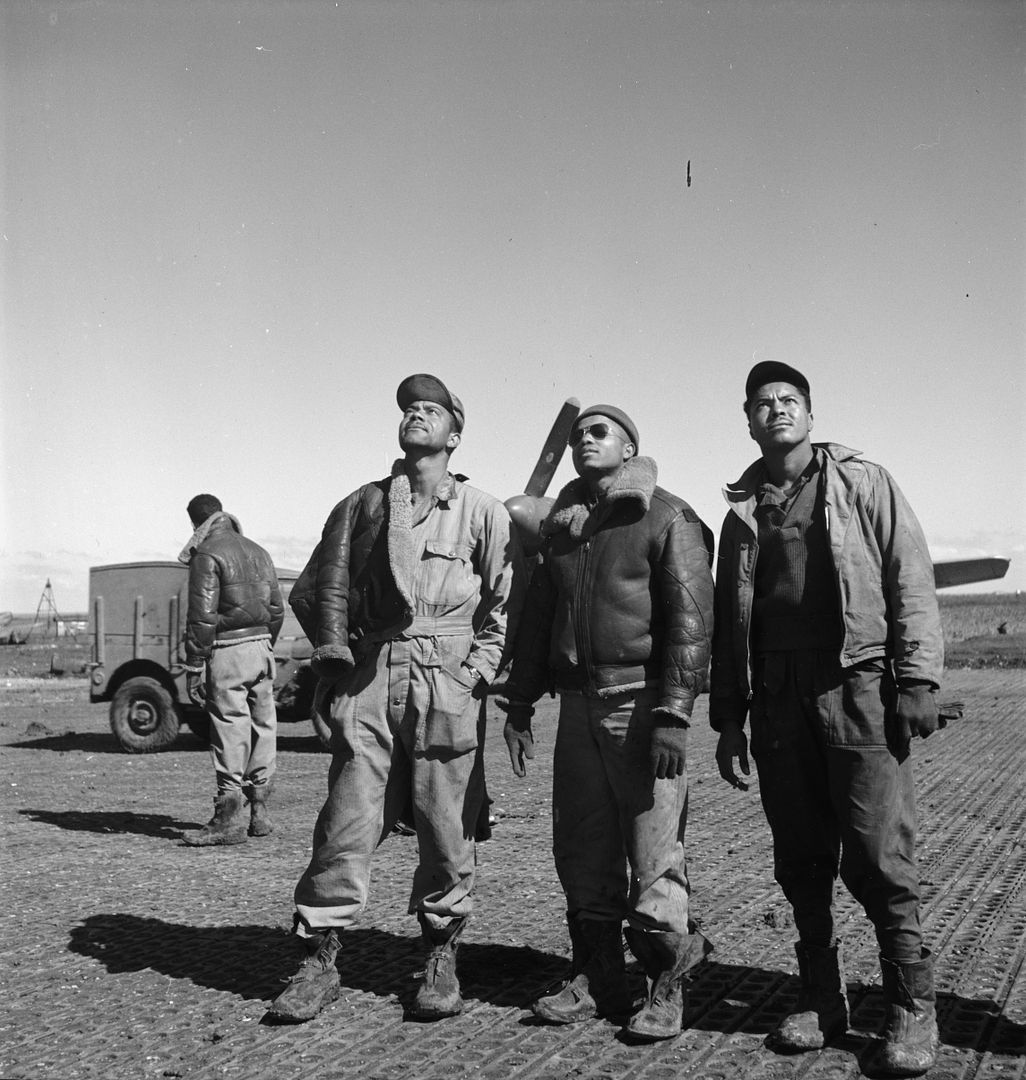
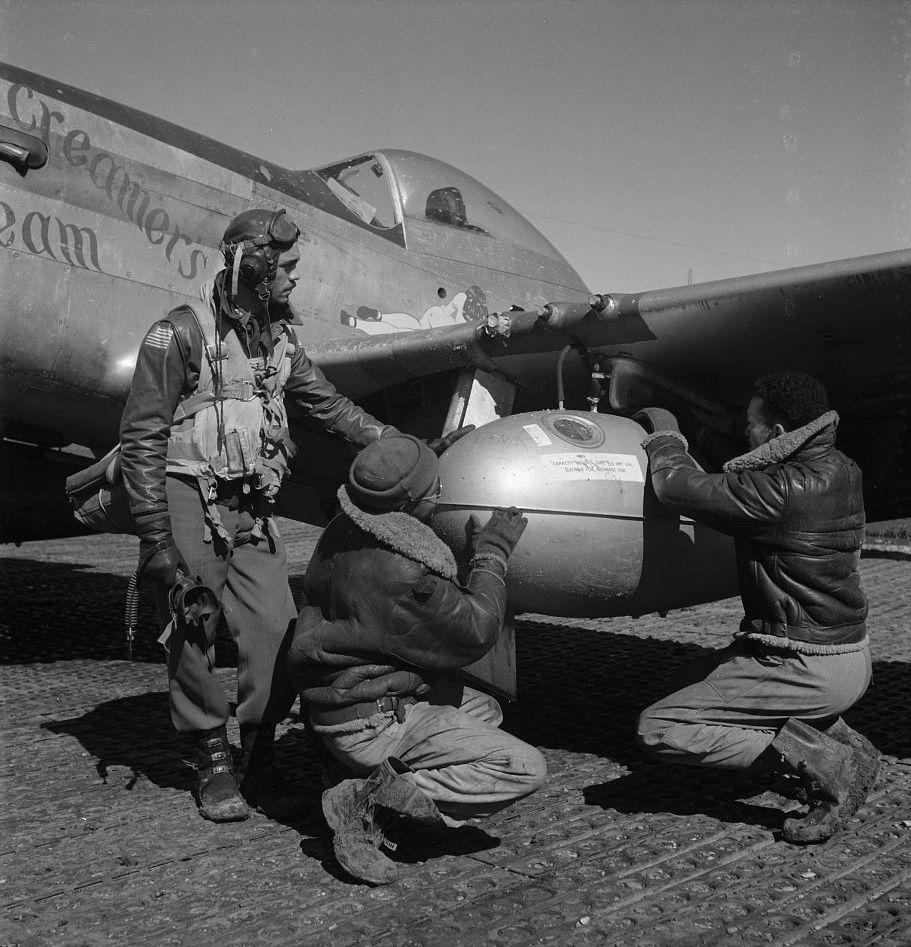
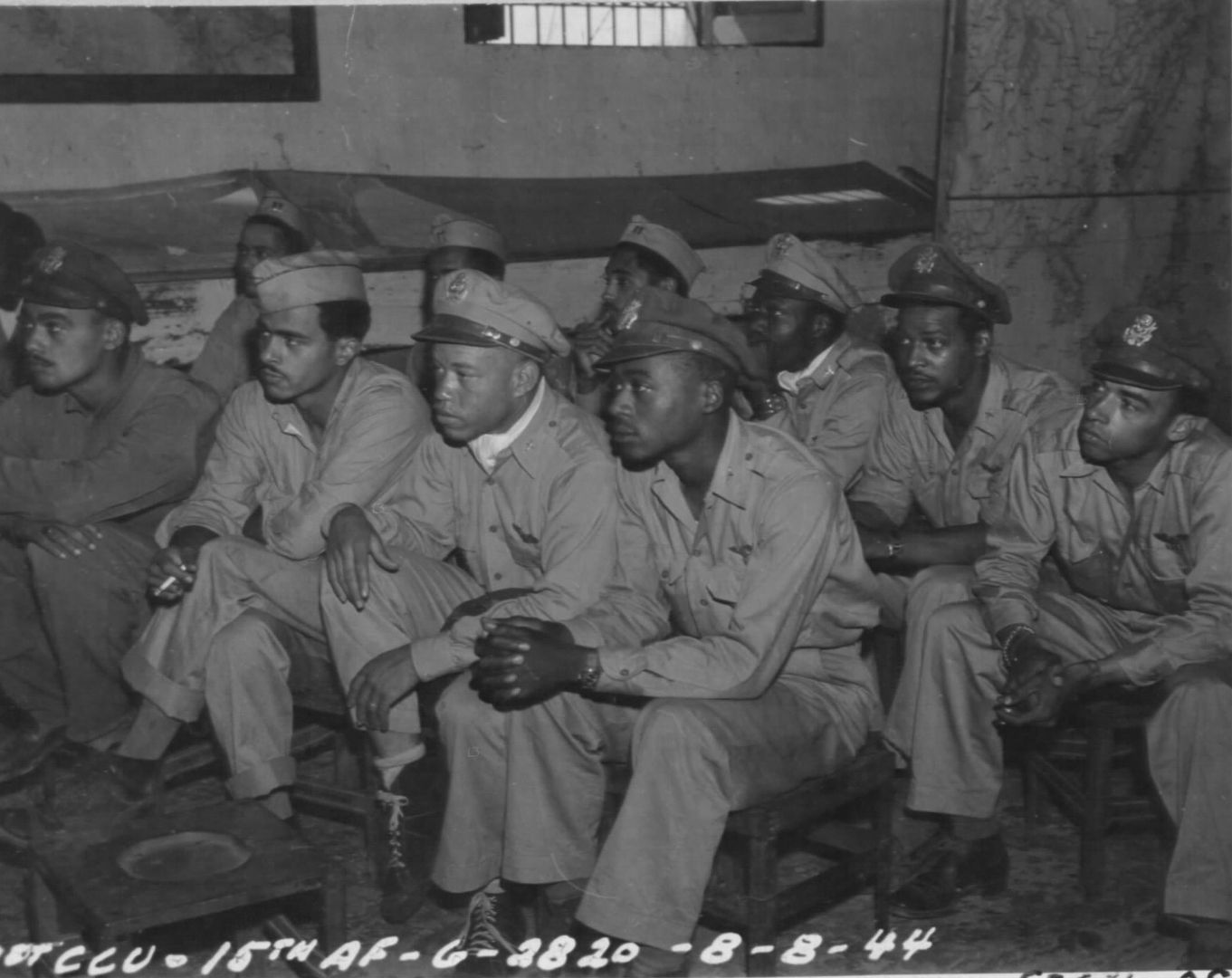
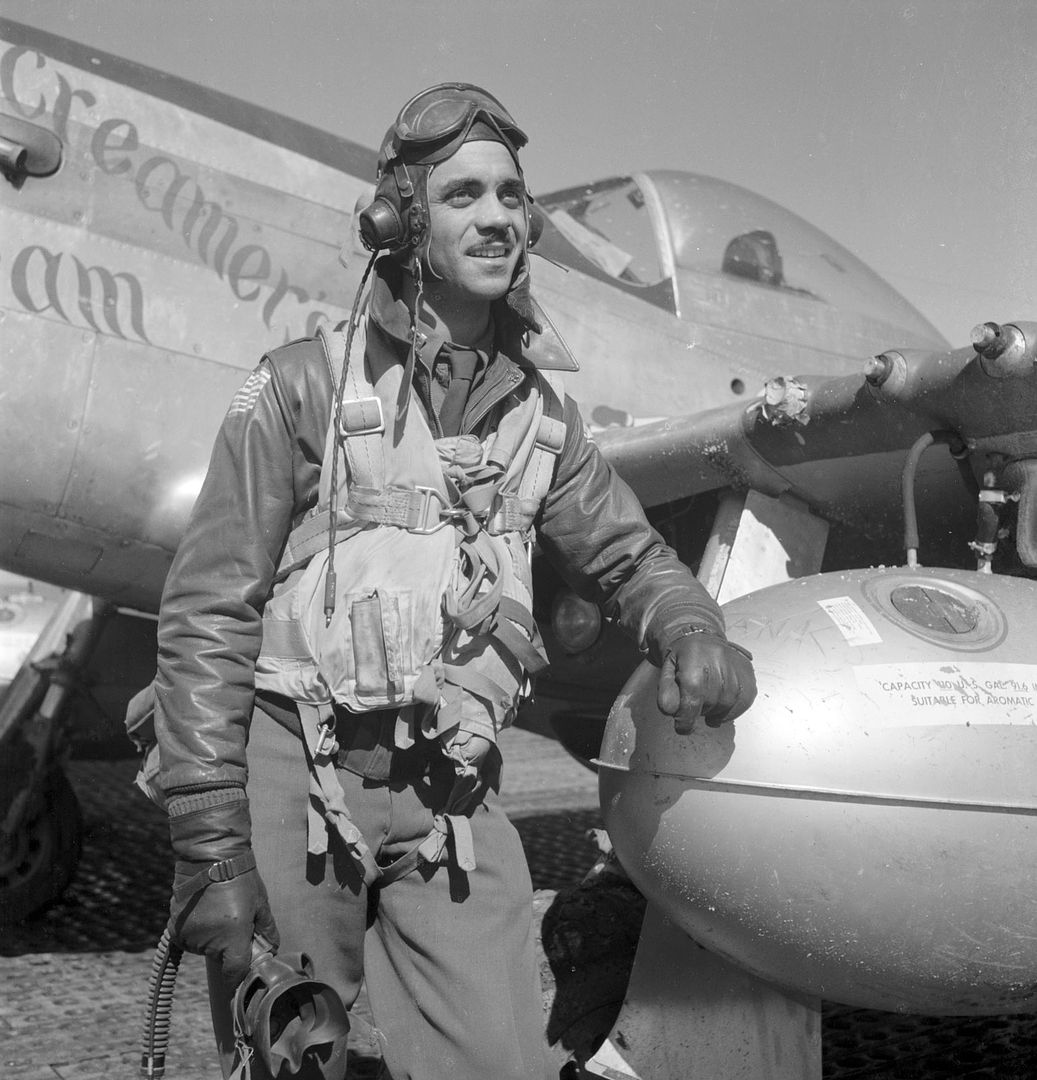
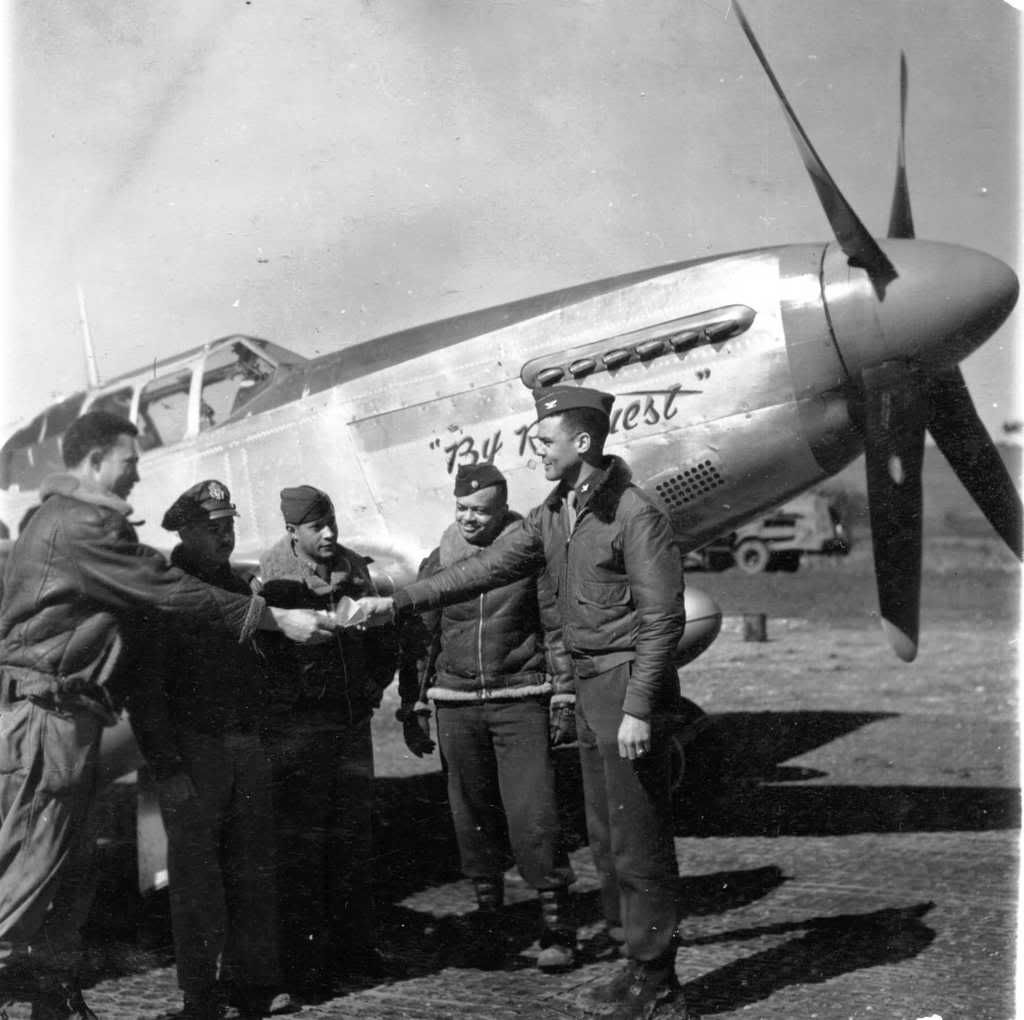
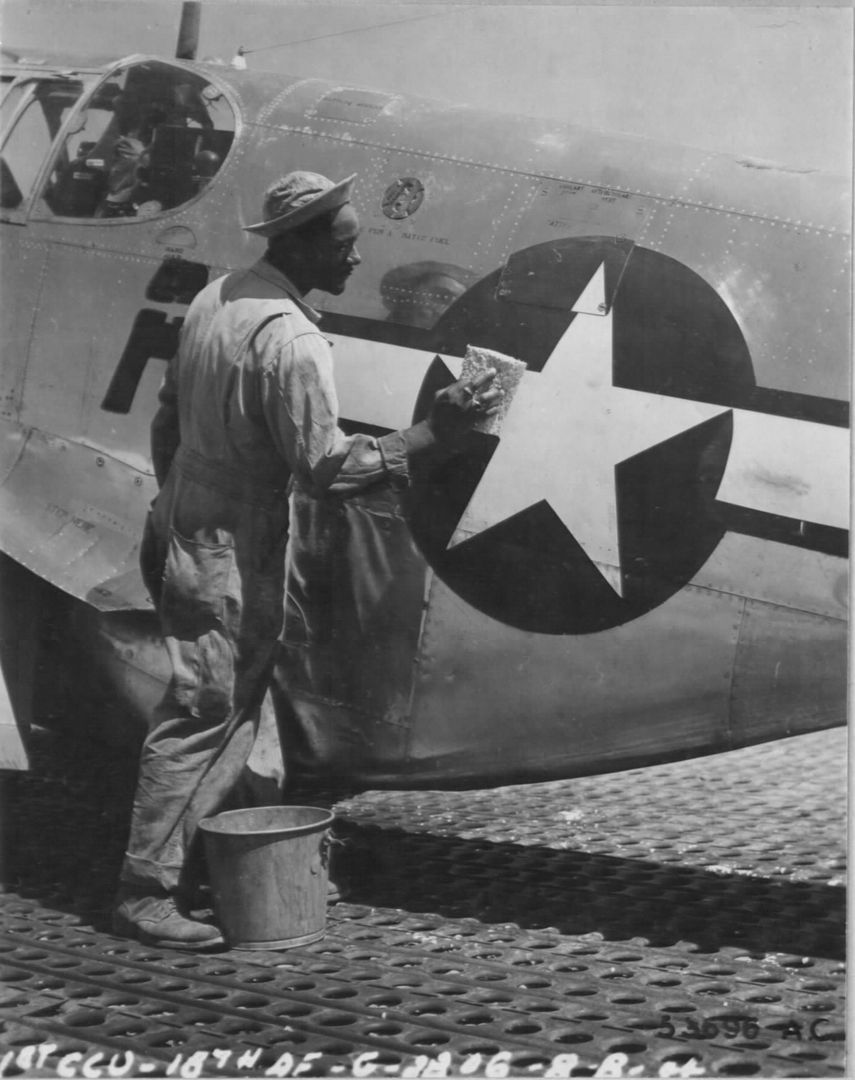
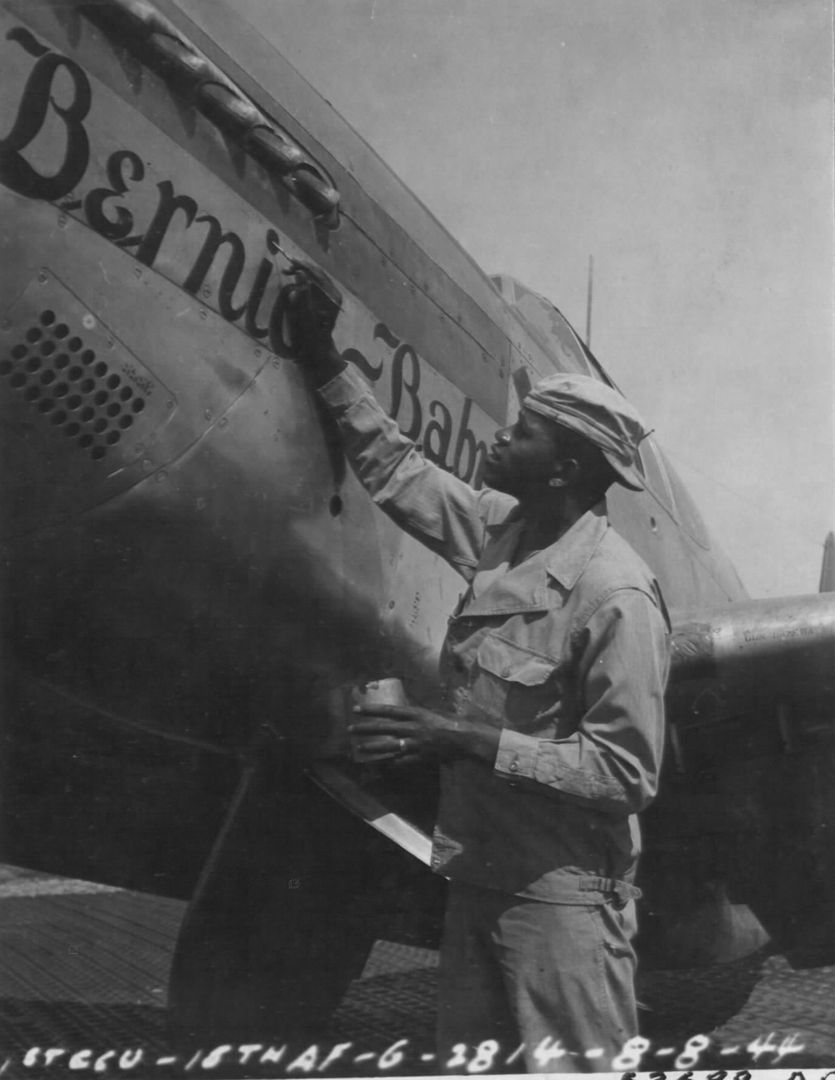
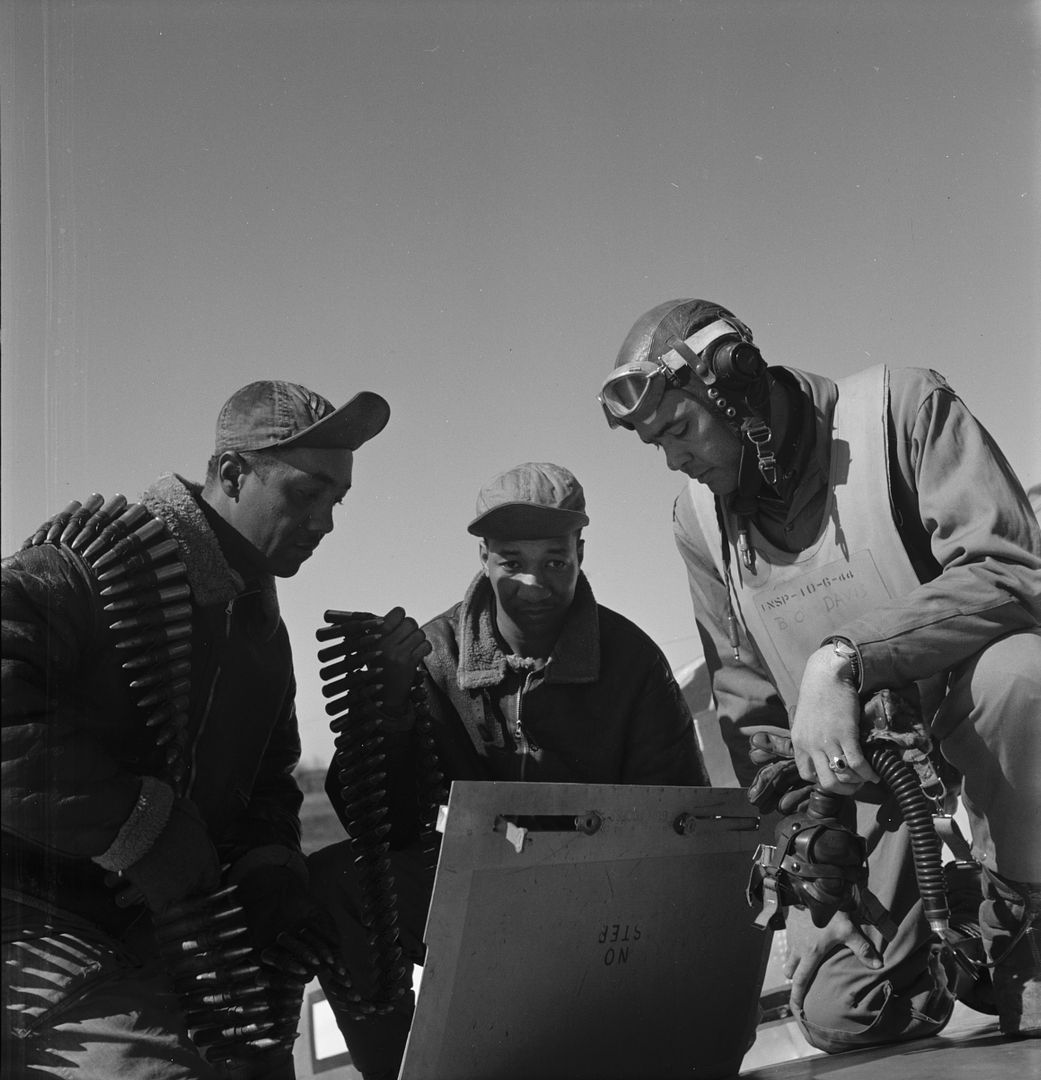
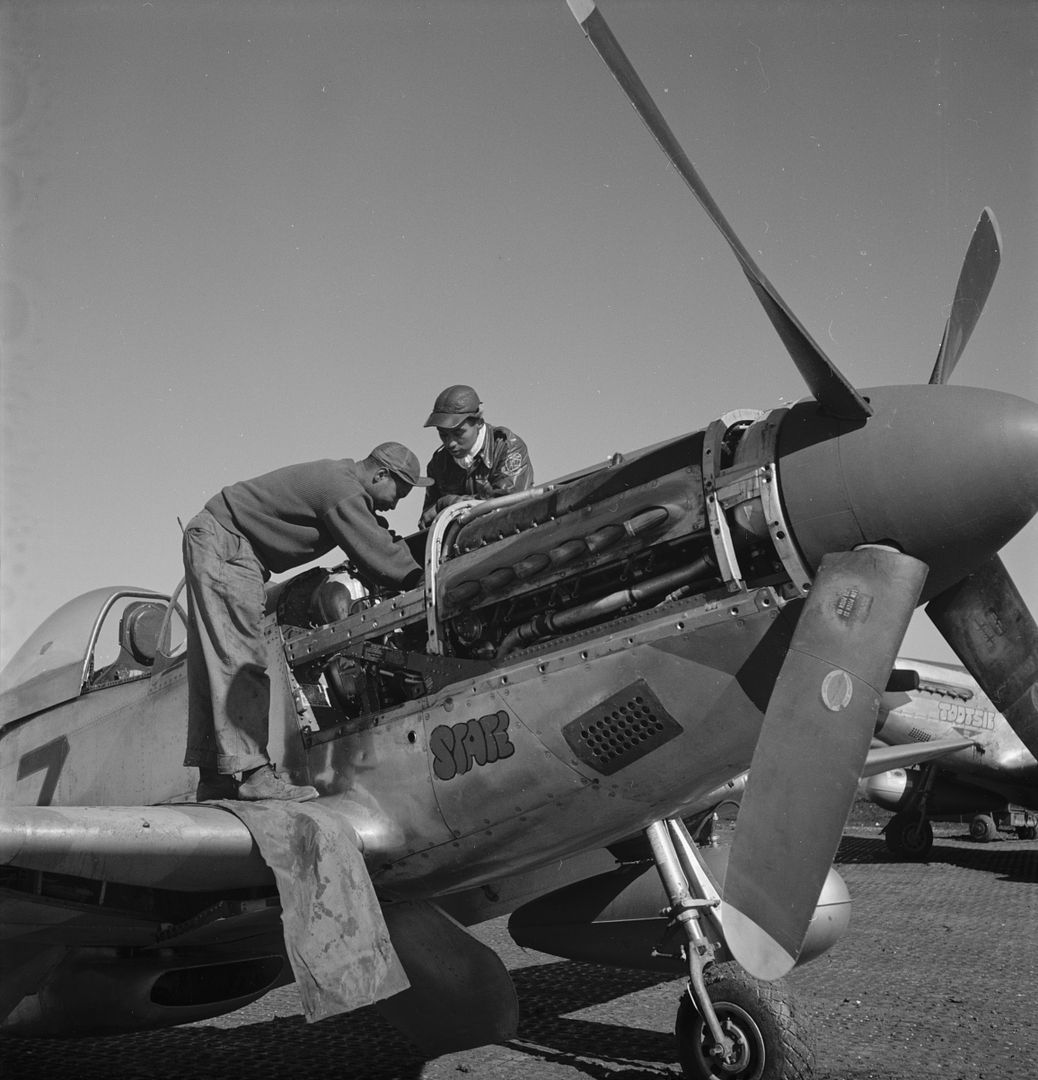
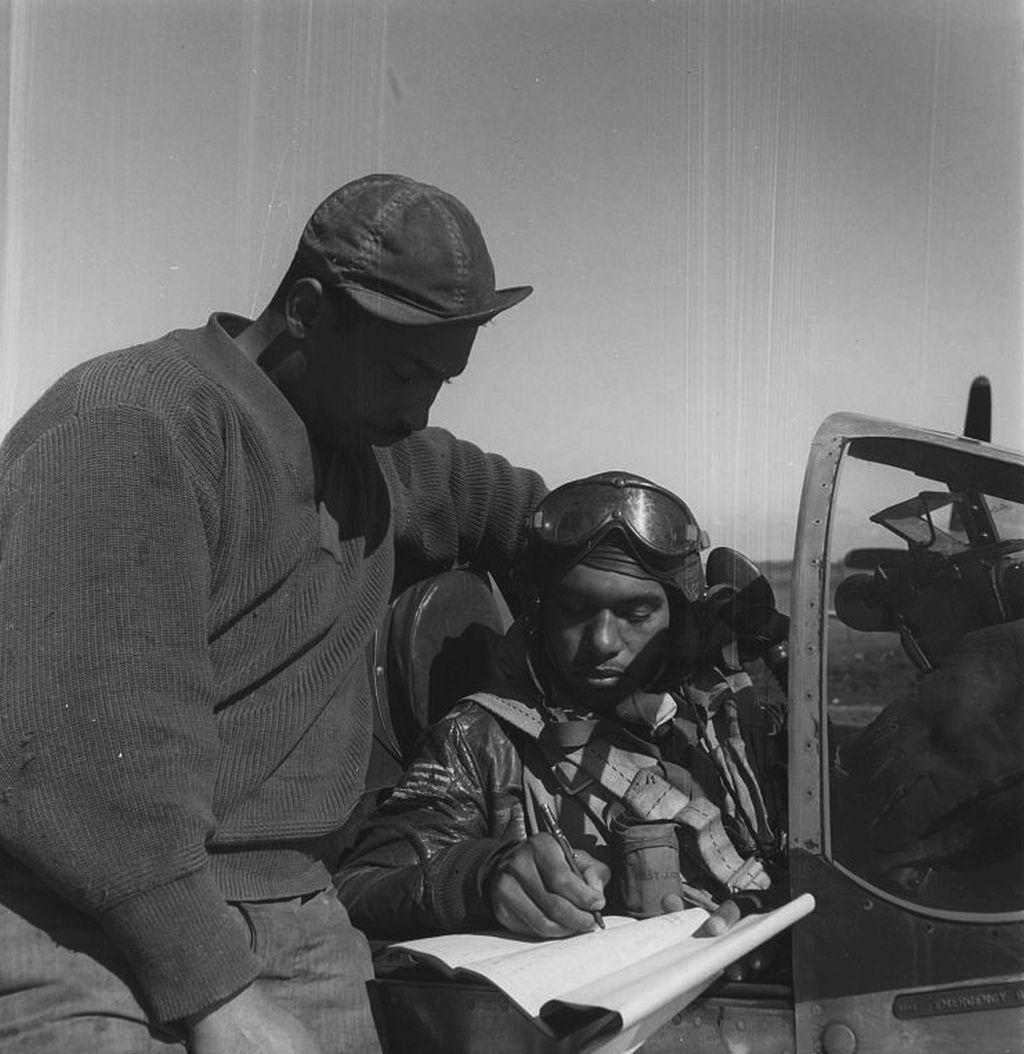
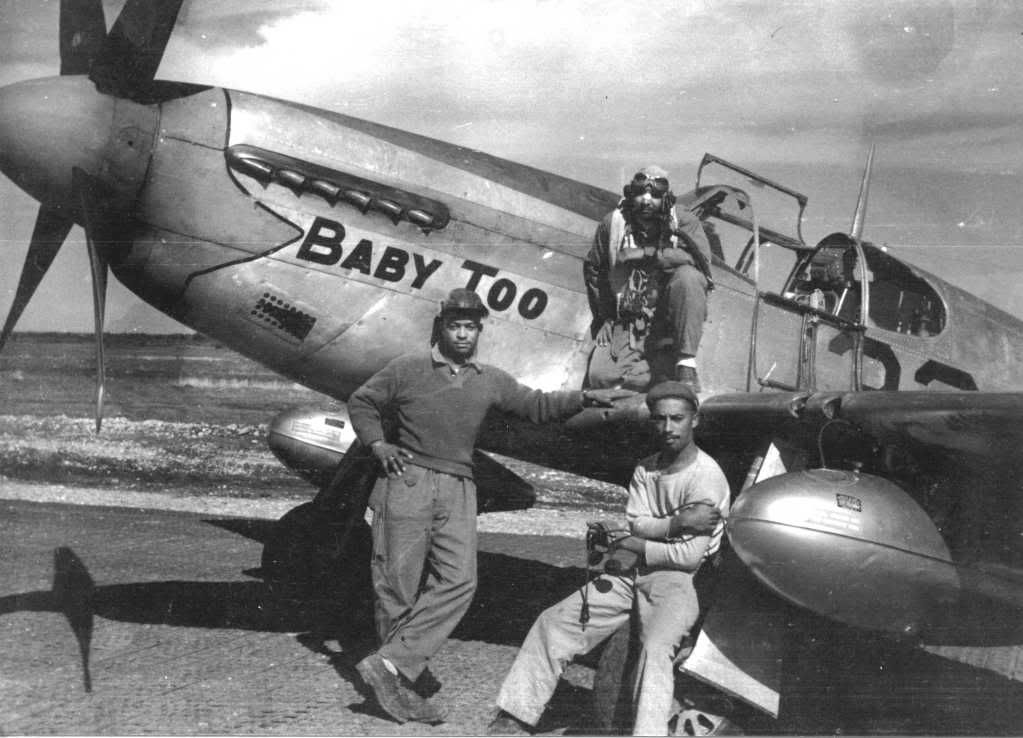
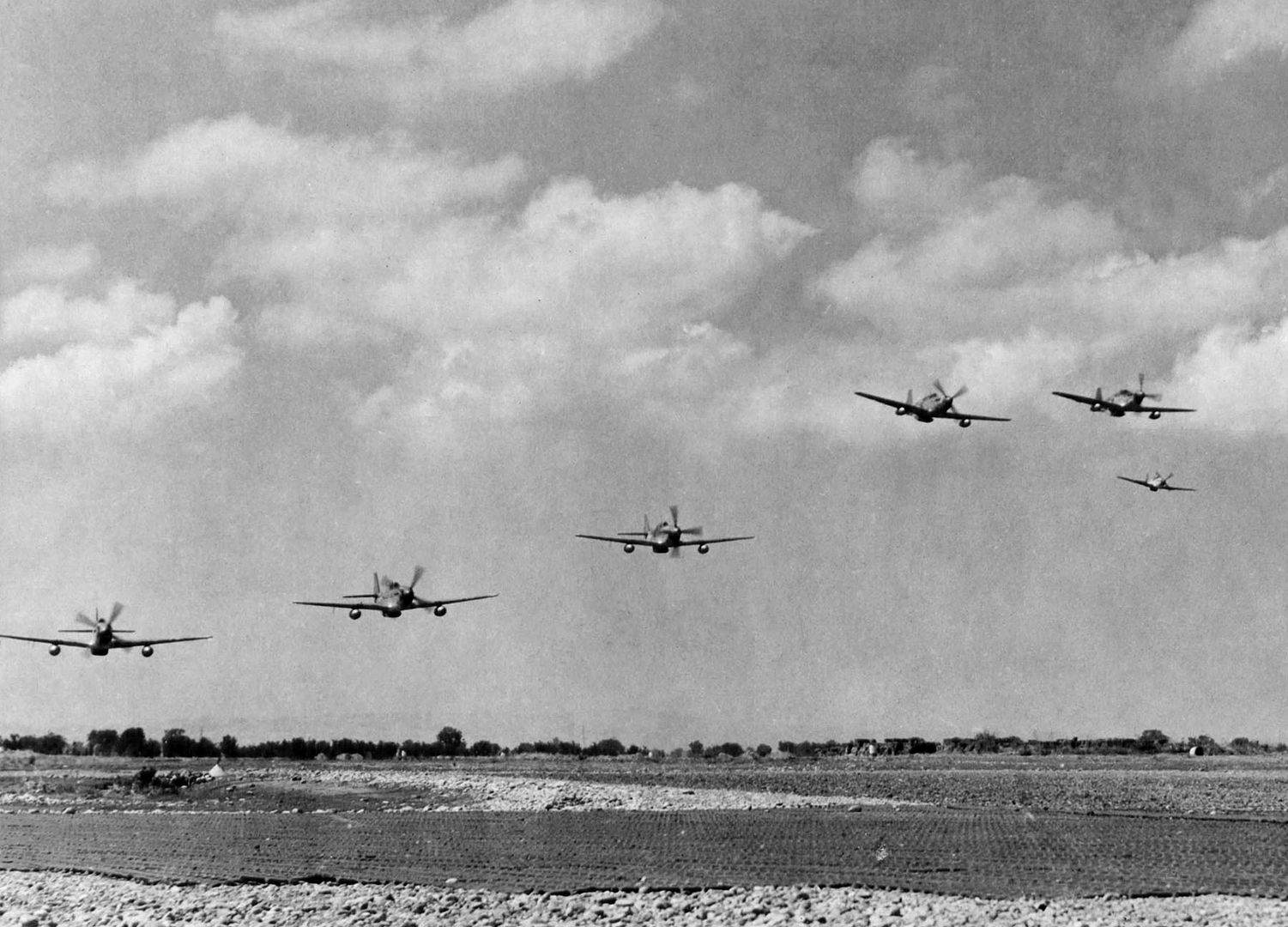
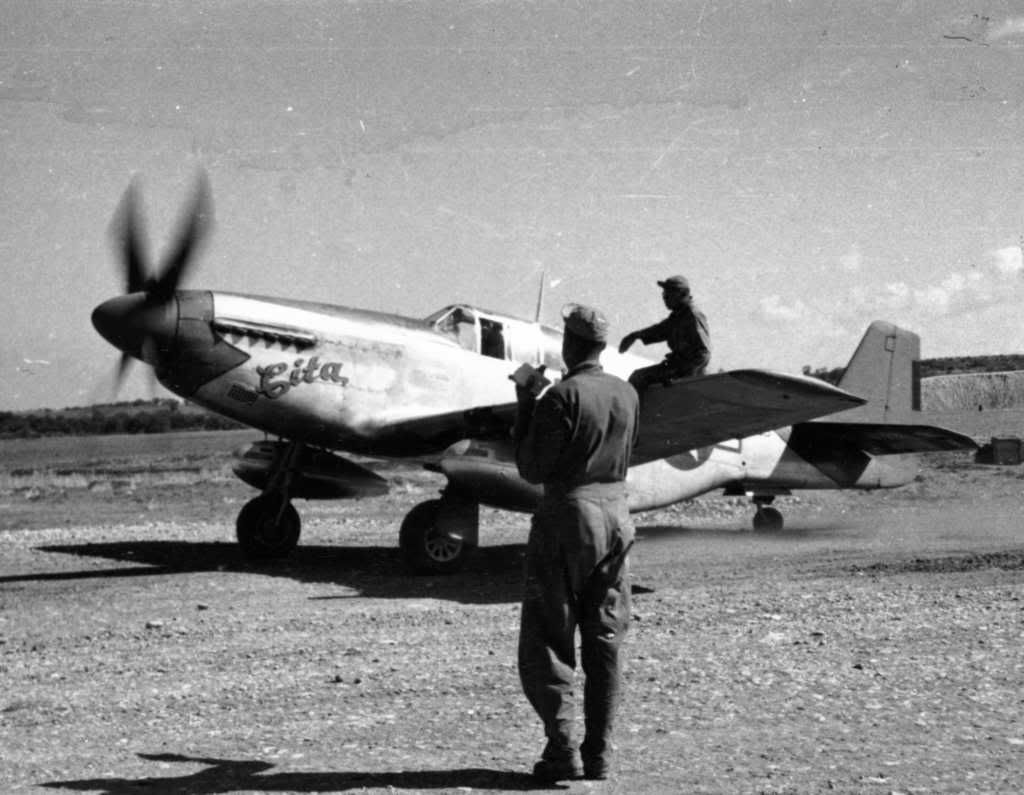
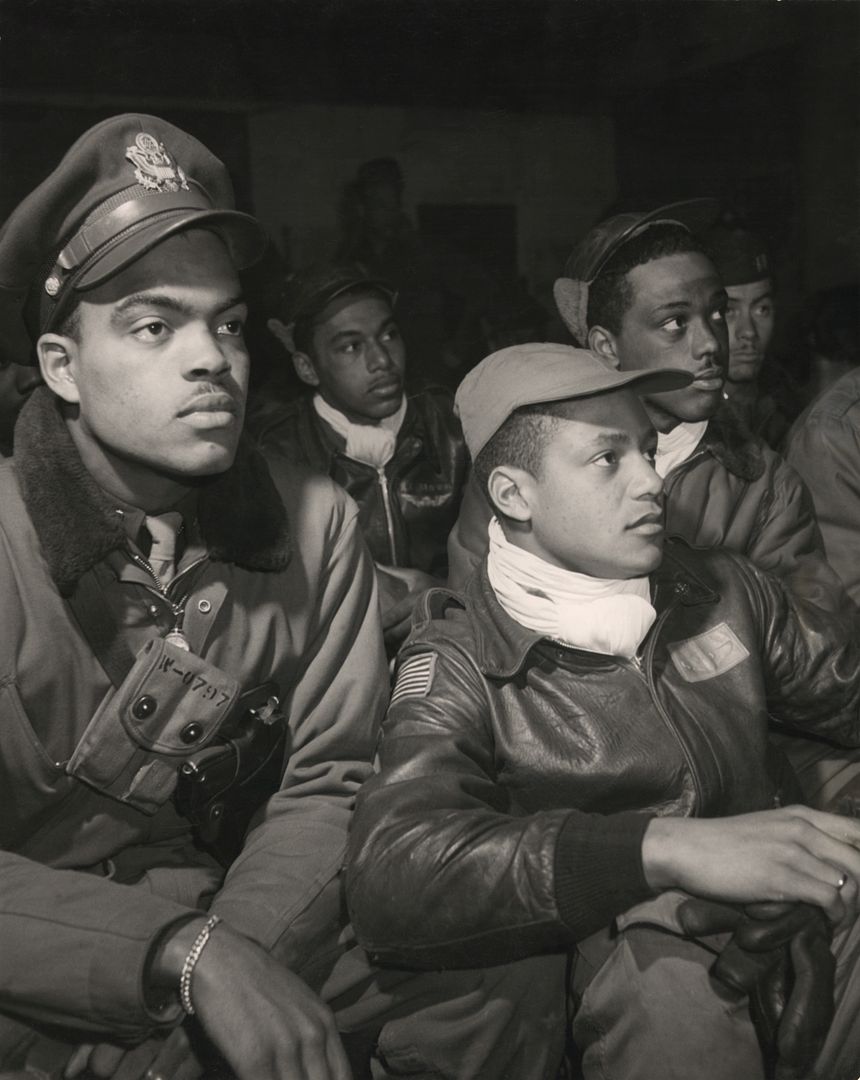
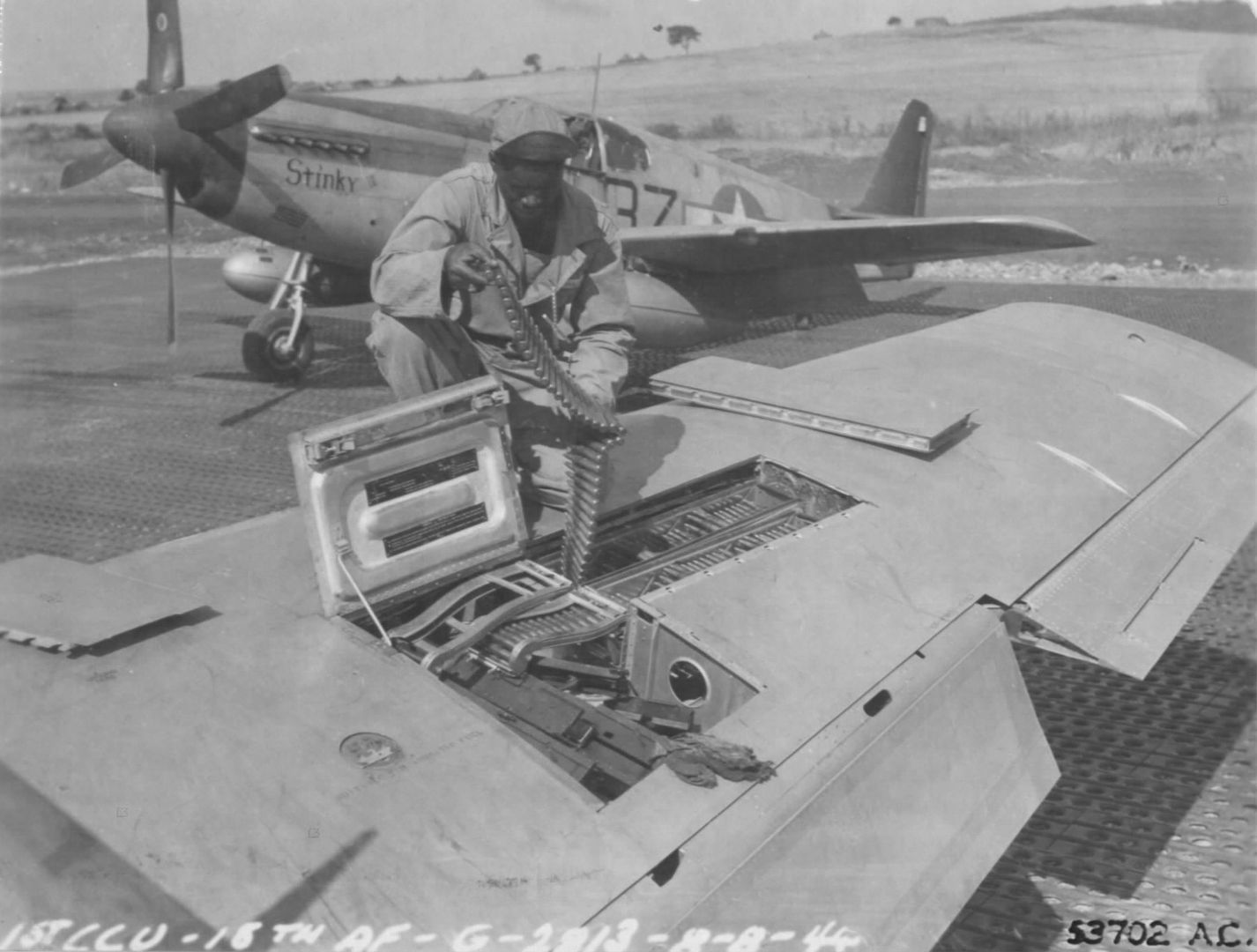
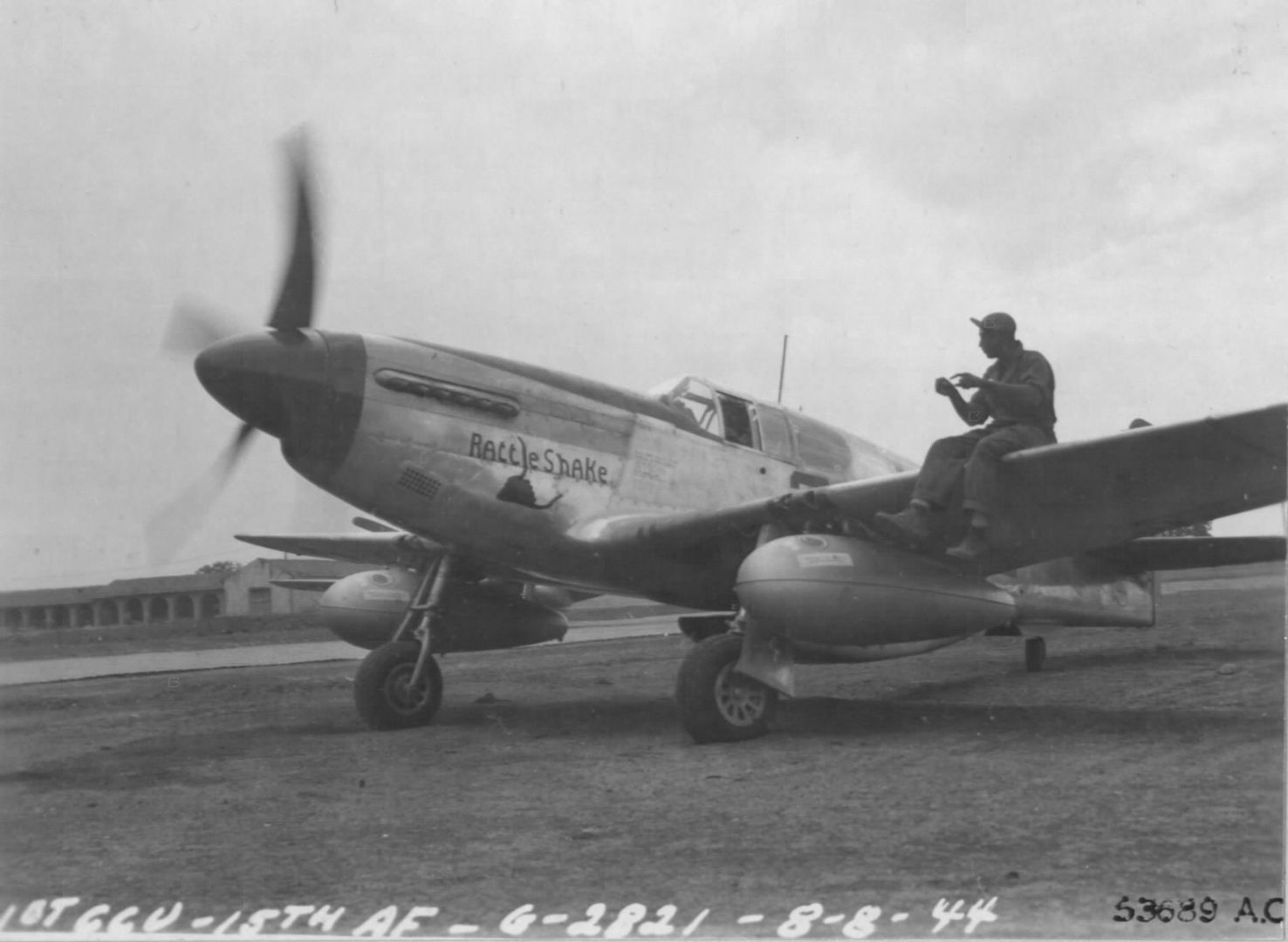
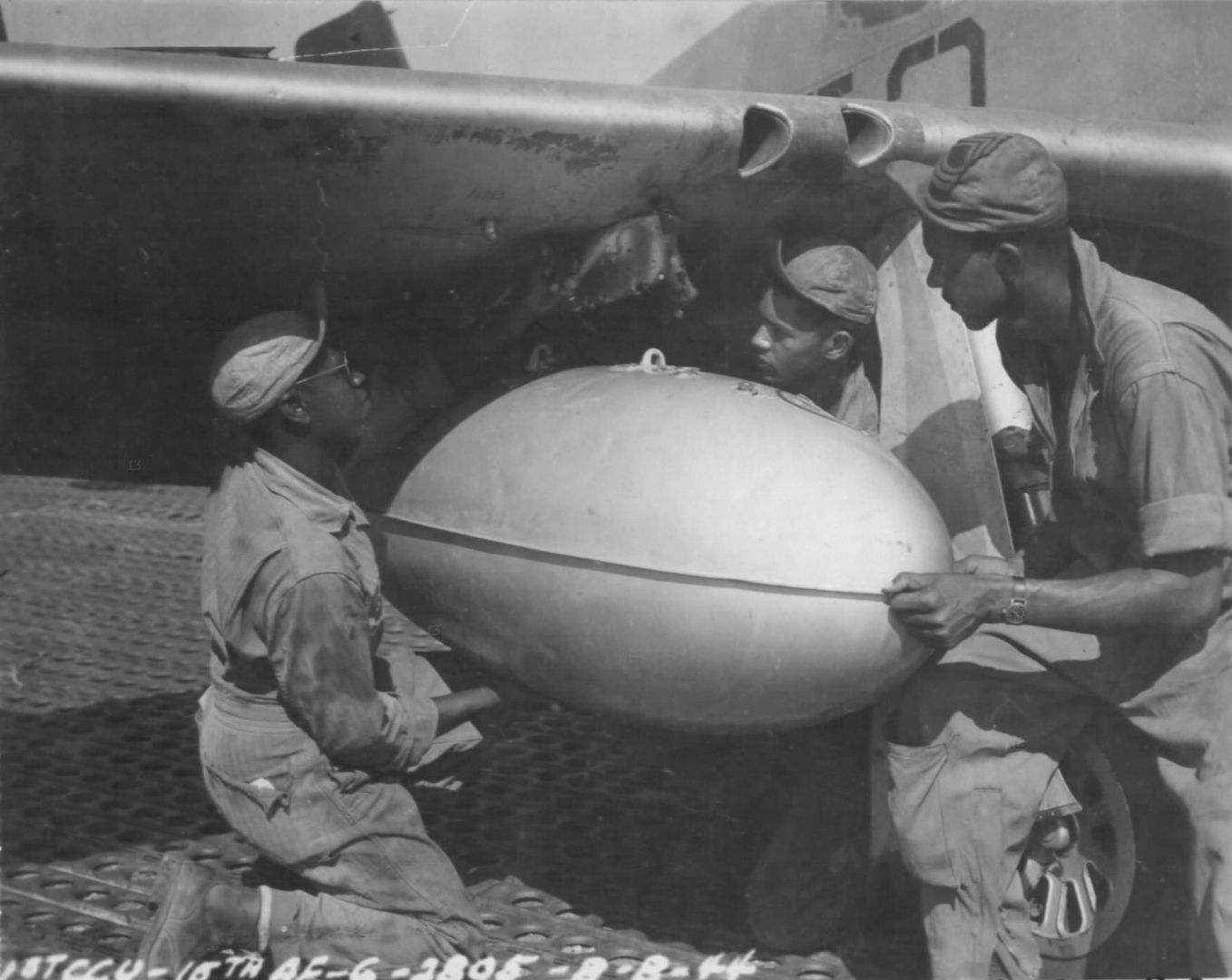
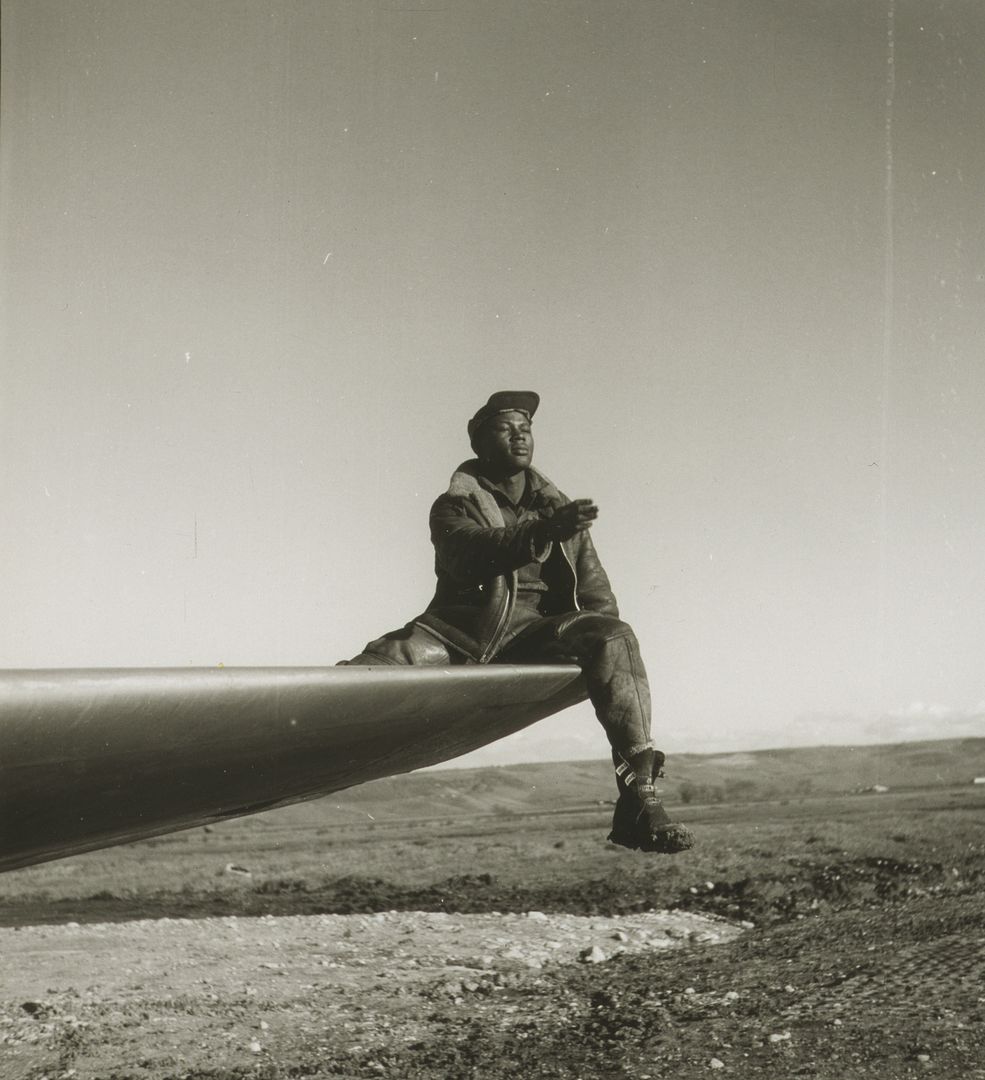
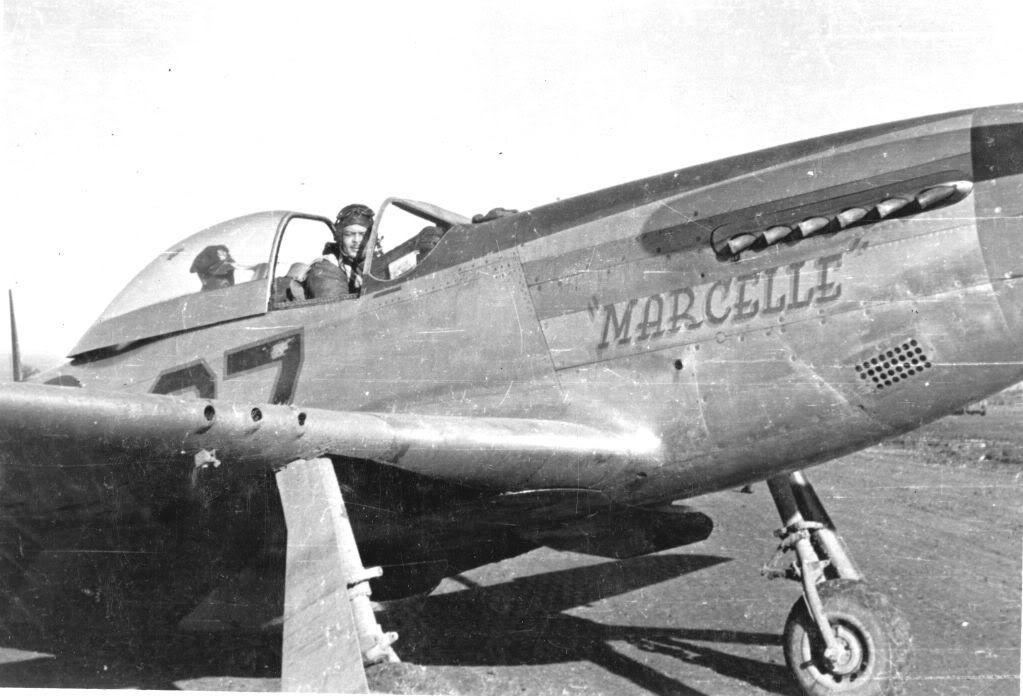
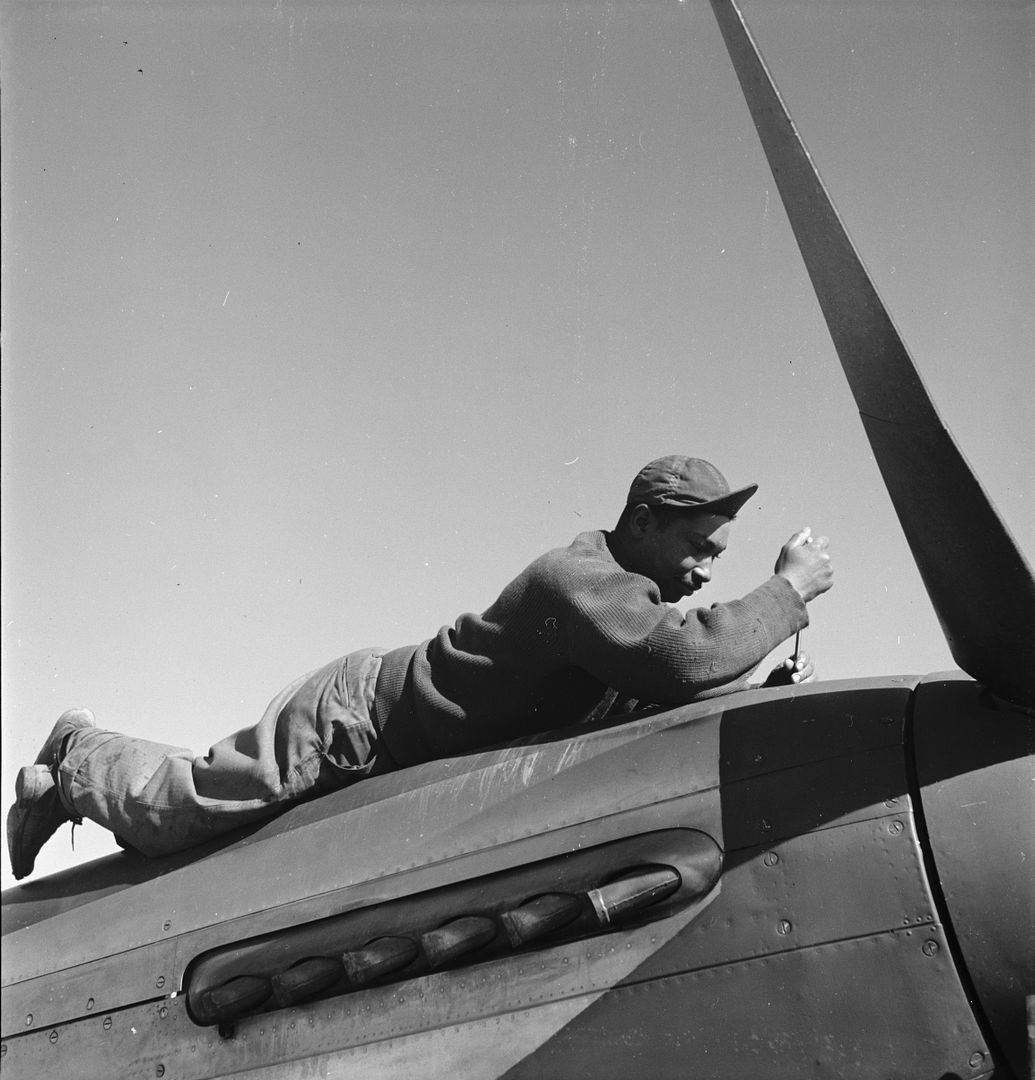
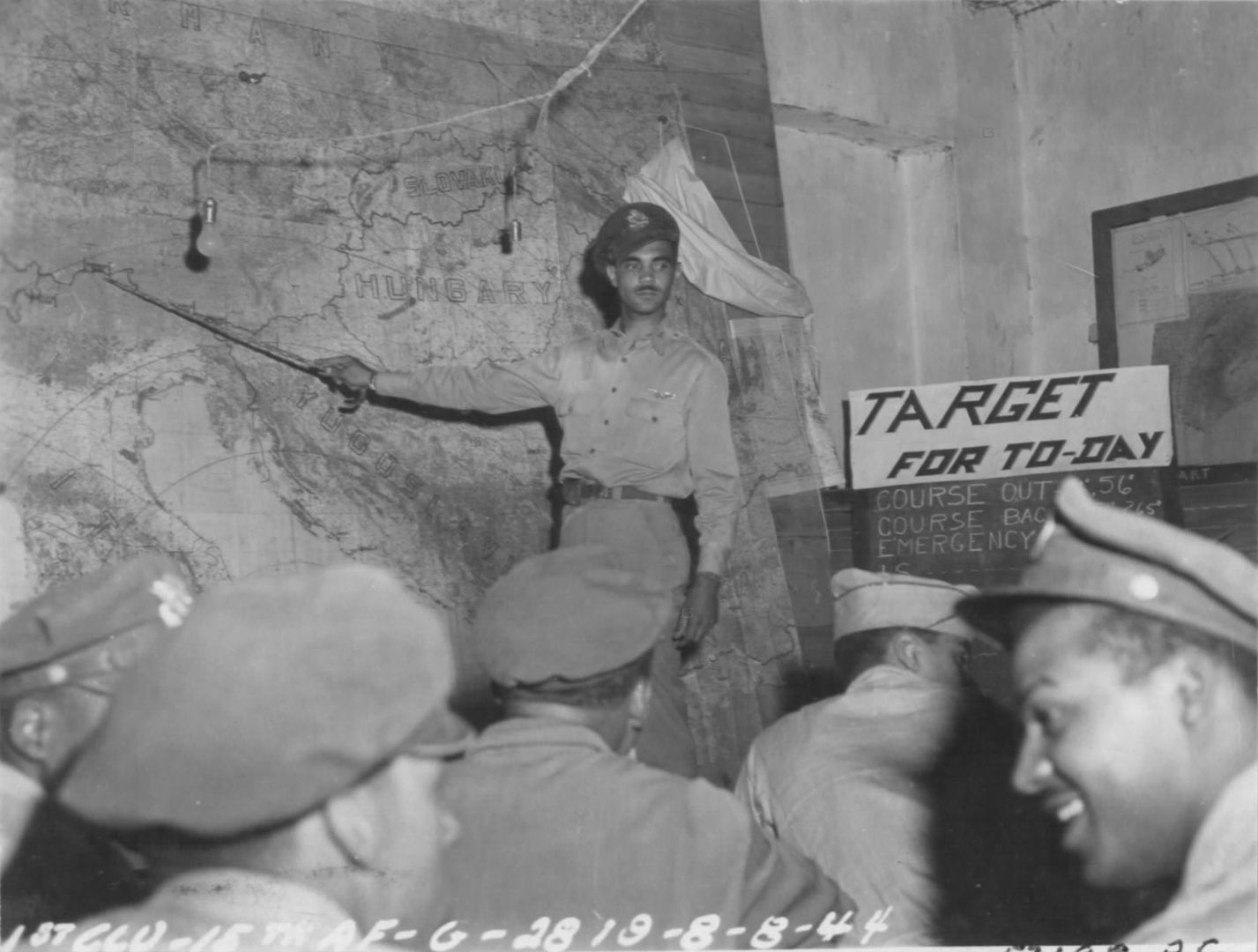
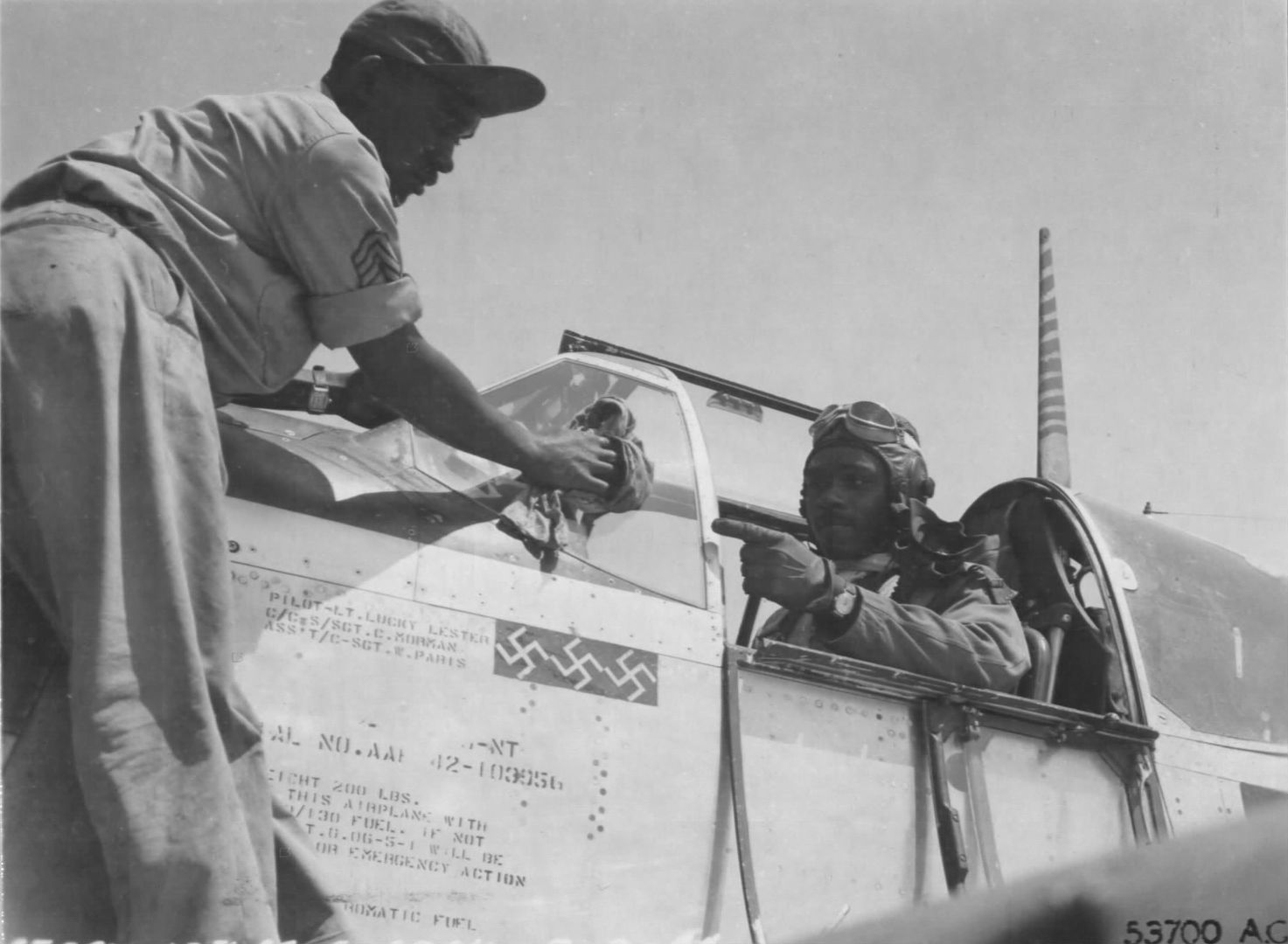
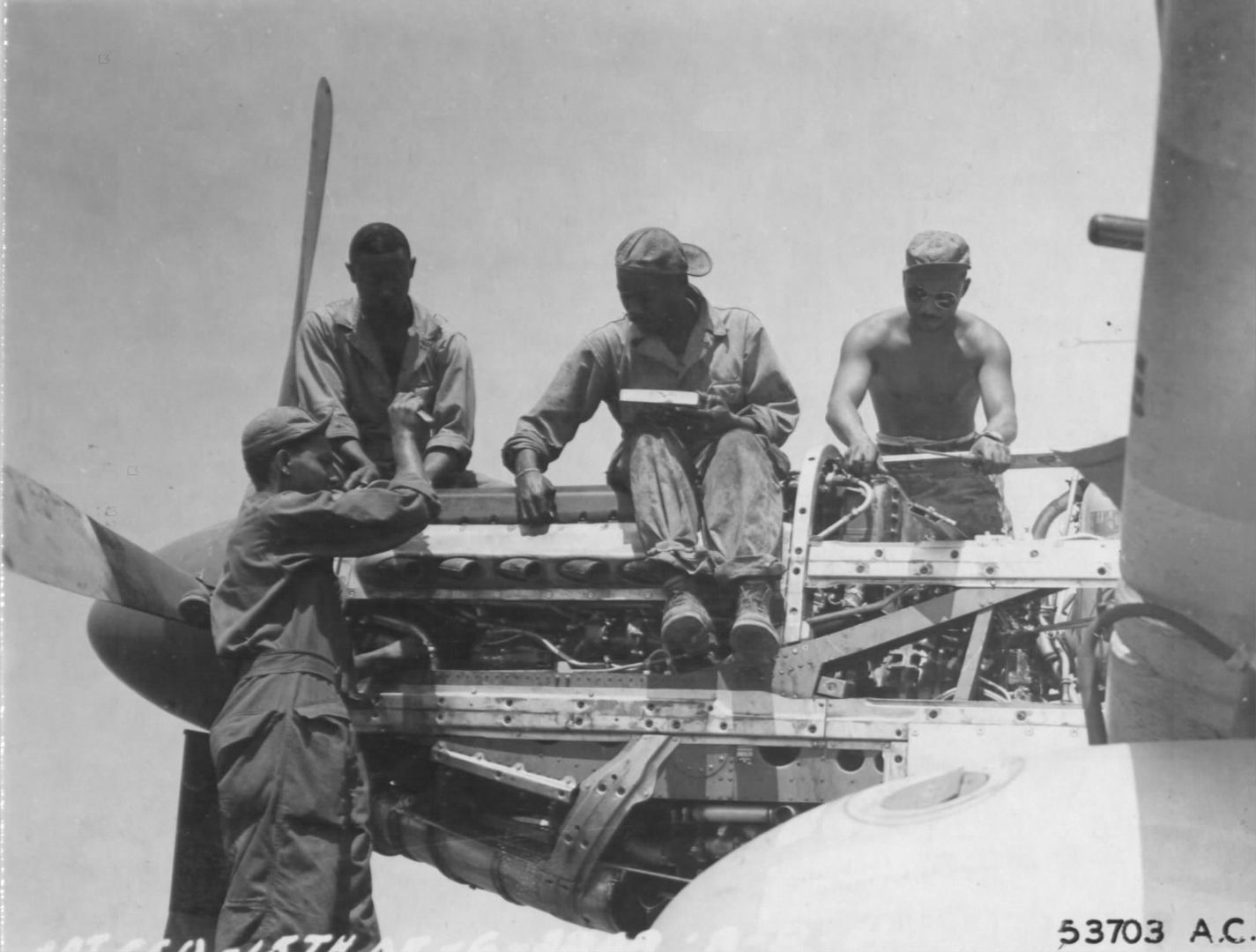
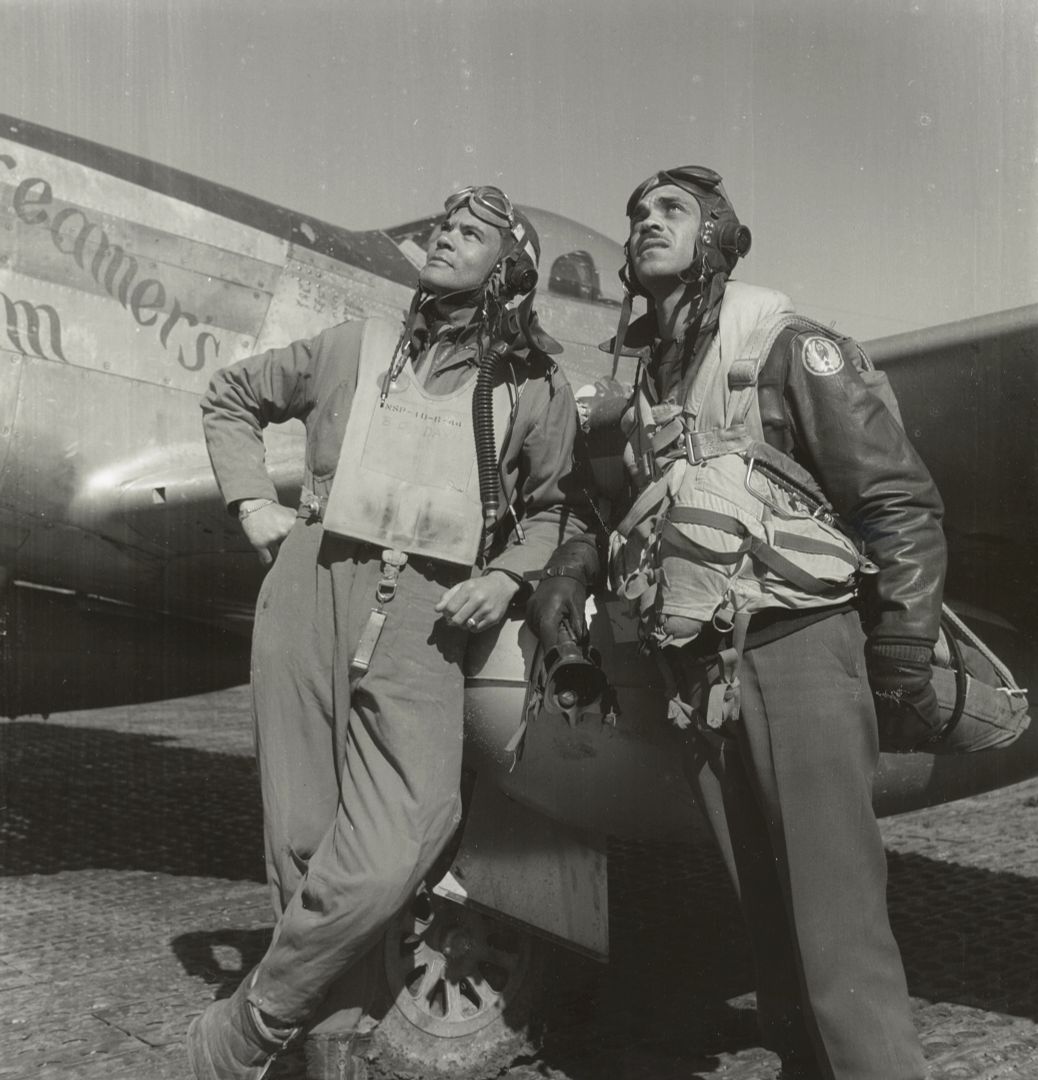
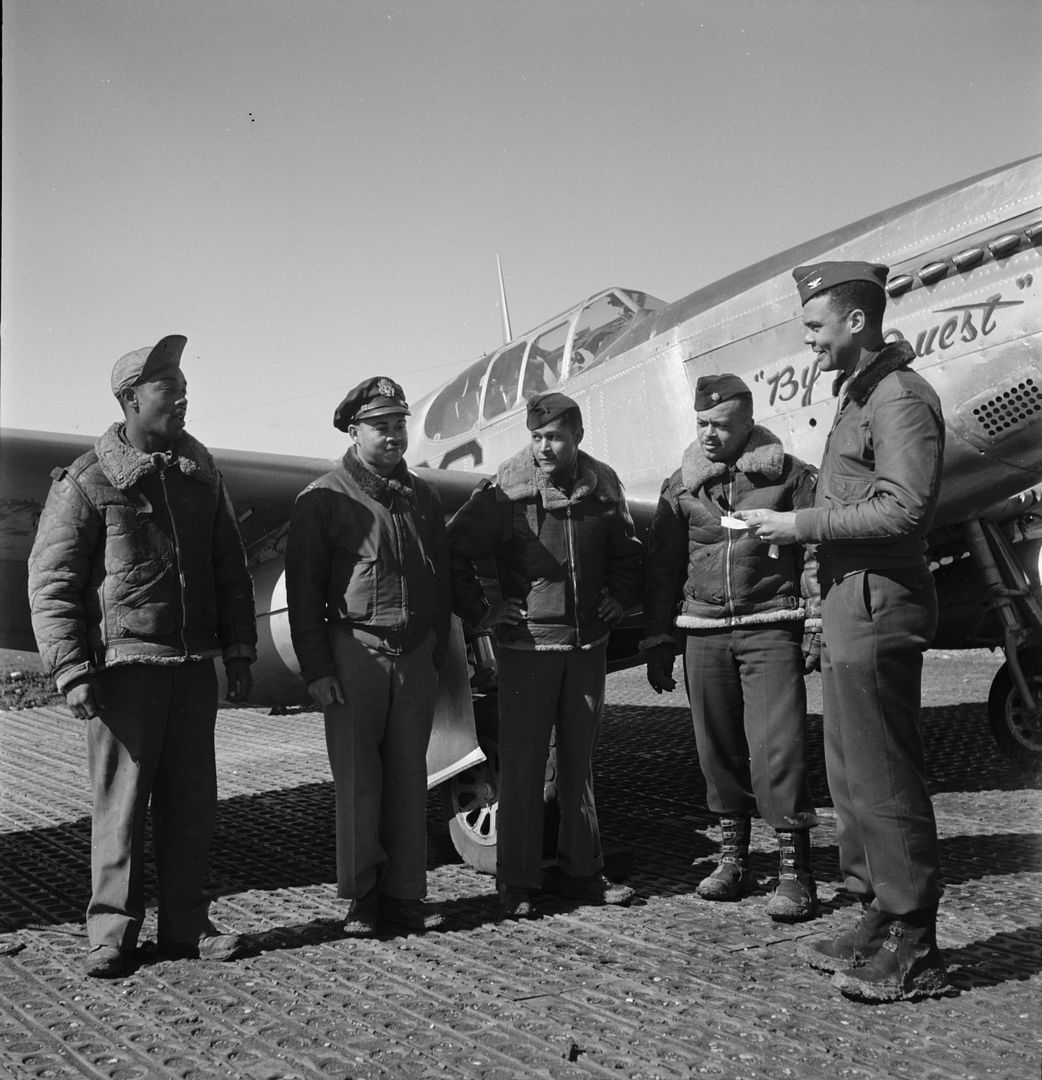
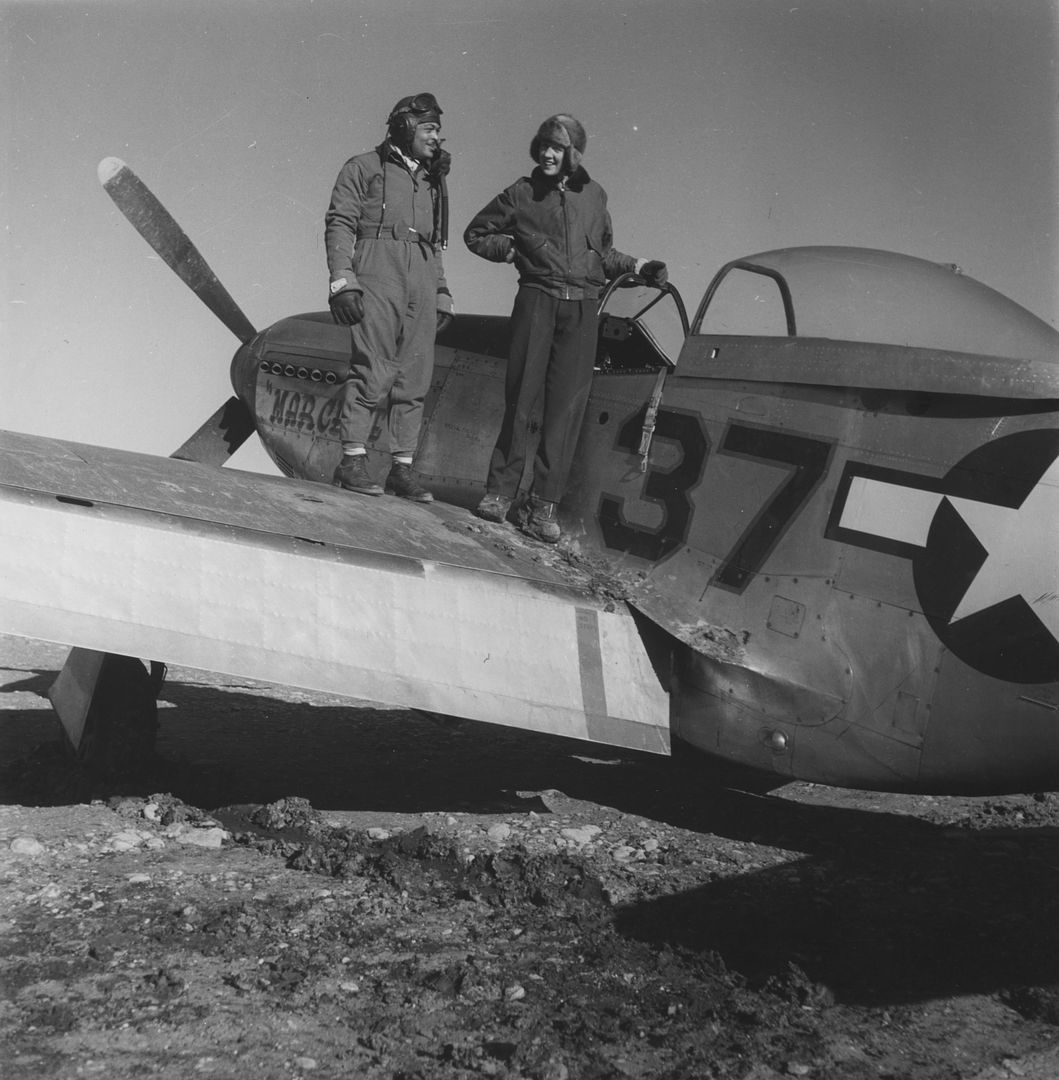
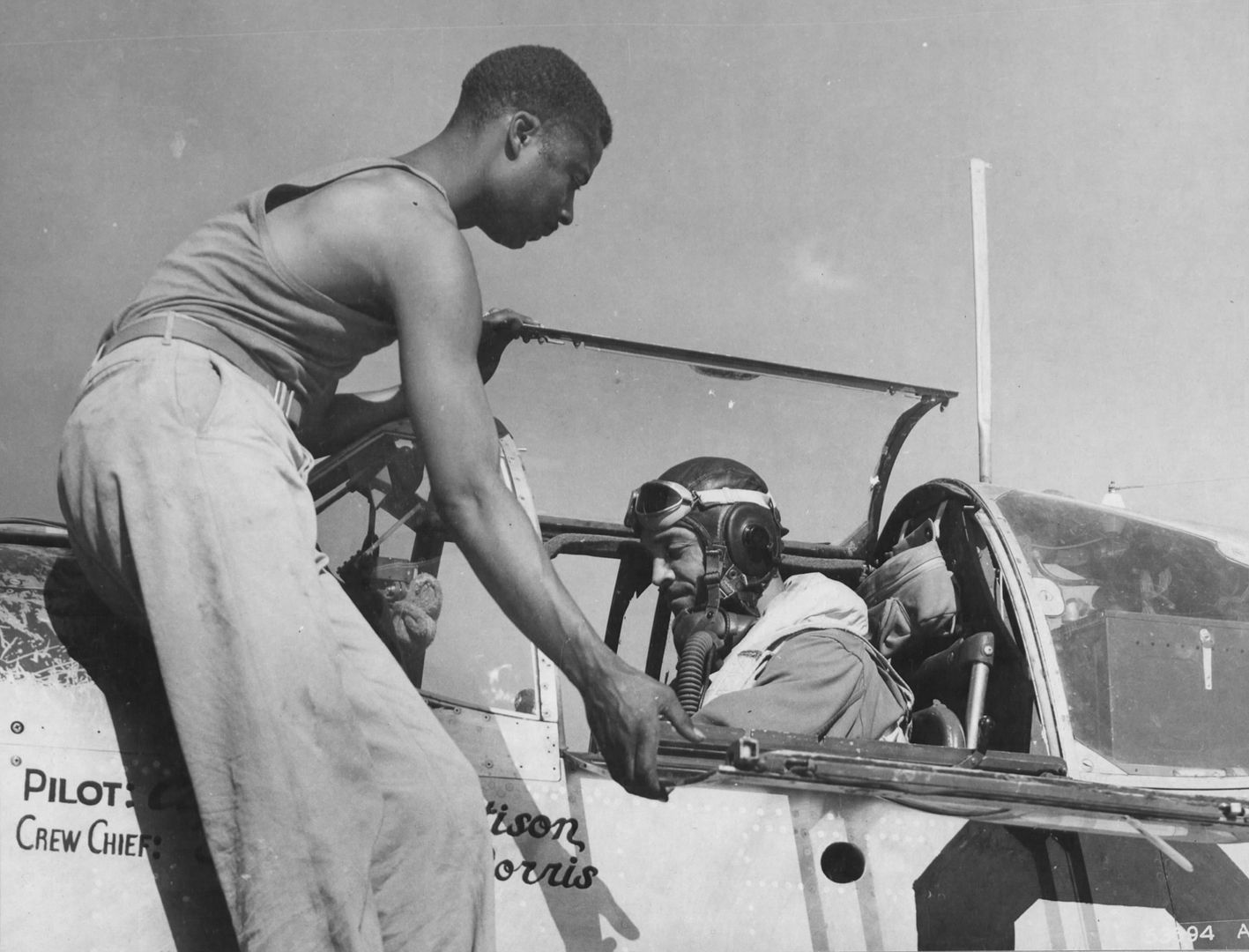
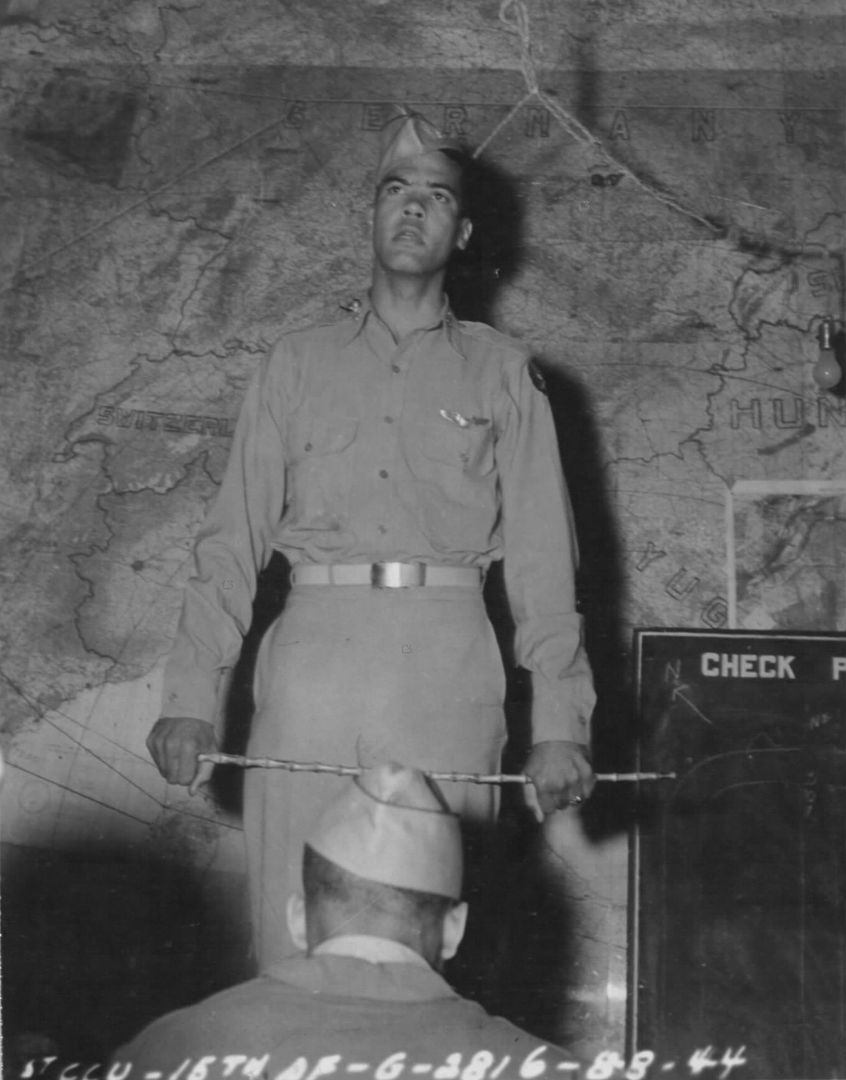
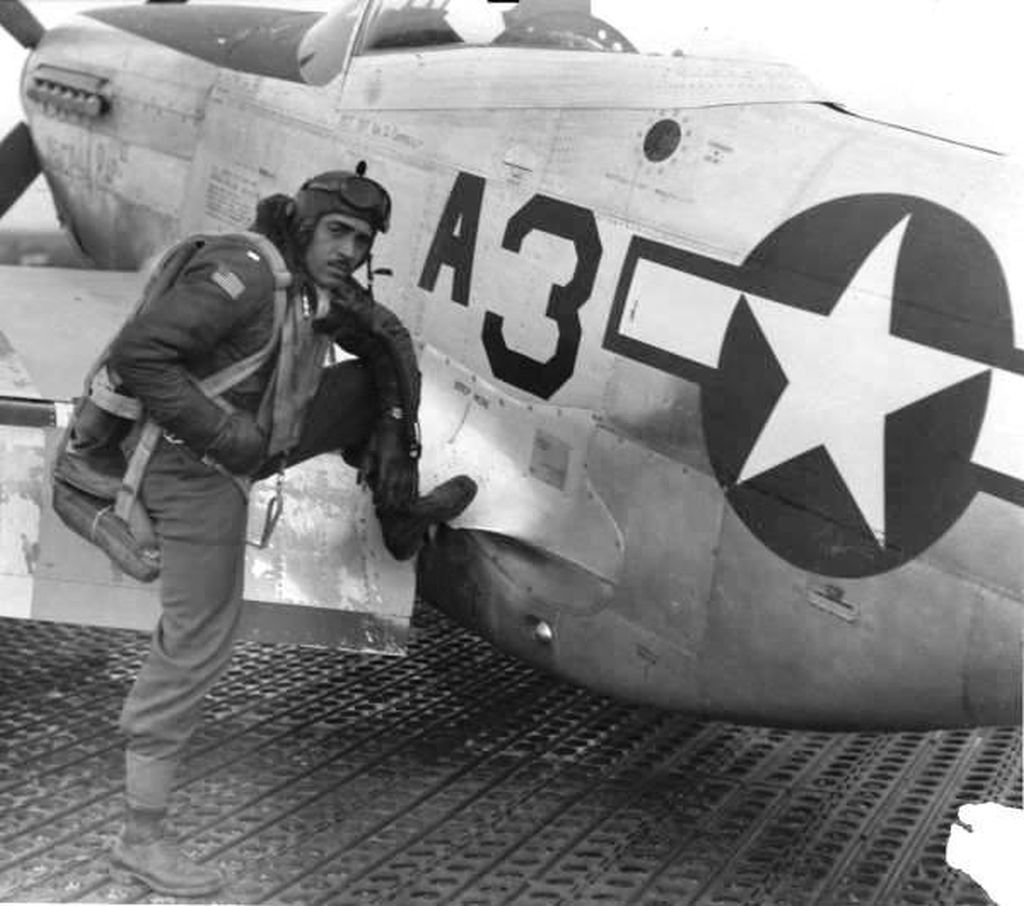
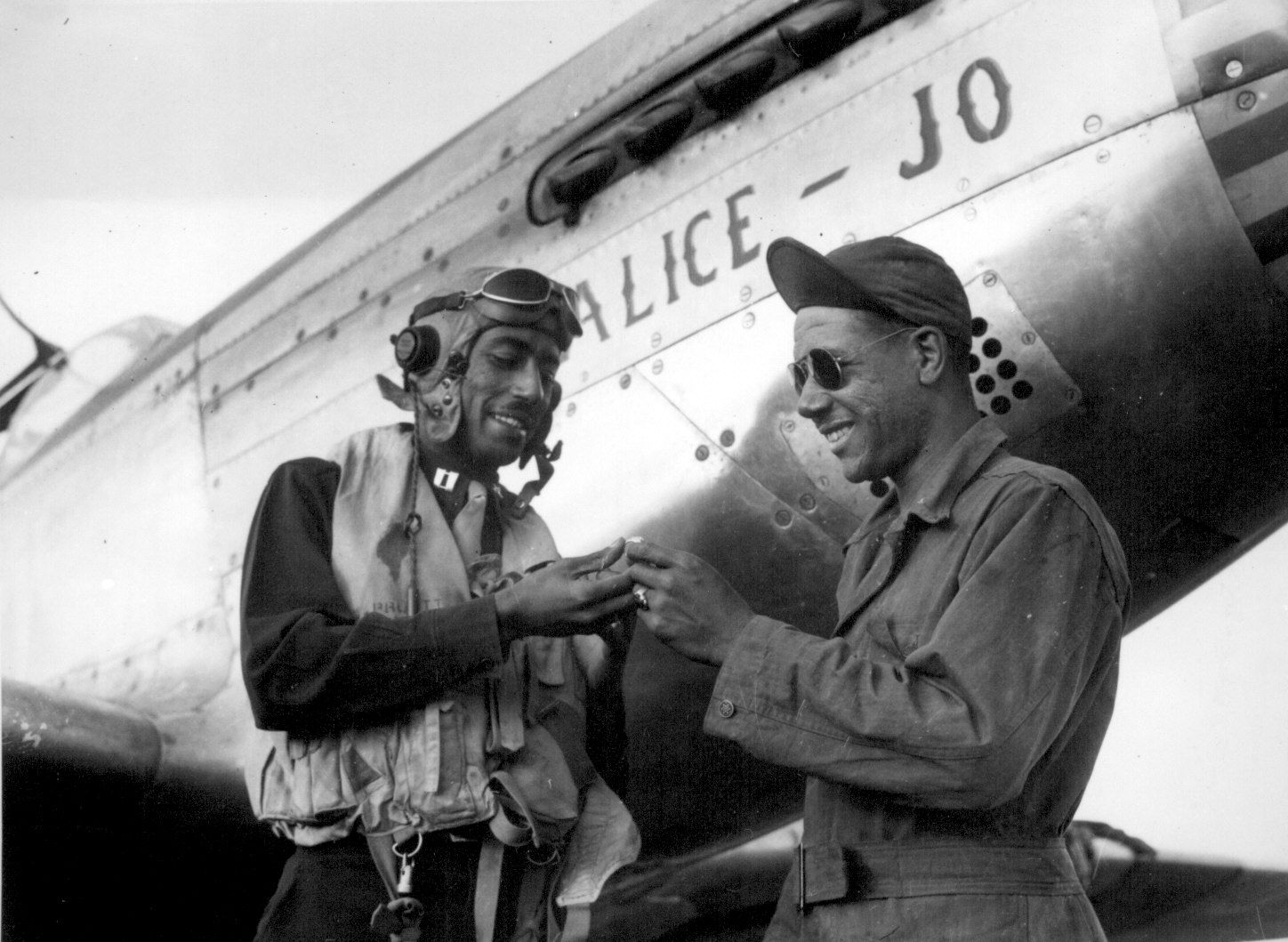
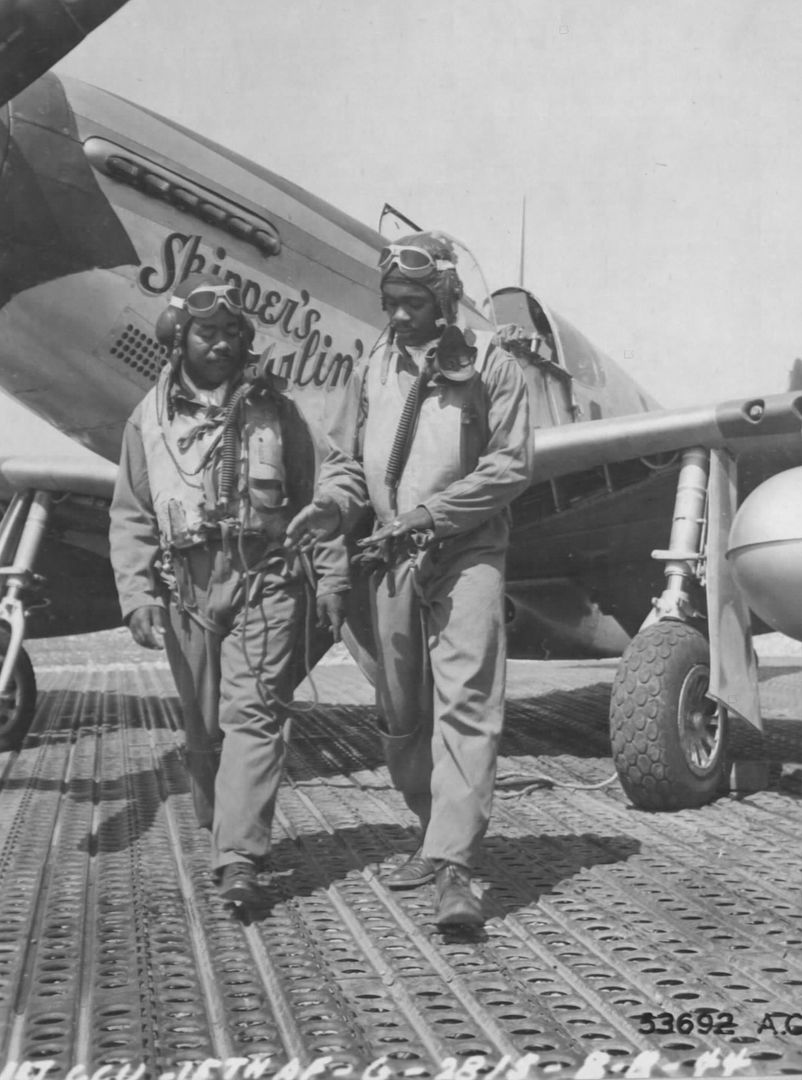
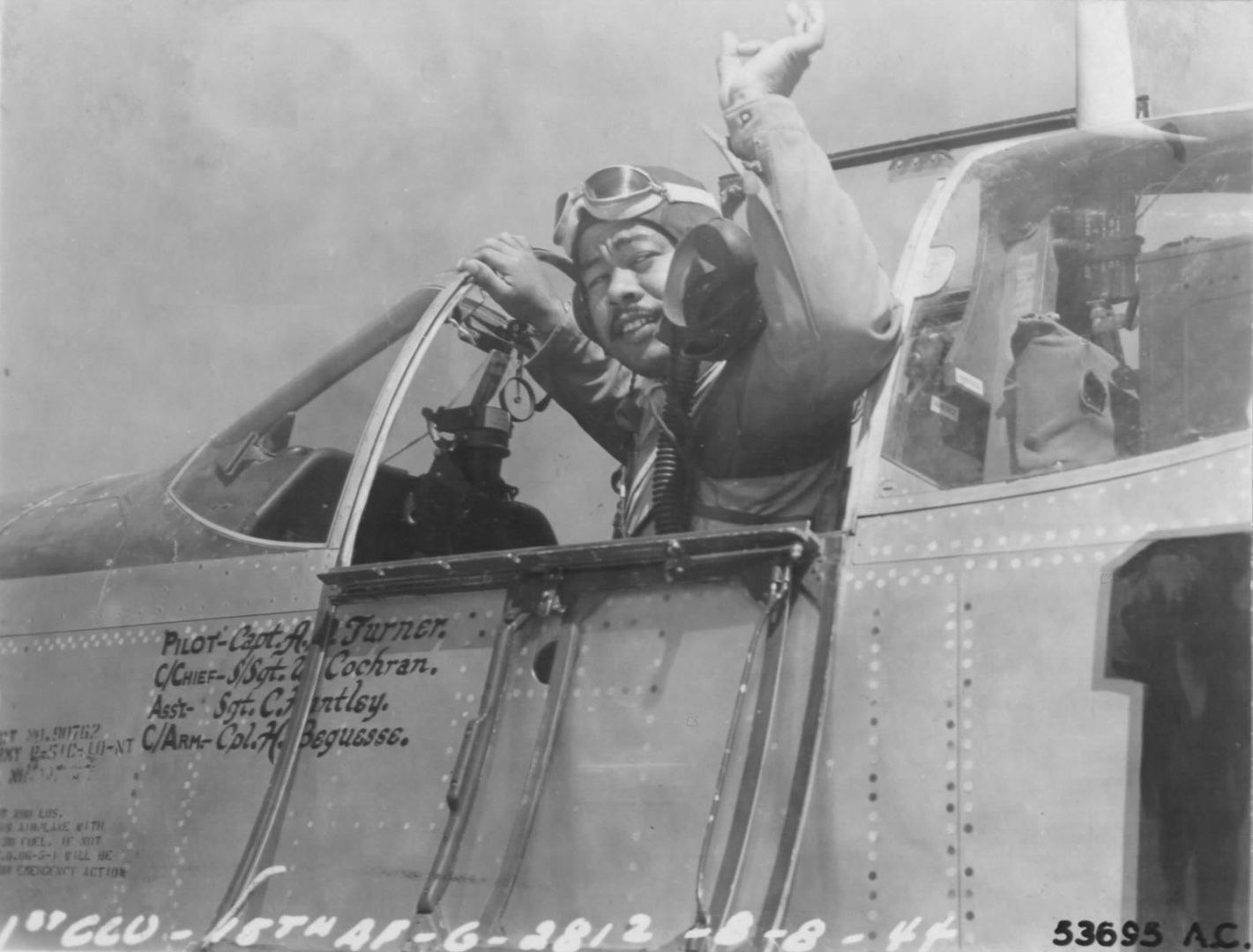
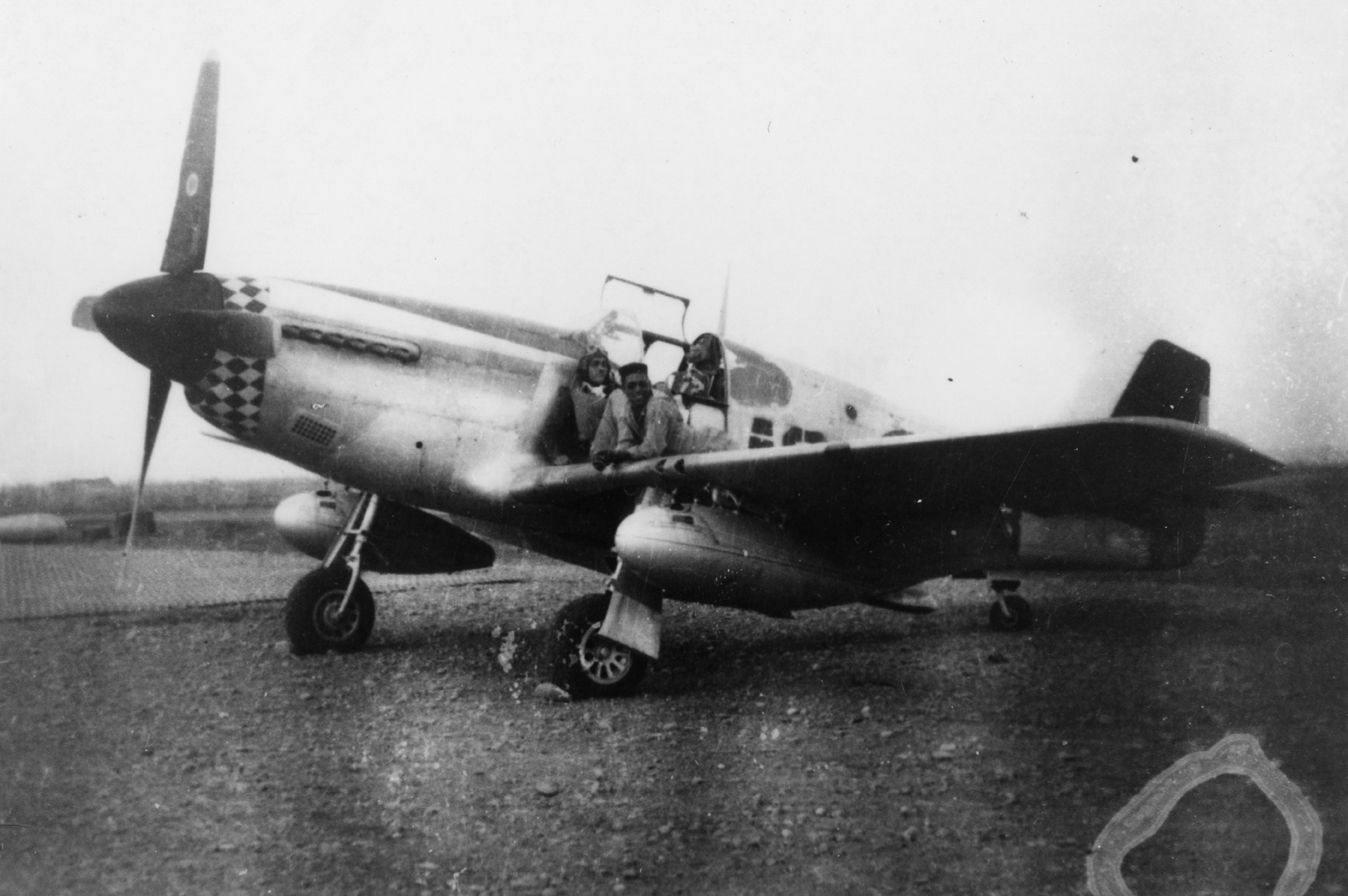
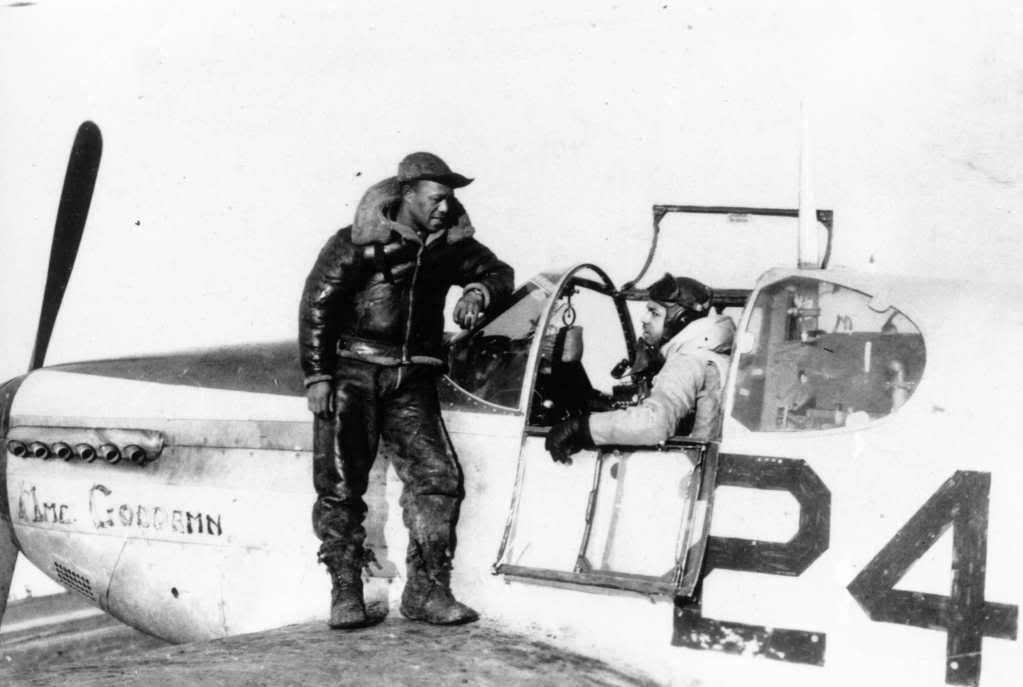
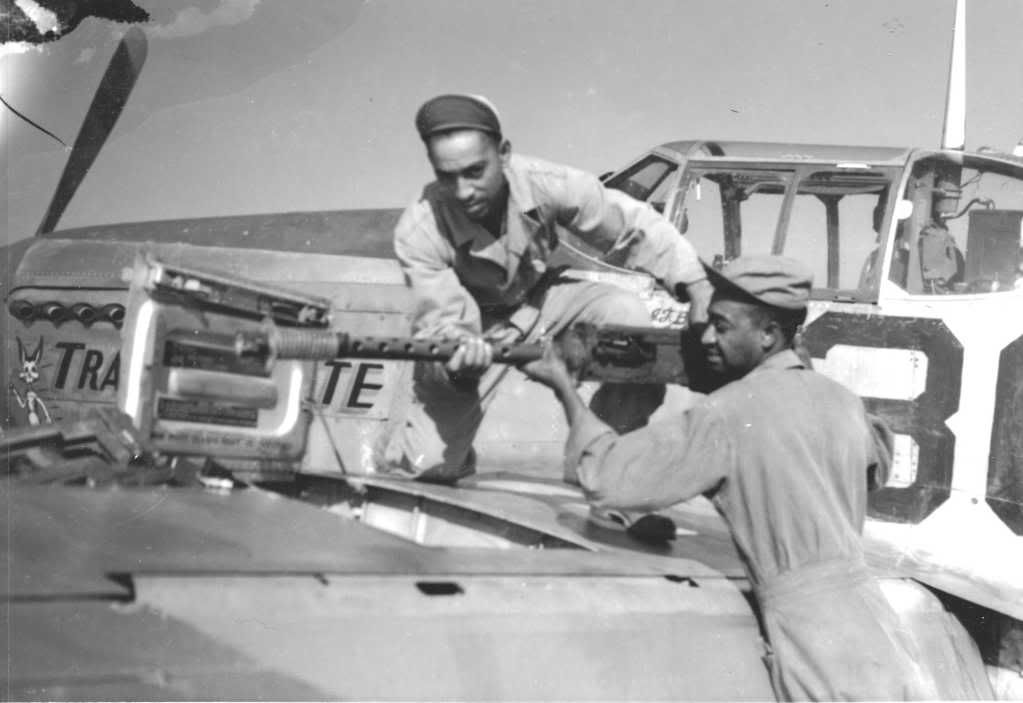
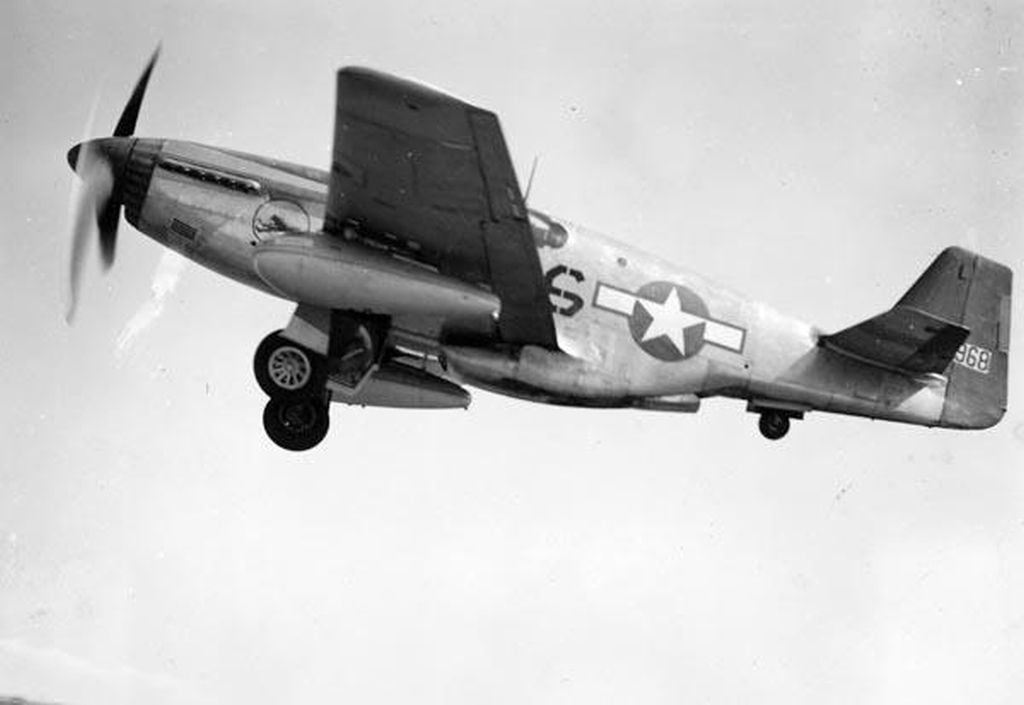
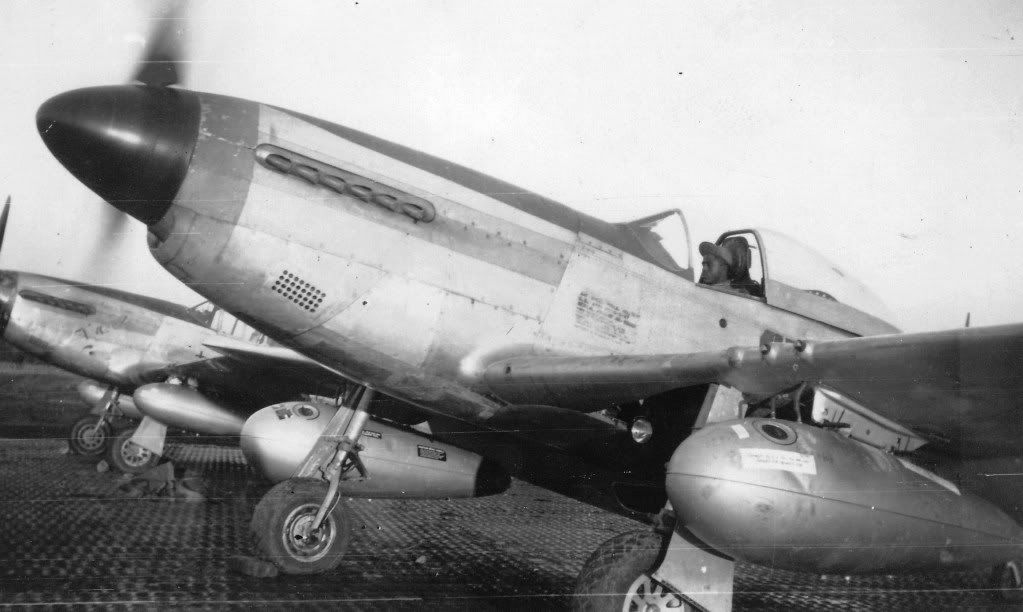
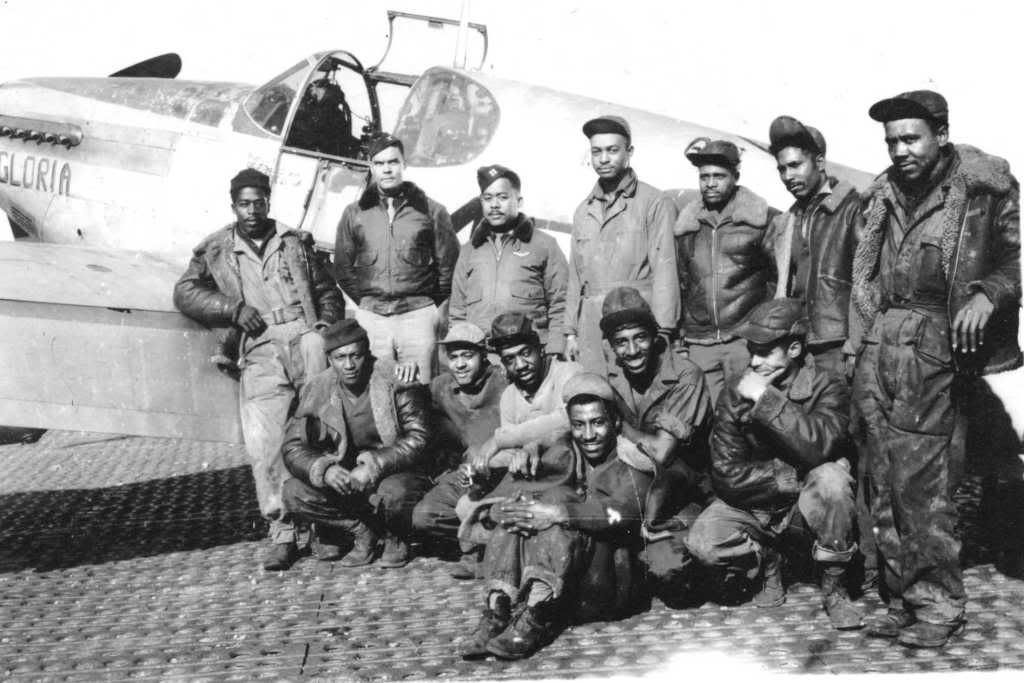
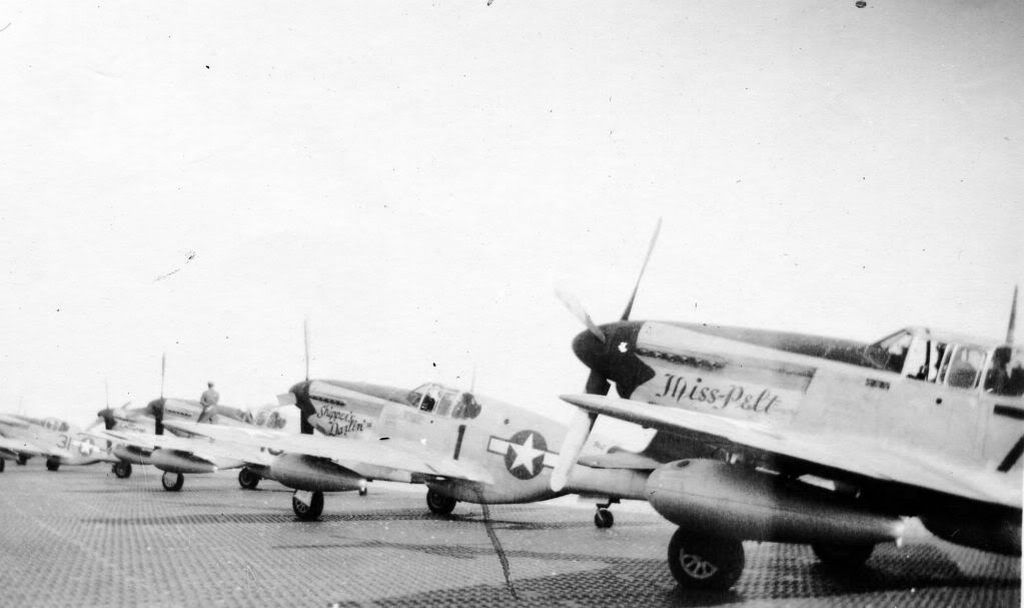
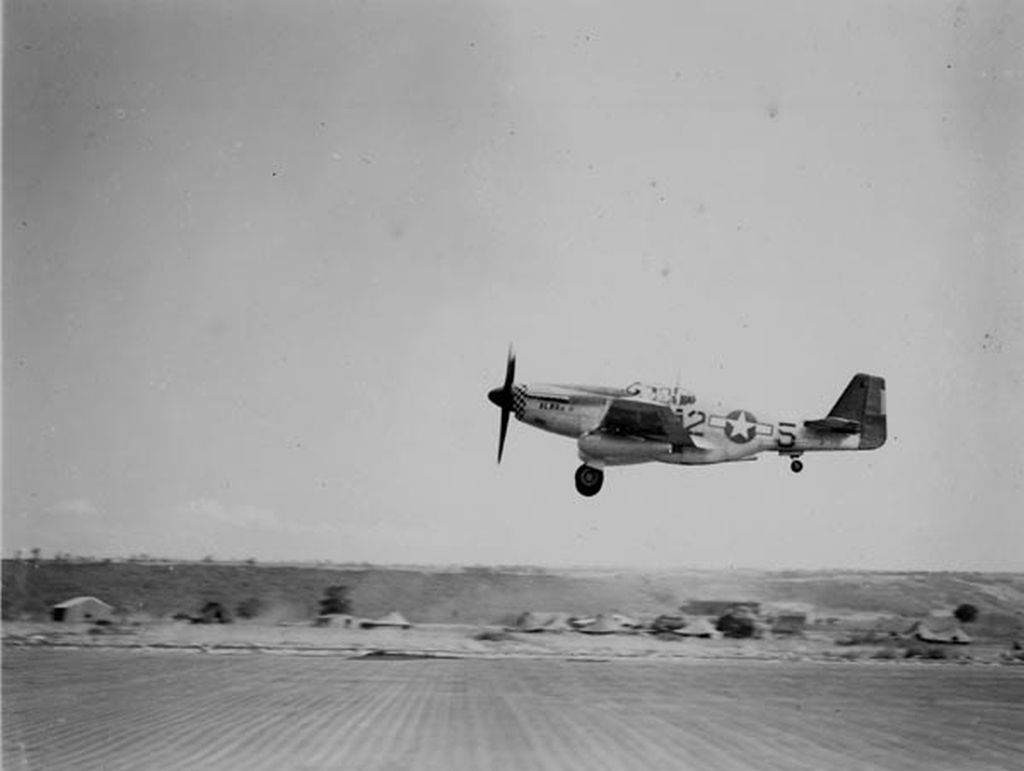
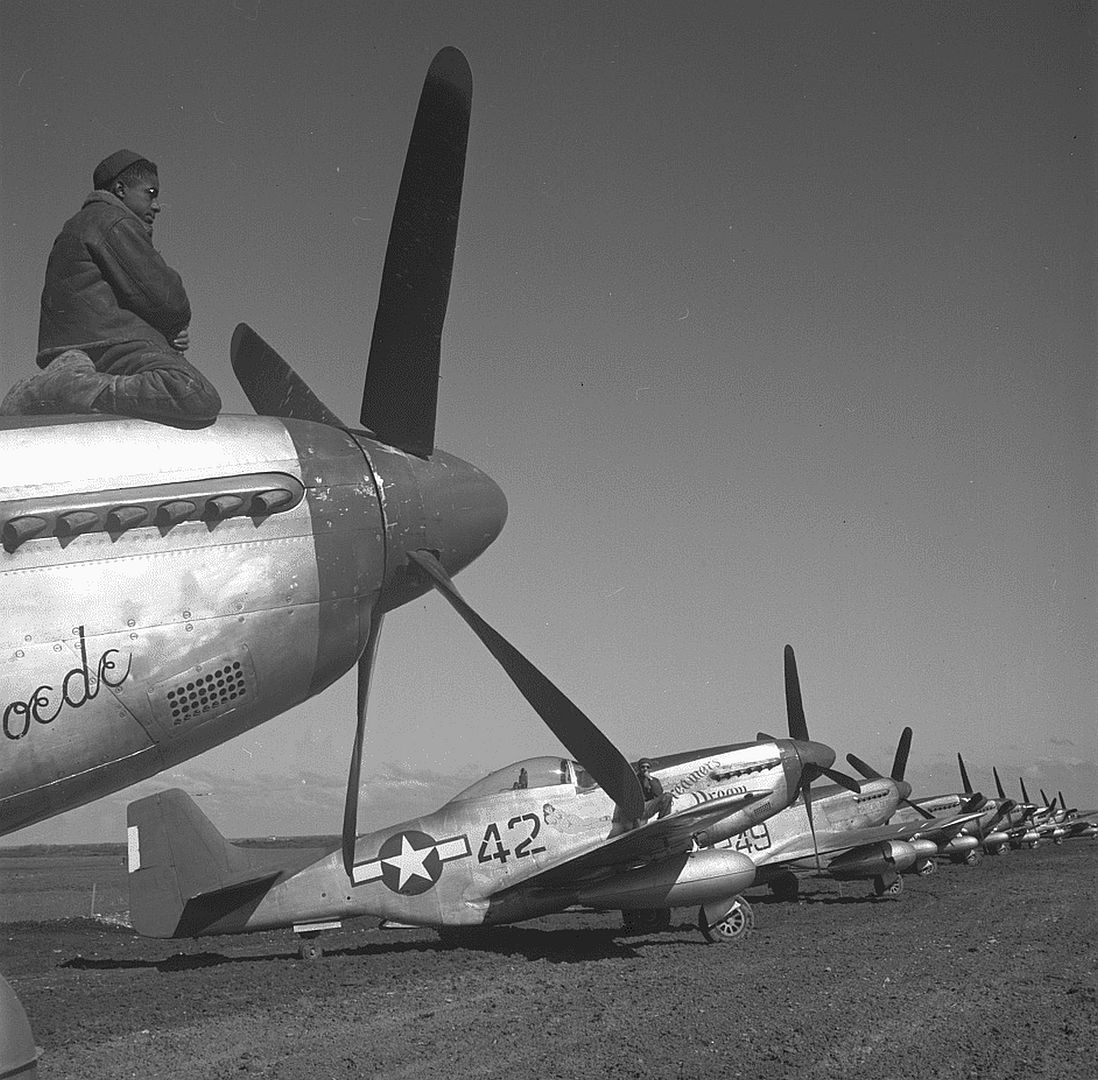
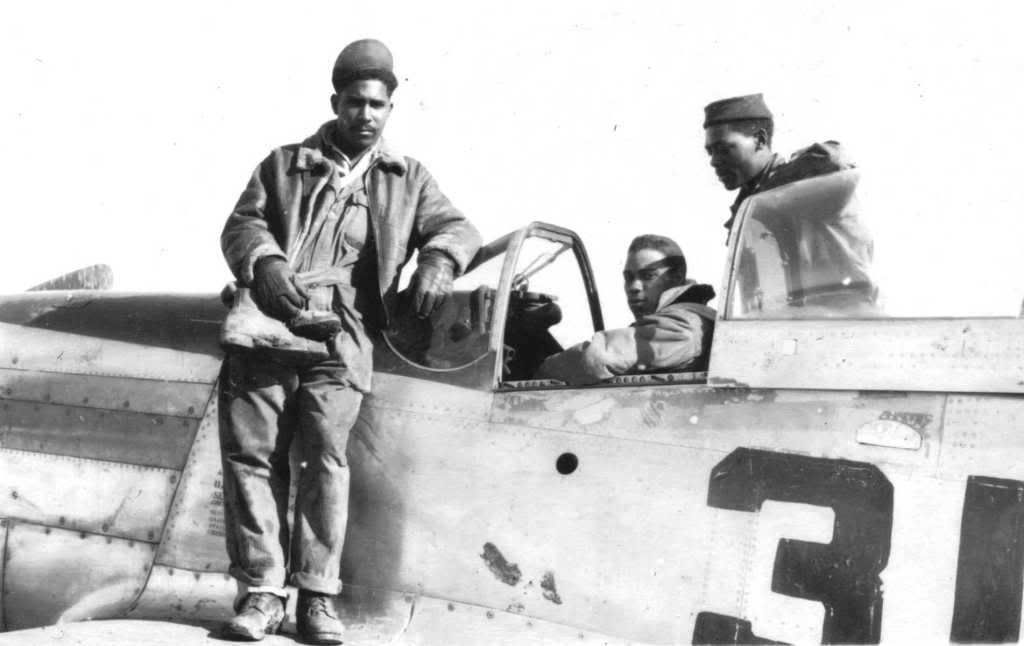
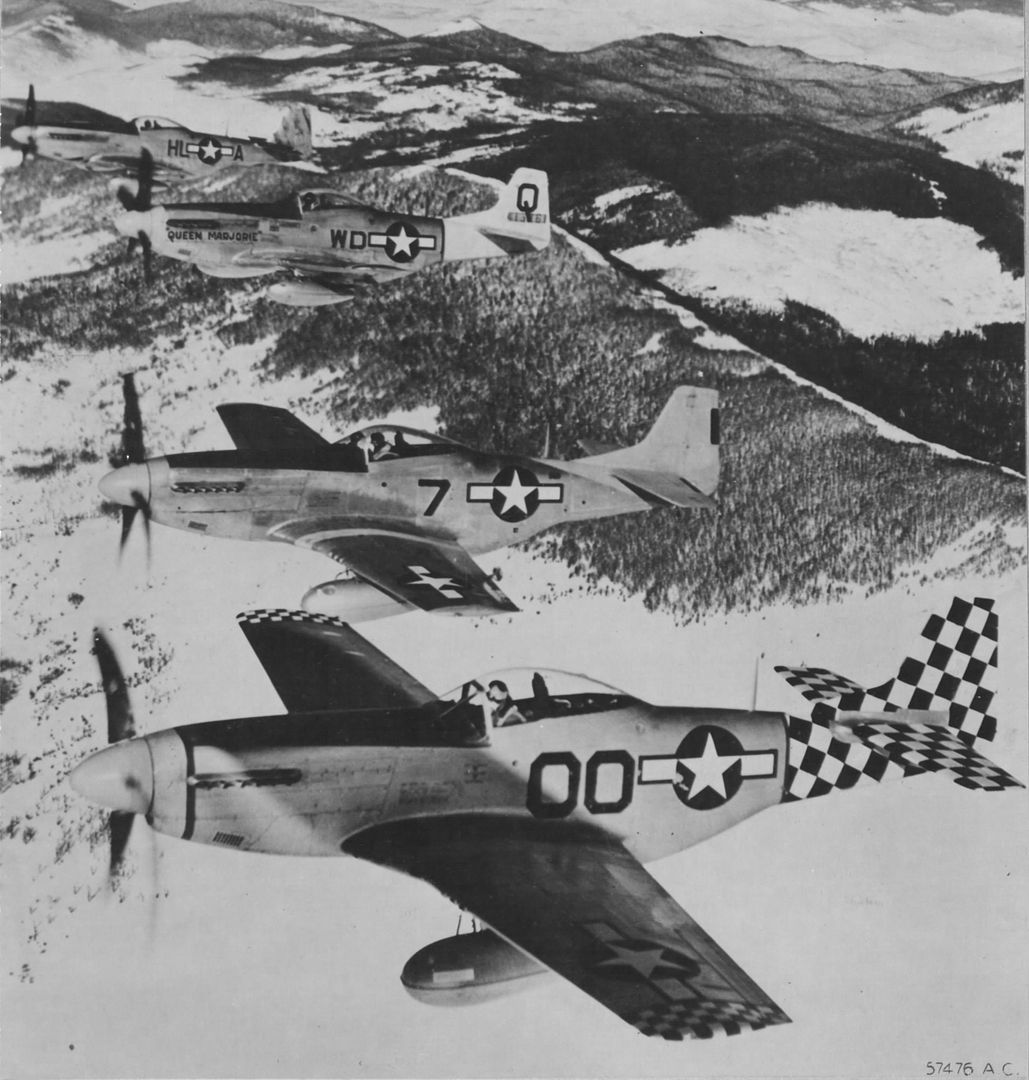
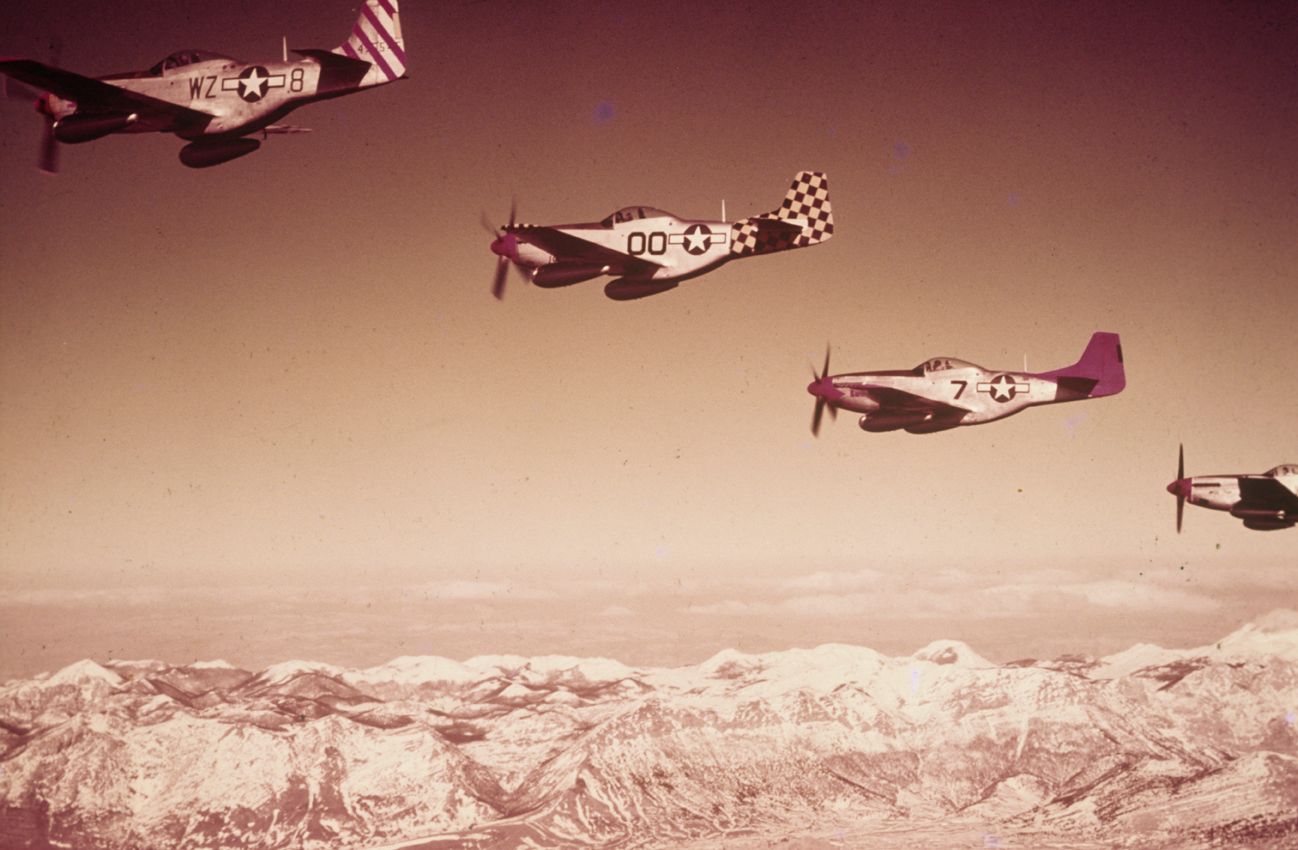
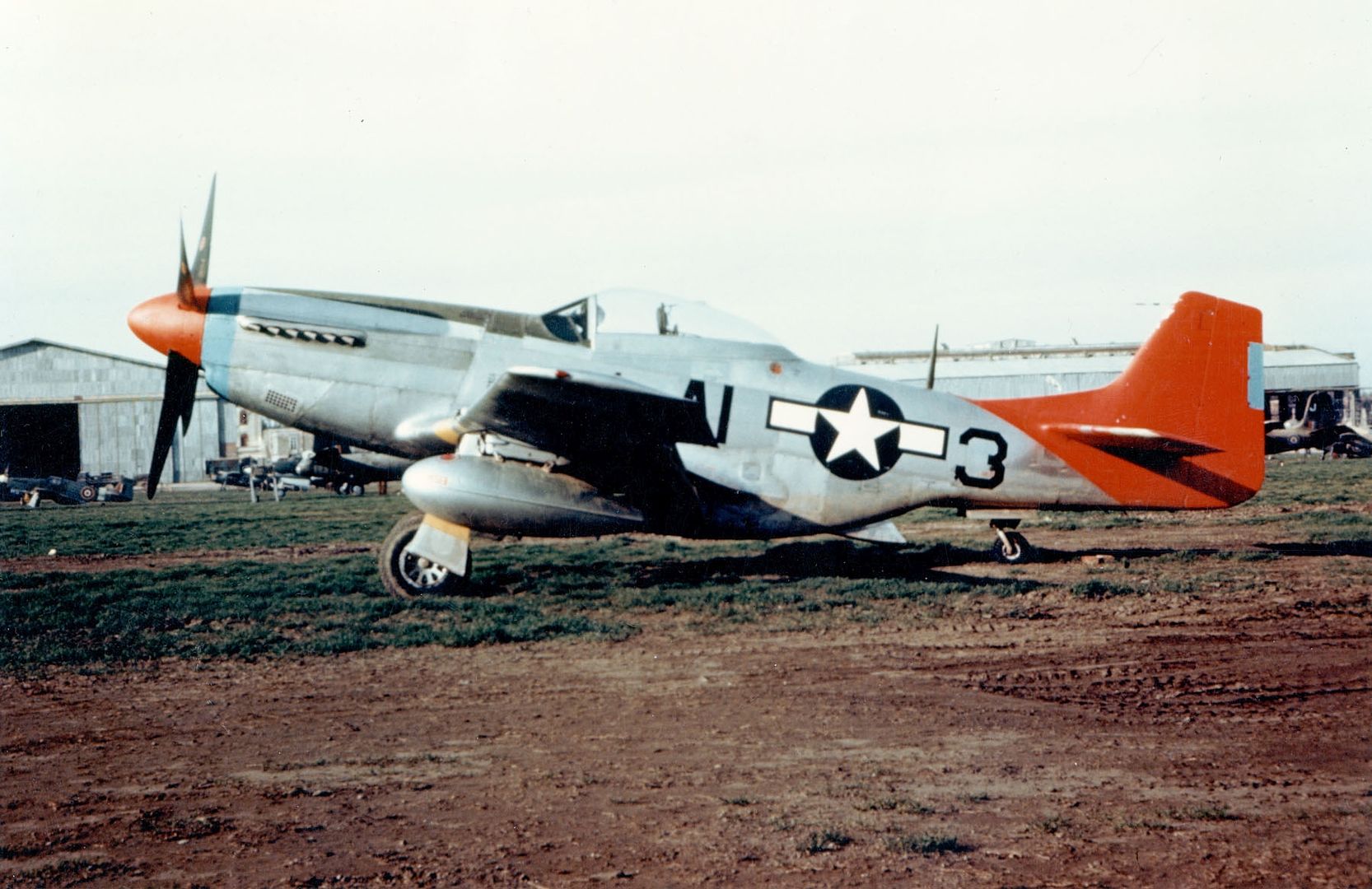
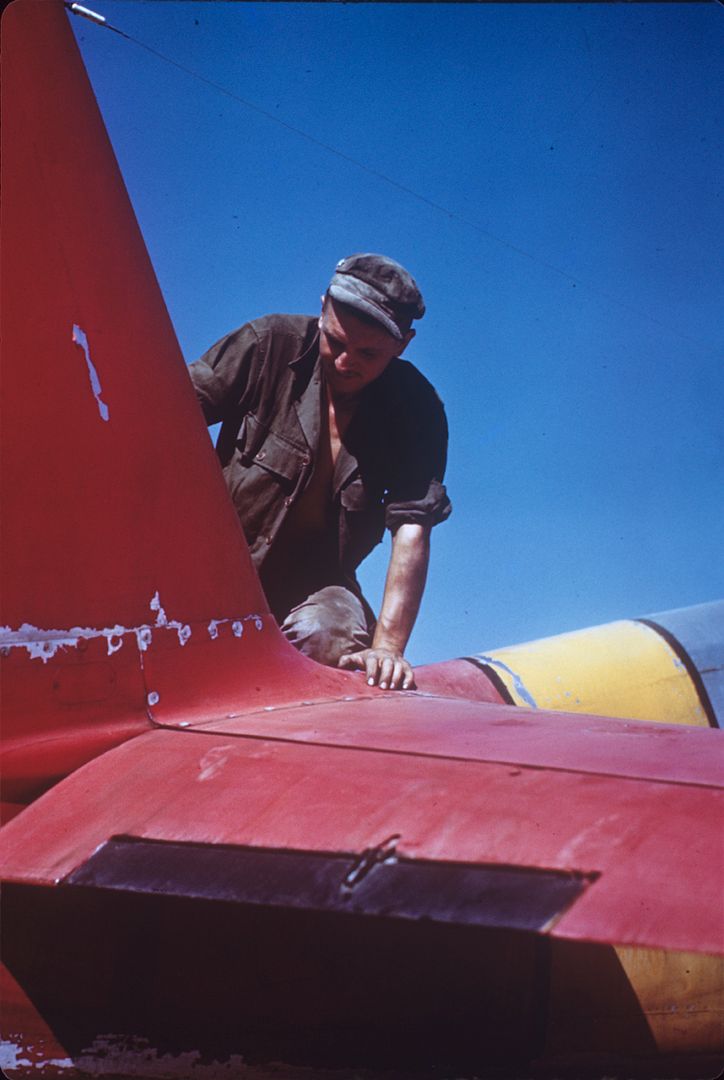
























































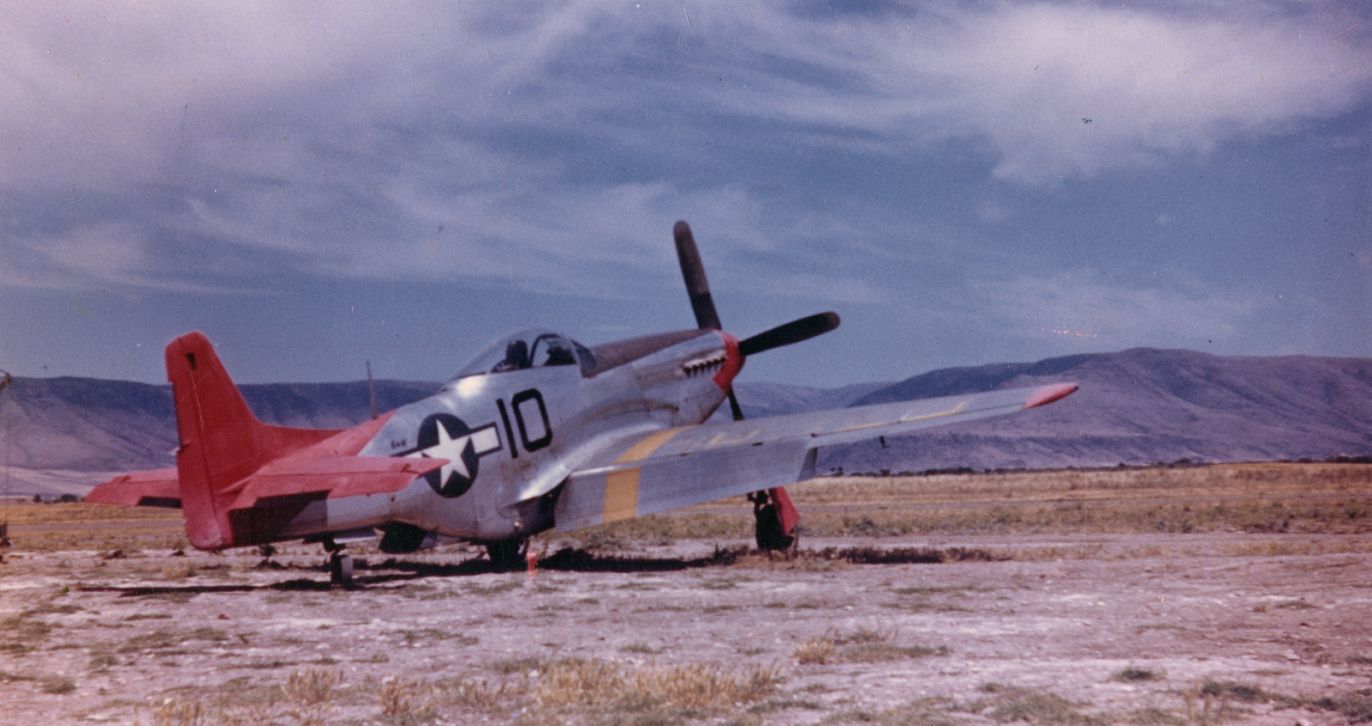


The combat record of the Tuskegee Airmen speaks for itself:
over 15,000 combat sorties (including 6000+ for the 99th prior to July '44)
111 German airplanes destroyed in the air, another 150 on the ground
950 railcars, trucks, and other motor vehicles destroyed
1 destroyer sunk by P-47 machine gun fire (Lt. Pierson's flight)
sixty-six pilots killed in action or accidents
thirty-two pilots downed and captured, POWs
150 Distinguished Flying Crosses earned
744 Air Medals
8 Purple Hearts
14 Bronze Stars
On July 26, 1948, President Truman issued Executive Order #9981 desegregating the Armed Forces.
Thanks to Stephen Sherman for parts of the text.
-
 AdminReally nice set of photos, thanks Alan.
AdminReally nice set of photos, thanks Alan.
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
