Forums
- Forums
- Duggy's Reference Hangar
- USAAF / USN Library
- Lockheed Hudson
Lockheed Hudson
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
-
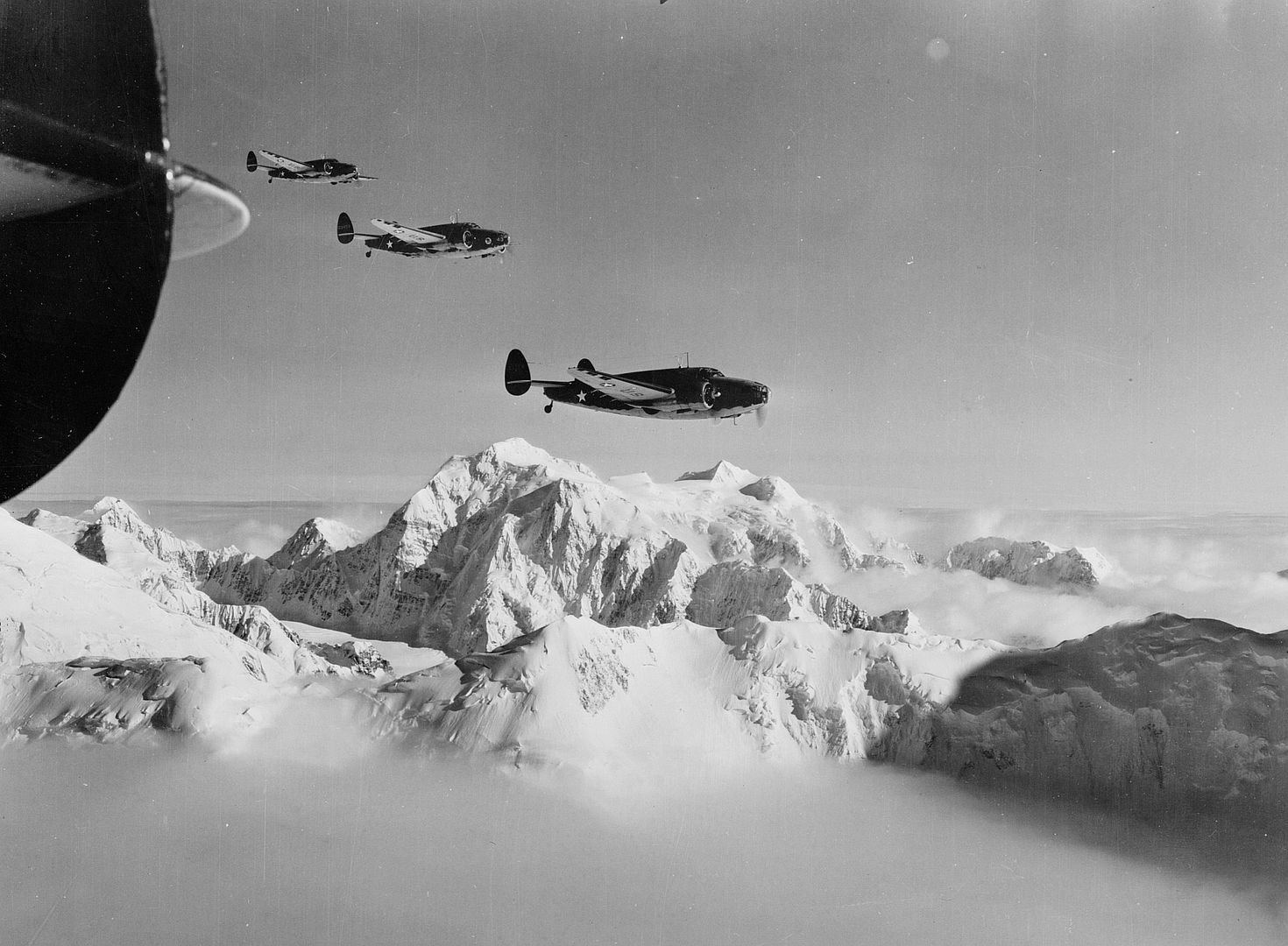
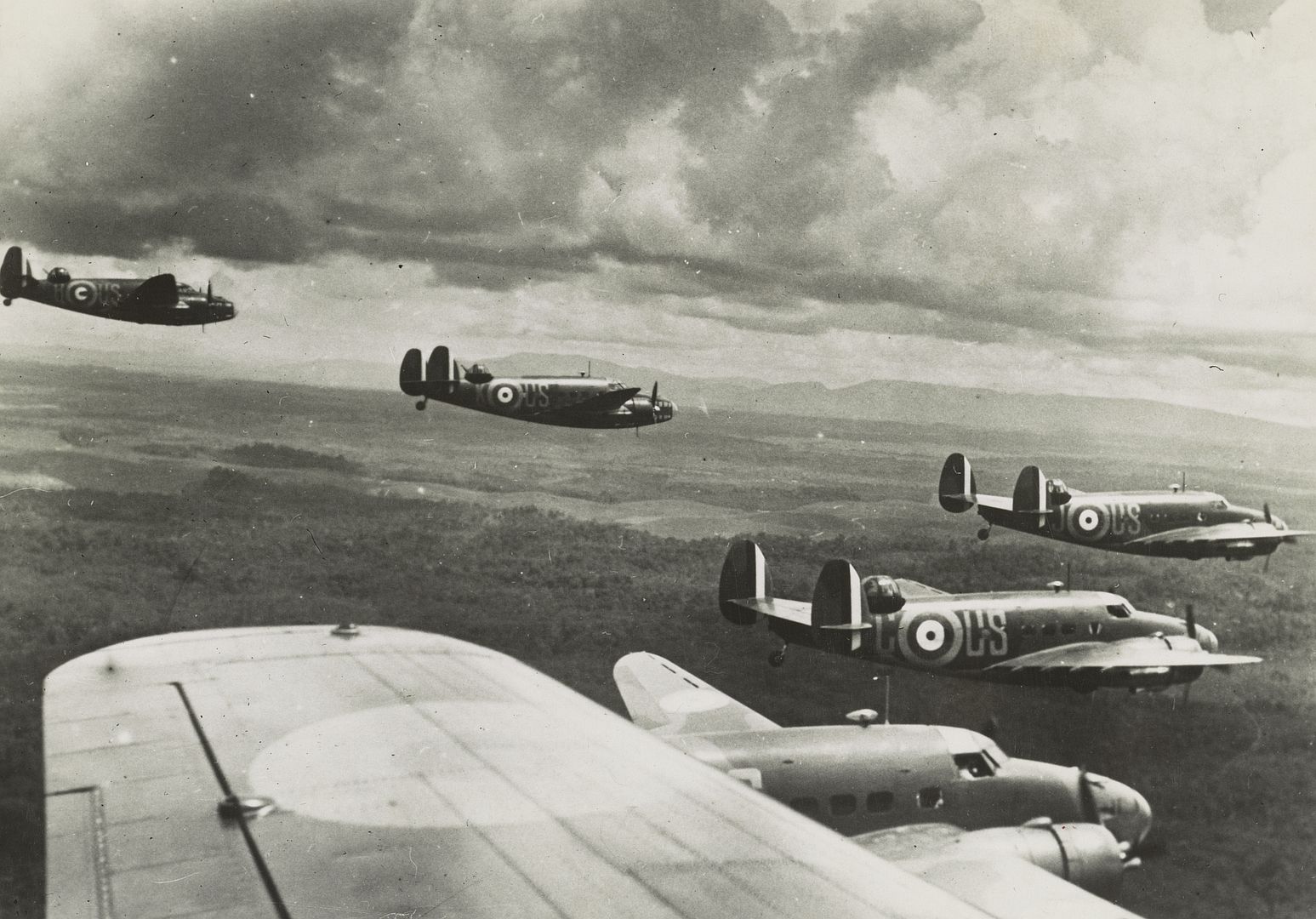
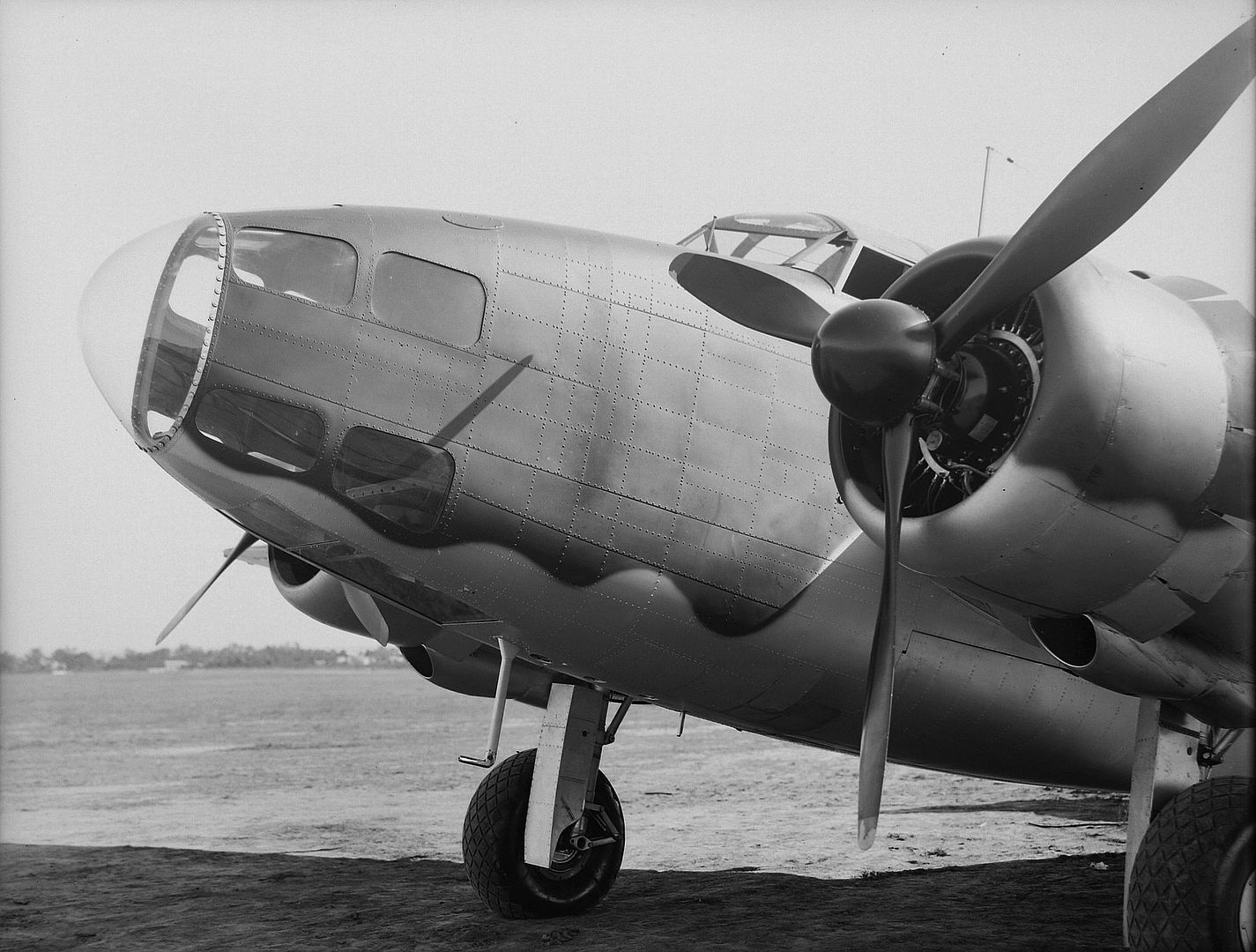
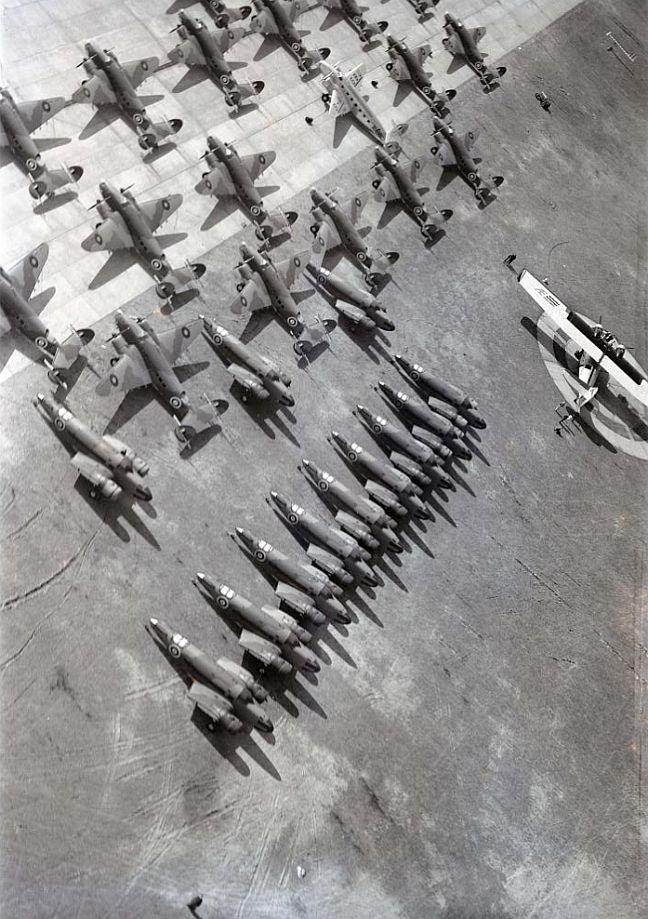
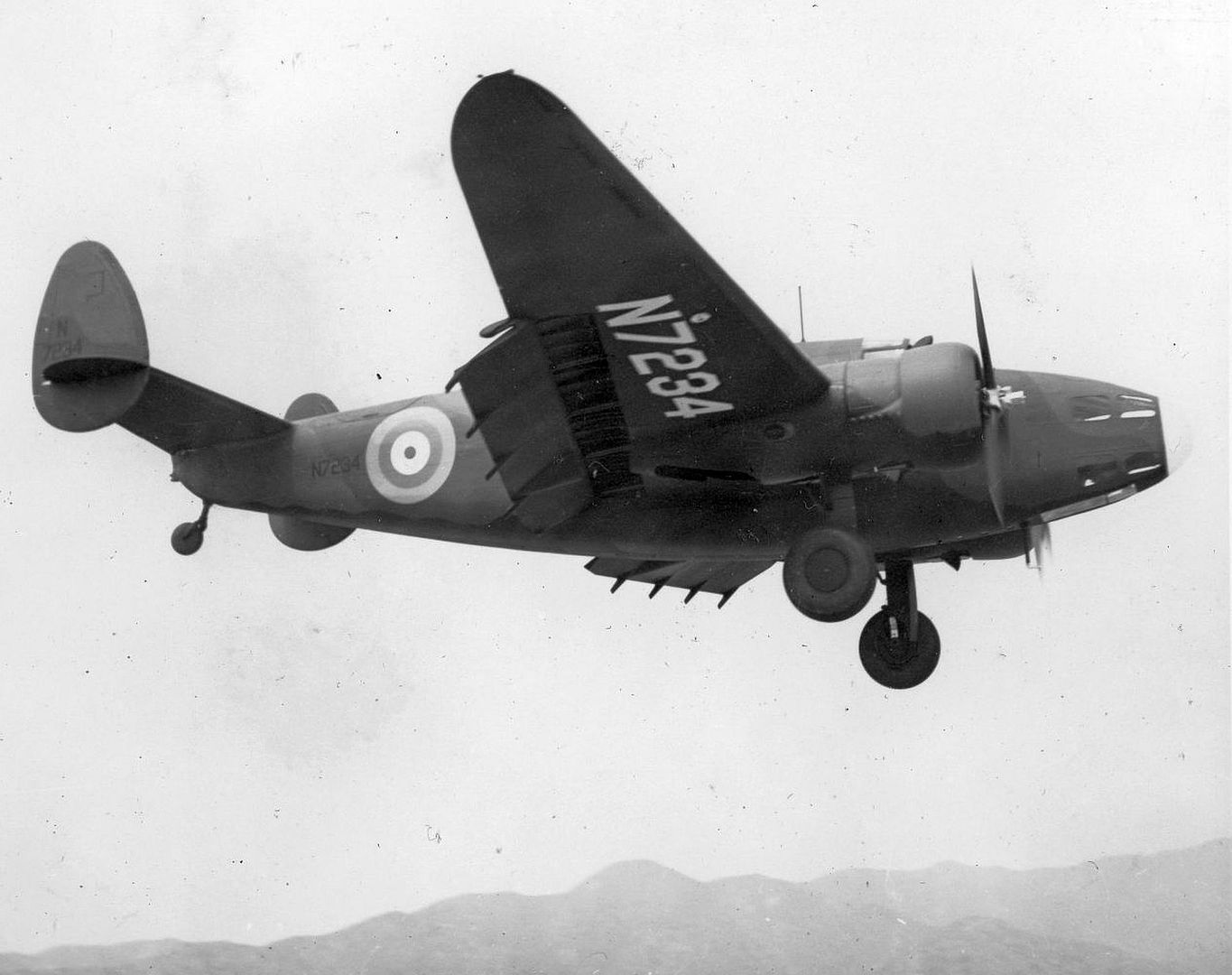
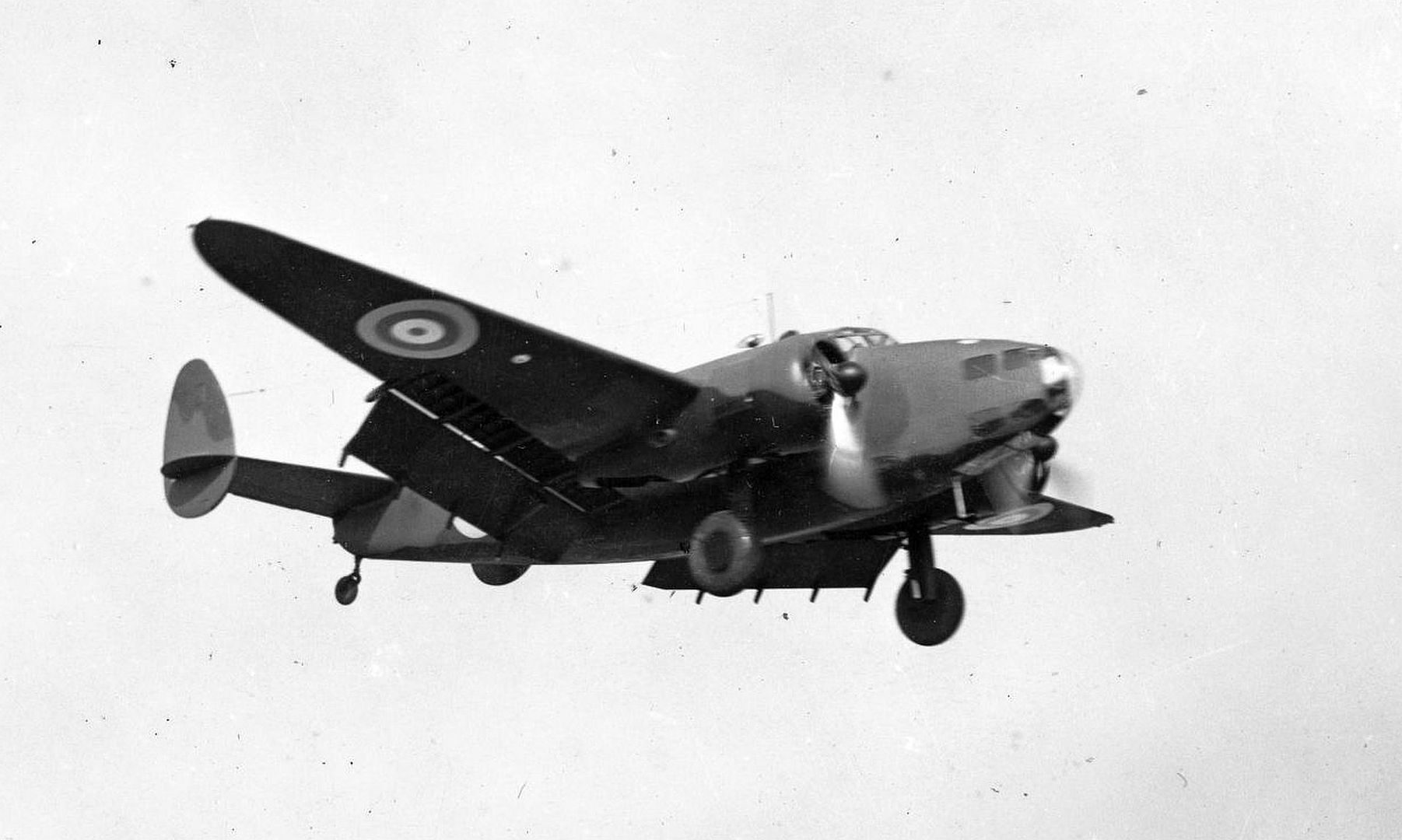
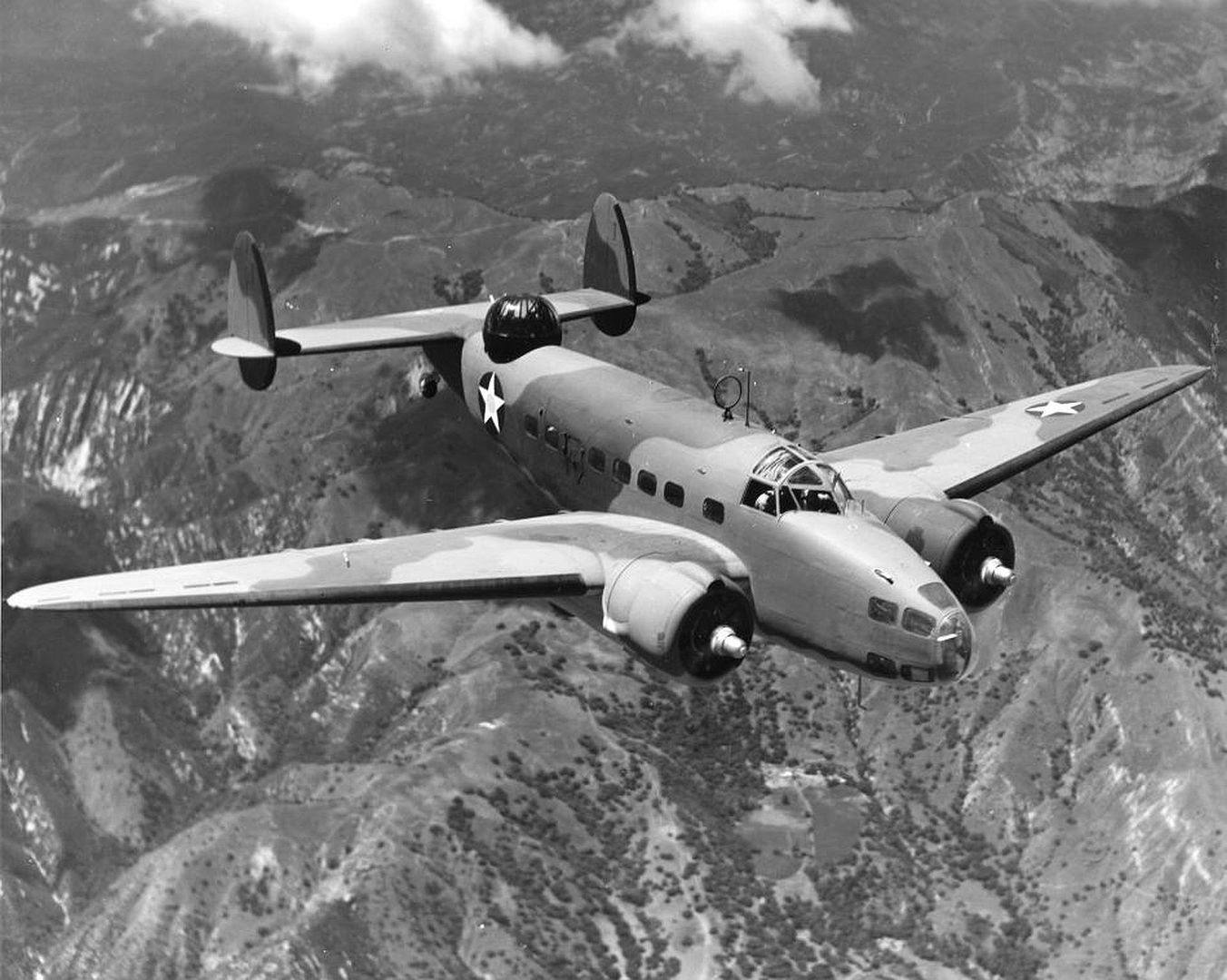
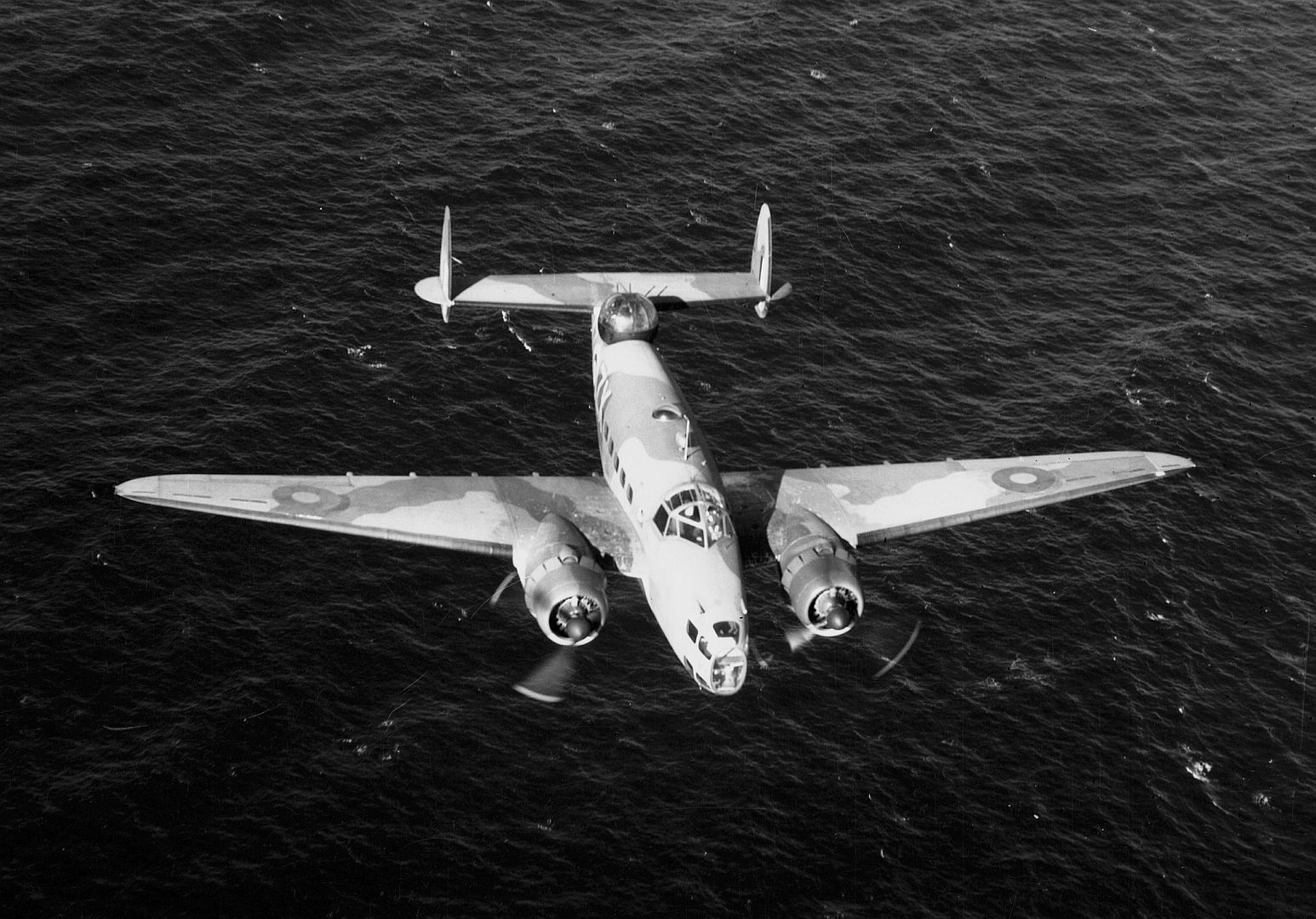
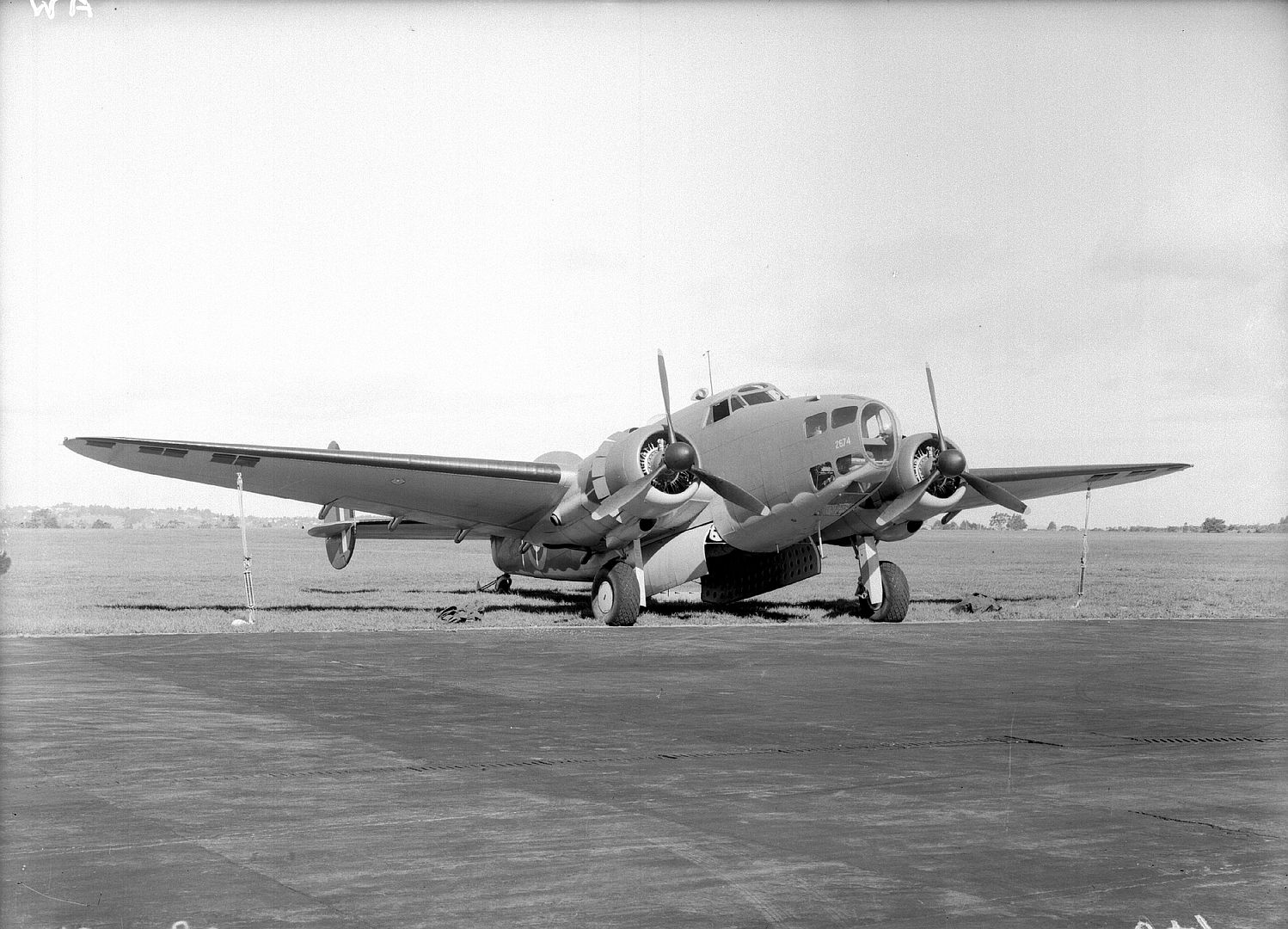
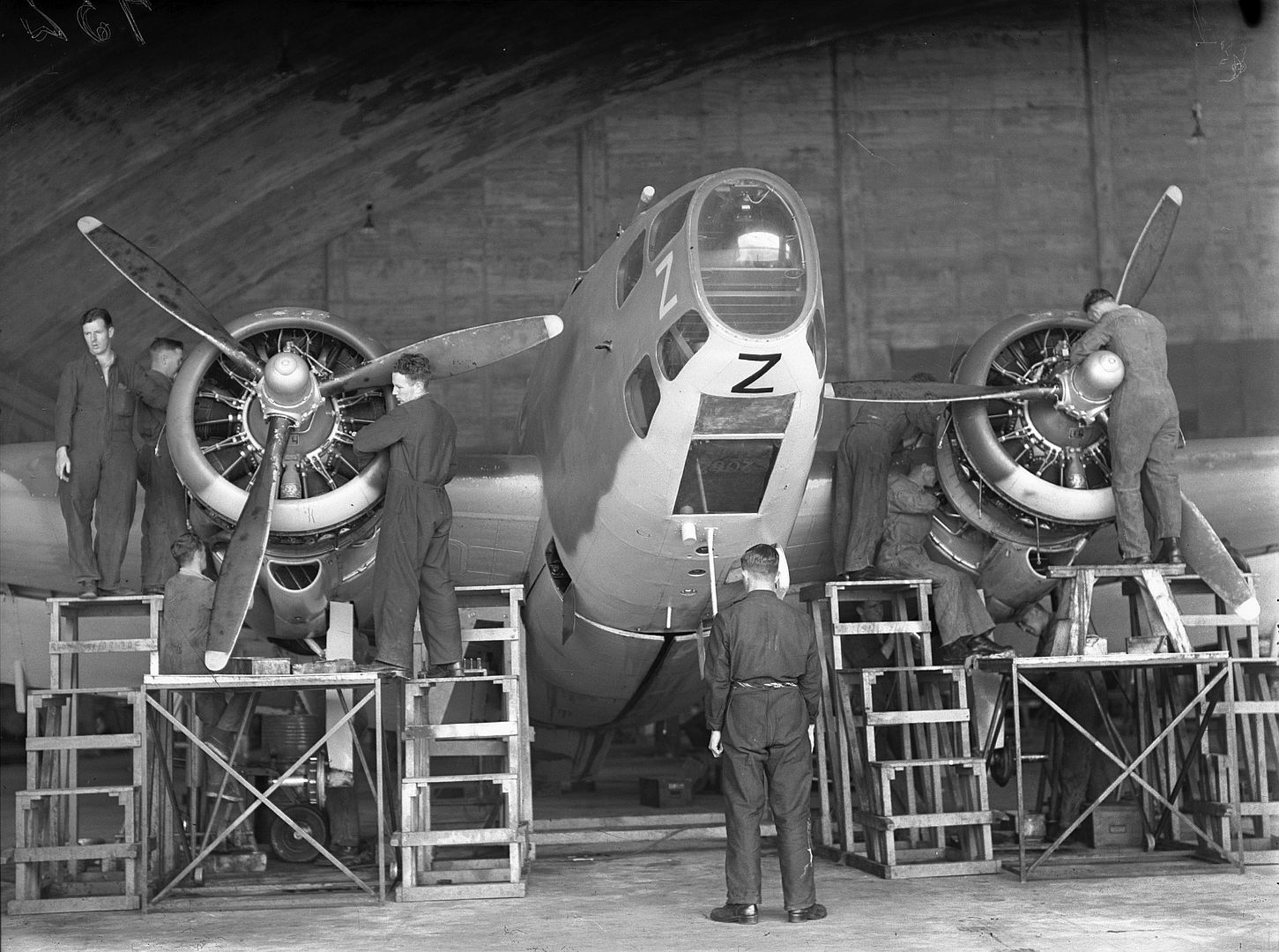
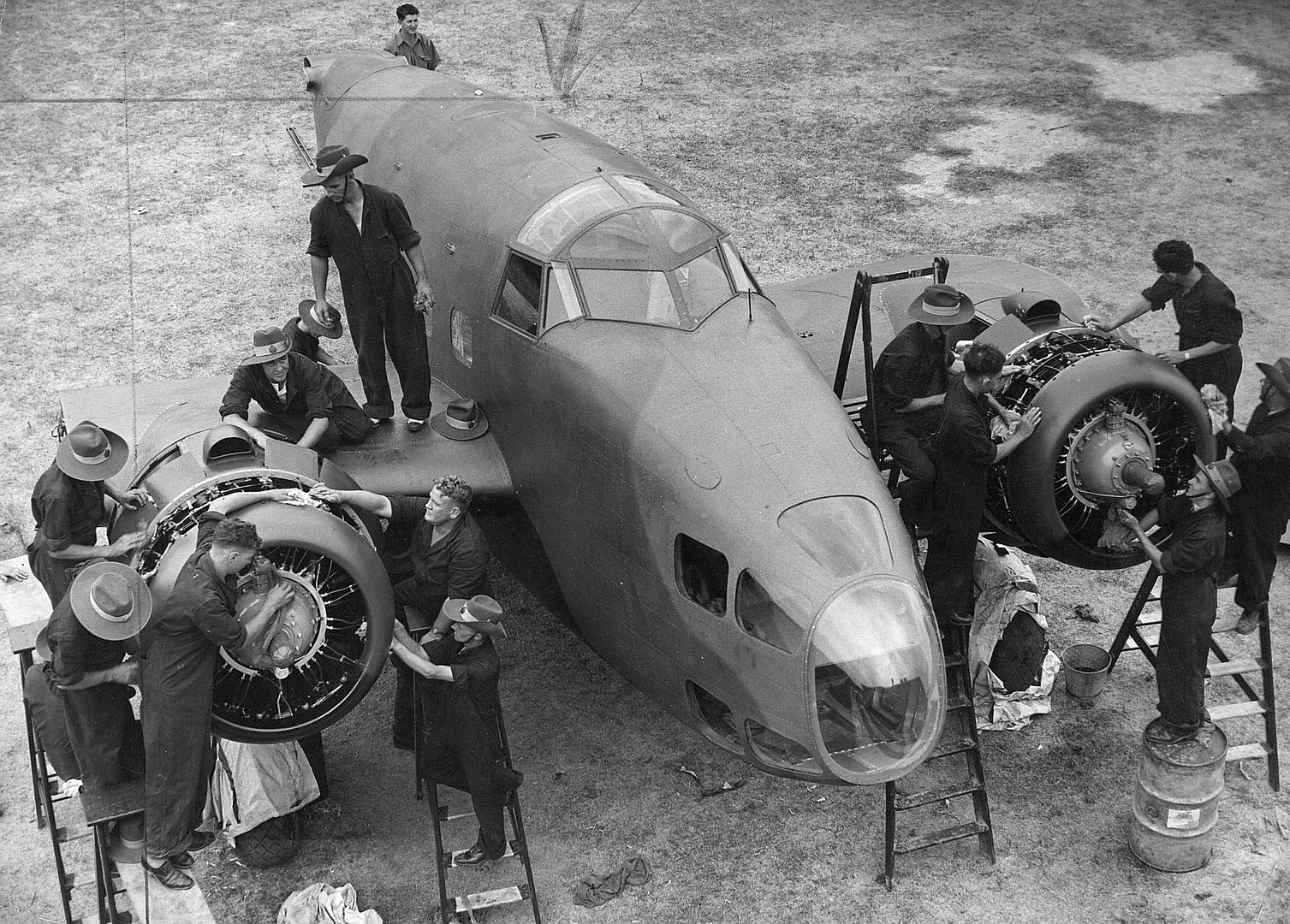
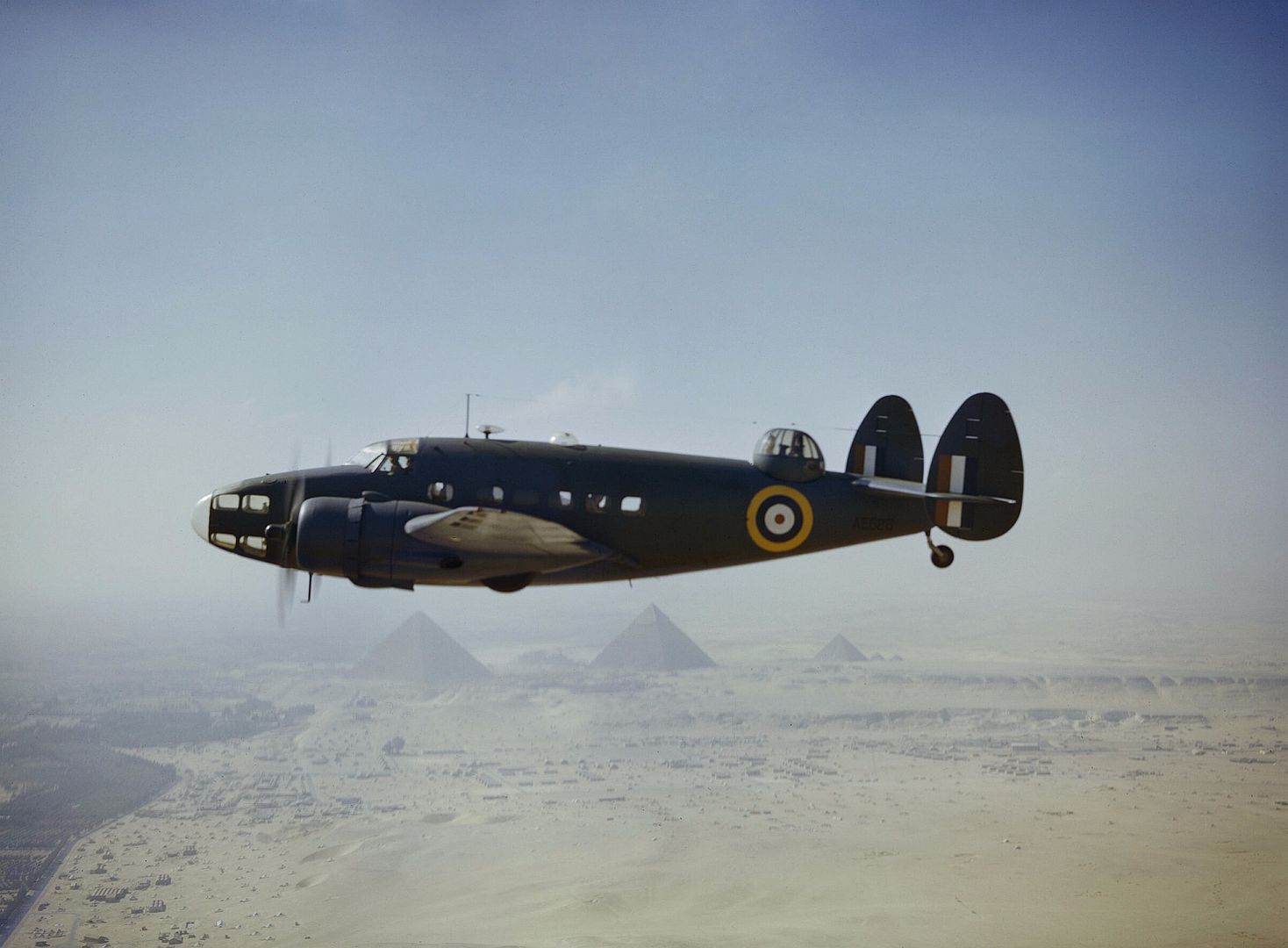
 Main AdminThe Lockheed Hudson was an American-built light bomber and coastal reconnaissance aircraft built initially for the Royal Air Force shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War and primarily operated by the RAF thereafter. The Hudson was a military conversion of the Lockheed Model 14 Super Electra airliner, and was the first significant aircraft construction contract for the Lockheed Aircraft Corporation?the initial RAF order for 200 Hudsons far surpassed any previous order the company had received.The Hudson served throughout the war, mainly with Coastal Command but also in transport and training roles as well as delivering agents into occupied France. They were also used extensively with the Royal Canadian Air Force's anti-submarine squadrons and by the Royal Australian Air Force.
Main AdminThe Lockheed Hudson was an American-built light bomber and coastal reconnaissance aircraft built initially for the Royal Air Force shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War and primarily operated by the RAF thereafter. The Hudson was a military conversion of the Lockheed Model 14 Super Electra airliner, and was the first significant aircraft construction contract for the Lockheed Aircraft Corporation?the initial RAF order for 200 Hudsons far surpassed any previous order the company had received.The Hudson served throughout the war, mainly with Coastal Command but also in transport and training roles as well as delivering agents into occupied France. They were also used extensively with the Royal Canadian Air Force's anti-submarine squadrons and by the Royal Australian Air Force.
Design and development
In late 1937 Lockheed sent a cutaway drawing of the Model 14 to various publications, showing the new aircraft as a civilian aircraft and converted to a light bomber. This attracted the interest of various air forces and in 1938, the British Purchasing Commission sought an American maritime patrol aircraft for the United Kingdom to support the Avro Anson.
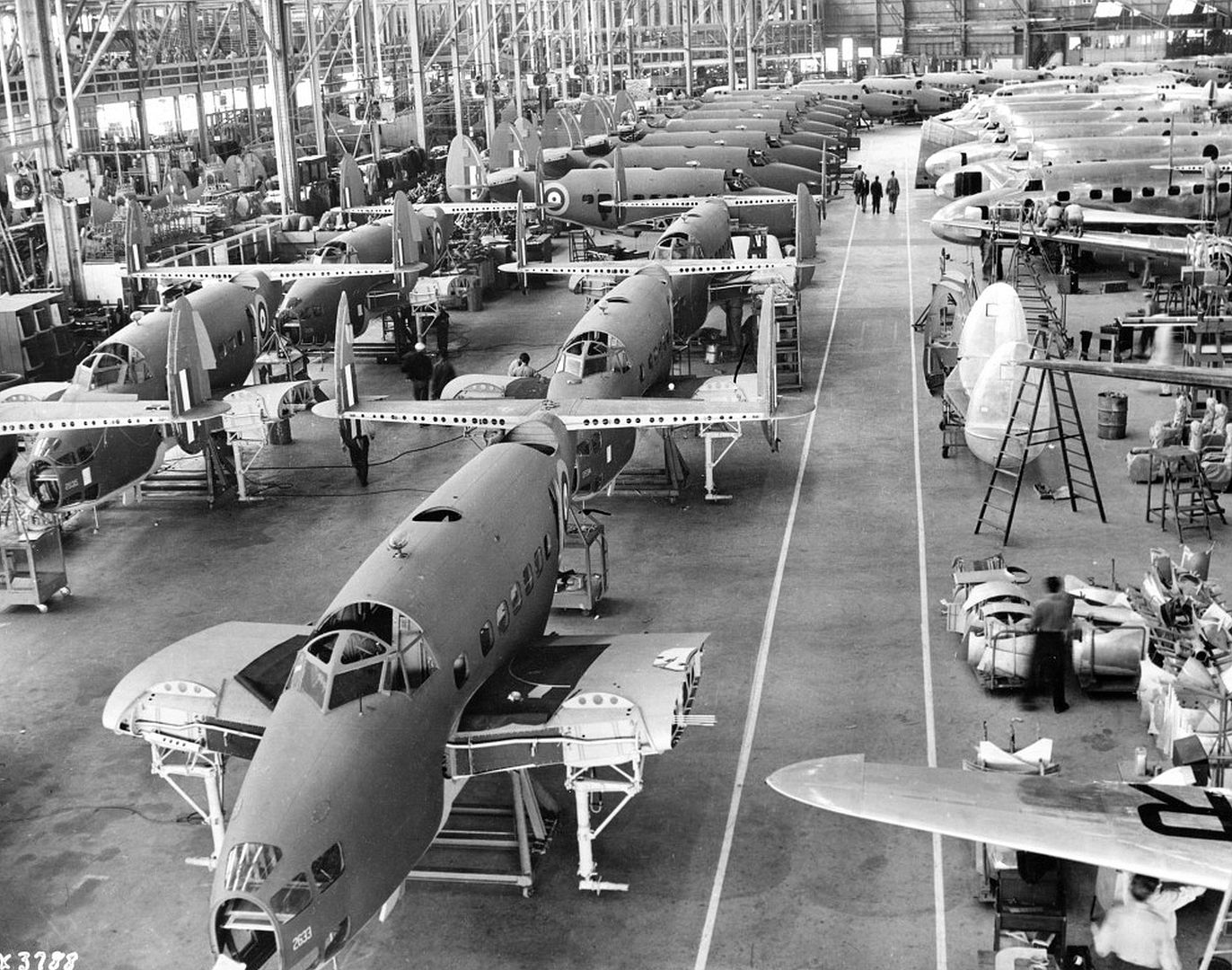
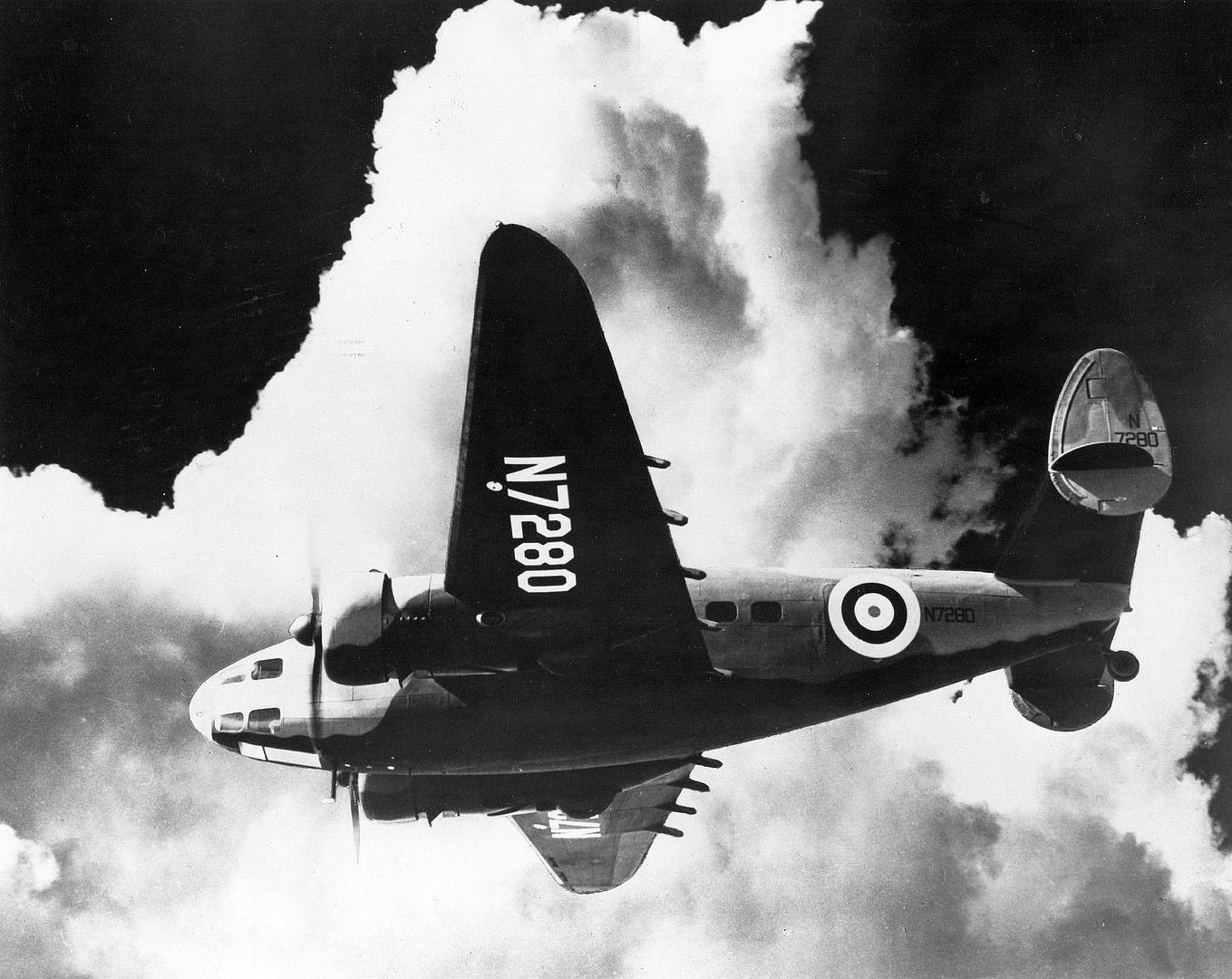
The British Purchasing Commission ordered 200 aircraft for use by the Royal Air Force and the first aircraft started flight trials from Burbank on 10 December 1938. The flight trials showed no major issues and deliveries to the RAF began on 15 February 1939. Production was sped up after the British indicated they would order another 50 aircraft if the original 200 could be delivered before the end of 1939. Lockheed sub-contracted some parts assembly to Rohr Aircraft of San Diego and increased its workforce, allowing the company to produce the 250th aircraft seven and a half weeks before the deadline.
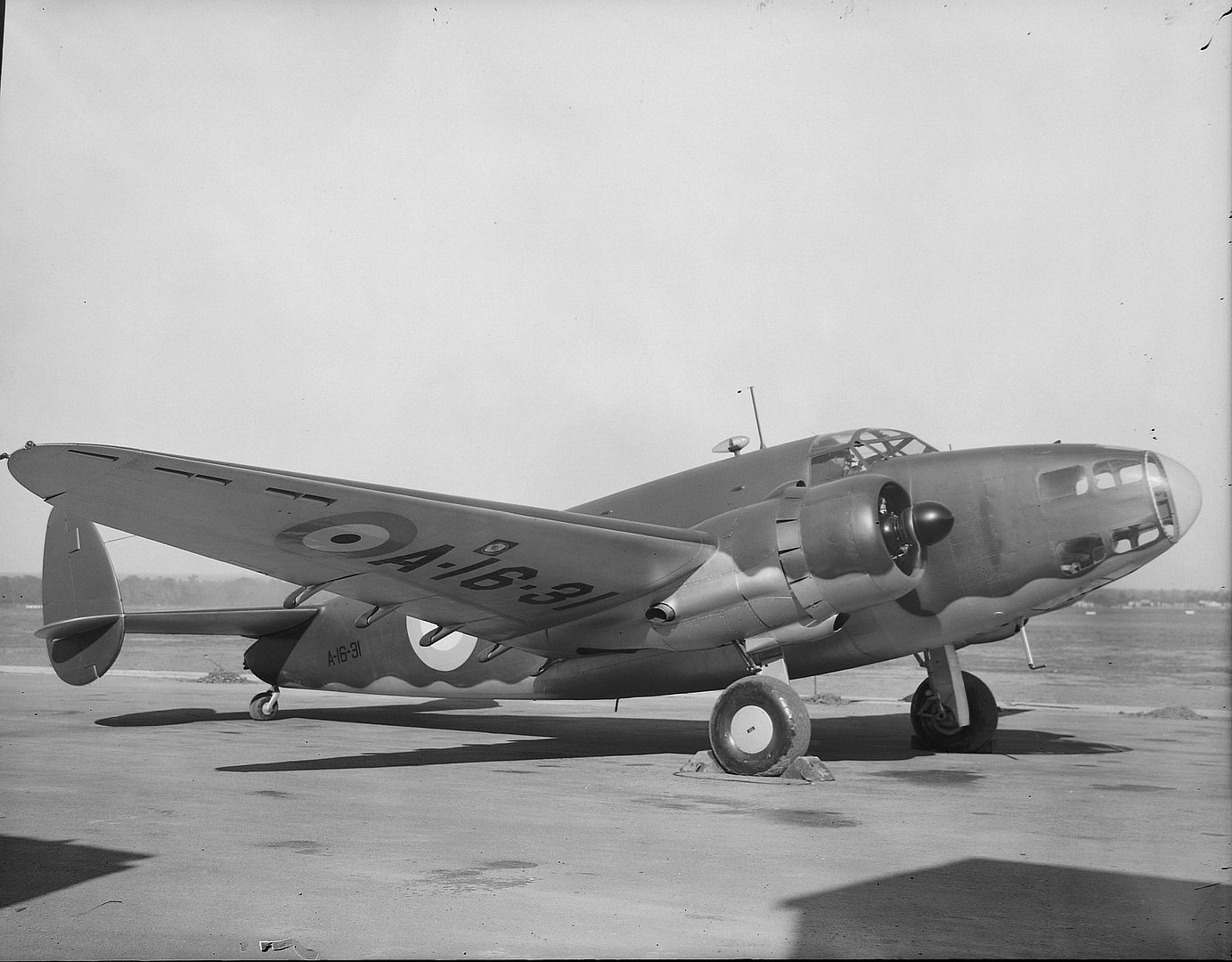
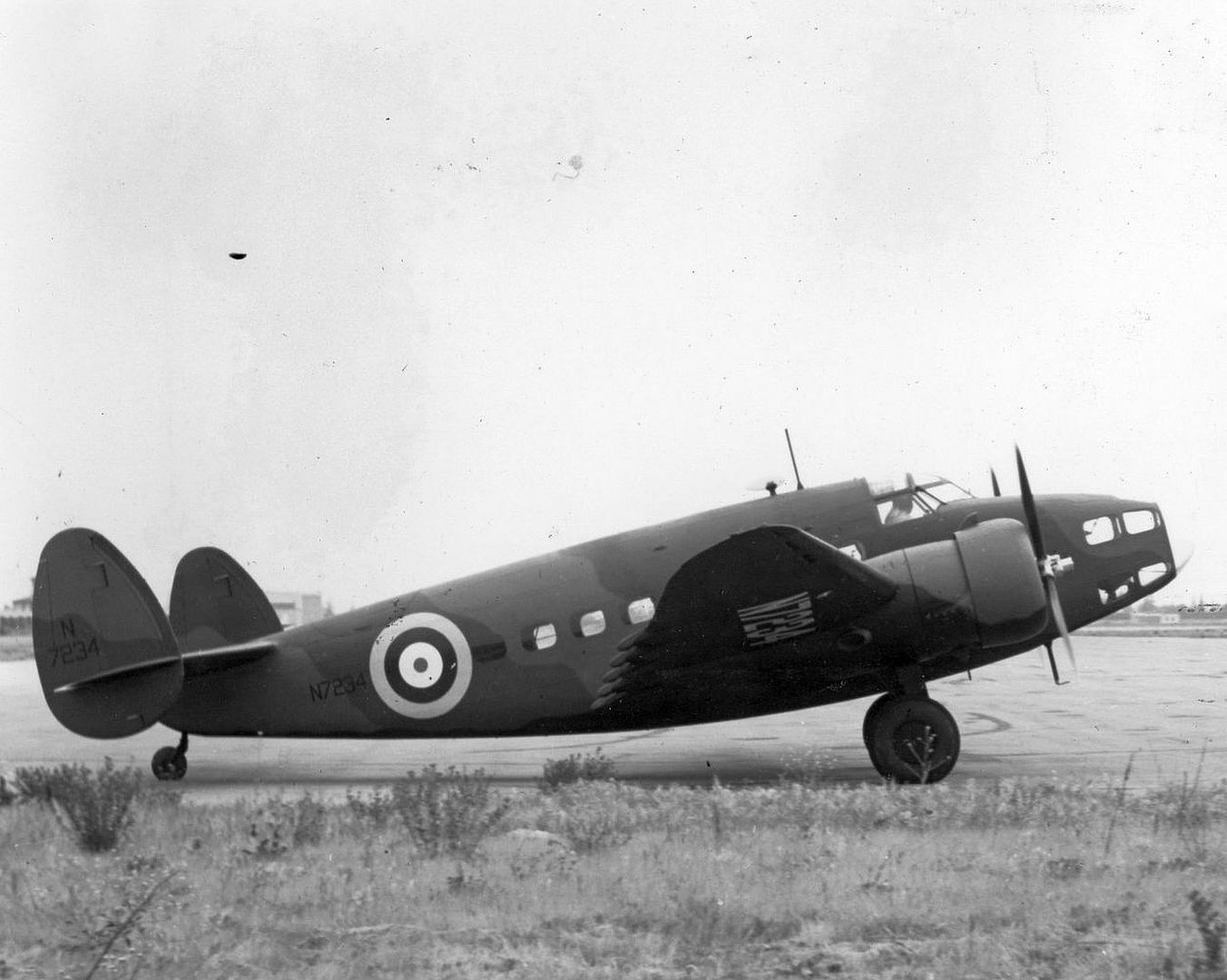
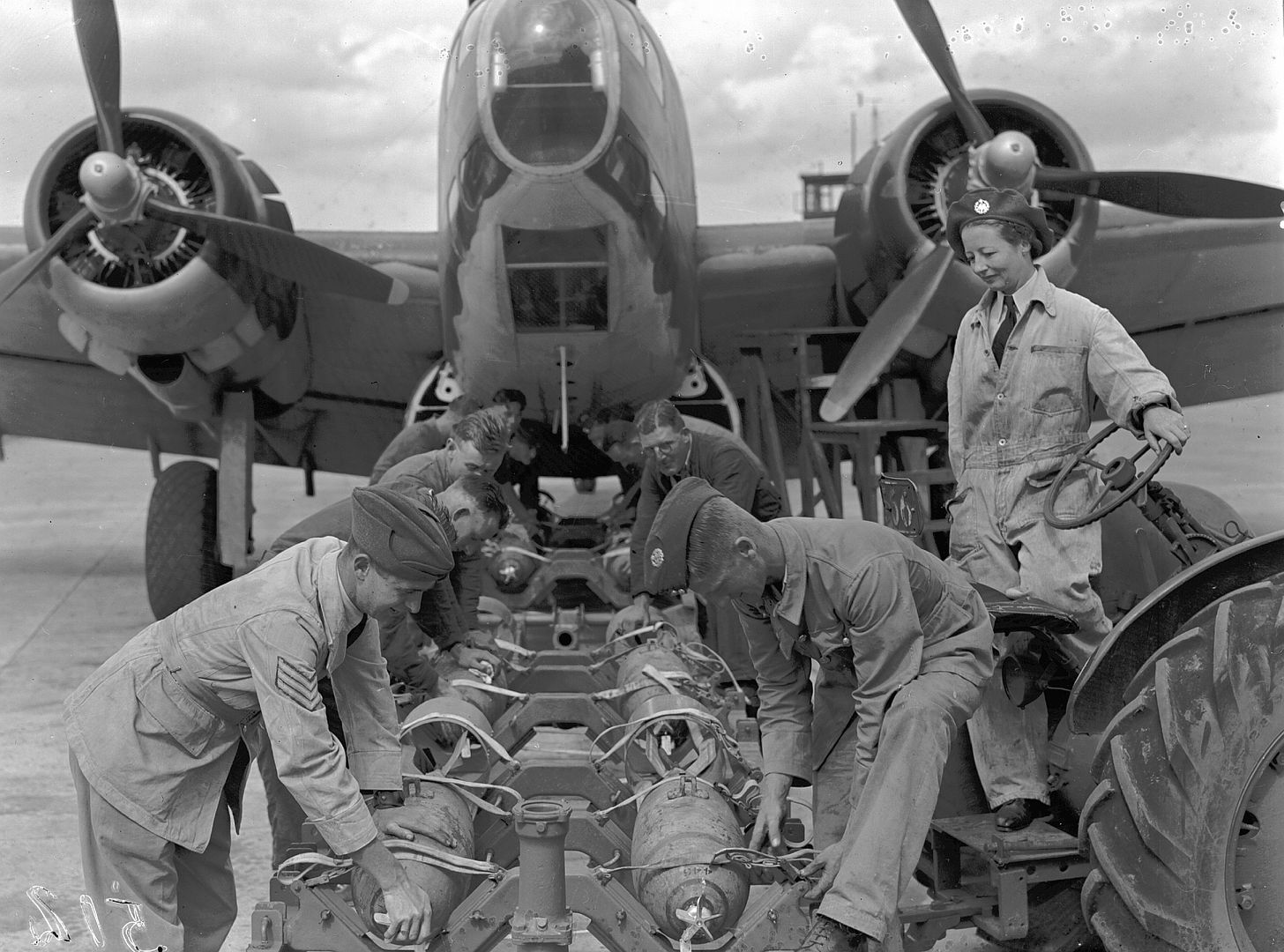
A total of 350 Mk I and 20 Mk II Hudsons were supplied (the Mk II had different propellers). These had two fixed Browning machine guns in the nose and two more in the Boulton Paul dorsal turret. The Hudson Mk III added one ventral and two beam machine guns and replaced the 1,100 hp Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9-cylinder radials with 1,200 hp versions (428 produced).
The Hudson Mk V (309 produced) and Mk VI (450 produced) were powered by the 1,200 hp Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp 14-cylinder two-row radial. The RAF also obtained 380 Mk IIIA and 30 Mk IV Hudsons under the Lend-Lease programme.
Operational history
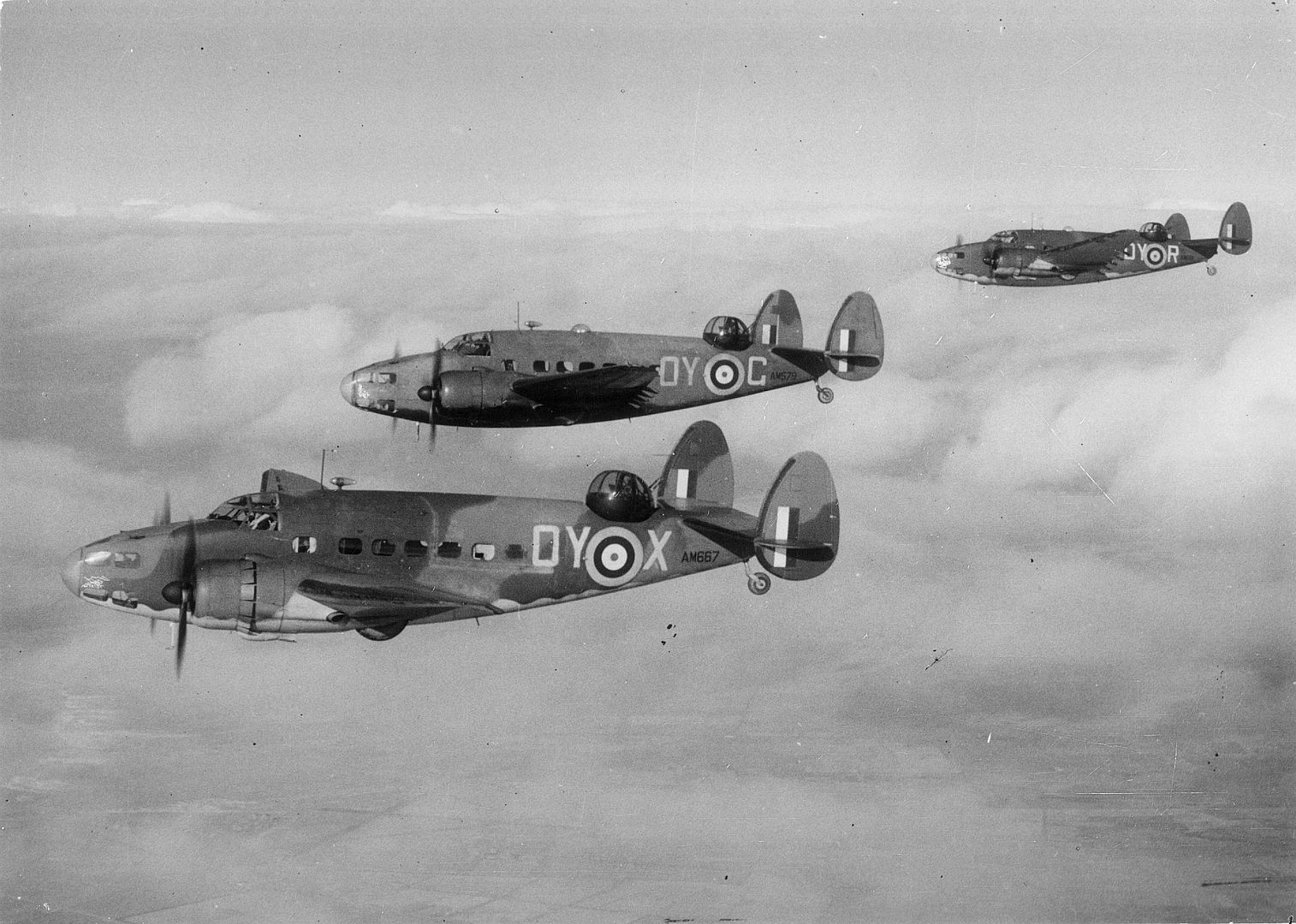
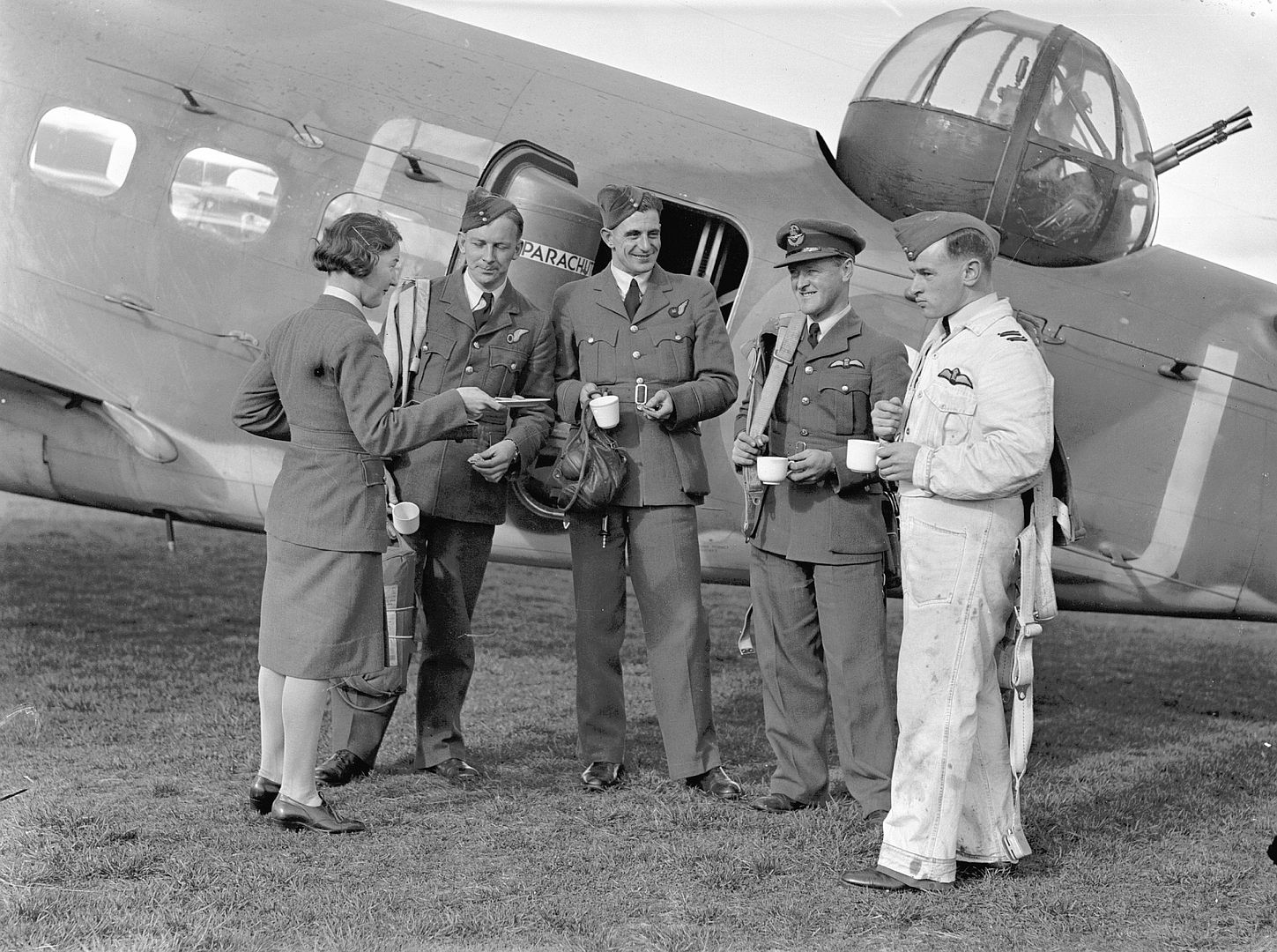
By February 1939, RAF Hudsons began to be delivered, initially equipping No. 224 Squadron RAF at RAF Leuchars, Scotland in May 1939. By the start of the war in September, 78 Hudsons were in service. Due to the United States' neutrality at that time, early series aircraft were flown to the Canada?US border, landed, and then towed on their wheels over the border into Canada by tractors or horse drawn teams, before then being flown to Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) airfields where they were then dismantled and "cocooned" for transport as deck cargo, by ship to Liverpool. The Hudsons were supplied without the Boulton Paul dorsal turret, which was installed on arrival in the United Kingdom.
Although later outclassed by larger bombers, the Hudson achieved some significant feats during the first half of the war. On 8 October 1939, over Jutland, a Hudson became the first Allied aircraft operating from the British Isles to shoot down an enemy aircraft (earlier victories by a Fairey Battle on 20 September 1939 over Aachen and by Blackburn Skuas of the Fleet Air Arm on 26 September 1939 had been by aircraft based in France or on an aircraft carrier). Hudsons also provided top cover during the Battle of Dunkirk.
On 27 August 1941, a Hudson of No. 269 Squadron RAF, operating from Kaldadarnes, Iceland, attacked and damaged the German submarine U-570 causing the submarine's crew to display a white flag and surrender ? the aircraft achieved the unusual distinction of capturing a naval vessel. The Germans were taken prisoner and the submarine taken under tow when Royal Navy ships subsequently arrived on the scene. A PBO-1 Hudson of the United States Navy squadron VP-82 became the first US aircraft to destroy a German submarine, when it sank U-656 southwest of Newfoundland on 1 March 1942. U-701 was destroyed on 7 July 1942 while running on the surface off Cape Hatteras by a Hudson of the 396th Bombardment Squadron (Medium), United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). A Hudson of No. 113 Squadron RCAF became the first aircraft of the RCAF's Eastern Air Command to sink a submarine, when Hudson 625 sank U-754 on 31 July 1942.
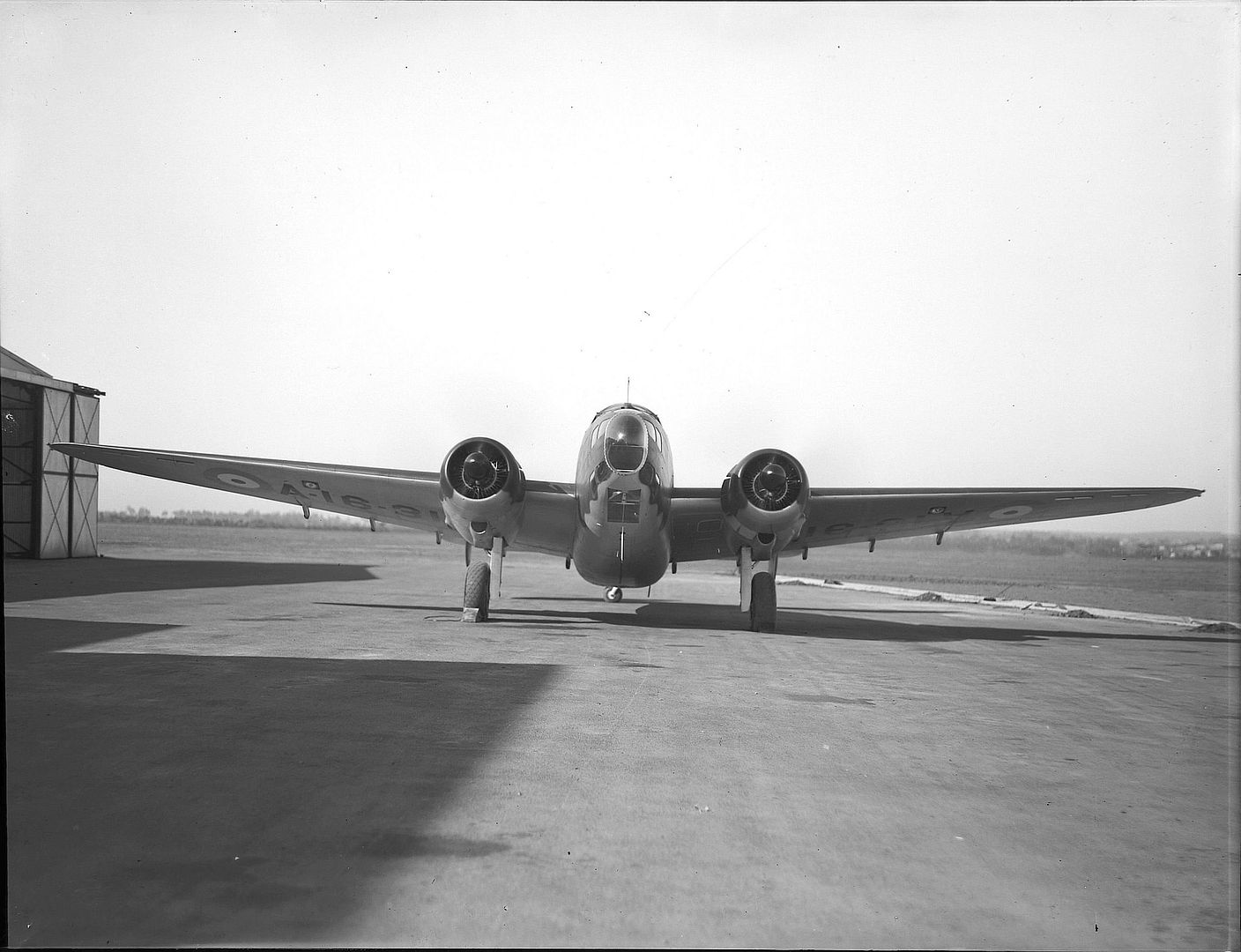
A Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) Hudson was involved in the Canberra air disaster of 1940, in which three ministers of the Australian government were killed.
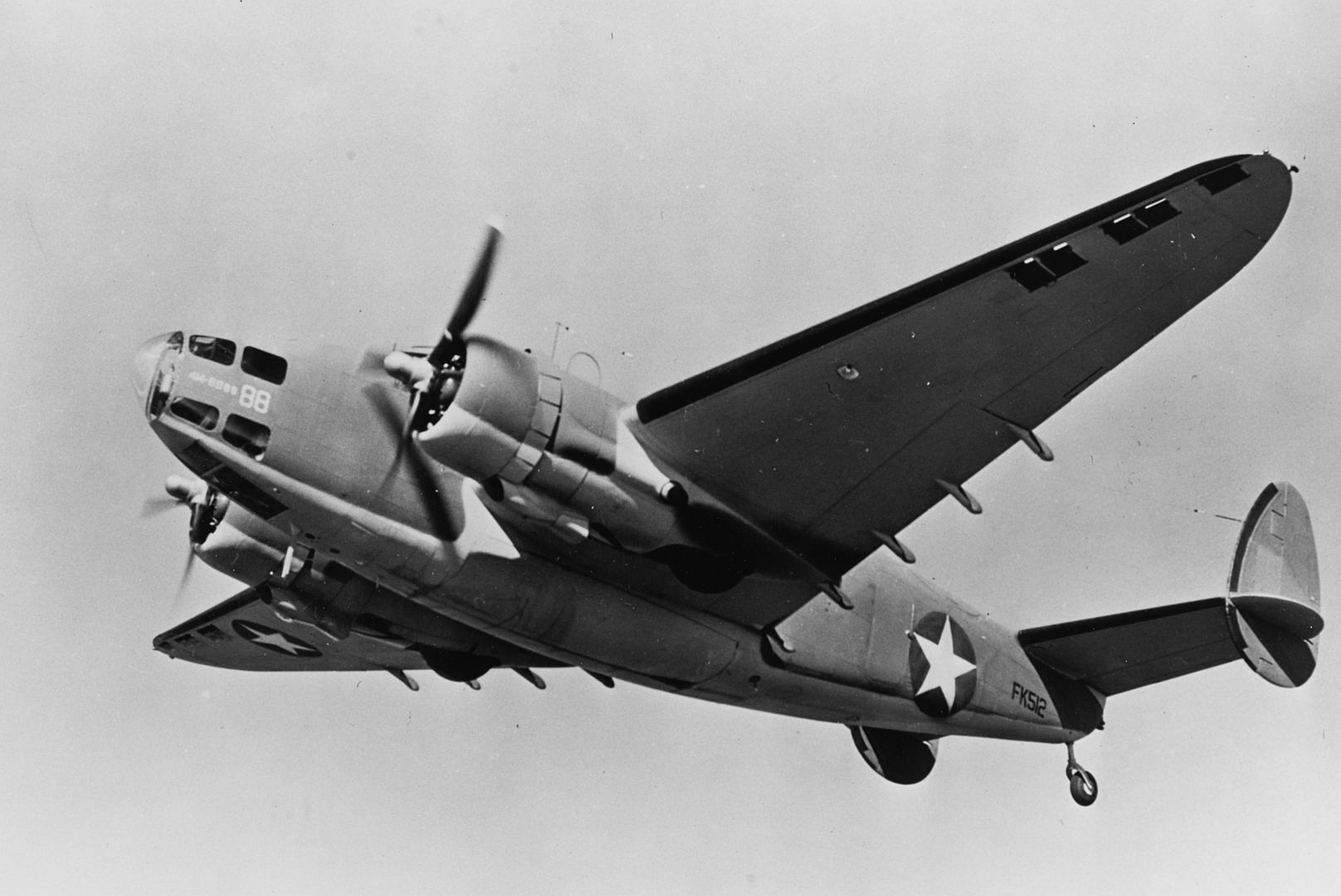
In 1941, the USAAF began operating the Hudson; the Twin Wasp-powered variant was designated the A-28 (82 acquired) and the Cyclone-powered variant was designated the A-29 (418 acquired). The US Navy operated 20 A-29s, redesignated the PBO-1. A further 300 were built as aircrew trainers, designated the AT-18.
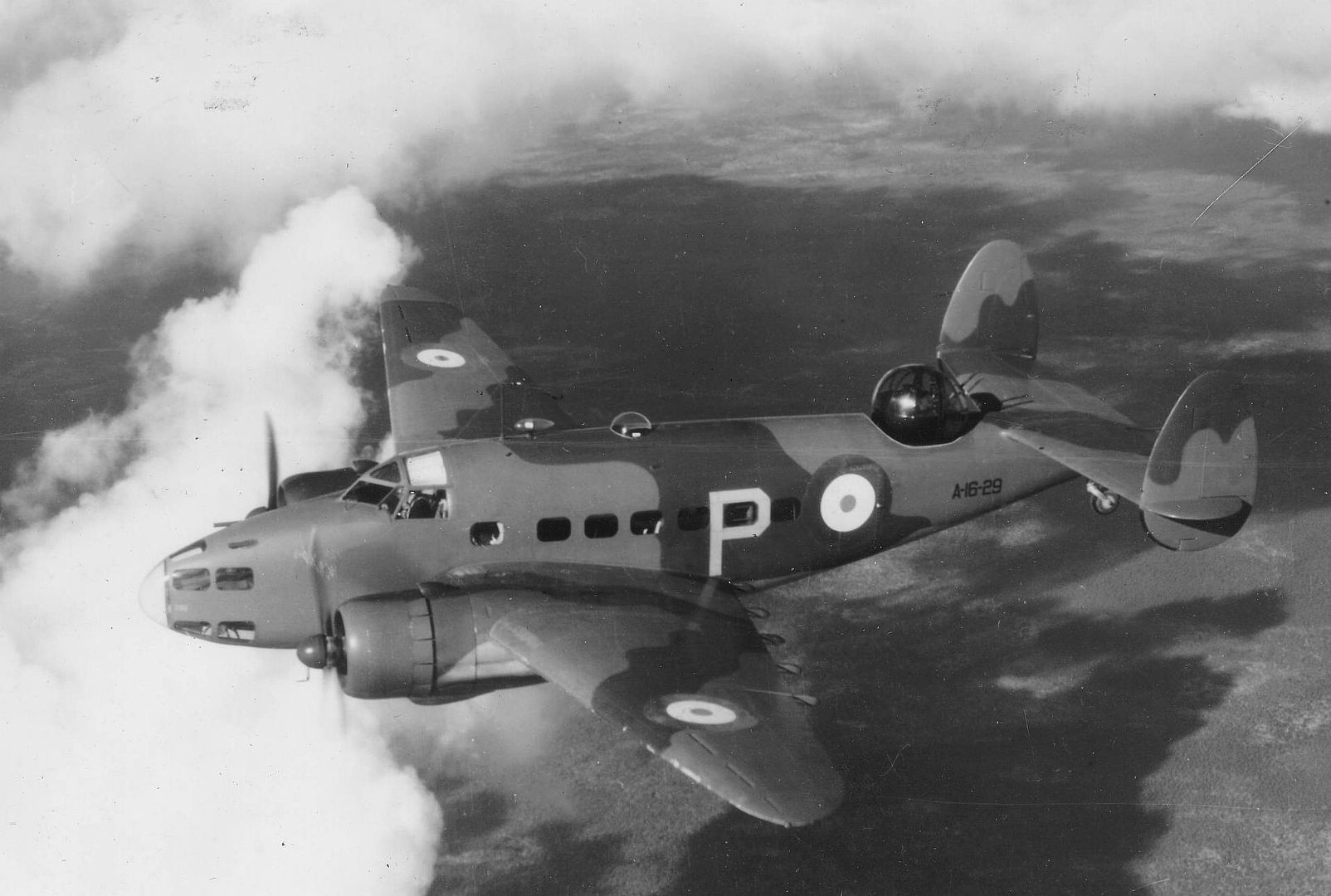
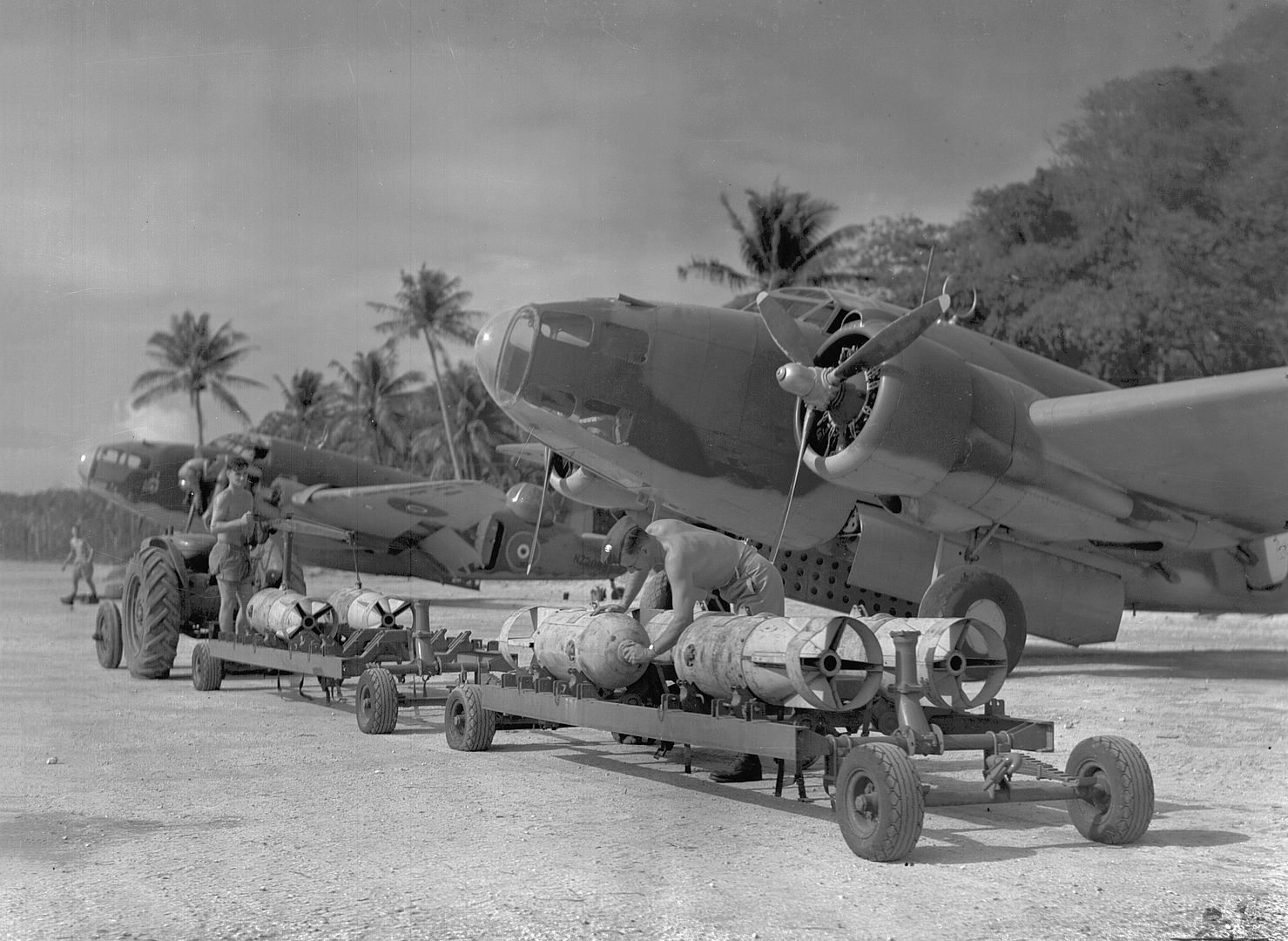
Following Japanese attacks on Malaya, Hudsons from No. 1 Squadron RAAF became the first Allied aircraft to make an attack in the Pacific War, sinking a Japanese transport ship, the Awazisan Maru, off Kota Bharu at 0118h local time, an hour before the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Its opponents found that the Hudson had exceptional manoeuvrability for a twin-engine aircraft; it was notable for the tight turns achievable if either engine was briefly feathered.
The highest-scoring Japanese ace of the war, Sabur? Sakai, praised the skill and fighting abilities of an RAAF Hudson crew killed in action over New Guinea after being engaged by nine highly-manoeuvrable Mitsubishi A6M Zeroes on 22 July 1942. The crew, captained by P/O Warren Cowan, in Hudson Mk IIIA A16-201 (bu. no. 41-36979) of No. 32 Squadron RAAF, was intercepted over Buna by nine Zeroes of the Tainan Kaigun K?k?tai led by Sakai. The Hudson crew accomplished many aggressive and unexpected turns, engaging the Japanese pilots in a dogfight for more than 10 minutes. It was only after Sakai scored hits on the rear/upper turret that the Hudson could be destroyed. Its crew made such an impression on Sakai that, after the war's end, he sought to identify them. In 1997, Sakai wrote formally to the Australian government, recommending that Cowan be "posthumously awarded your country's highest military decoration".
On 23 November 1942, the crew of a No. 3 Squadron, Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) Hudson Mk IIIA, NZ2049, (41-46465) after spotting an enemy convoy near Vella Lavella, was engaged by three Japanese floatplane fighters. After skilled evasive manoeuvring at an altitude of less than 50 feet (15 metres), by the Hudson's captain, Flying Officer George Gudsell, the crew returned with no casualties to Henderson Field, Guadalcanal.
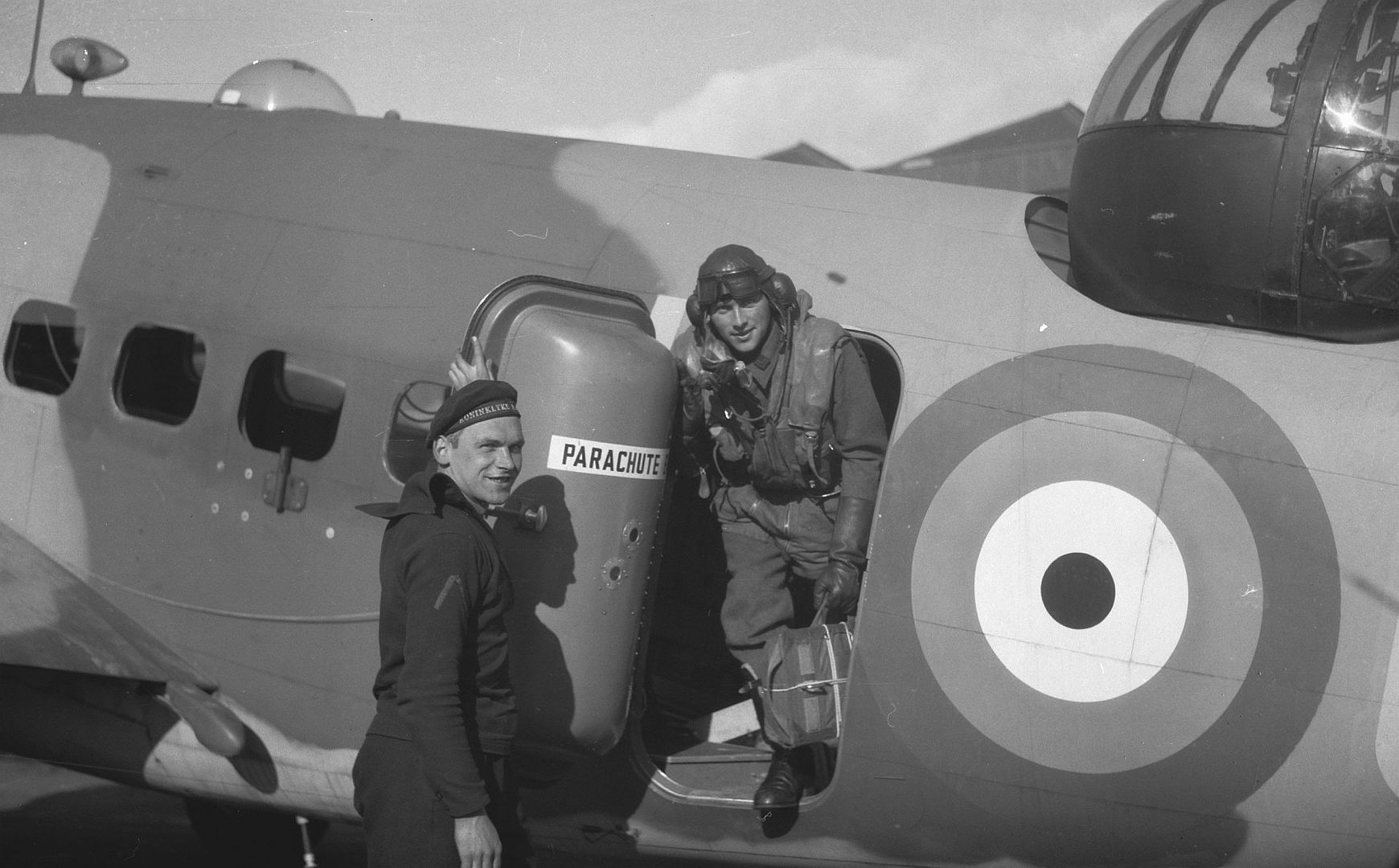
Hudsons were also operated by RAF Special Duties squadrons for clandestine operations; No. 161 Squadron in Europe and No. 357 Squadron in Burma.
Postwar
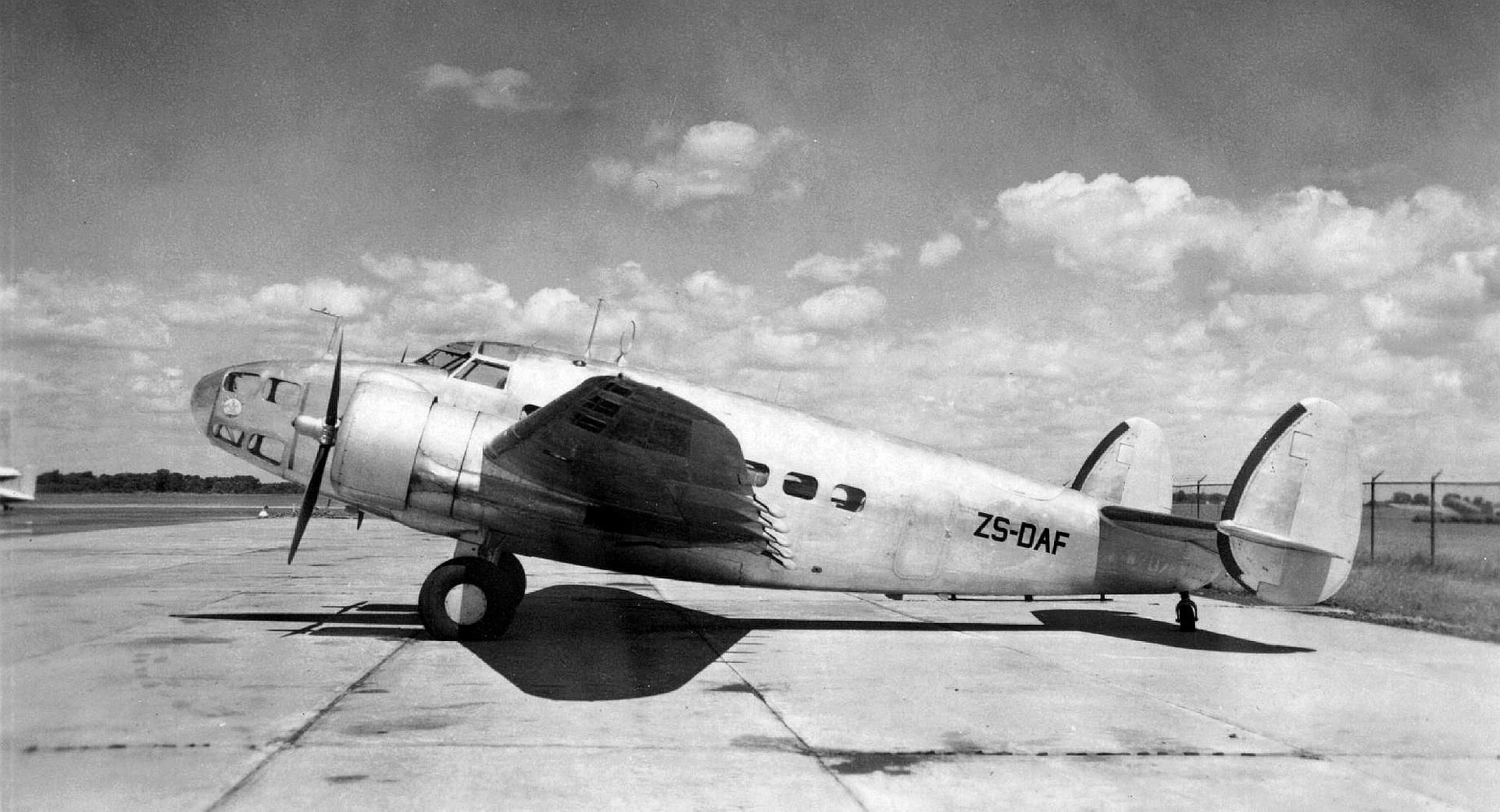
Postwar, numbers of Hudsons were sold by the military for civil operation as airliners and survey aircraft. In Australia, East-West Airlines of Tamworth, New South Wales (NSW), operated four Hudsons on scheduled services from Tamworth to many towns in NSW and Queensland between 1950 and 1955.[16] Adastra Aerial Surveys based at Sydney's Mascot Airport operated seven L-414s between 1950 and 1972 on air taxi, survey and photographic flights.
A total of 2,941 Hudsons were built.
The type formed the basis for development of the Lockheed Ventura resulting in them being withdrawn from front line service from 1944, though many survived the war to be used as civil transports, primarily in Australia and a single example was briefly used as an airline crew trainer in New Zealand.
Variants
Model 414
Company designation for the military A-28 / A-29 and Hudson variants.
Hudson I
Production aircraft for the Royal Air Force (RAF); 351 built and 50 for the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
Hudson II
As the Mk I but with spinnerless constant speed propellers; 20 built for the RAF and 50 for the RAAF.
Hudson III
Production aircraft with retractable ventral gun position; 428 built.
Hudson IIIA
Lend-lease variants of the A-29 and A-29A aircraft; 800 built.
Hudson IV
As Mk II with ventral gun removed; 30 built and RAAF Mk I and IIs were converted to this standard.
Hudson IVA
52 A-28s delivered to the RAAF.
Hudson V
Mk III with two 1,200 hp (890 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1830-S3C4-G Twin Wasp engines; 409 built.
Hudson VI
A-28As under lend-lease; 450 built.
A-28
US Military designation powered by two 1,050 hp (780 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1830-45 engines; 52 lend-lease to Australia as Hudson IVA.[19]
A-28A
US Military designation powered by two 1,200 hp (890 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1830-67 engines, interiors convertible to troop transports; 450 lend-lease to RAF/RCAF/RNZAF as Hudson VI; 27 units passed to the Brazilian Air Force.
A-29
US Military designation powered by two 1,200 hp (890 kW) Wright R-1820-87 engines; lend lease version intended for the RAF, 153 diverted to United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) as the RA-29 and 20 to the United States Navy (USN) as the PBO-1.
A-29A
as A-29 but with convertible interiors as troop transports; 384 lend-lease to the RAF/RAAF/RCAF/RNZAF Chinese Air Force as Hudson IIIA, some retained by USAAF as the RA-29A.
A-29B
24 of the 153 A-29s retained by the USAAF converted for photo-survey
AT-18
Gunnery trainer version of the A-29 powered by two Wright R-1820-87 engines, 217 built.
AT-18A
Navigational trainer version with dorsal turret removed, 83 built.
C-63
Provisional designation changed to A-29A.
PBO-1
Twenty former RAF Hudson IIIAs repossessed for use by Patrol Squadron 82 (VP-82) of the USN.
As usual right click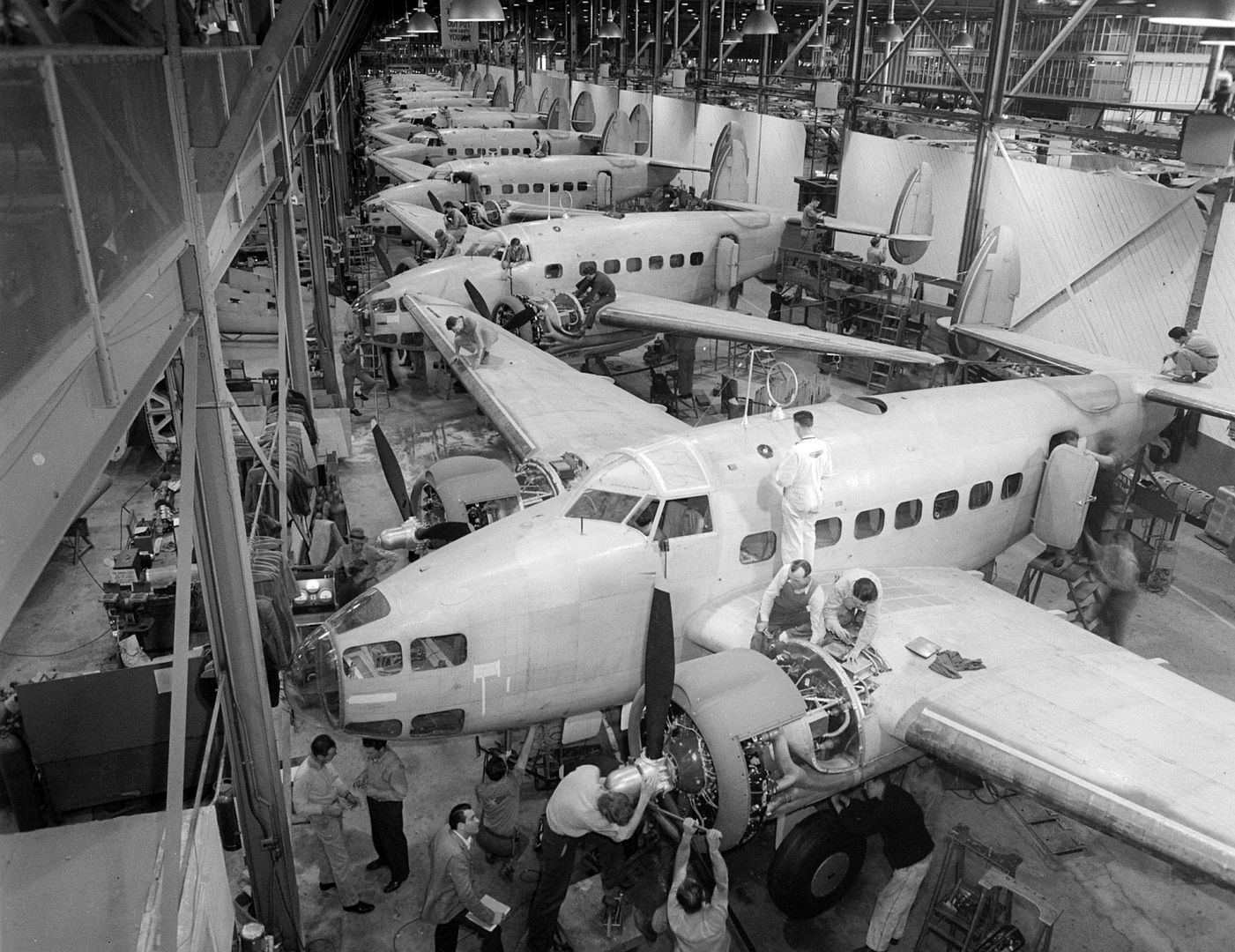
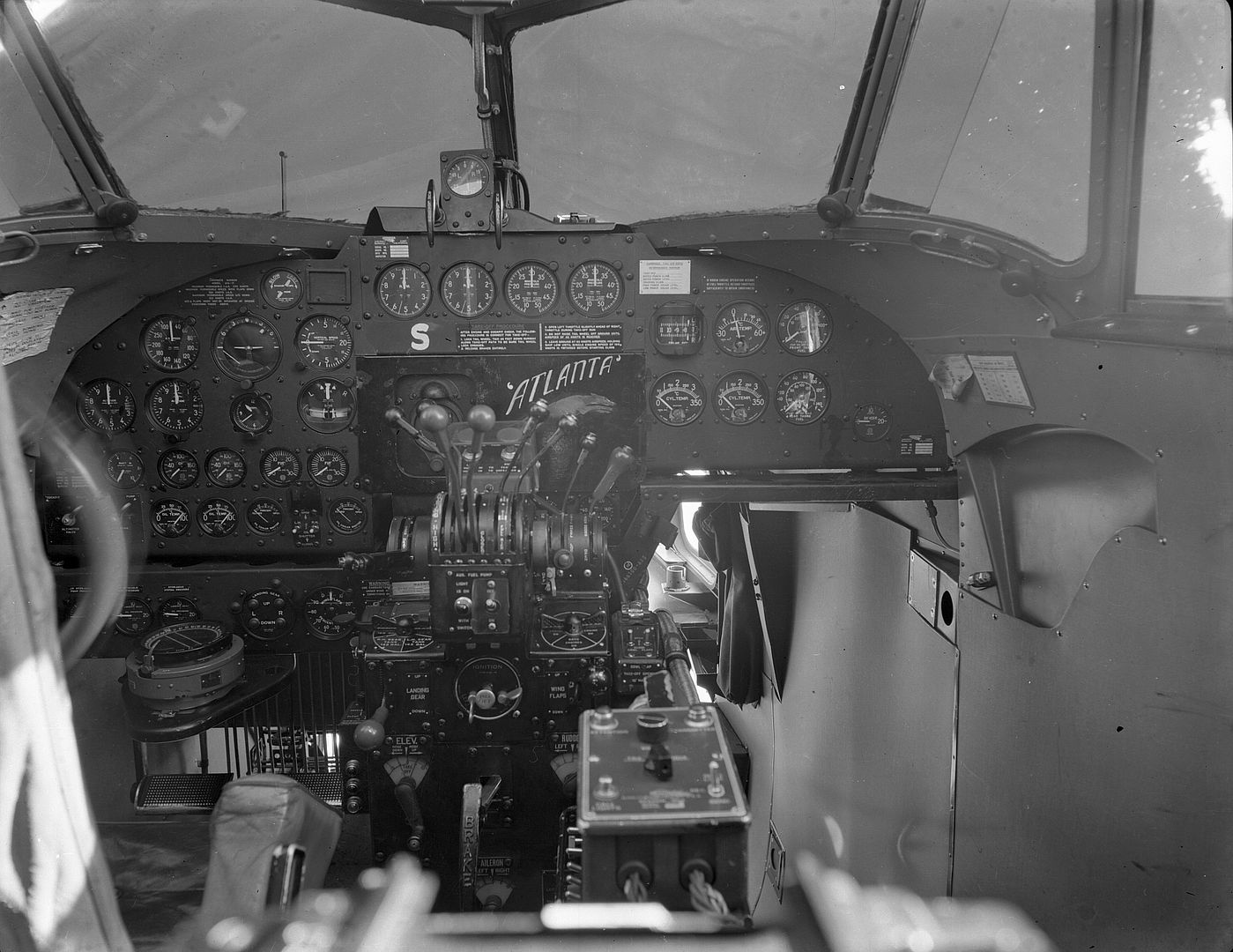
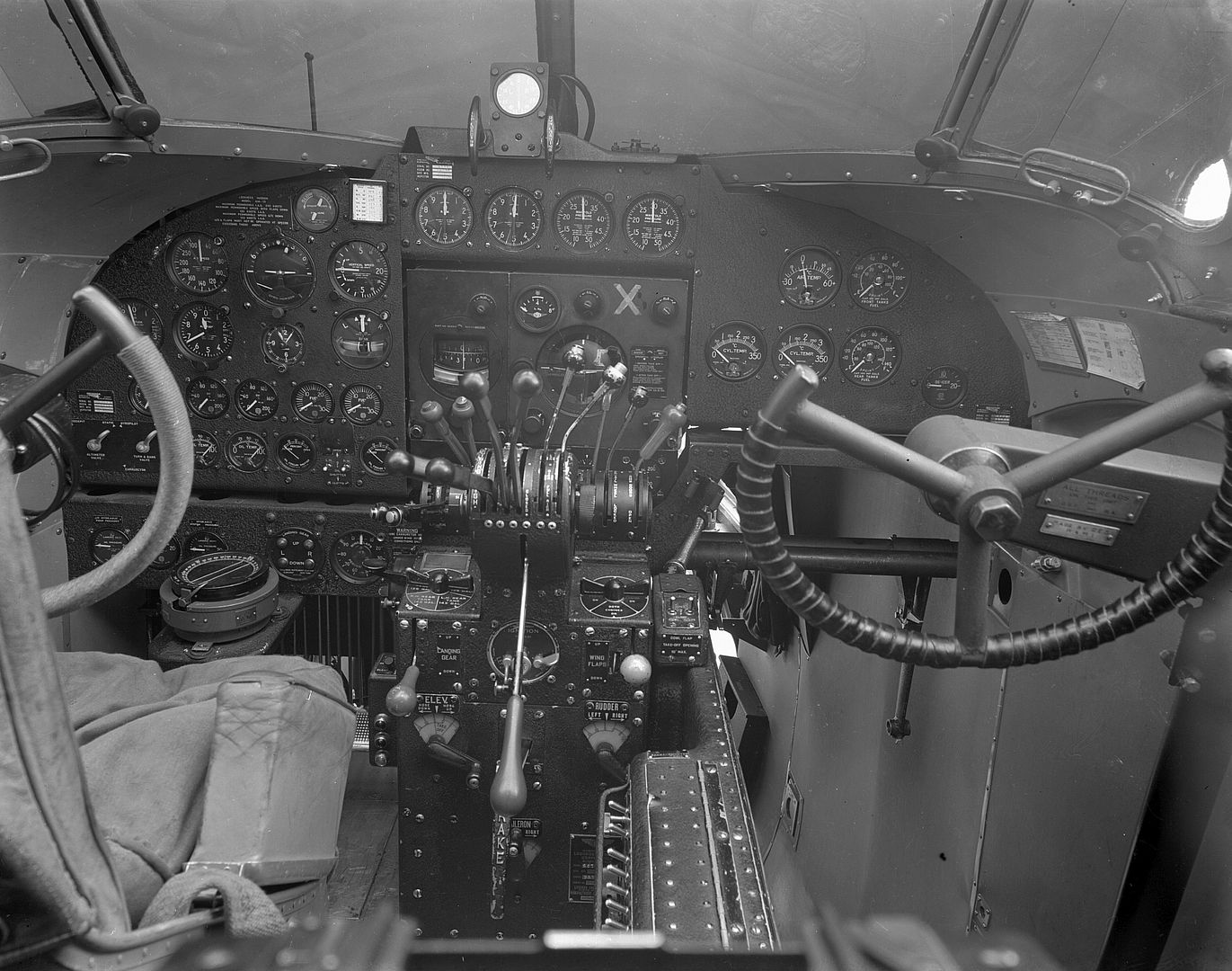
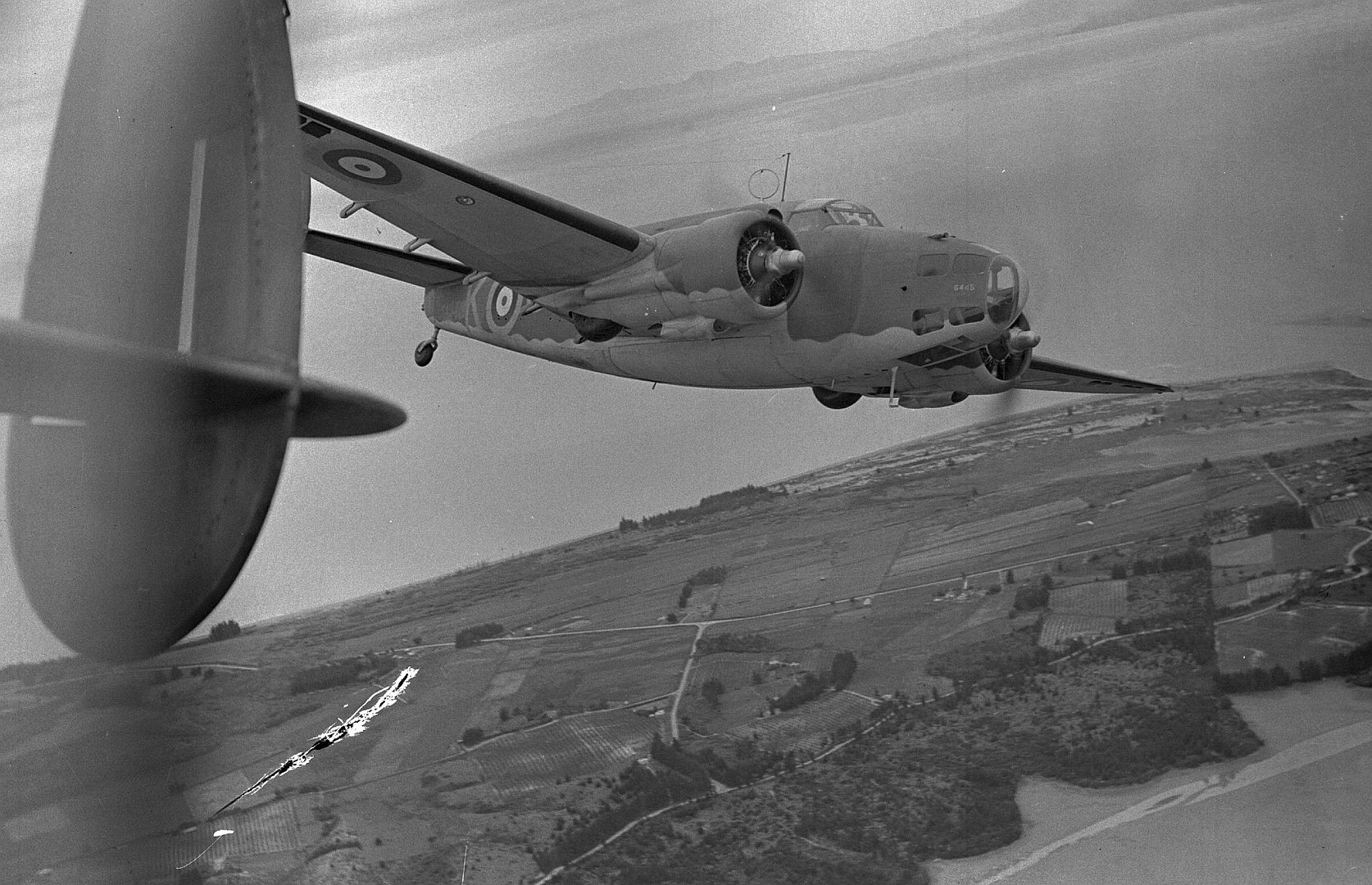
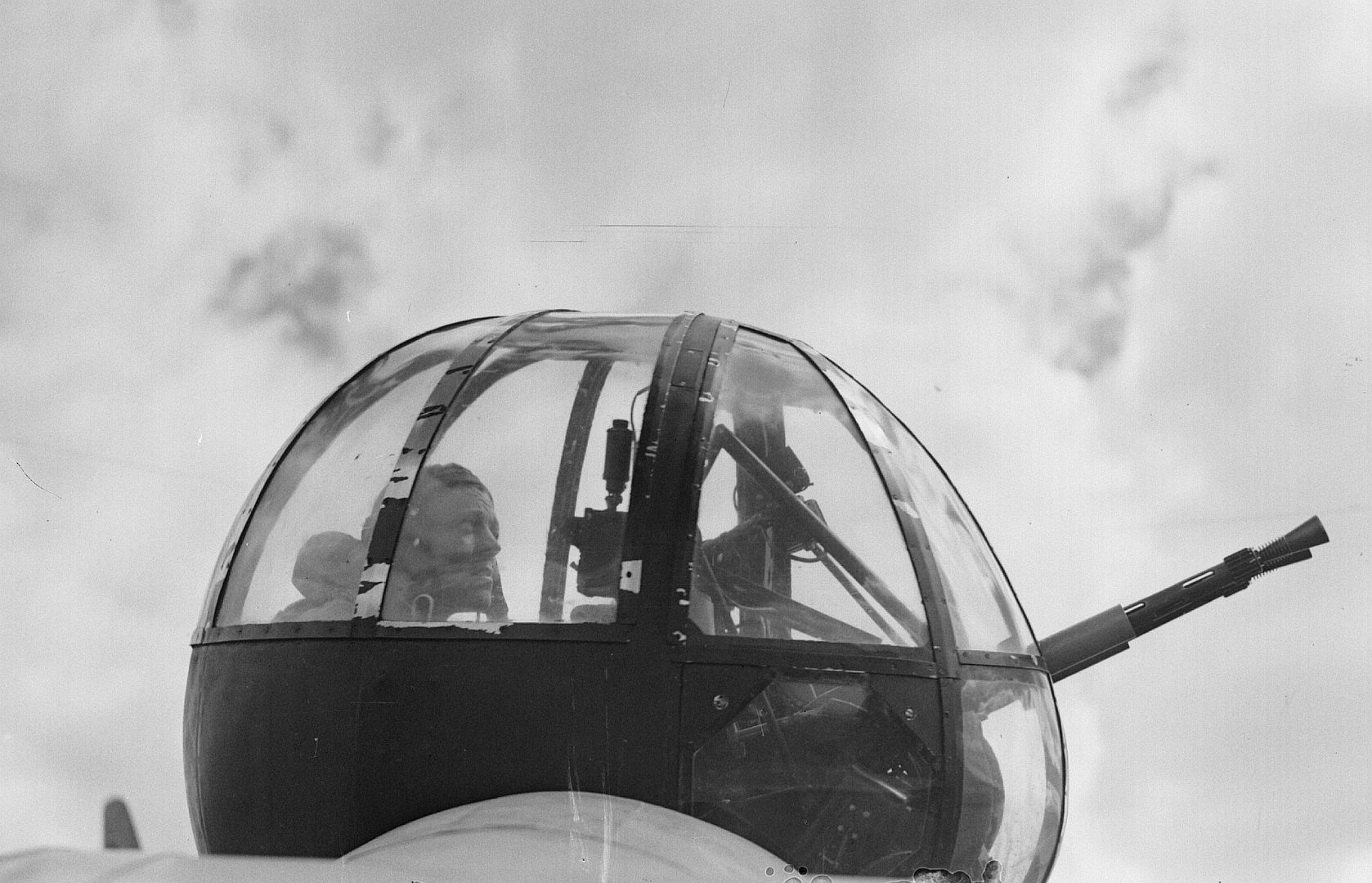
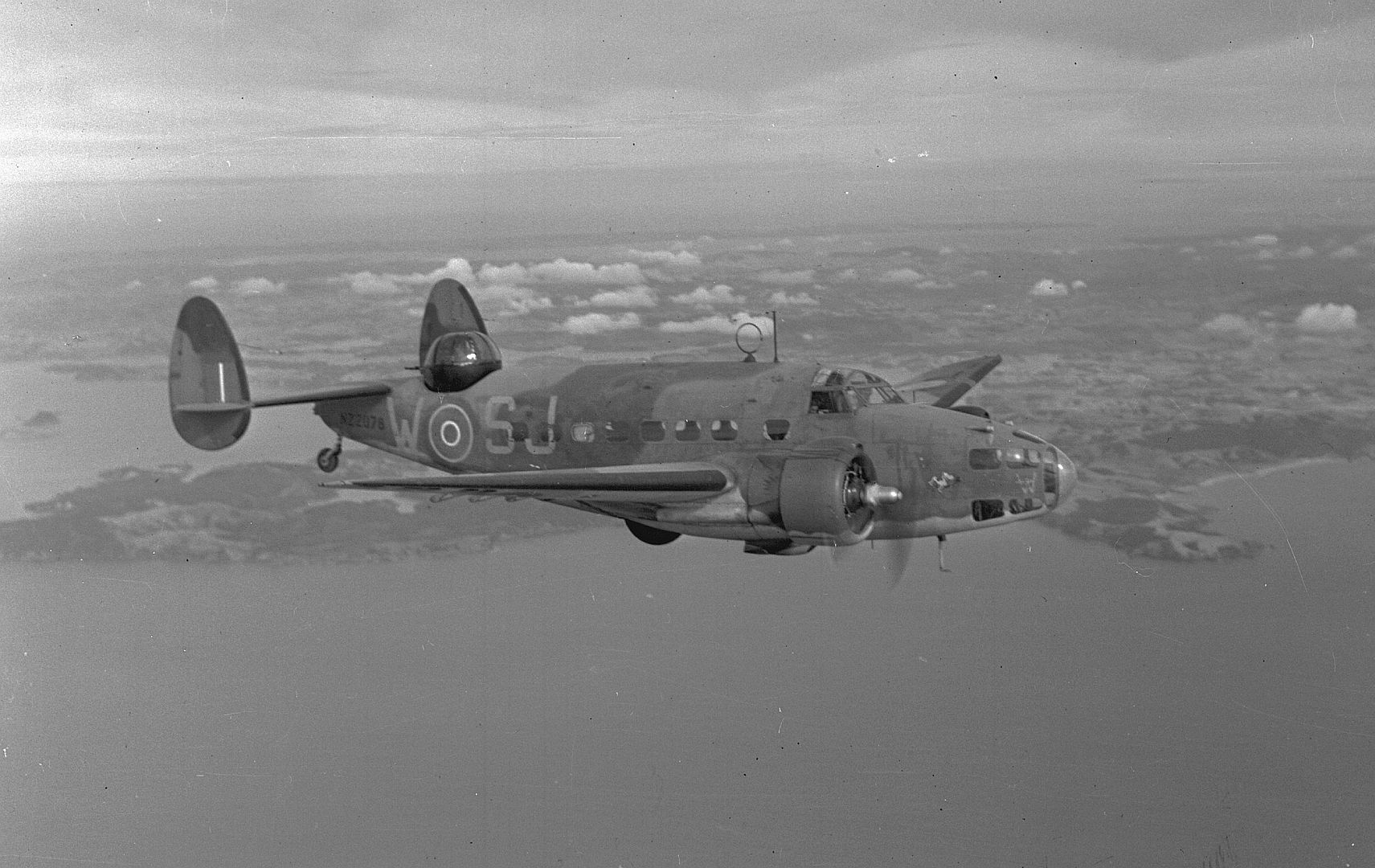
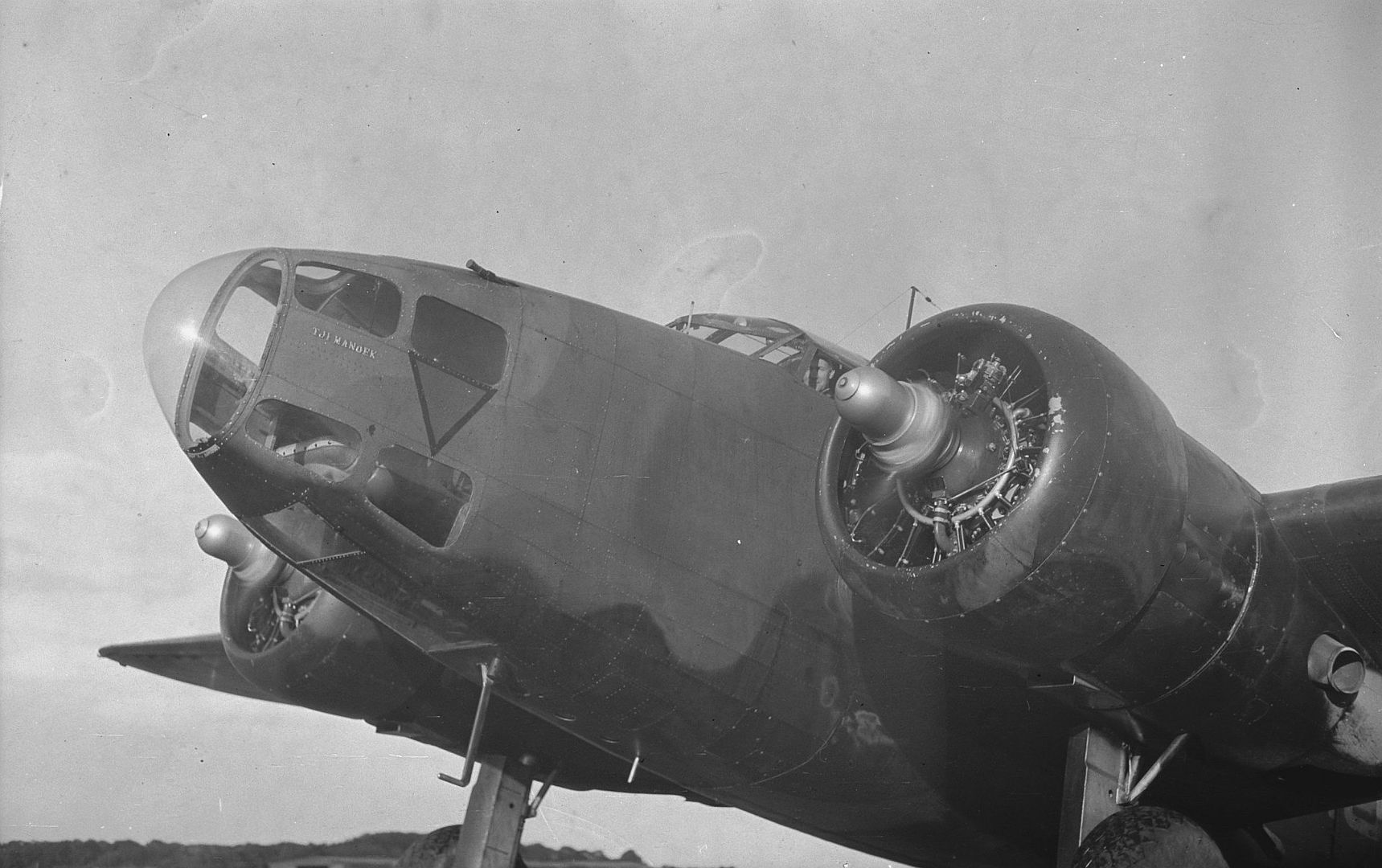
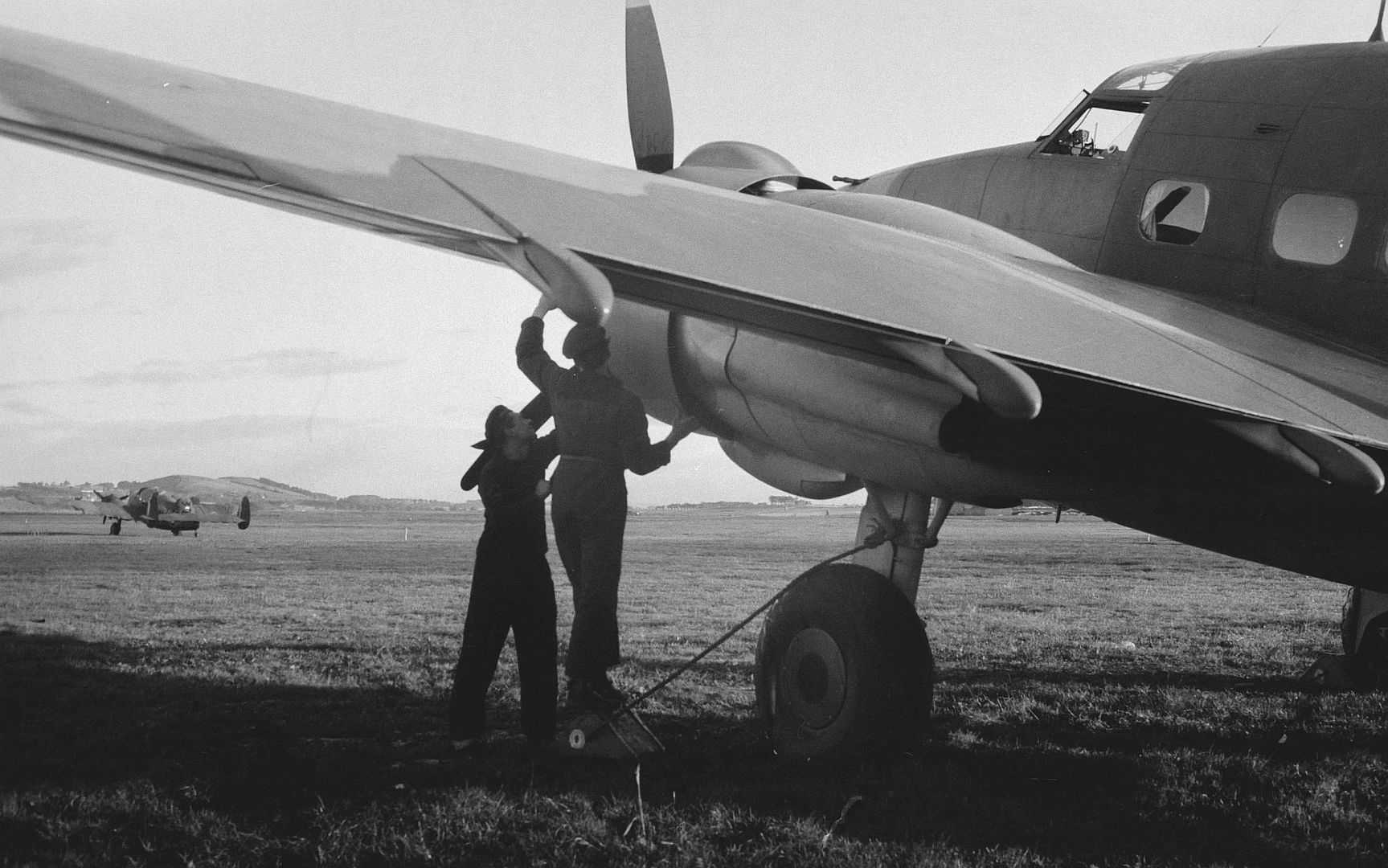
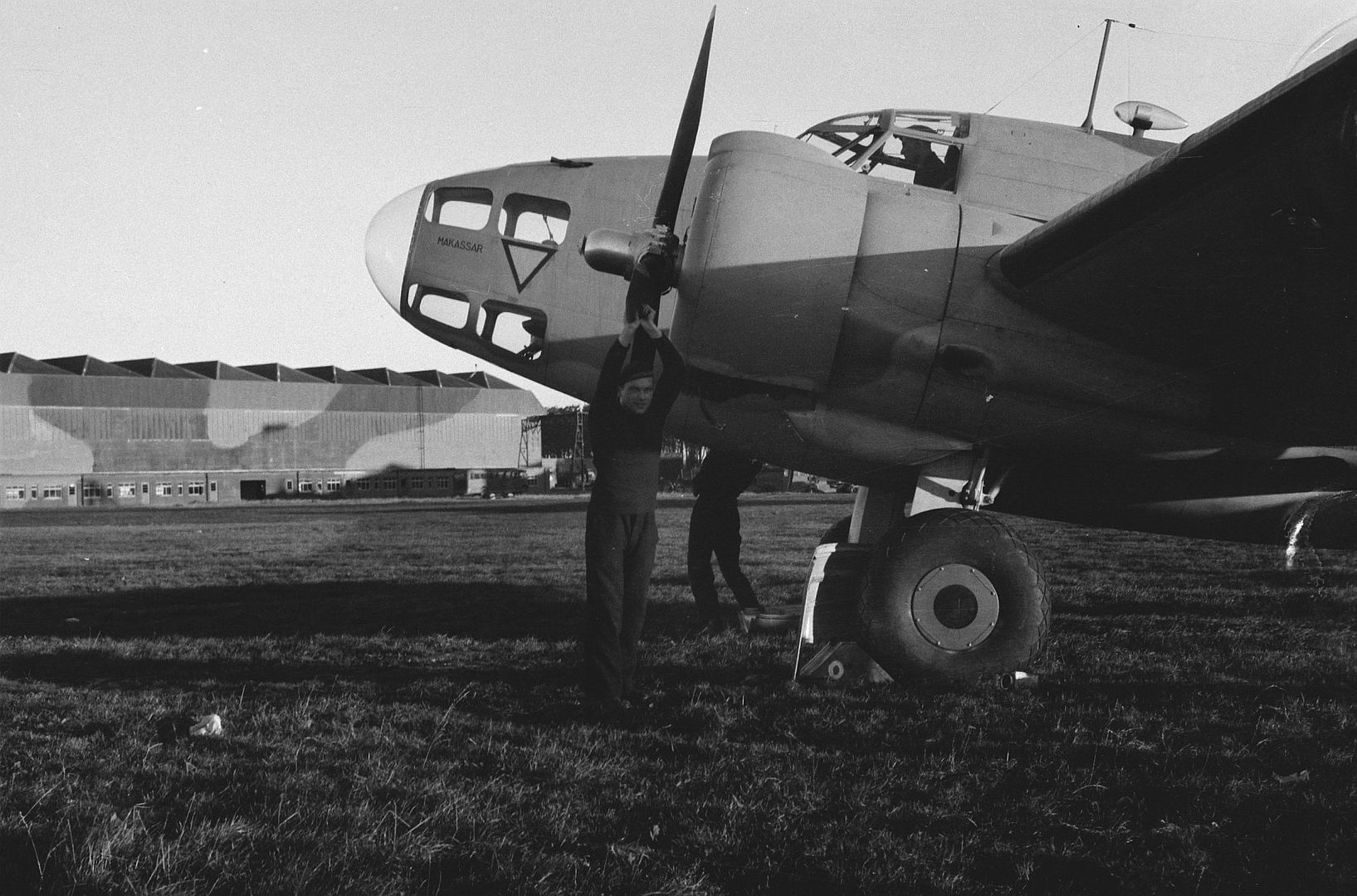
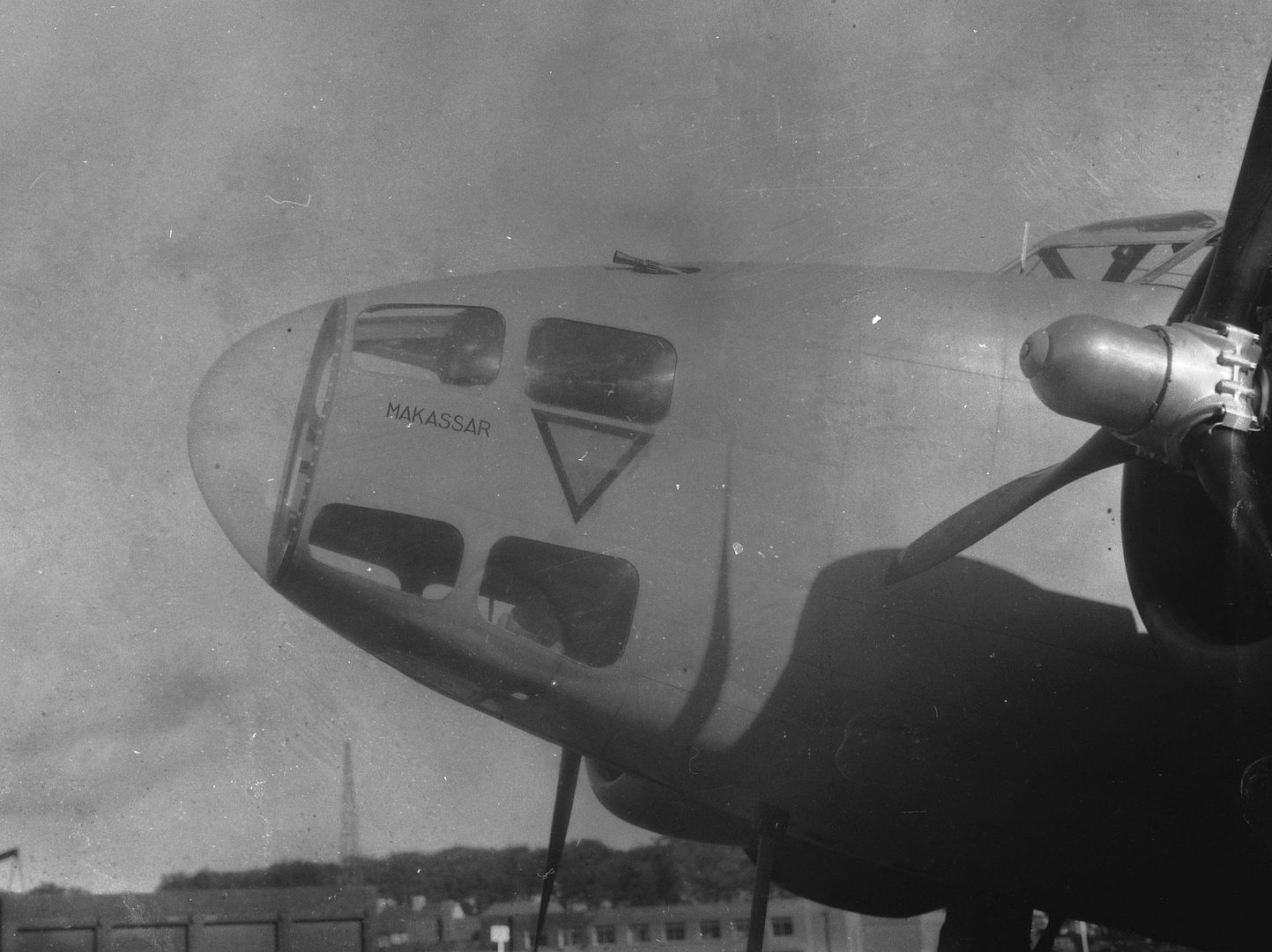


































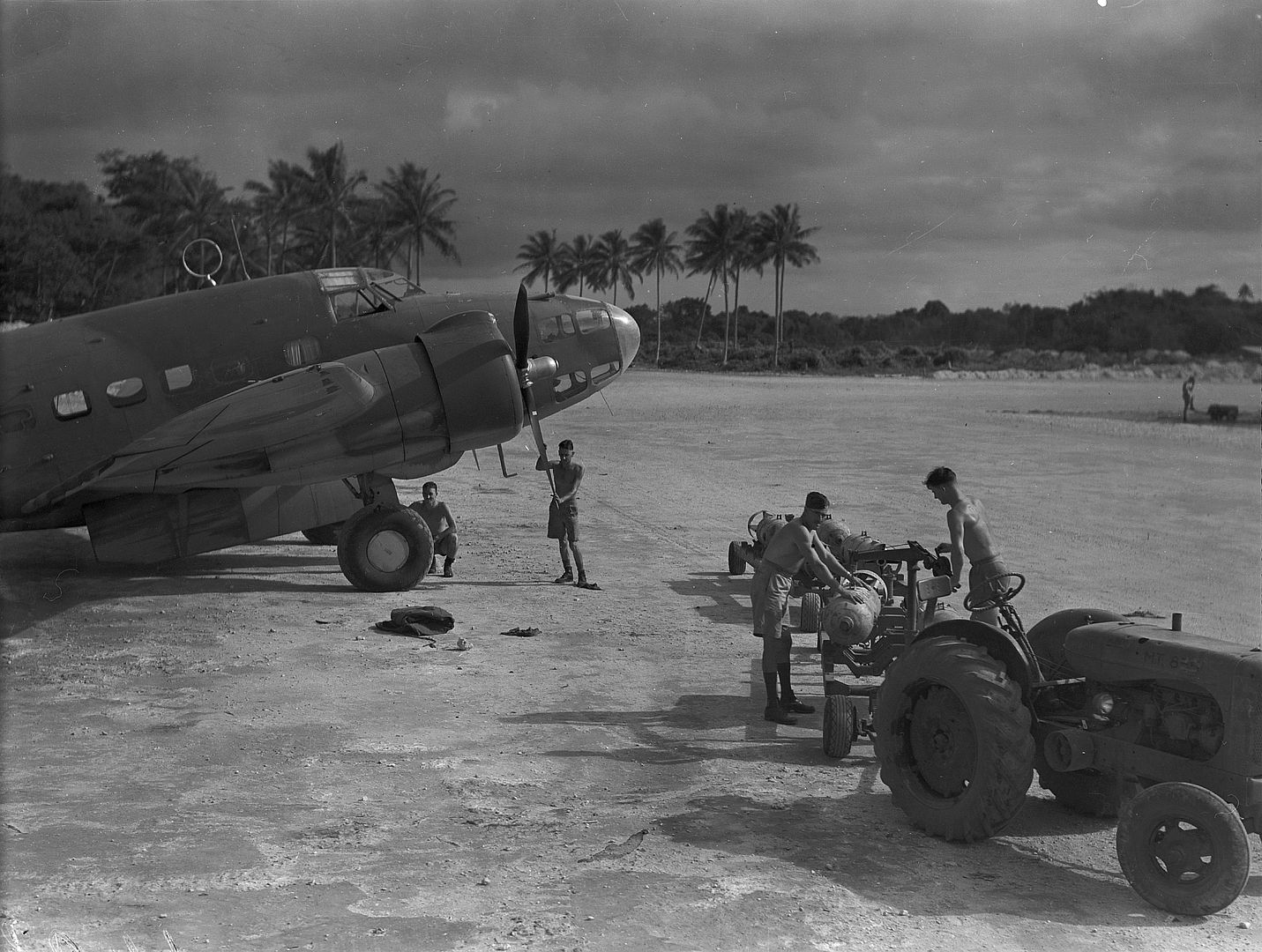





-
5 years agoSun May 04 2025, 11:18amDuggy
 Main Admin
Main Admin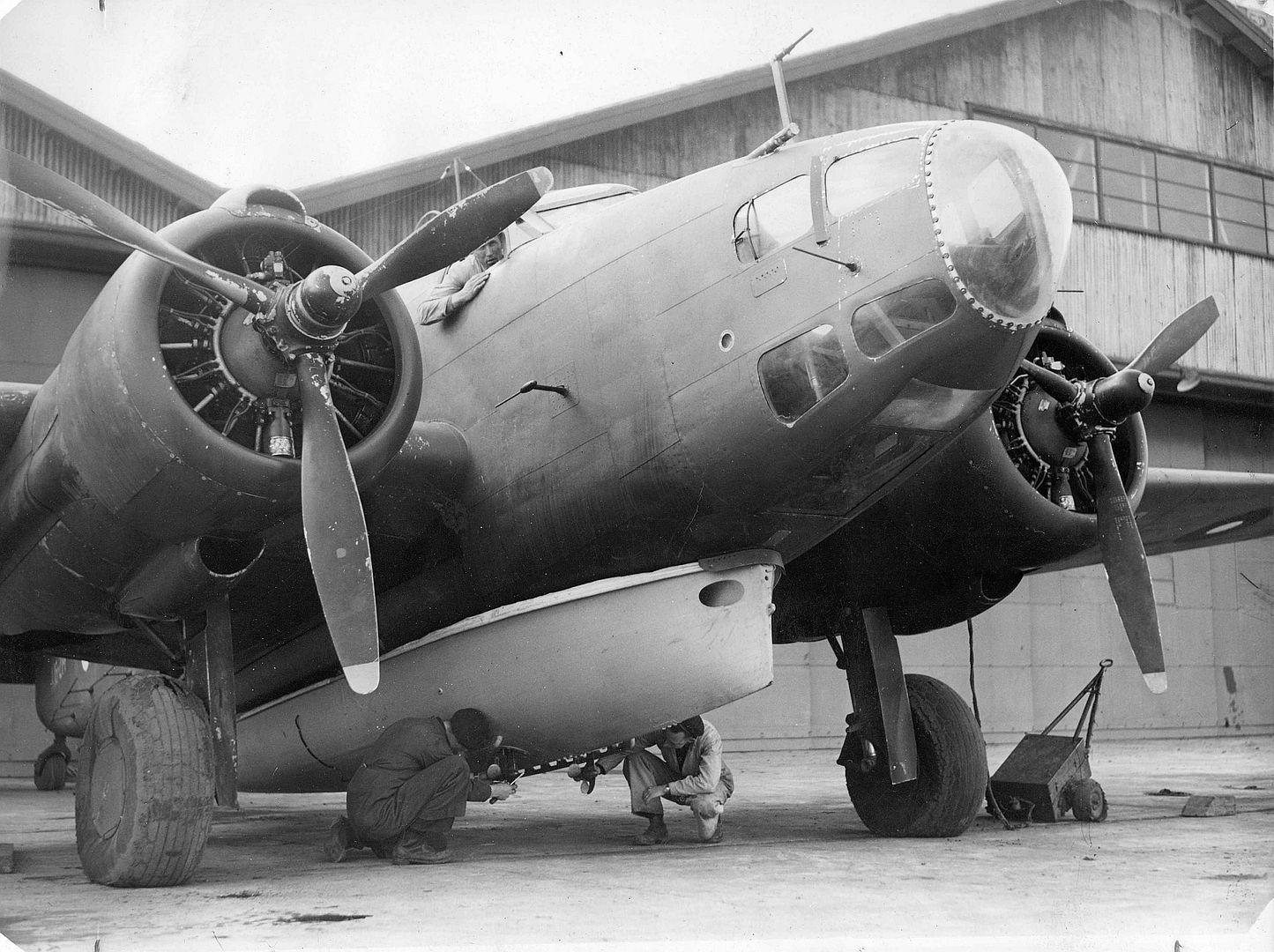
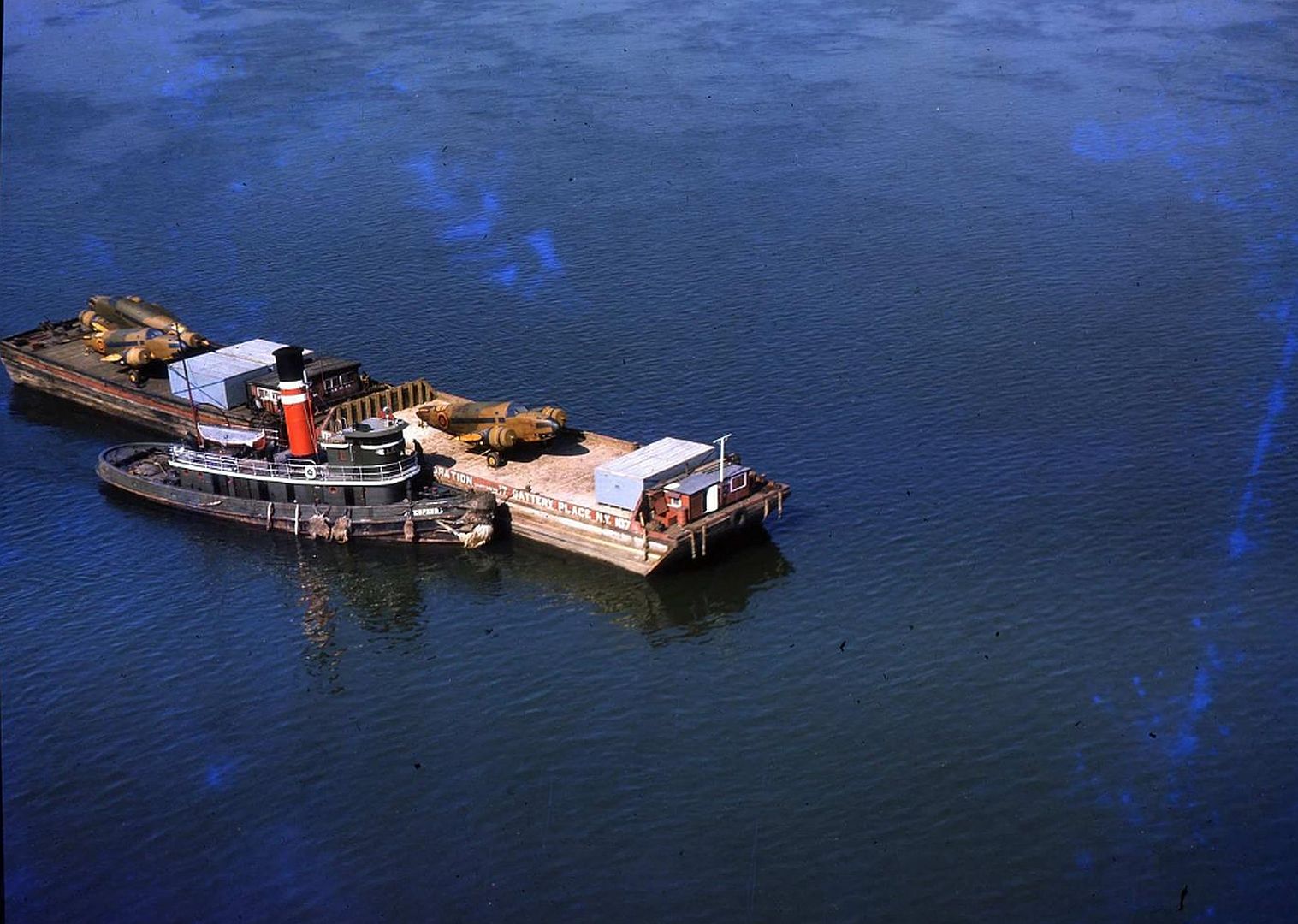
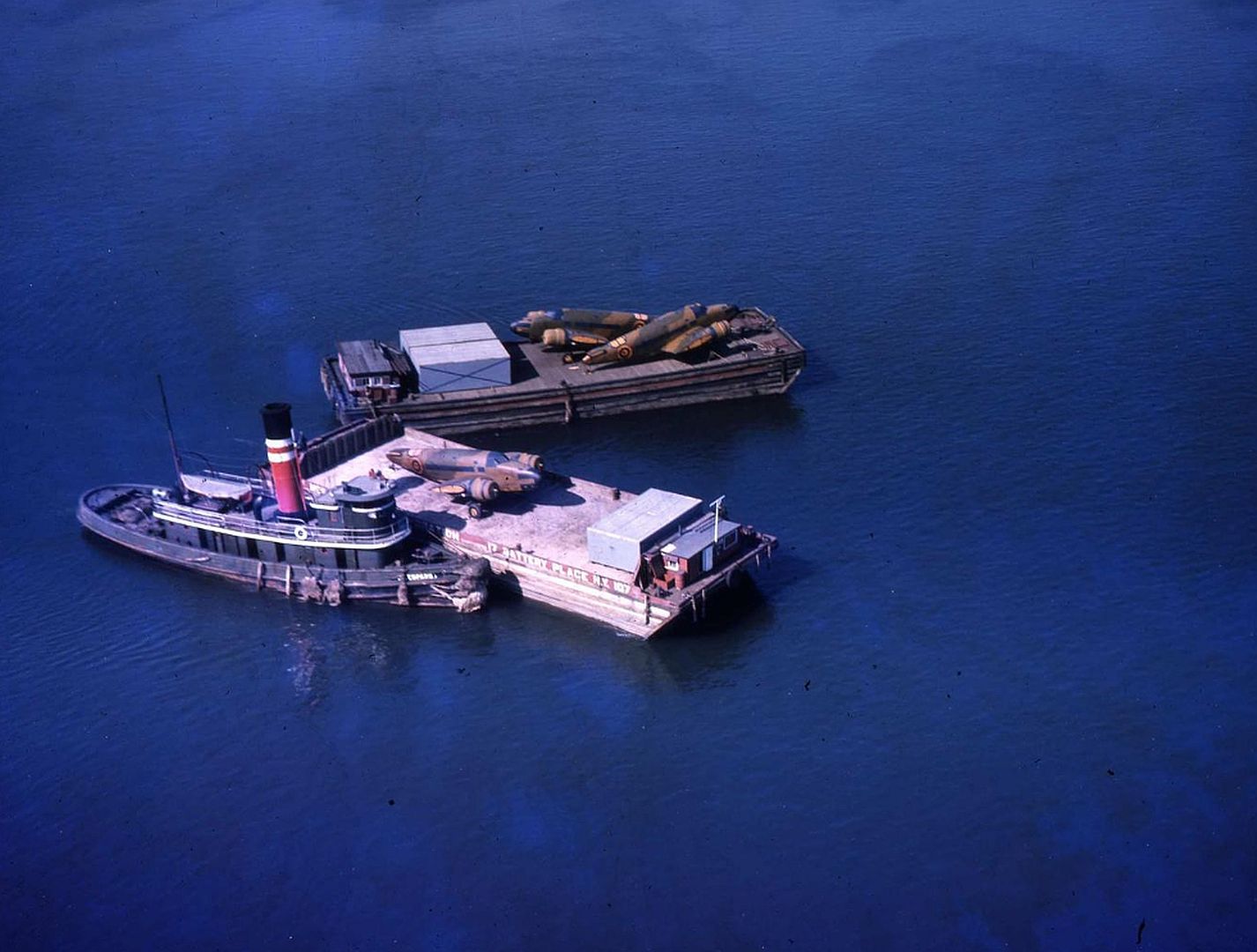
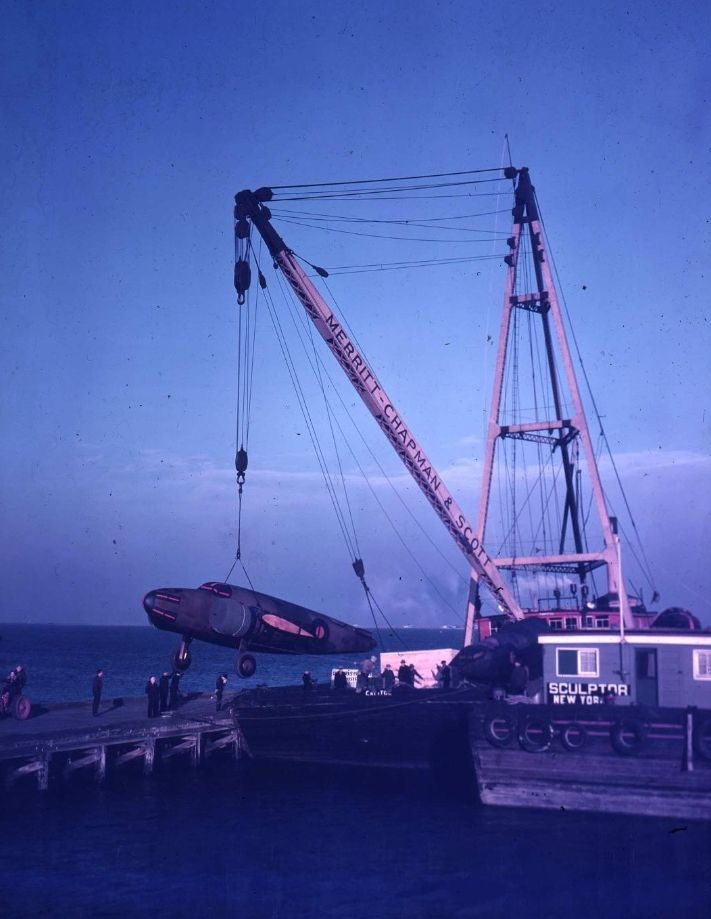
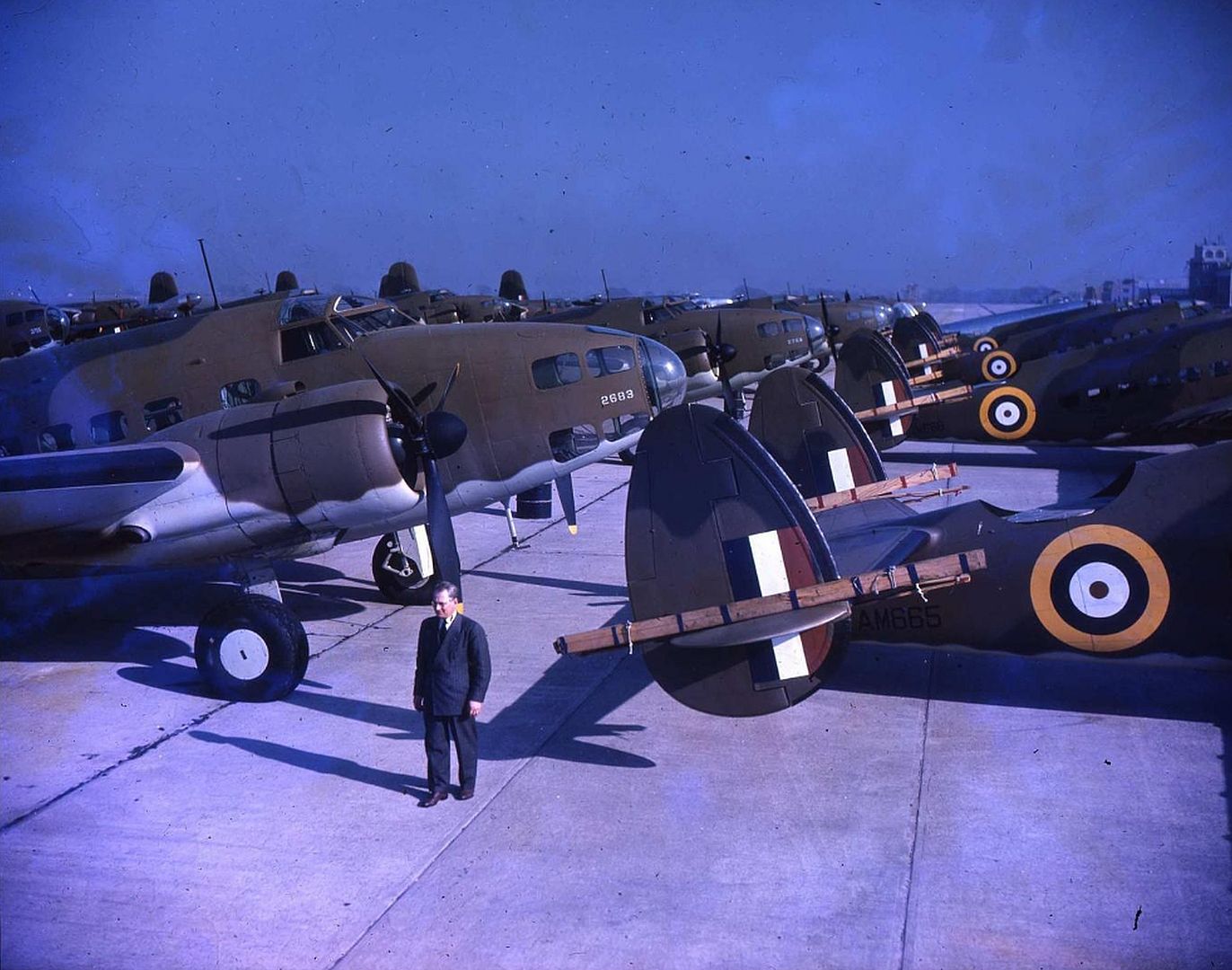
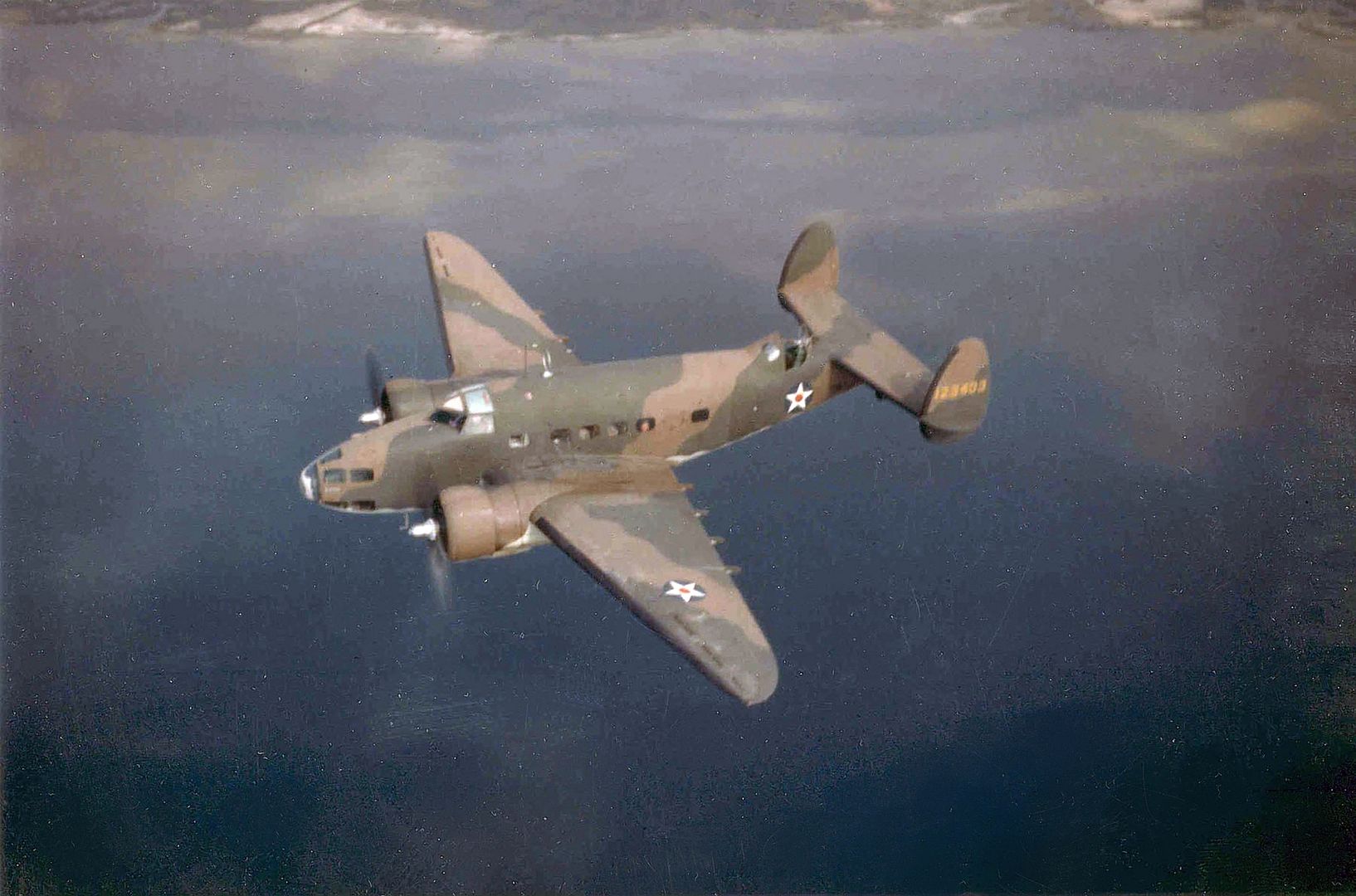
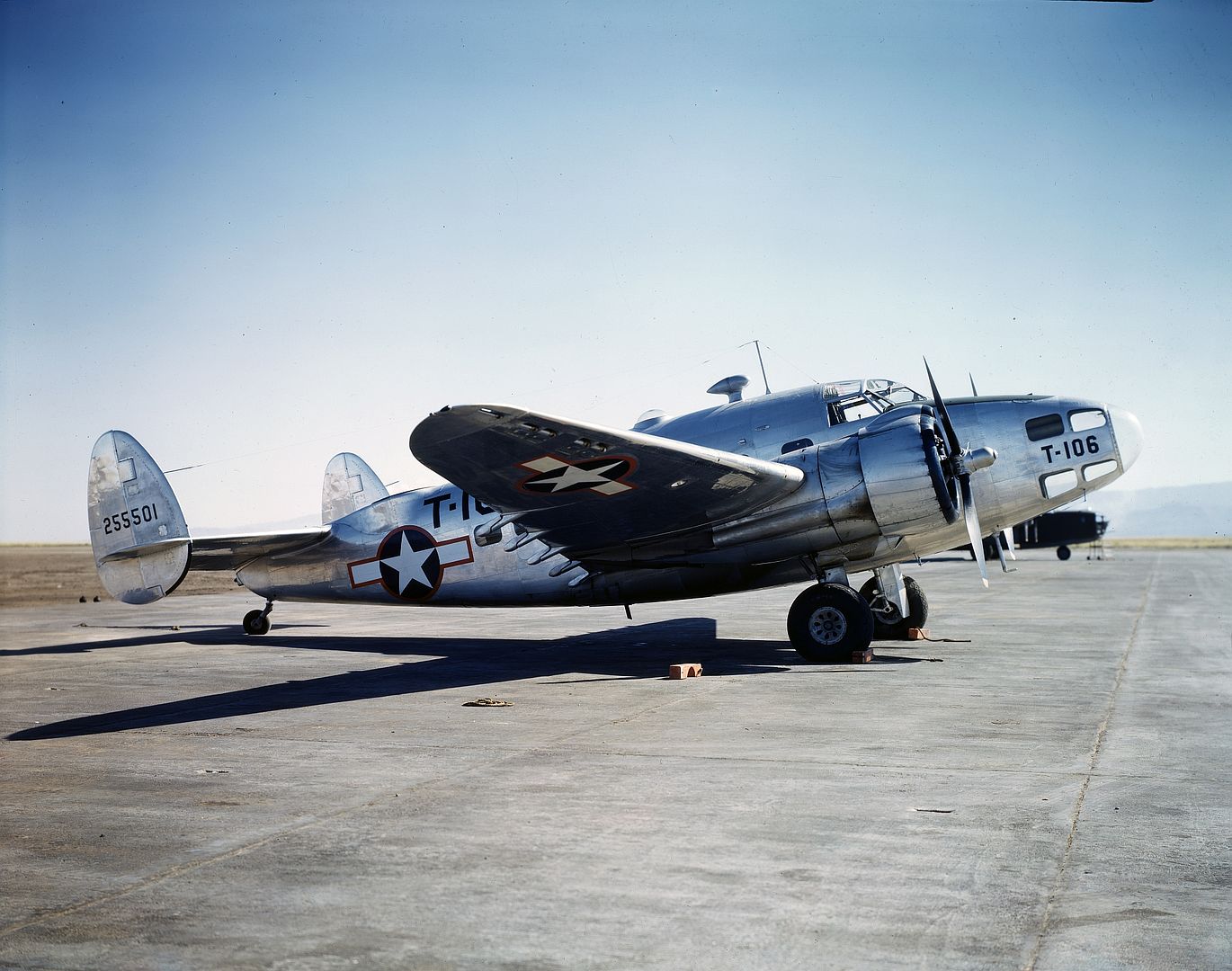








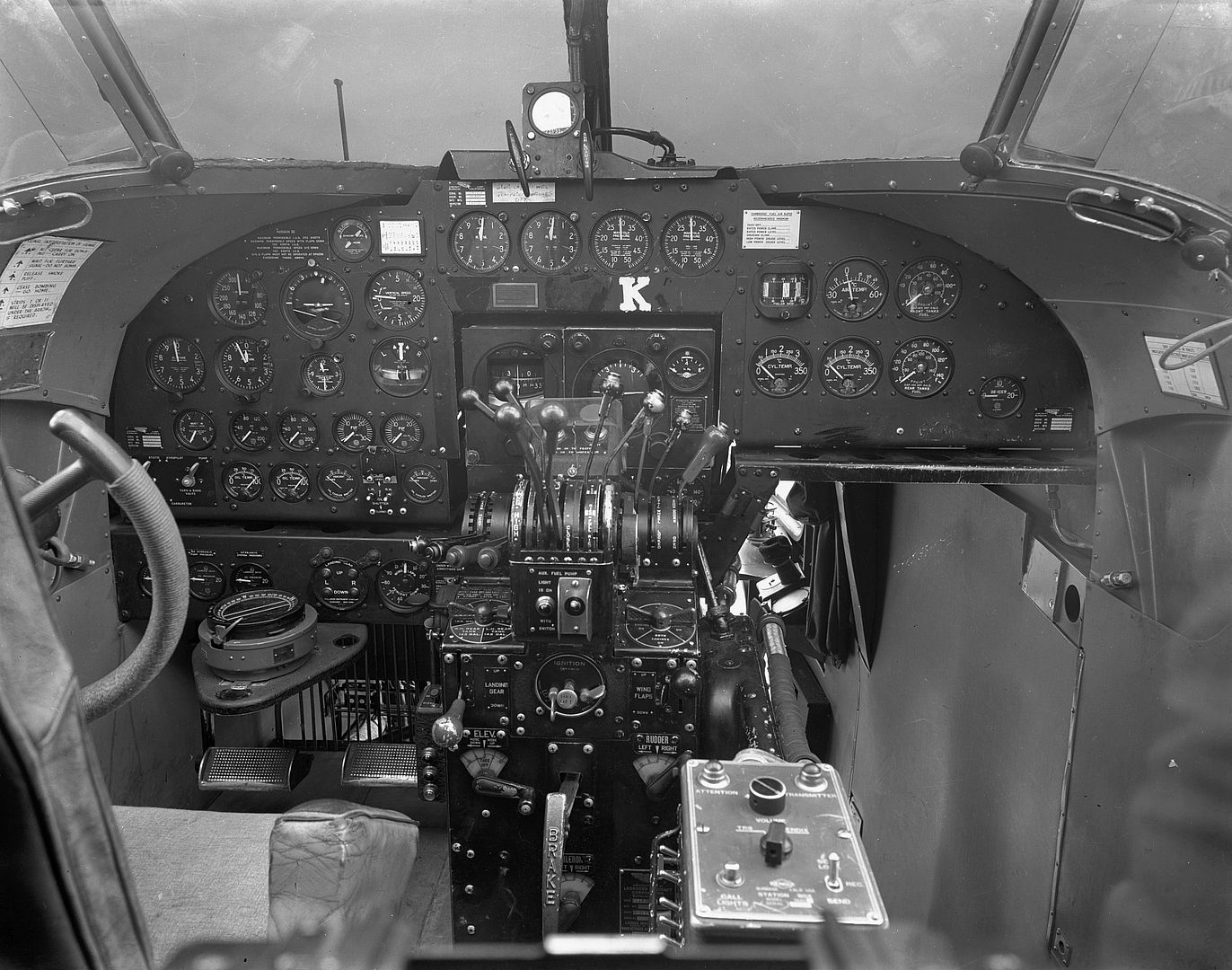
Specifications (Hudson Mk I)
General characteristics
Crew: Five
Length: 44 ft 4 in (13.51 m)
Wingspan: 65 ft 6 in (19.96 m)
Height: 11 ft 10 in (3.61 m)
Wing area: 551 sq ft (51.2 m2)
Empty weight: 11,630 lb (5,275 kg)
Gross weight: 17,500 lb (7,938 kg)
Powerplant: 2 ? Wright GR-1820-G102A Cyclone 9-cylinder radial engines, 1,100 hp (820 kW) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 246 mph (396 km/h, 214 kn) at 6,500 ft (2,000 m)
Cruise speed: 220 mph (350 km/h, 190 kn)
Range: 1,960 mi (3,150 km, 1,700 nmi)
Service ceiling: 25,000 ft (7,600 m)
Rate of climb: 2,180 ft/min (11.1 m/s)
Armament
Guns:
2 ? .303 in (7.7 mm) Browning machine guns in dorsal turret
2? .303 Browning machine guns in nose
Bombs: 1,400 lb (640 kg) of bombs or depth charges -
 AdminGreat thread as always Duggy
AdminGreat thread as always Duggy
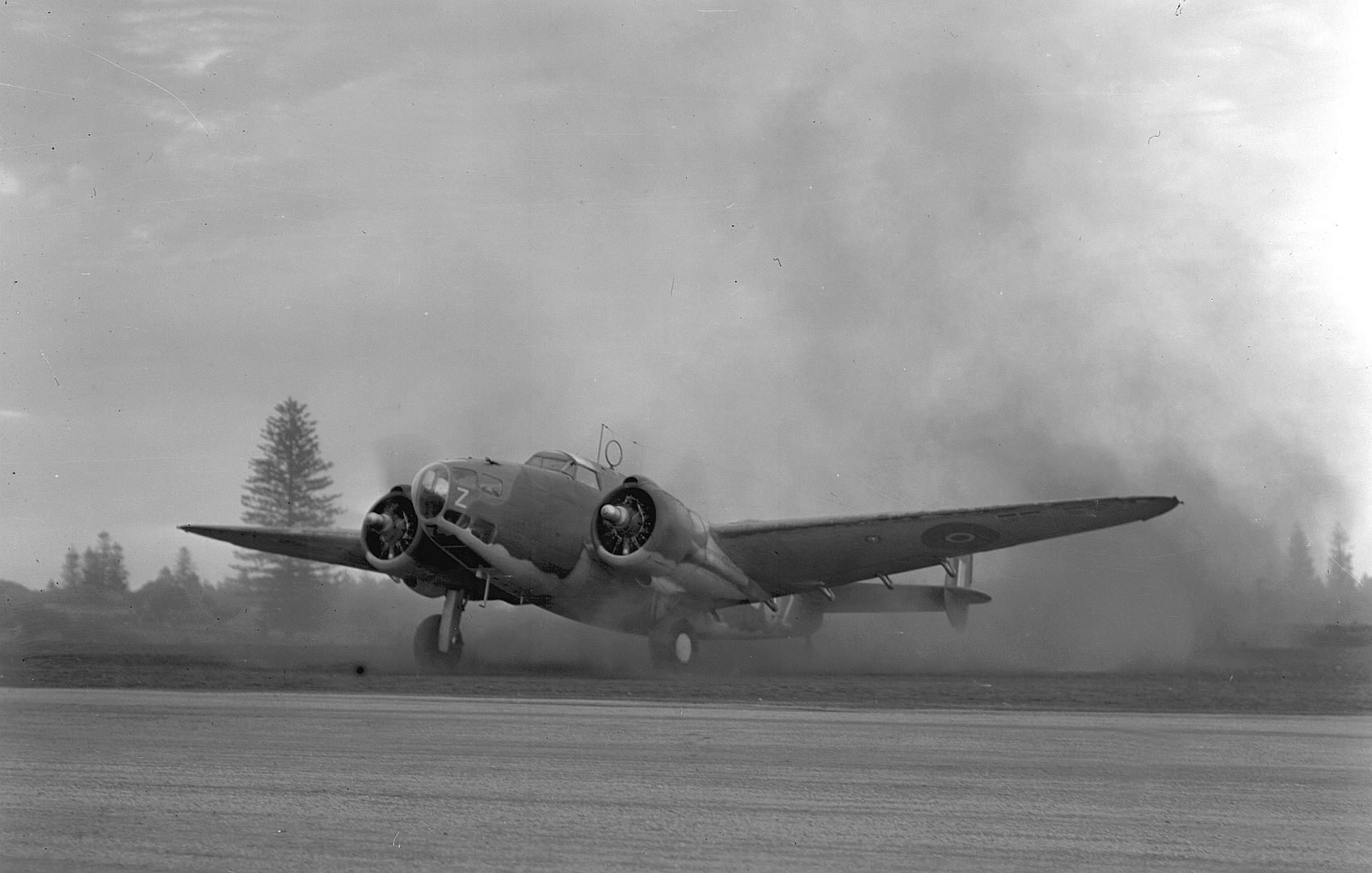
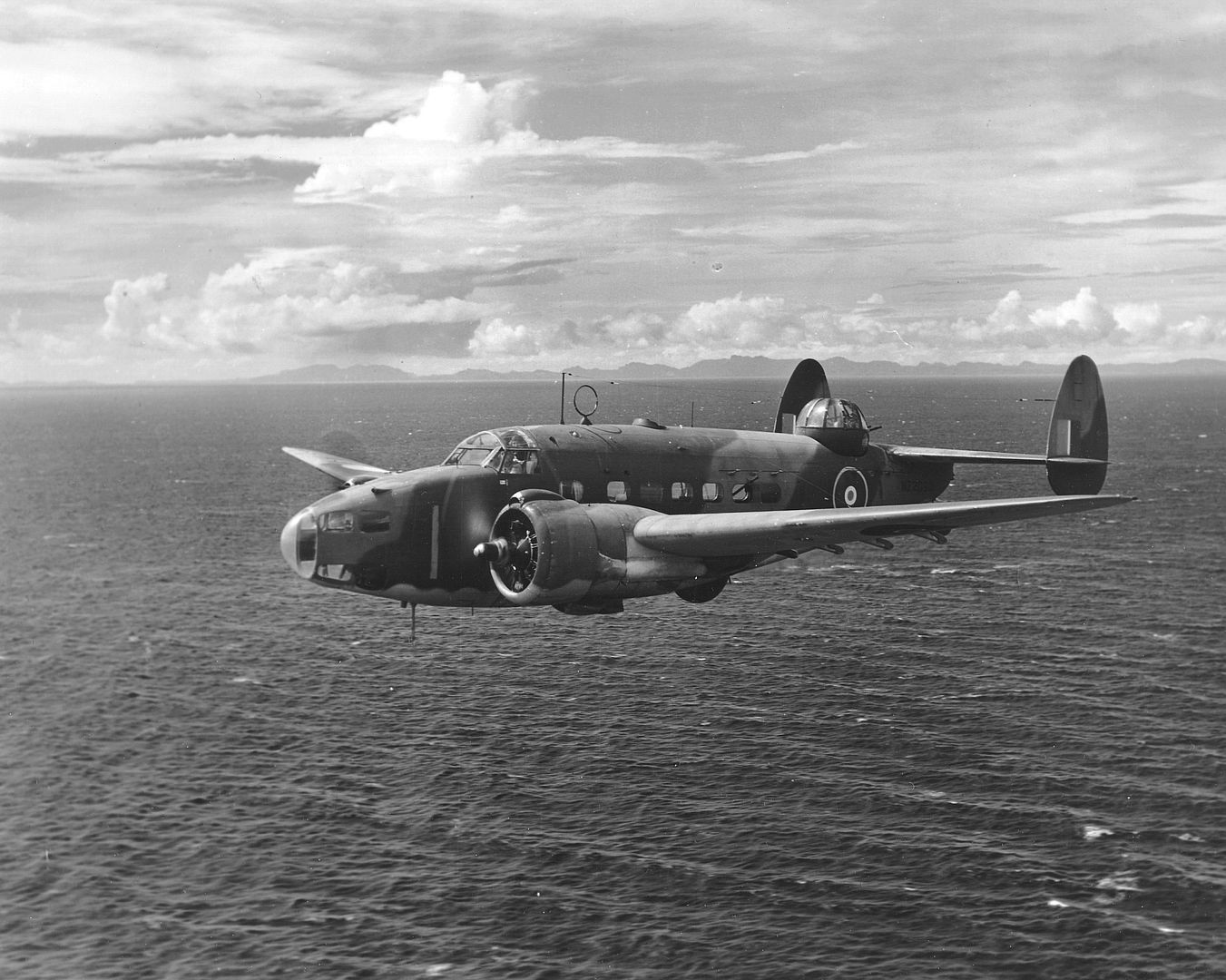
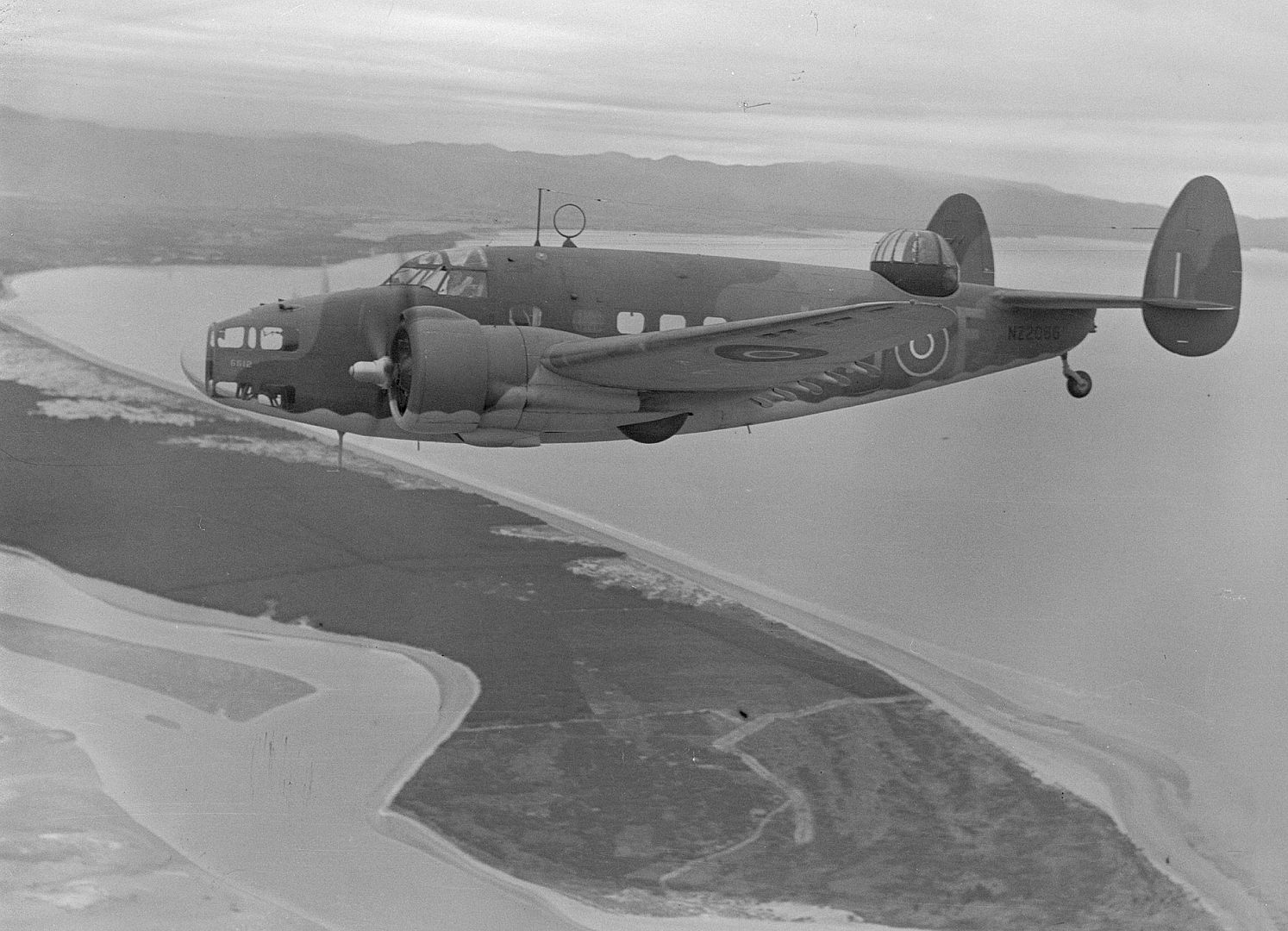
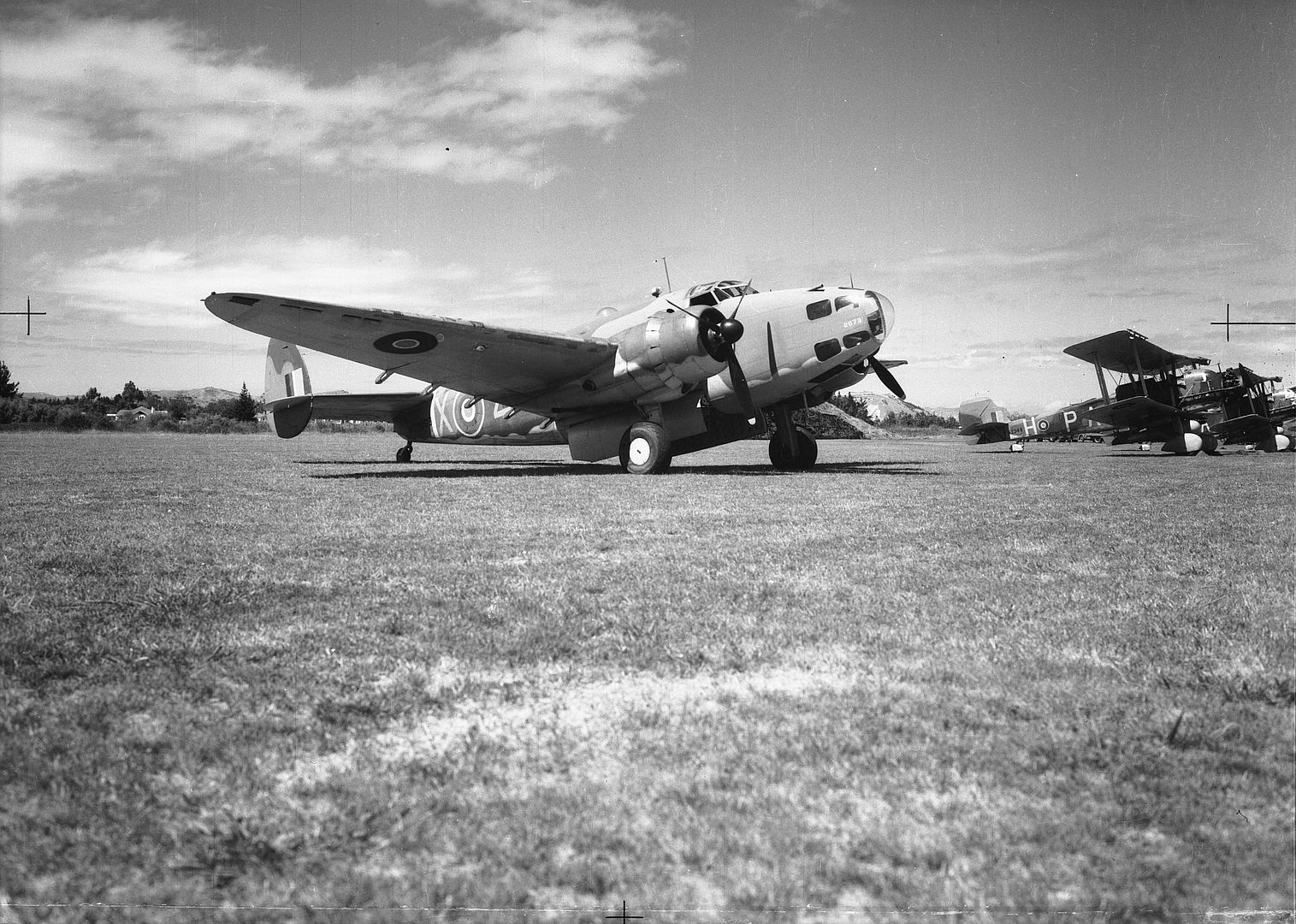
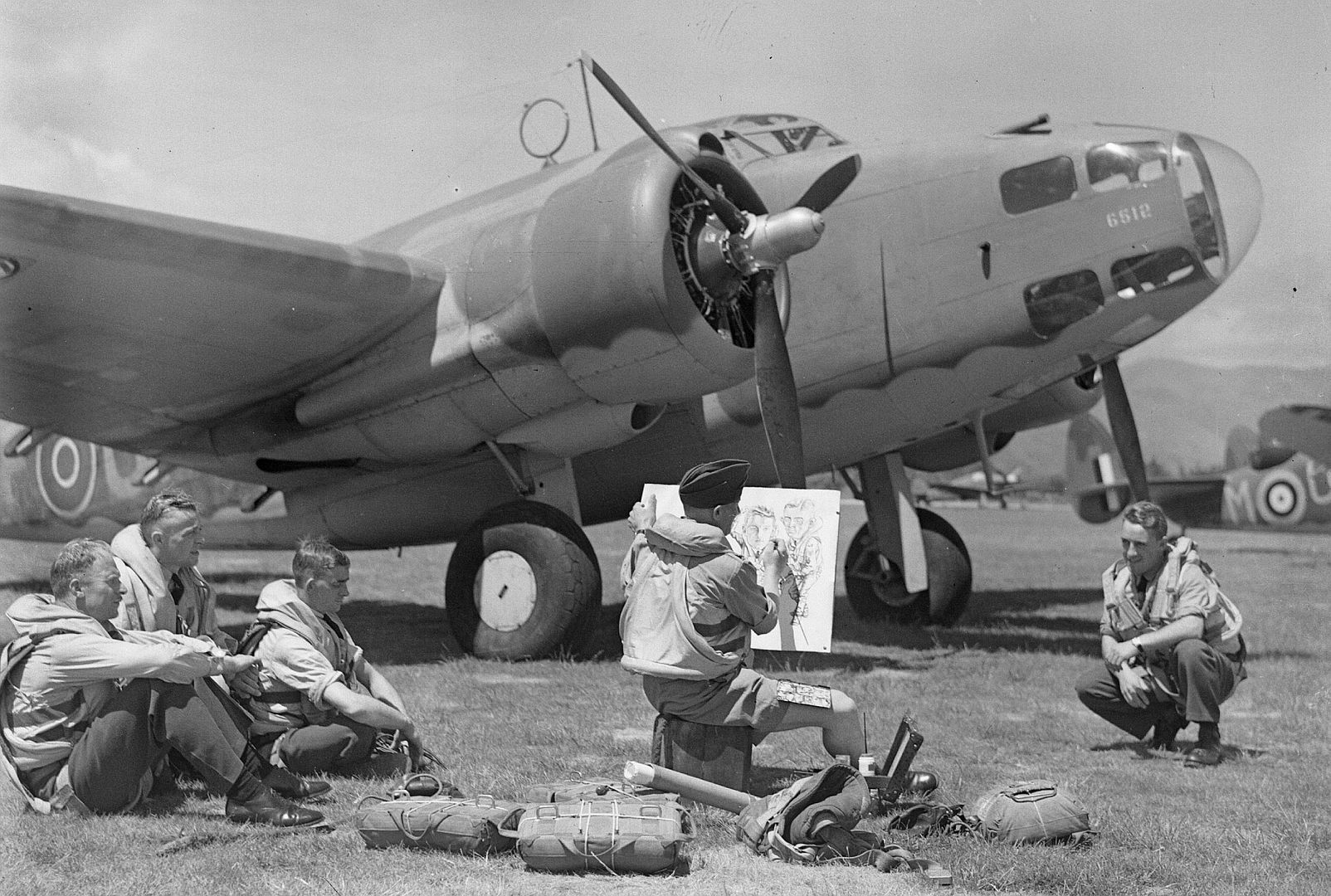
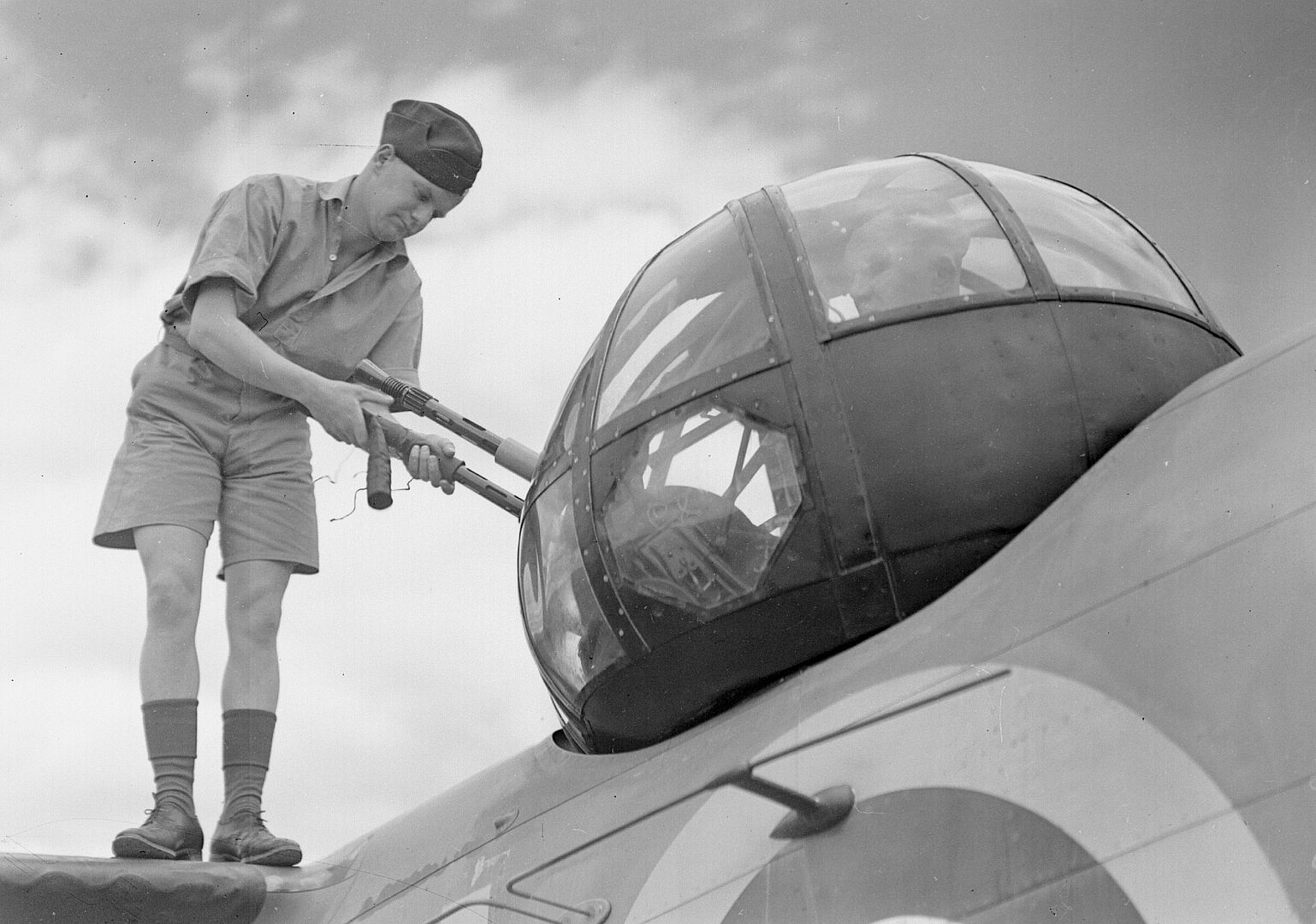
As a little bit of history, the Hudson in this photo (NZ2090) scored the RNZAF's* first air-to-air victory on 2 April 1943 when it shot down a F1M Pete float plane, we can just see the kill marking underneath the cockpit. IIRC they were patrolling The Slot and when they flew out of a cloud they found themselves behind the Pete, so they caught up to the Japanese aircraft (whose crew didn't appear to be keeping a look out) and the pilot shot it down with the two fixed .50cals in the nose.
*by that I mean the RNZAF as it's own independent force so not counting RNZAF personal and Article XV squadrons in the RAF.
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
