Forums
- Forums
- Duggy's Reference Hangar
- Luftwaffe Library
- Dornier Do 335
Dornier Do 335
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
-
4 years agoSun May 19 2024, 11:20amDuggy
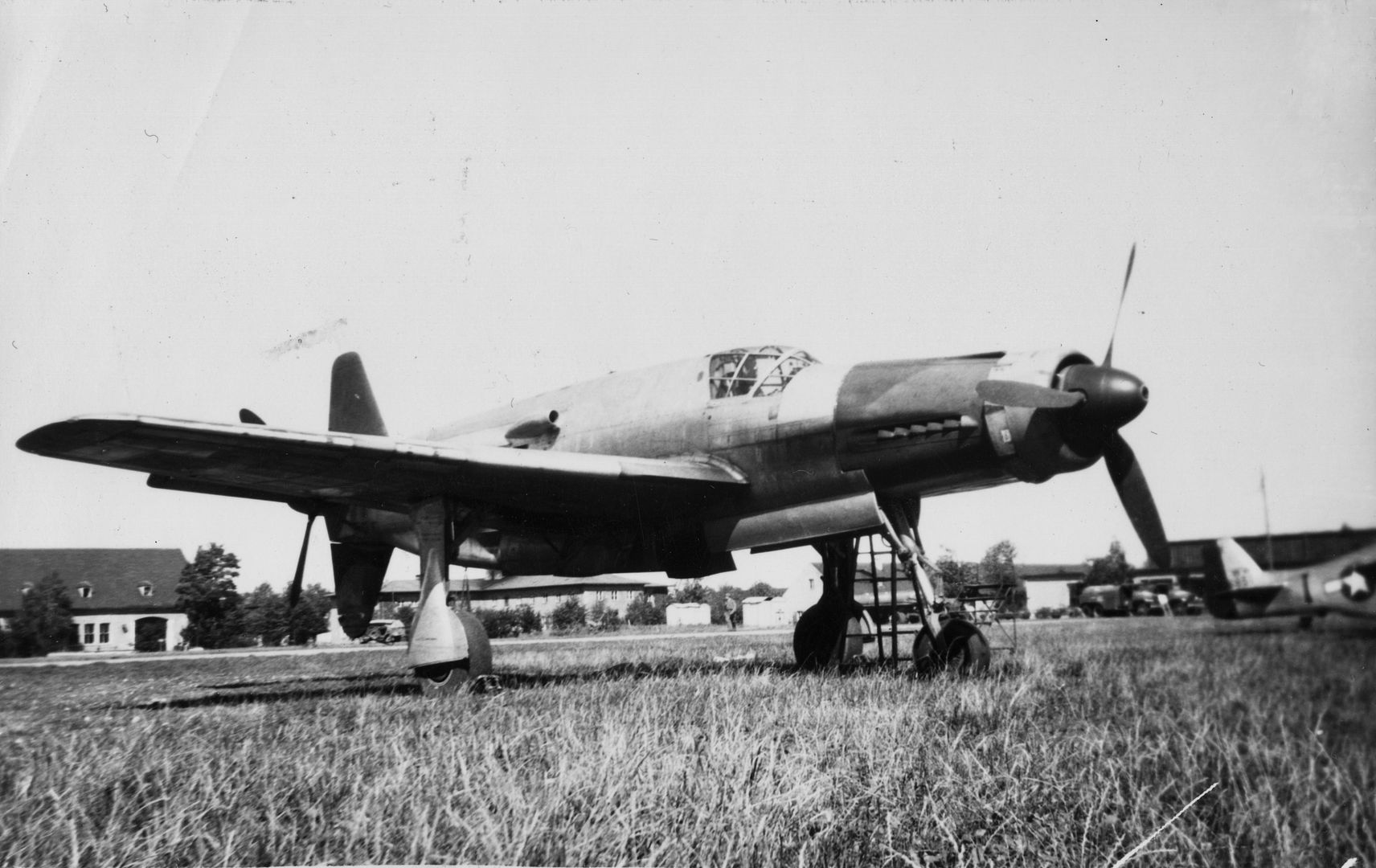
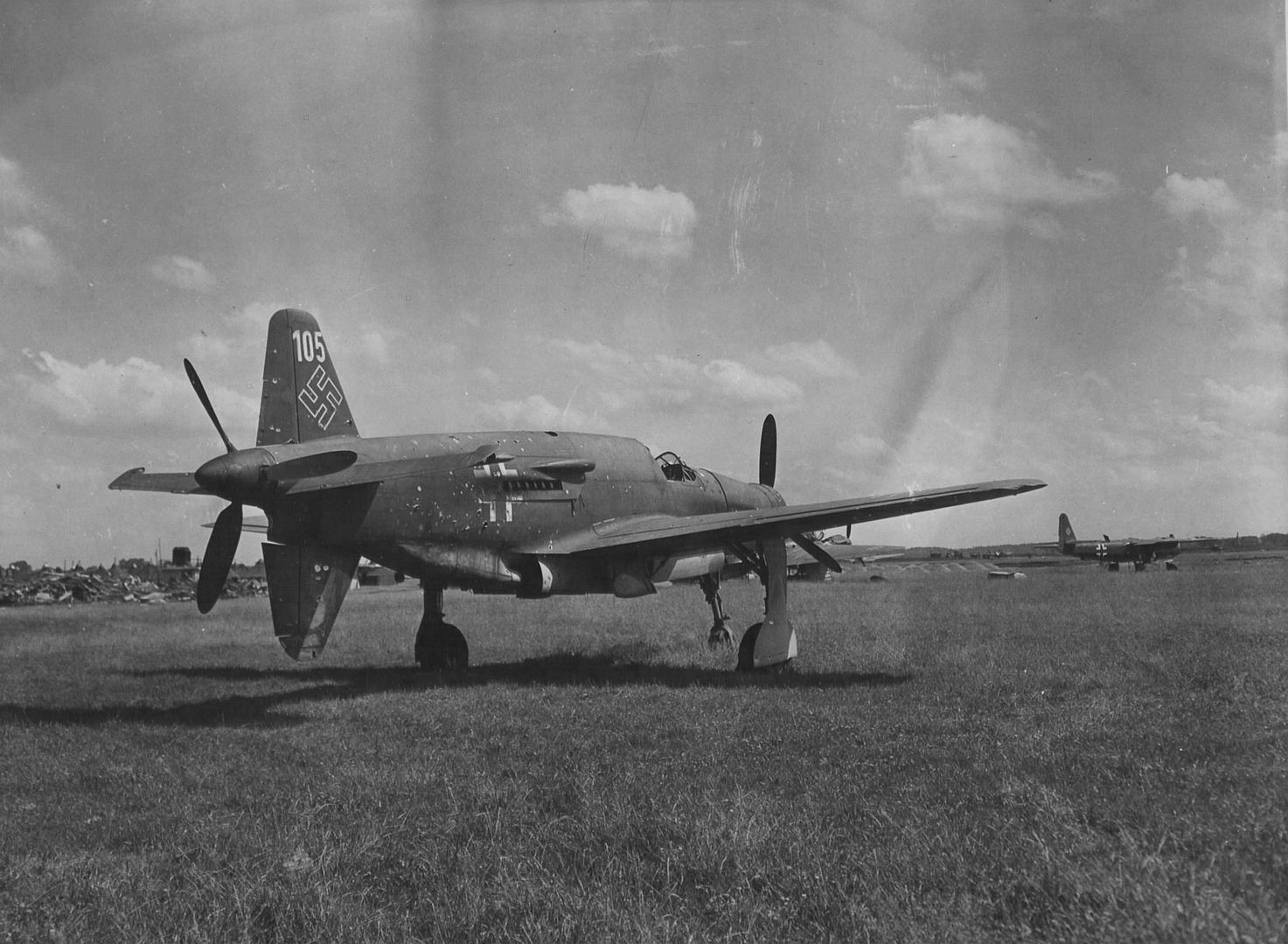
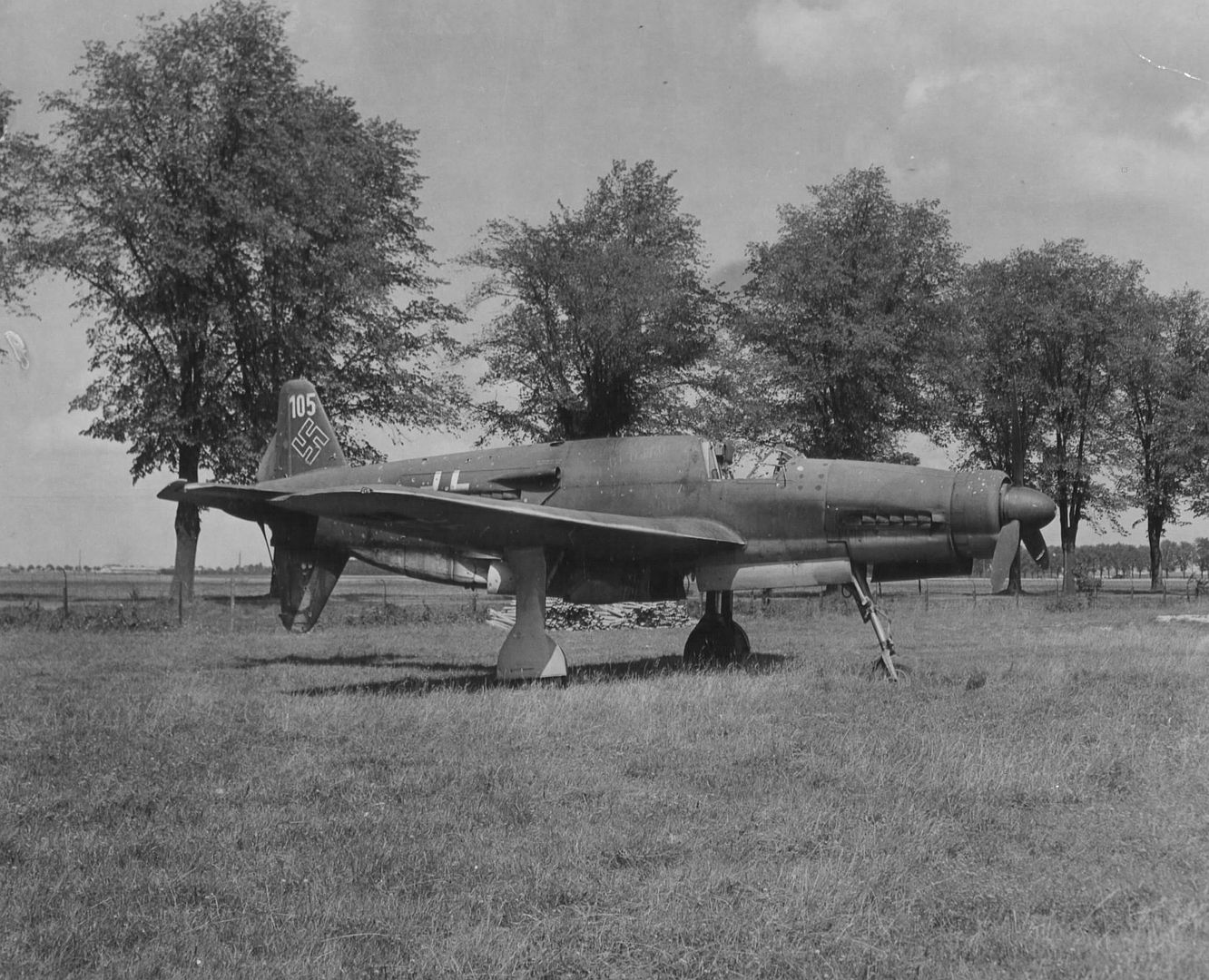
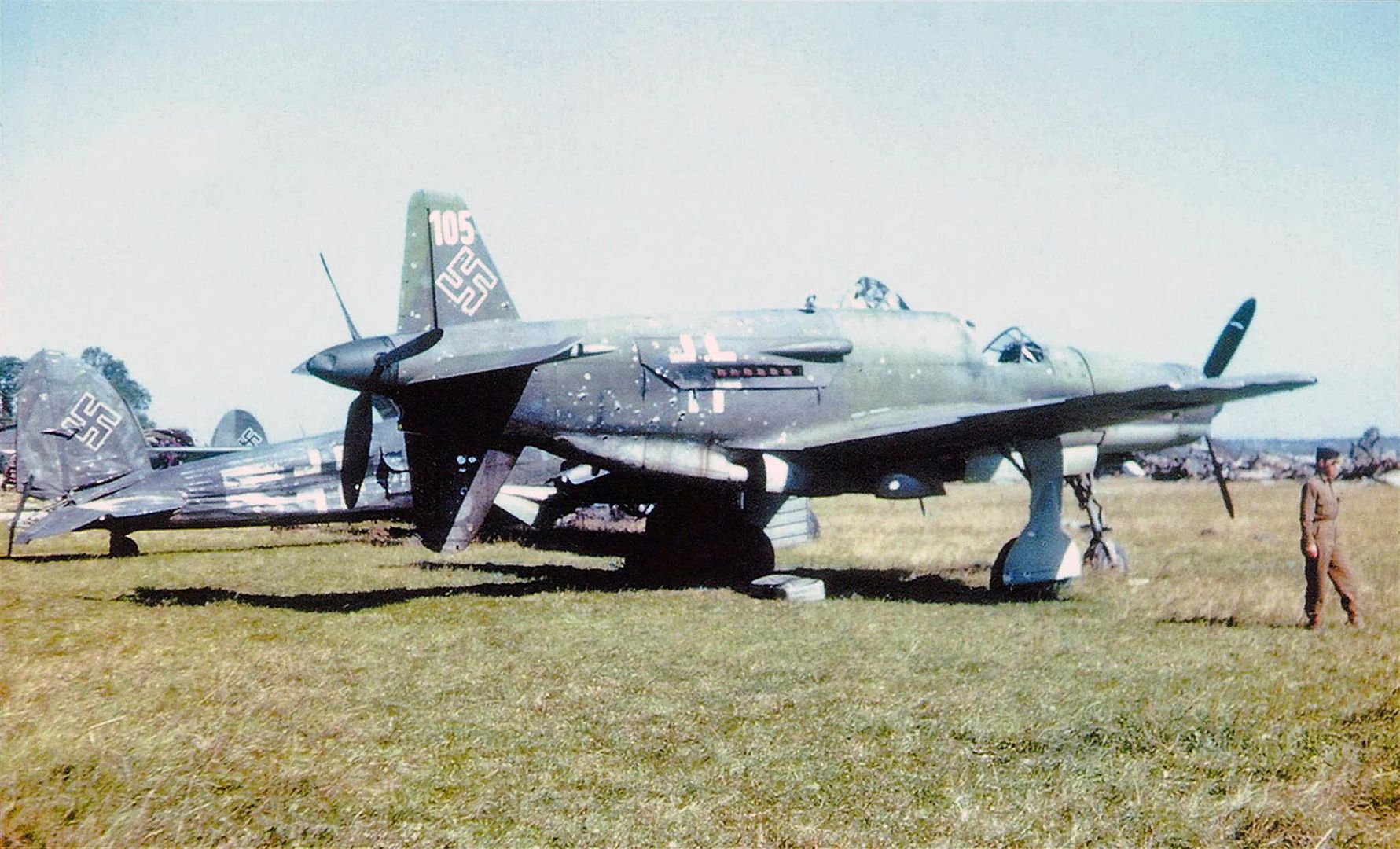
 Main AdminThe Dornier Do 335 Pfeil ("Arrow") was a Nazi Germany World War II heavy fighter built by the Dornier company. The two-seater trainer version was called Ameisenbär ("anteater"). The Pfeil's performance was much better than other twin-engine designs due to its unique push-pull configuration and the lower aerodynamic drag of the in-line alignment of the two engines. It was Nazi Germany's fastest piston-engined aircraft of World War II. The Luftwaffe was desperate to get the design into operational use, but delays in engine deliveries meant that only a handful were delivered before the war ended.
Main AdminThe Dornier Do 335 Pfeil ("Arrow") was a Nazi Germany World War II heavy fighter built by the Dornier company. The two-seater trainer version was called Ameisenbär ("anteater"). The Pfeil's performance was much better than other twin-engine designs due to its unique push-pull configuration and the lower aerodynamic drag of the in-line alignment of the two engines. It was Nazi Germany's fastest piston-engined aircraft of World War II. The Luftwaffe was desperate to get the design into operational use, but delays in engine deliveries meant that only a handful were delivered before the war ended.
Design and development
The origins of the Do 335 trace back to World War I when Claude Dornier designed a number of flying boats featuring remotely driven propellers and later, due to problems with the drive shafts, tandem engines. Tandem engines were used on most of the multi-engine Dornier flying boats that followed, including the highly successful Do J Wal and the gigantic Do X. The remote propeller drive, intended to eliminate parasitic drag from the engine entirely, was tried in the innovative but unsuccessful Do 14, and elongated, tubular drive shafts as later used in the Do 335 saw use in the rear engines of the four-engined, twinned tandem-layout Do 26 flying boat.
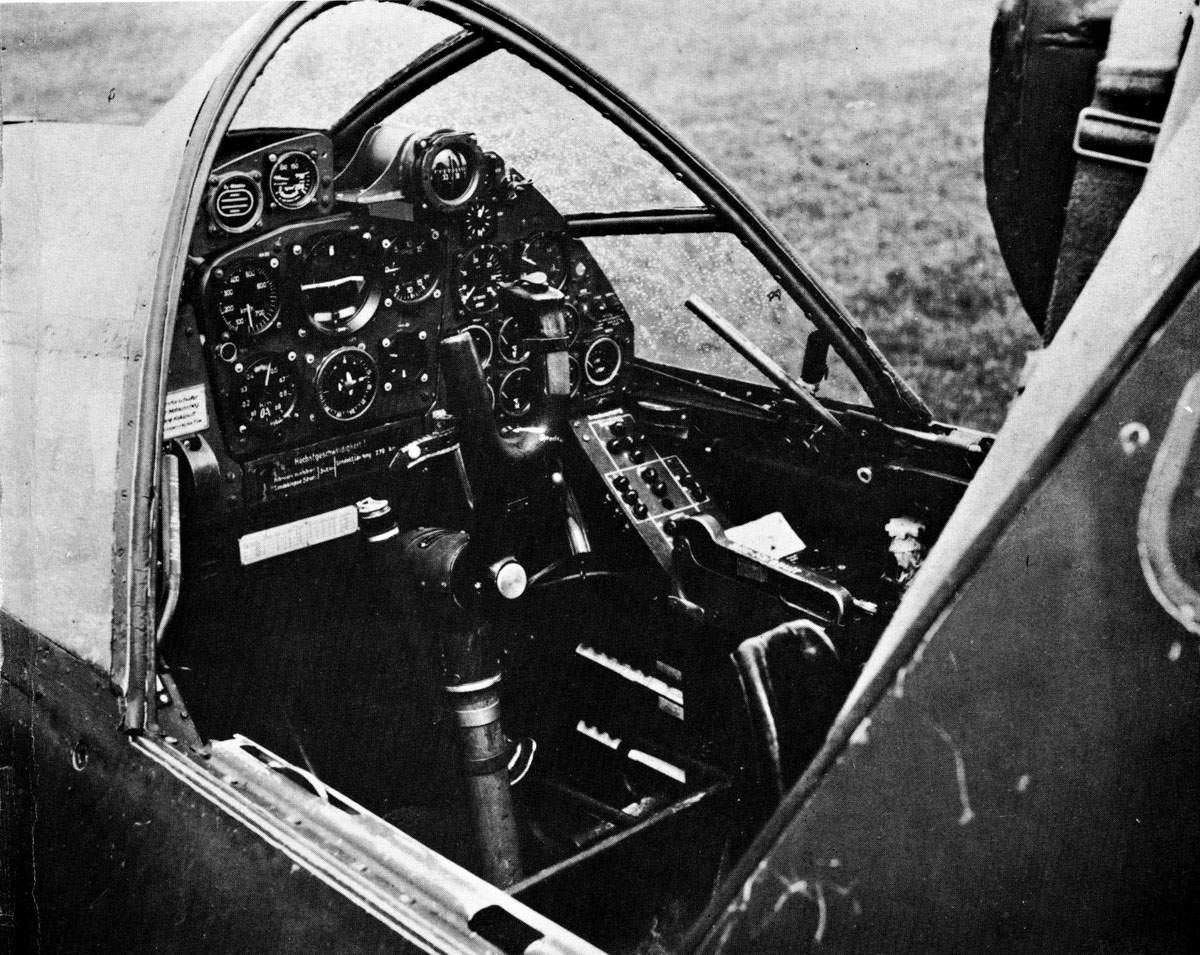
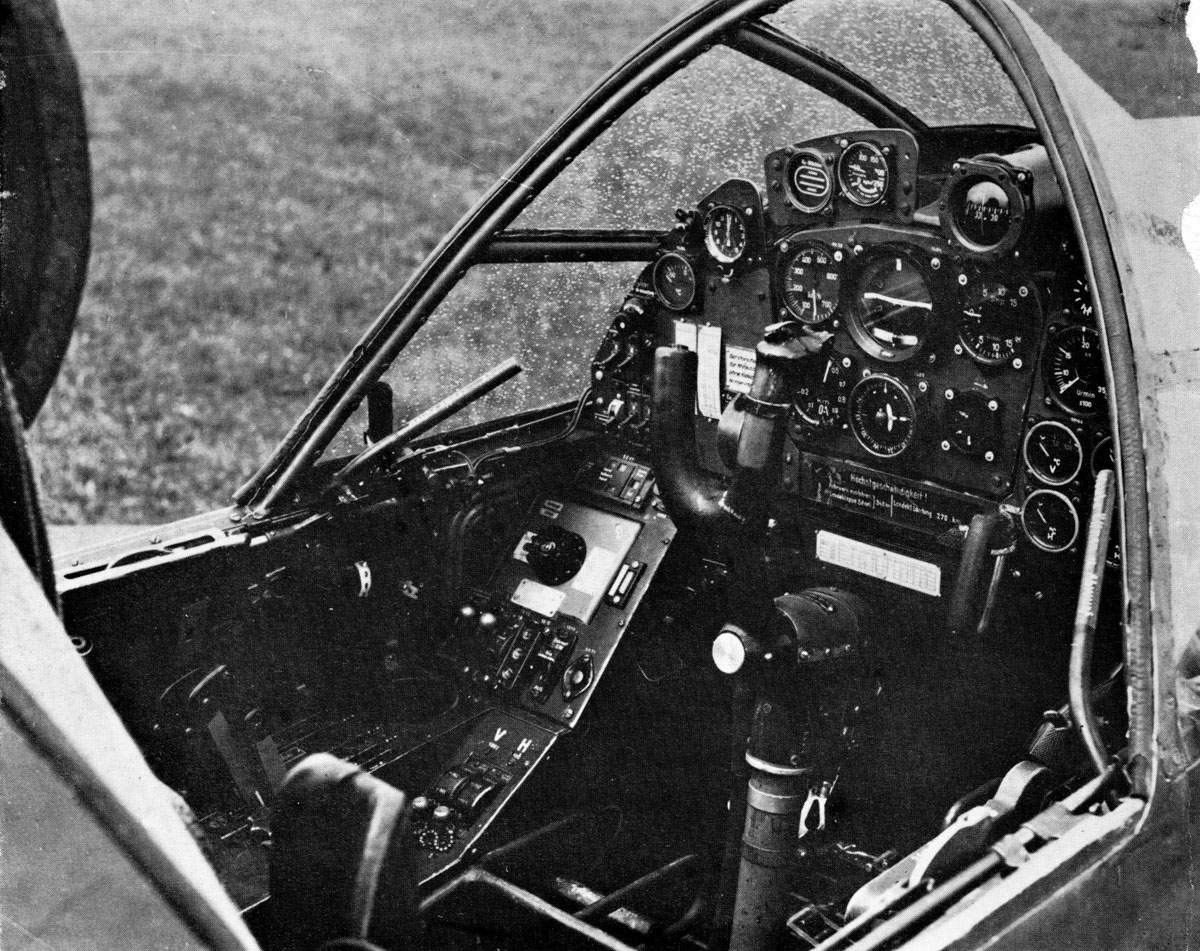
There are many advantages to this design over the more traditional system of placing one engine on each wing, the most important being power from two engines with the frontal area (and thus drag) of a single-engine design, allowing for higher performance. It also keeps the weight of the twin powerplants near, or on, the aircraft centerline, increasing the roll rate compared to a traditional twin. In addition, a single engine failure does not lead to asymmetric thrust, and in normal flight there is no net torque, so the plane is easy to handle. The four-surface set of cruciform tail surfaces in the Do 335's rear fuselage design included a ventral vertical fin–rudder assembly that projected downwards from the extreme rear of the fuselage, to protect the rear propeller from an accidental ground strike on takeoff. The presence of the rear pusher propeller also mandated the provision for an ejection seat for safe escape from a damaged aircraft, and designing the rear propeller and dorsal fin mounts to use explosive bolts to jettison them before an ejection was attempted – as well as twin canopy jettison levers, one per side located to either side of the forward cockpit interior just below the sills of the five-panel windscreen's sides, to jettison the canopy from atop the cockpit before ejection.
In 1939, Dornier was busy working on the P.59 high-speed bomber project, which featured the tandem engine layout. In 1940, he commissioned a test aircraft, closely modeled on the airframe of the early versions of the Dornier Do 17 bomber but only 40% of the size of the larger bomber, with no aerodynamic bodies of any sort on the wing panels (the original Do 17 had twin engine nacelles on its wings) and fitted with a retractable tricycle landing gear to validate his concept for turning the rear pusher propeller with an engine located far away from it, through the use of a long tubular driveshaft. This aircraft, the Göppingen Gö 9, showed no unforeseen difficulties with this arrangement, but work on the P.59 was stopped in early 1940 when Hermann Göring ordered the cancellation of all projects that would not be completed within a year or so.
In May 1942, Dornier submitted an updated version with a 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombload as the P.231, in response to a requirement for a single seat, Schnellbomber-like high-speed bomber/intruder. The P.231 proposal was selected as the winner after beating rival designs from Arado, Junkers, and Blohm & Voss. A development contract was awarded, by the RLM issuing the Dornier firm the airframe approval number 8-335, for what would become known as the Do 335. In autumn 1942, Dornier was told that the Do 335 was no longer required, and instead a multi-role fighter based on the same general layout would be accepted. This delayed the prototype delivery as it was modified for the new role.
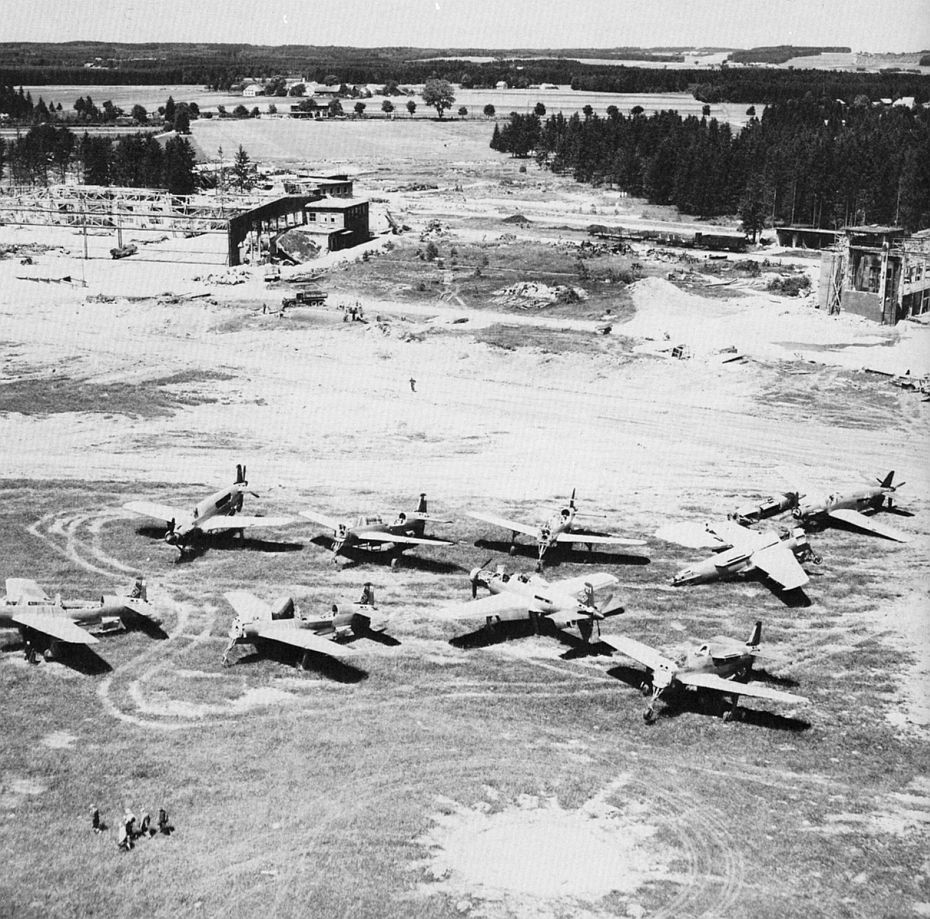
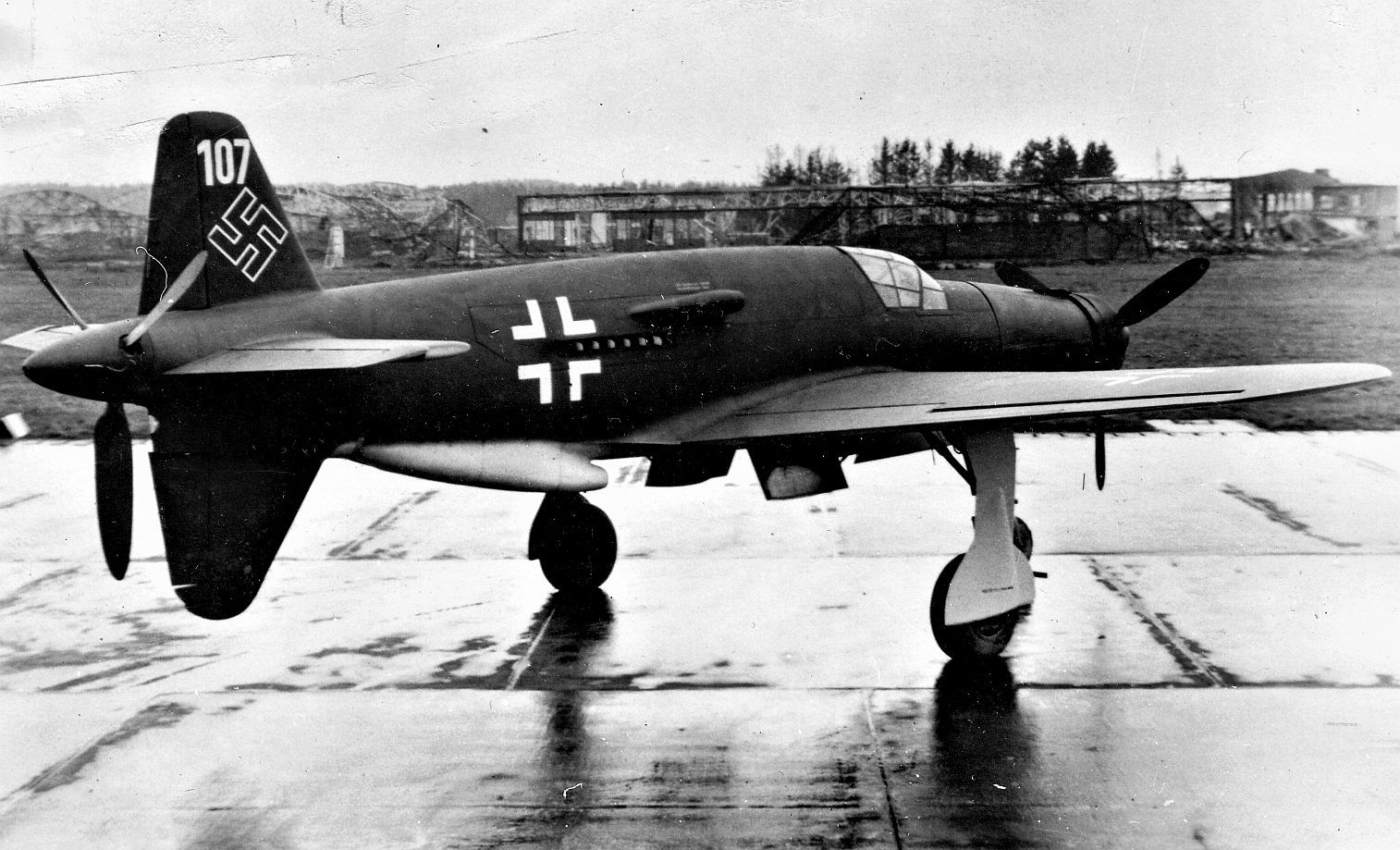
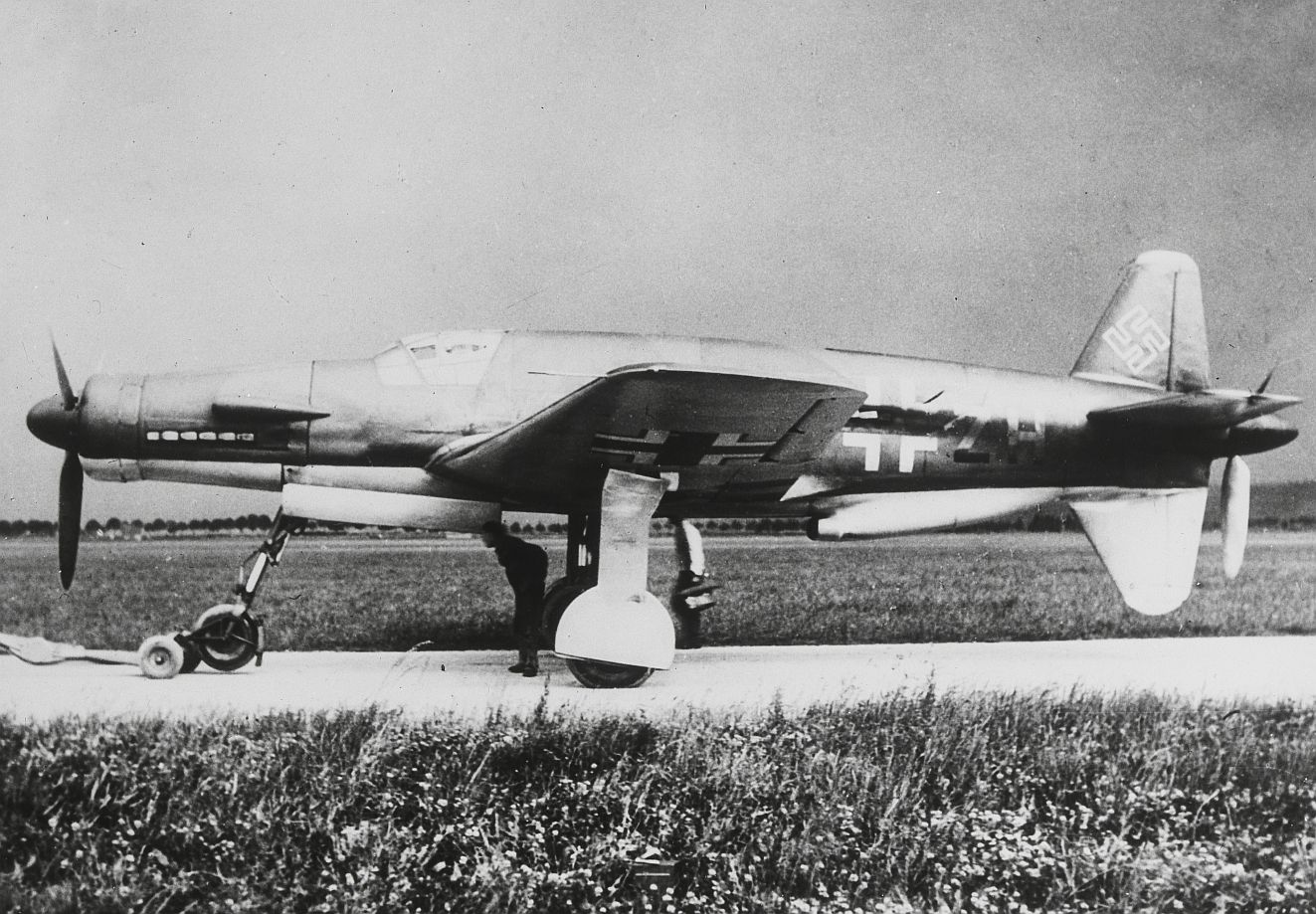
The use of a nose-mount annular radiator for the forward engine (much like a Jumo 211-powered Ju 88, or Jumo 213-powered Focke-Wulf Fw 190D-9) and a ventral-fuselage mount airscooped radiator installation for cooling the rear engine was distinctive. When fitted with DB 603A engines delivering 1,750 PS (1,287 kW, 1,726 hp) at takeoff it had a pair of the largest displacement -44.52 litres - inverted V12 aircraft engine design mass-produced during the Third Reich's existence. The Do 335 V1 first prototype, bearing the Stammkennzeichen (factory radio code) of CP+UA, flew on 26 October 1943 under the control of Flugkapitän Hans Dieterle, a regular Heinkel test pilot and later primary Dornier test pilot. However, several problems during the initial flight of the Do 335 would continue to plague the aircraft through most of its short history. Issues were found with the weak landing gear and with the main gear's wheel well doors, resulting in them being removed for the remainder of the V1's test flights. The Do 335 V1 made 27 flights, flown by three different pilots. During these test flights the second prototype, V2 (Werk Nr 230002) CP+UB, was completed and made its first flight on 31 December 1943, again under the control of Dieterle. New to the V2 were upgraded DB 603A-2 engines, and several refinements learned from the test flights of the V1 as well as further windtunnel testing. On 20 January 1944, the Do 335 V3 (W.Nr. 230004), CP+UC was completed and flown for its first time by Werner Altrogge. The V3 was powered by the new pre-production DB 603G-0 engines which could produce 1,900 PS (1,400 kW) at take-off and featured a slightly redesigned canopy which included twin rear-view mirrors in blisters, one in each of two matching side panels of the well-framed, eleven-panel main canopy's openable section. Following the flights of the V3, in mid January 1944, RLM ordered five more prototypes (V21–V25), to be built as night fighters. By this time, more than 60 hours of flight time had been put on the Do 335 and reports showed it to be a good handling, but more importantly, very fast aircraft, described by Generalfeldmarschall Erhard Milch himself as "...holding its own in speed and altitude with the P-38 and it does not suffer from engine reliability issues". The Do 335 was scheduled to begin mass construction, with the initial order of 120 preproduction aircraft to be manufactured by Dornier-Werke Friedrichshafen (DWF) to be completed no later than March 1946. This number included a number of bombers, destroyers (heavy fighters), and several yet to be developed variants. At the same time, Dornier-Werke München (DWM) was scheduled to build over 2,000 Do 335s in various models, due for delivery in March 1946 as well.
On 23 May 1944, Hitler, as part of the developing Jägernotprogramm (Emergency Fighter Program) directive, which took effect on 3 July, ordered maximum priority to be given to Do 335 production. The main production line was intended to be at Manzell, but a bombing raid in March destroyed the tooling and forced Dornier to set up a new line at Oberpfaffenhofen. The decision was made, along with the rapid shut-down of many other military aircraft development programs, to cancel the Heinkel He 219 night fighter, which also used the DB 603 engines (in well-unitized installations), and use its production facilities for the Do 335 as well. However, Ernst Heinkel managed to delay, and eventually ignore, its implementation, continuing to produce examples of the He 219A.
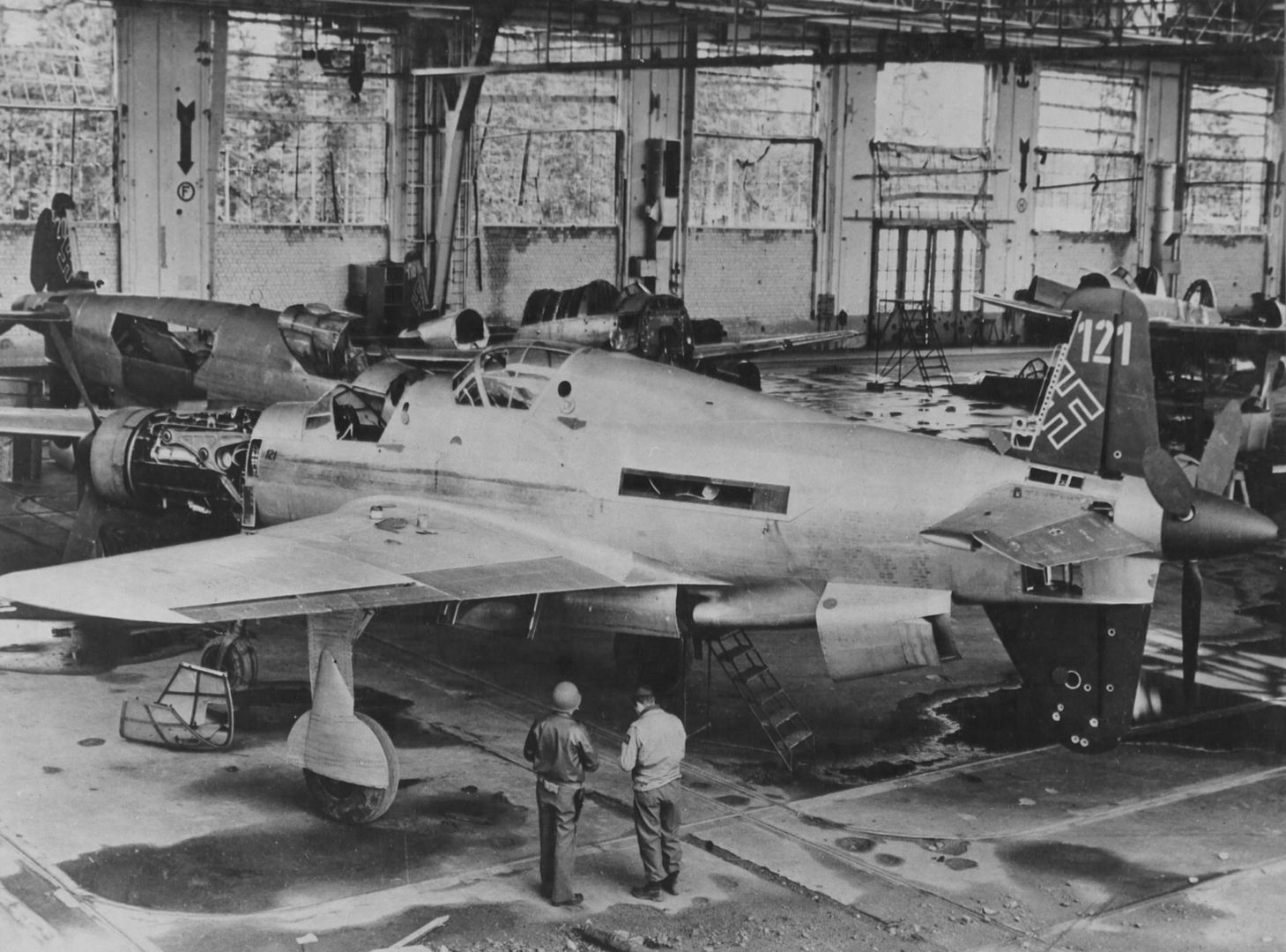
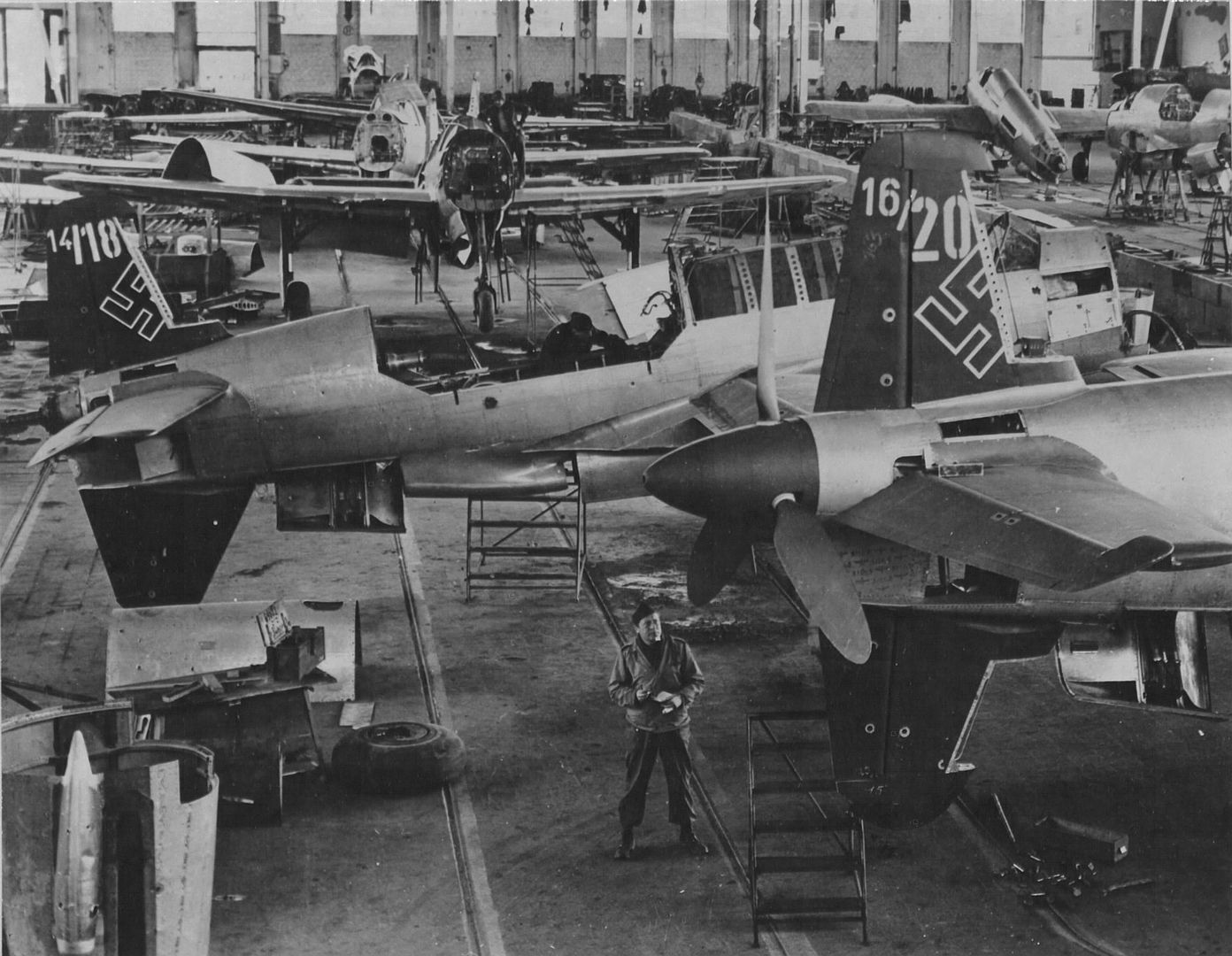
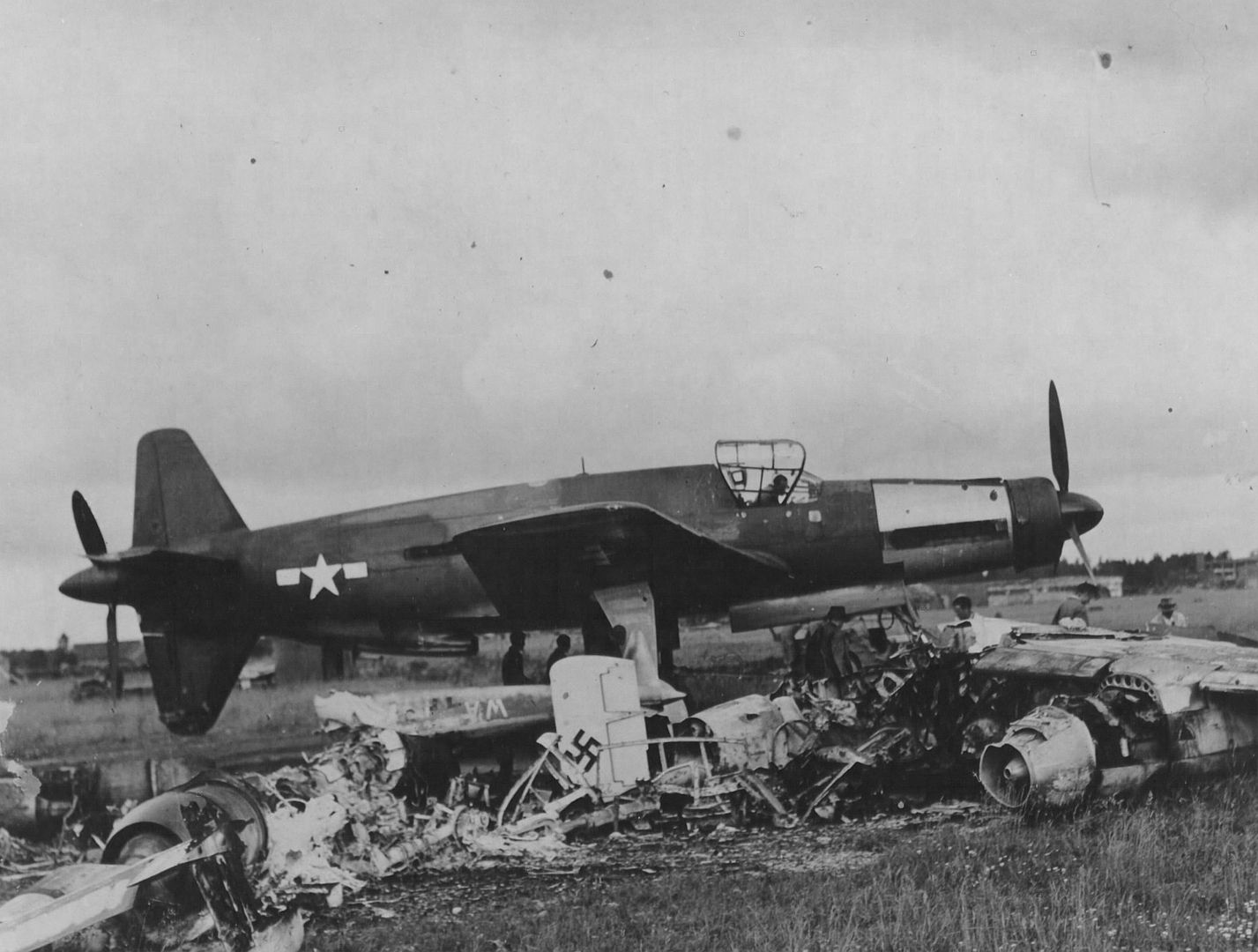
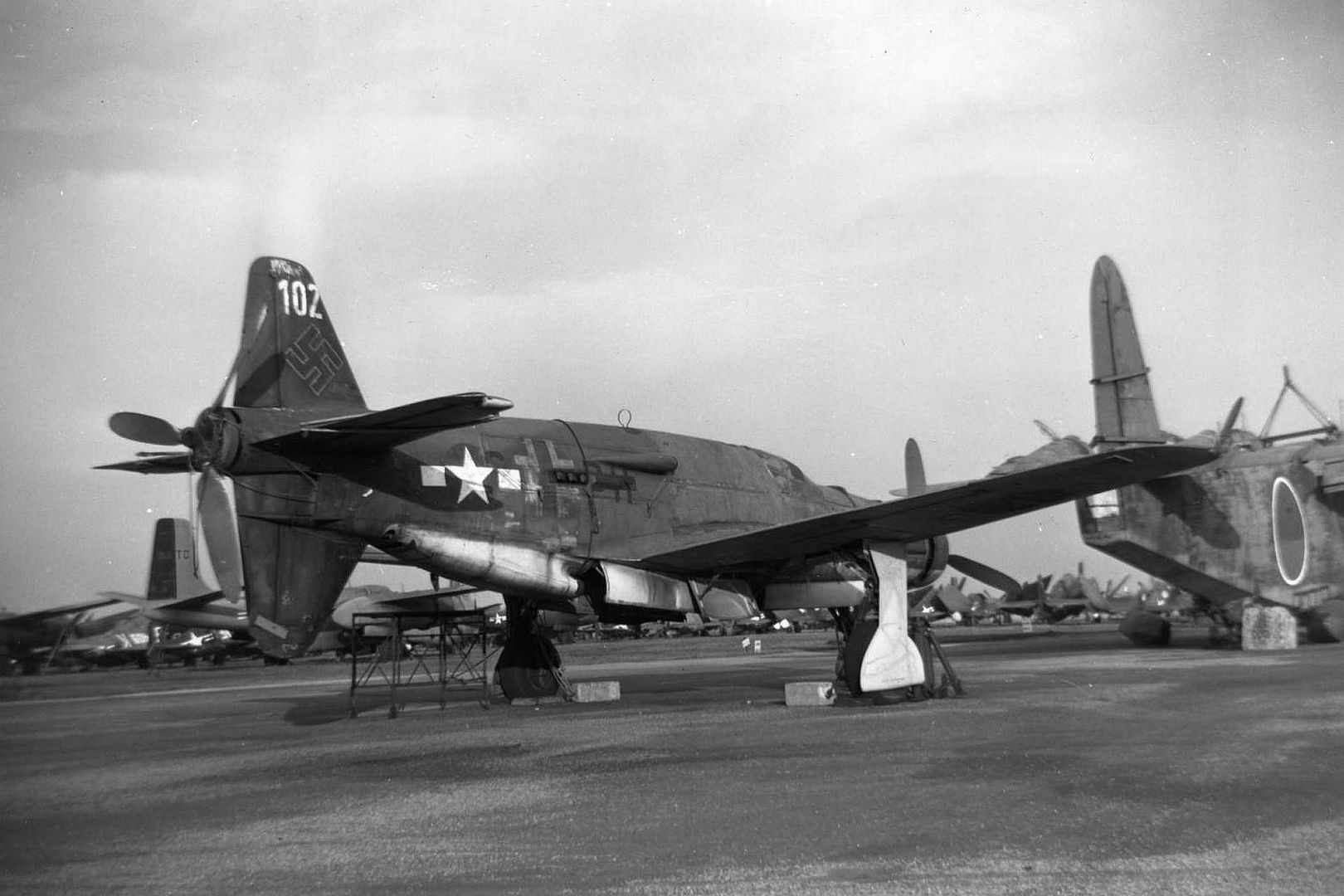
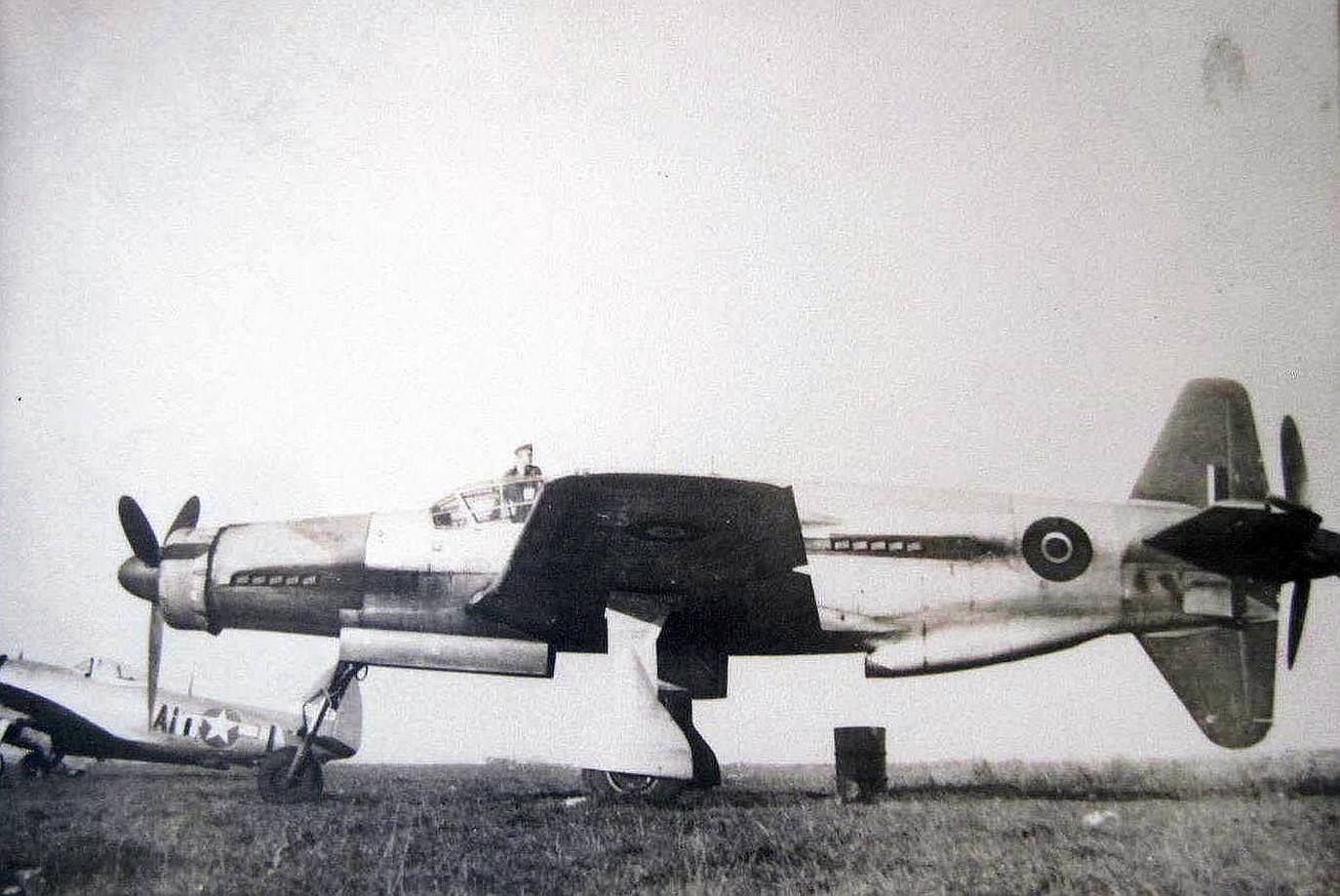
At least 16 prototype Do 335s were known to have flown (V1–V12, W.Nr 230001-230012 and Muster-series prototypes M13–M17, W.Nr 230013-230017) on a number of DB603 engine subtypes including the DB 603A, A-2, G-0, E and E-1. The first preproduction Do 335 (A-0s) starting with W.Nr 240101, Stammkennzeichen VG+PG, were delivered in July 1944. Approximately 22 preproduction aircraft were thought to have been completed and flown before the end of the war, including approximately 11 A-0s converted to A-11s for training purposes. One such aircraft was transferred to the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough, and later, after a rear-engine fire burnt through the elevator controls during a flight, crashed onto a local school.
Flight tests
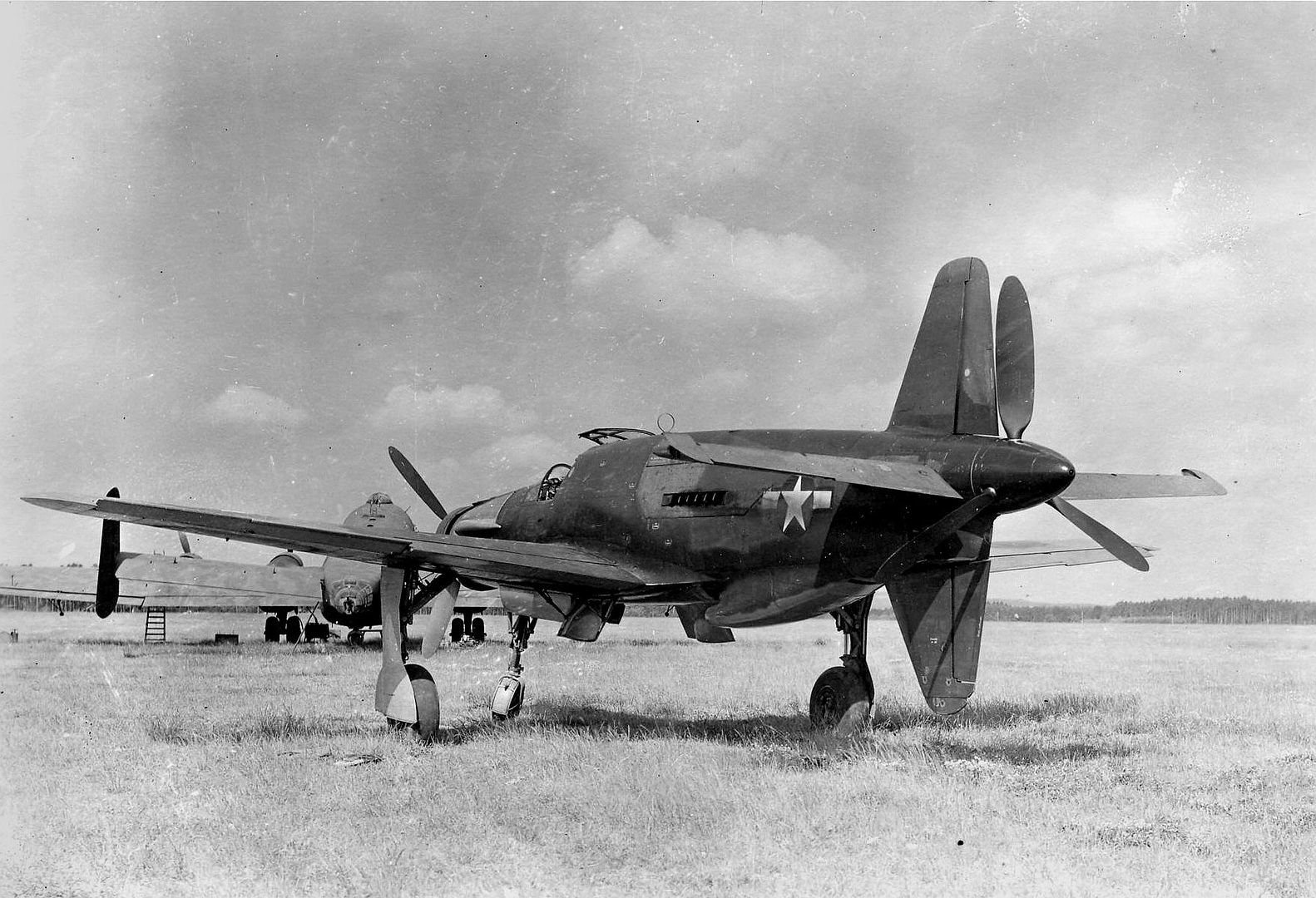
The first 10 Do 335 A-0s were delivered for testing in May. By late 1944, the Do 335 A-1 was on the production line. It was similar to the A-0 but with the uprated DB 603E-1 engines of some 1,324 kW (1,800 PS) take-off power rating apiece on 87 octane "B4" lignite-derived synthetic fuel, and two underwing hardpoints for additional bombs, drop tanks or guns. It had a maximum speed of 763 km/h (474 mph) at 6 500 m (21 300 ft) with MW 50 boost, or 686 km/h (426 mph) without boost, and climbed to 8 000 m (26 250 ft) in under 15 minutes. Even with one engine out, it reached about 563 km/h (350 mph)
Delivery commenced in January 1945. When the United States Army overran the Oberpfaffenhofen factory in late April 1945, only 11 Do 335 A-1 single-seat fighter-bombers and two Do 335 A-12 trainers had been completed.
French ace Pierre Clostermann claimed the first Allied combat encounter with a Pfeil in April 1945. He describes leading a flight of four Hawker Tempests from No. 3 Squadron RAF over northern Germany, when they came across an unknown aircraft flying at maximum speed at treetop level. Detecting the British aircraft, the German pilot reversed course to evade. Two pilots fired on the Dornier but Clostermann, despite the Tempests' considerable low altitude speed, decided not to attempt to chase it as it was obviously much faster.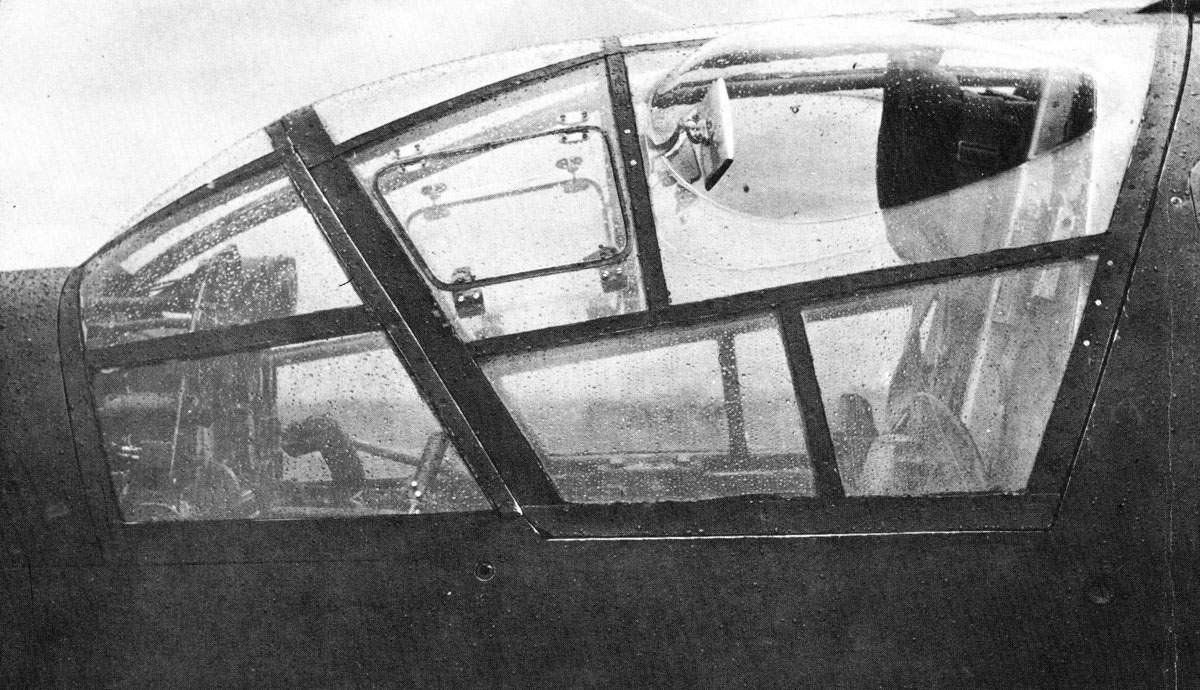
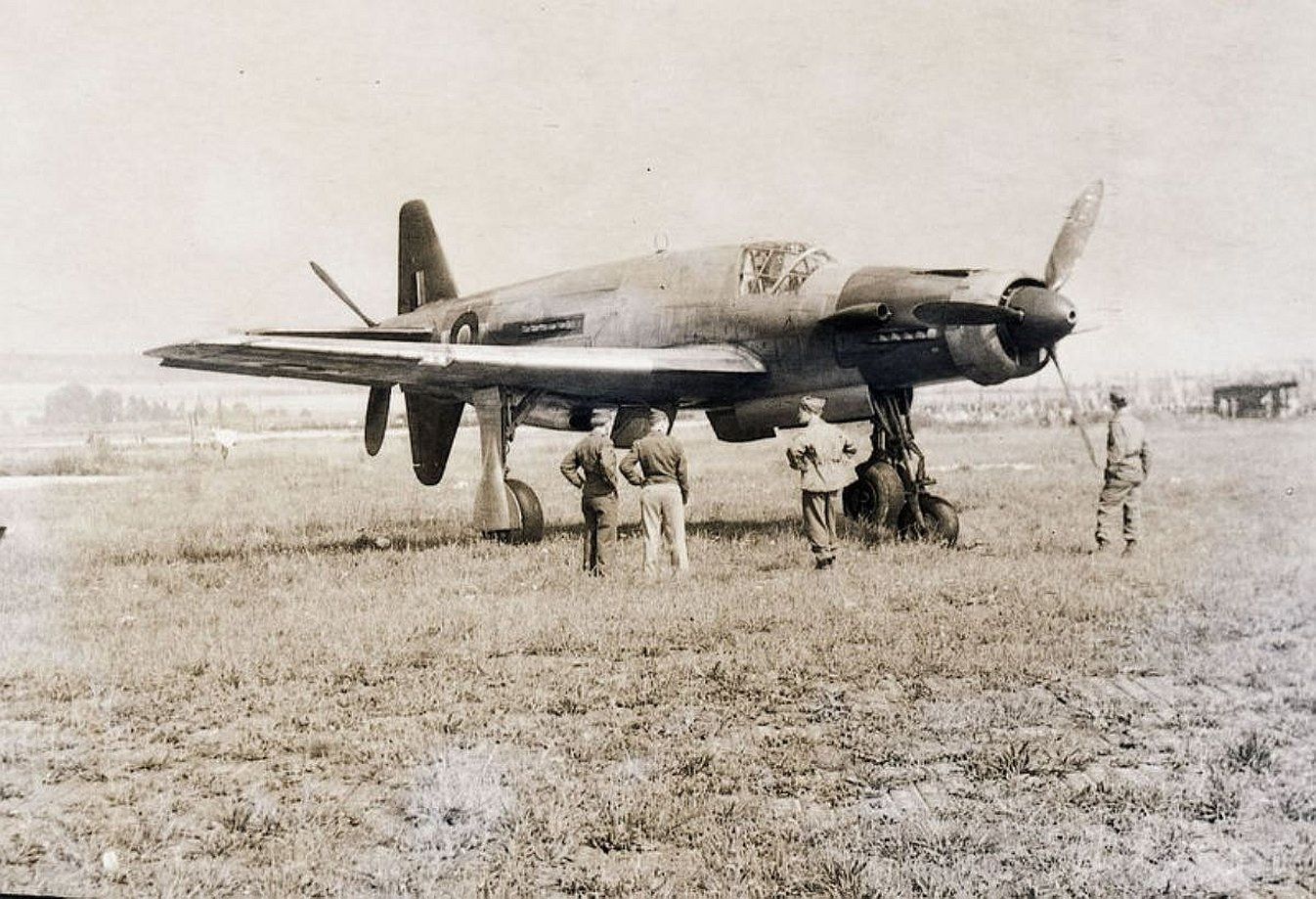
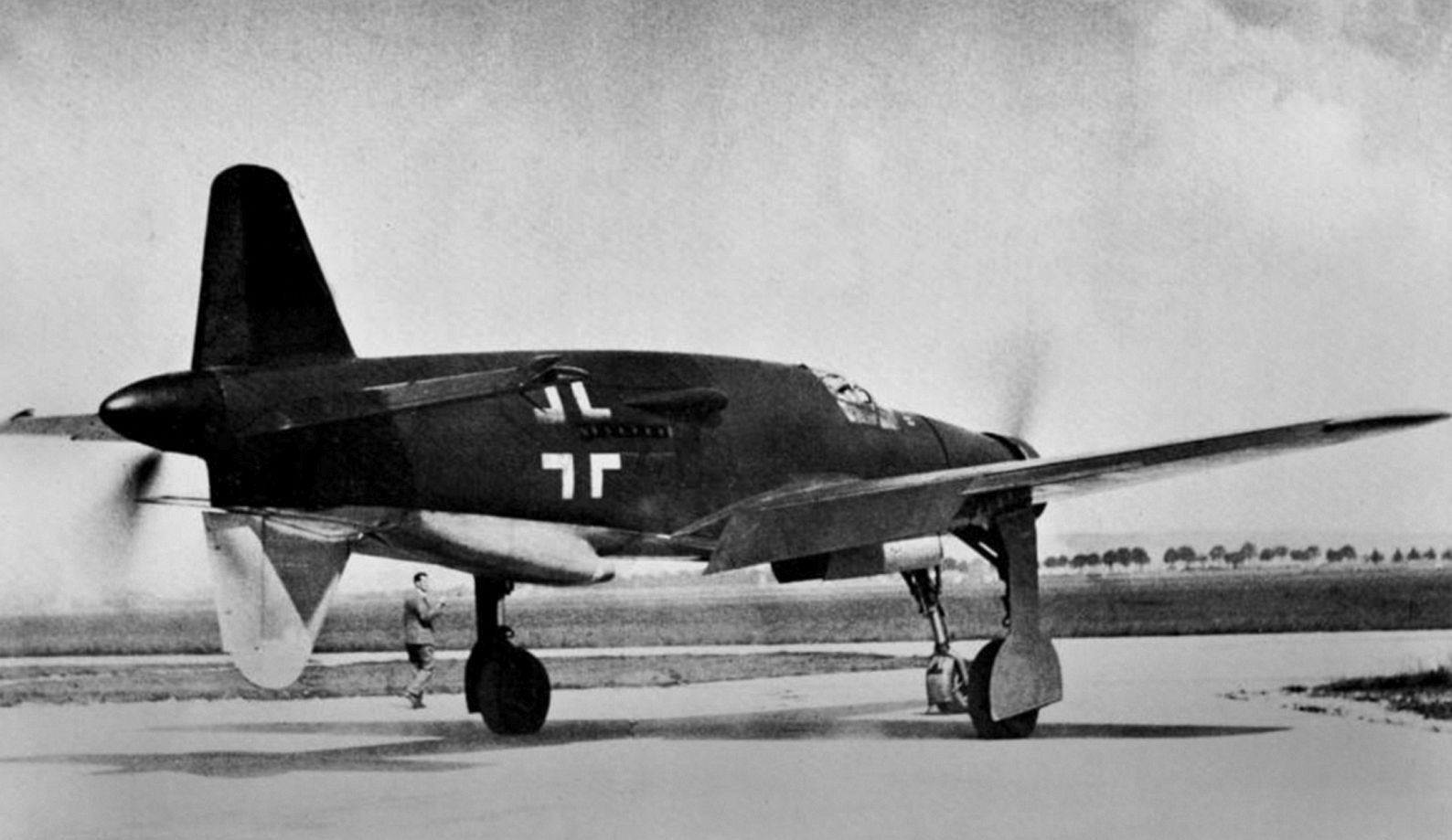
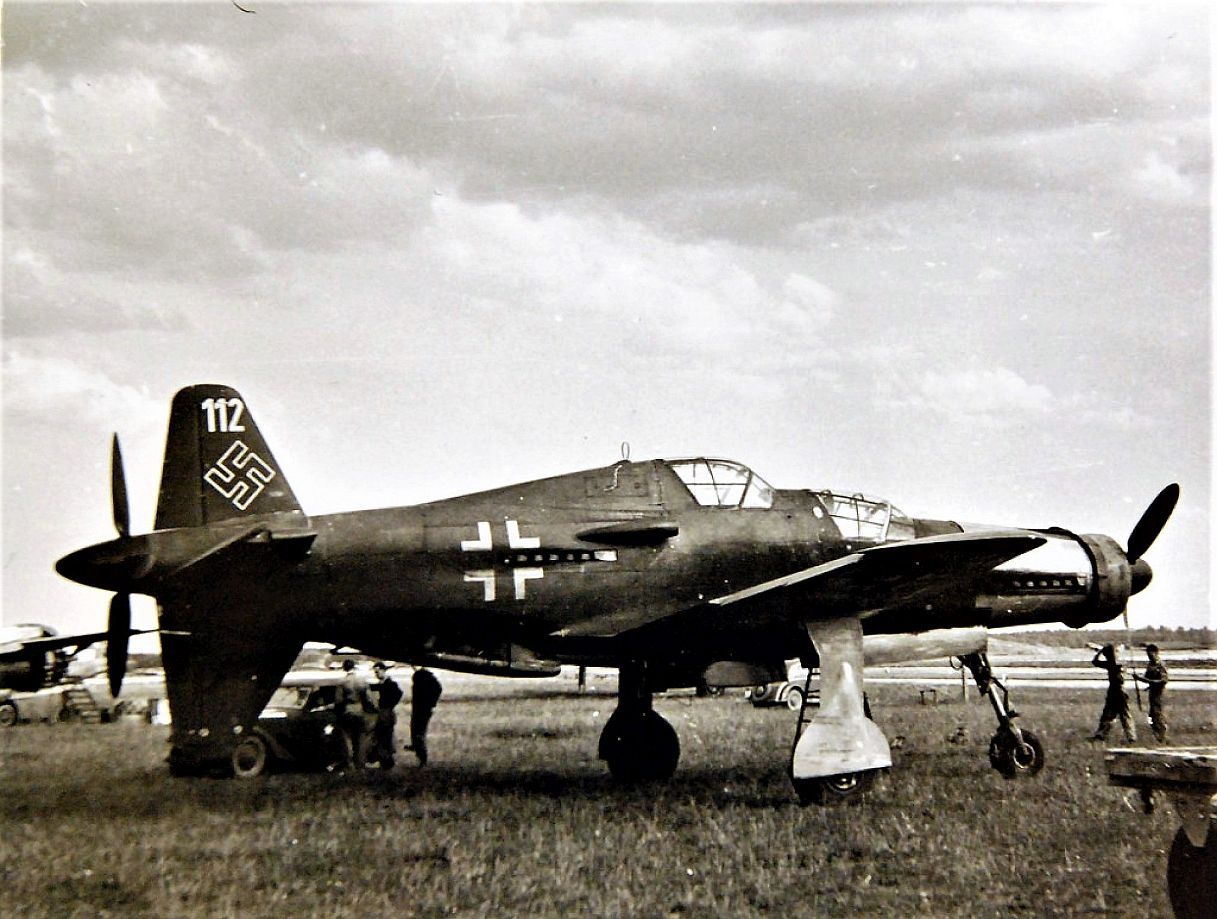
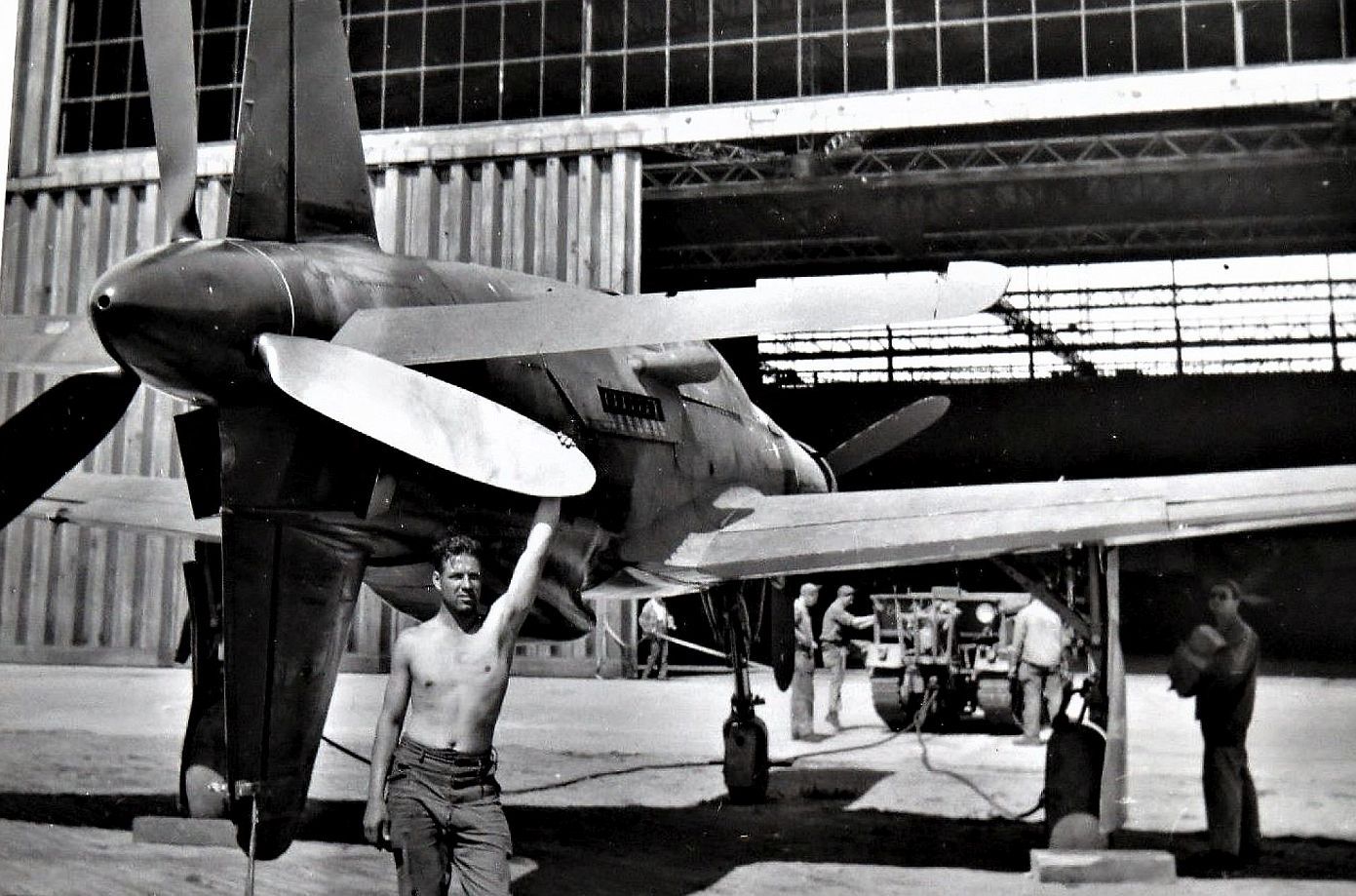
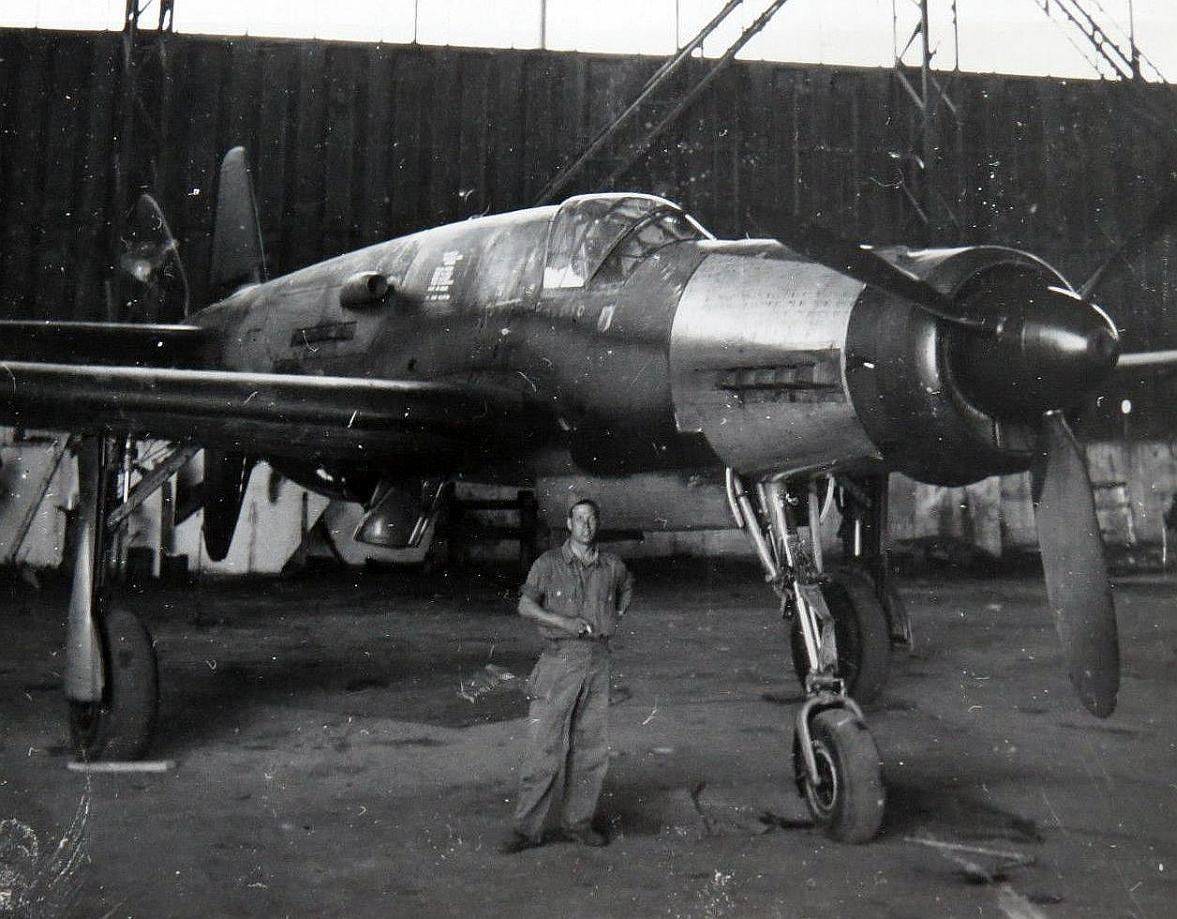
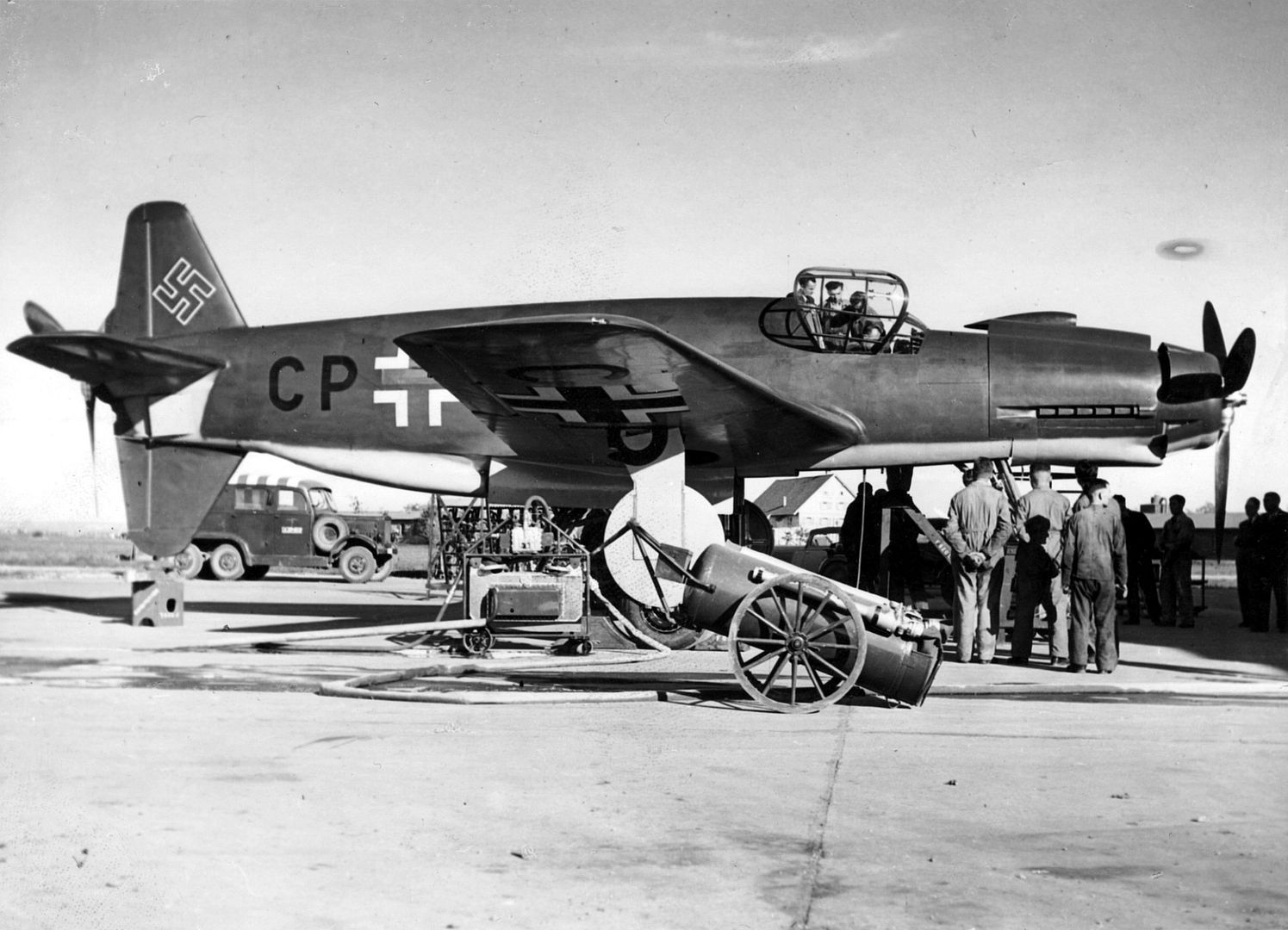
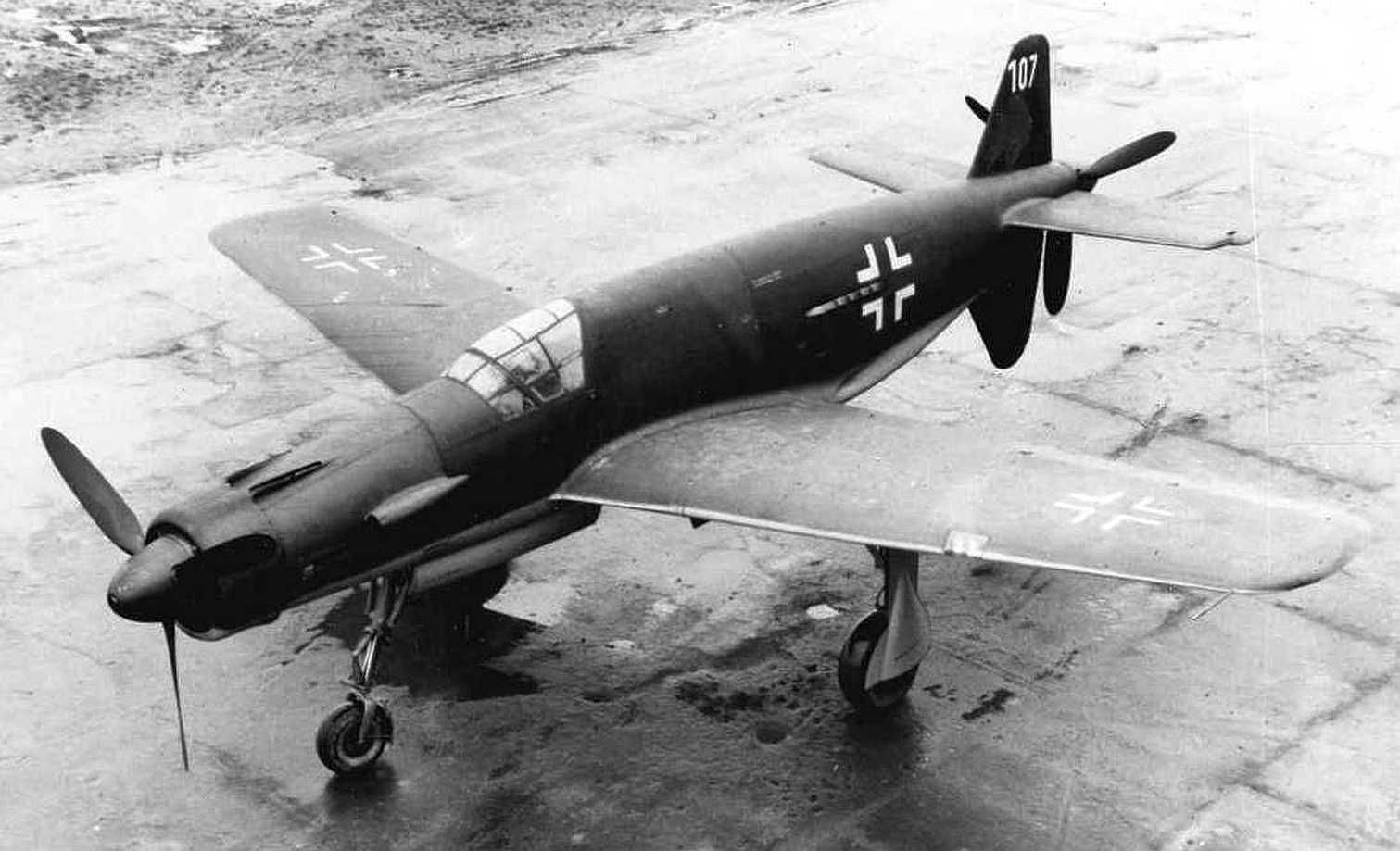














, circa 1944. German personnel work around the airplane.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)
 being prepared by German personnel, circa 1944..jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)
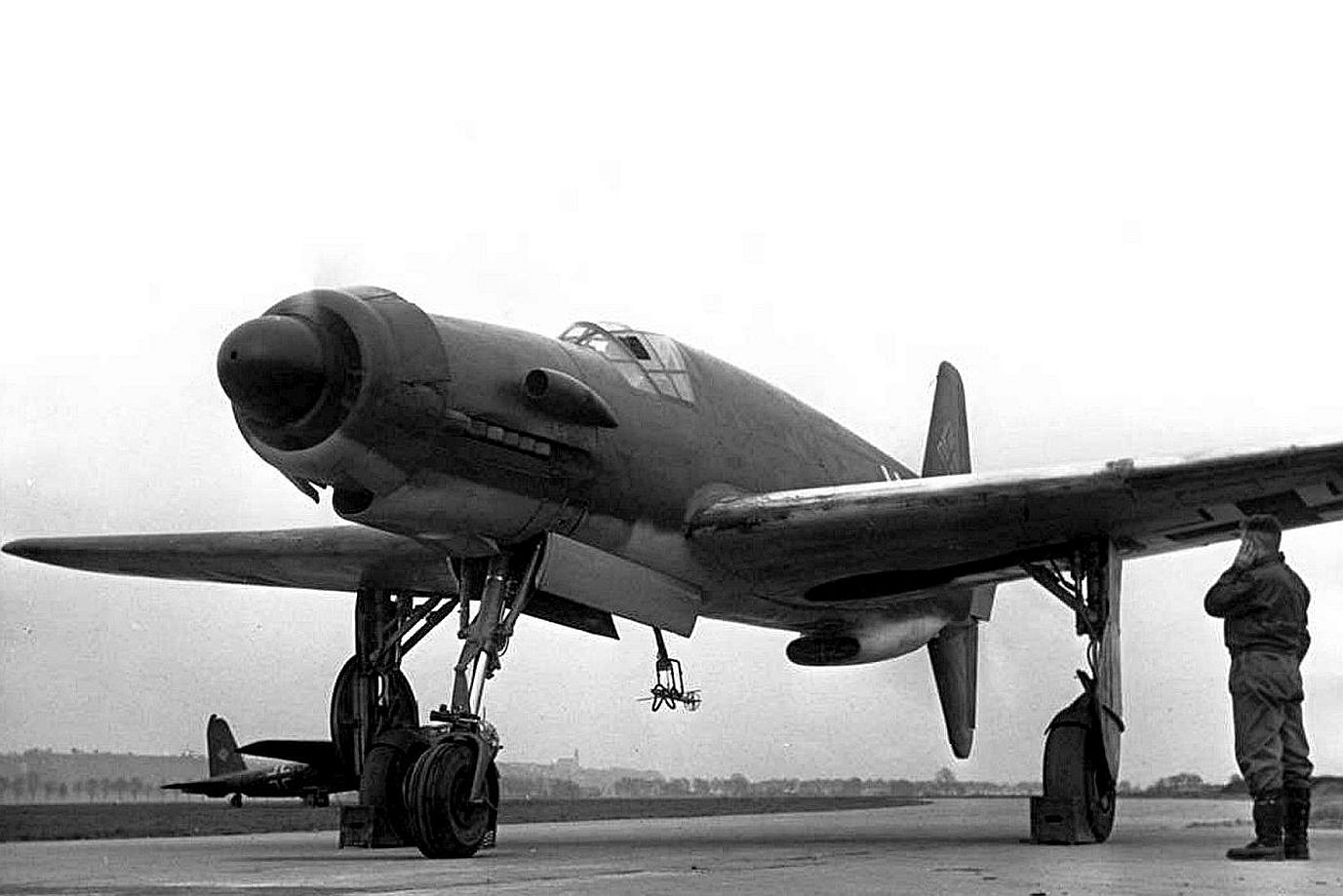
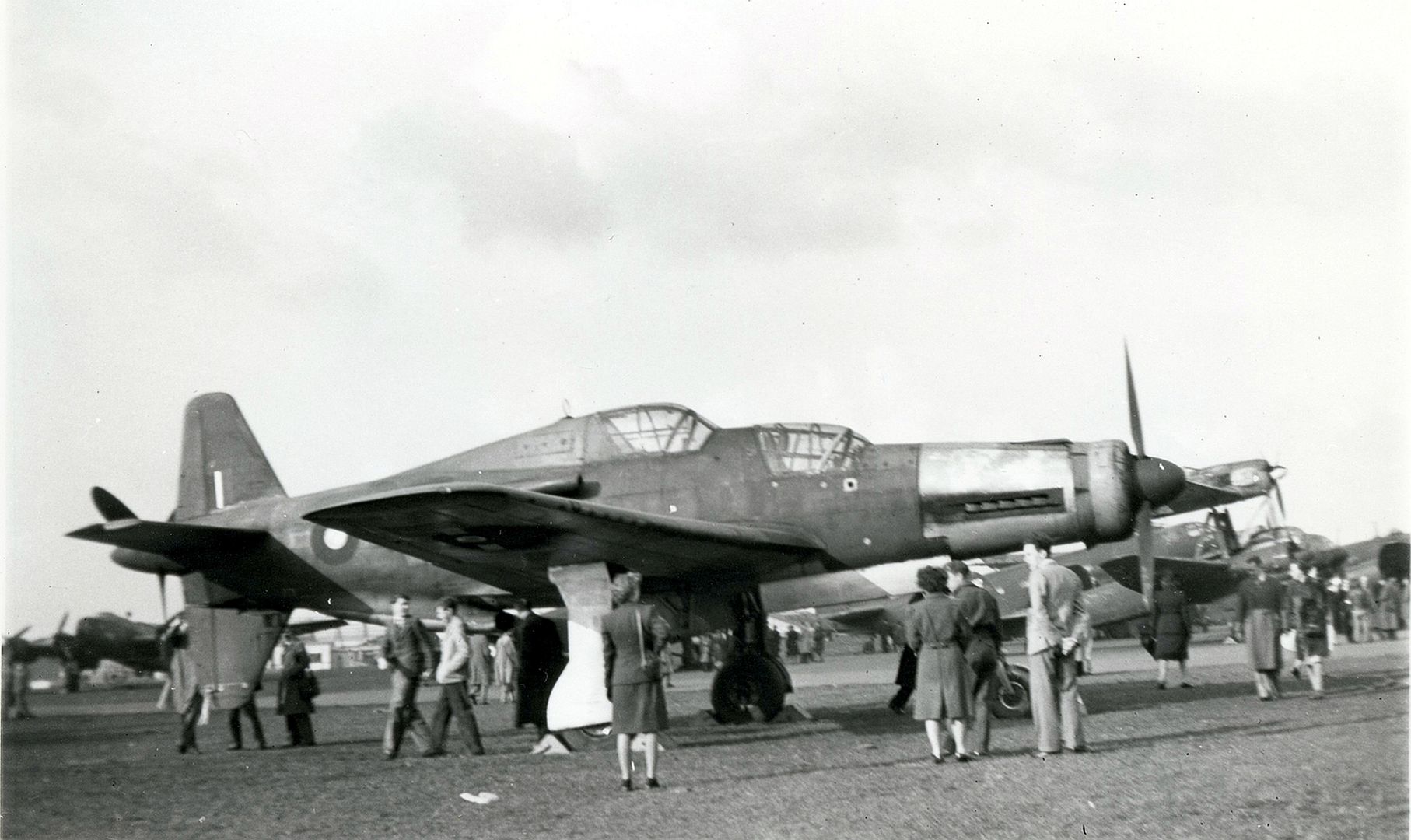
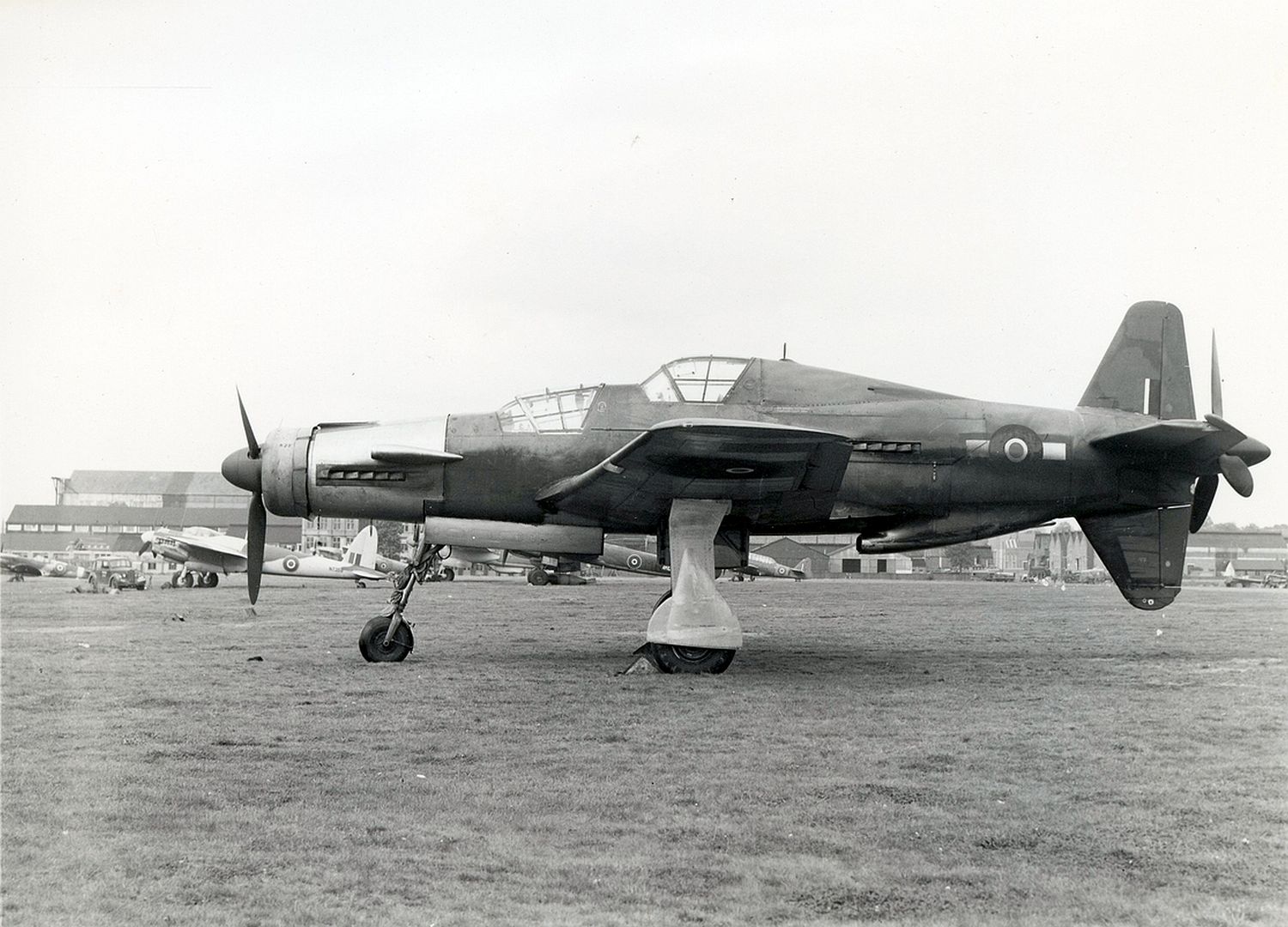
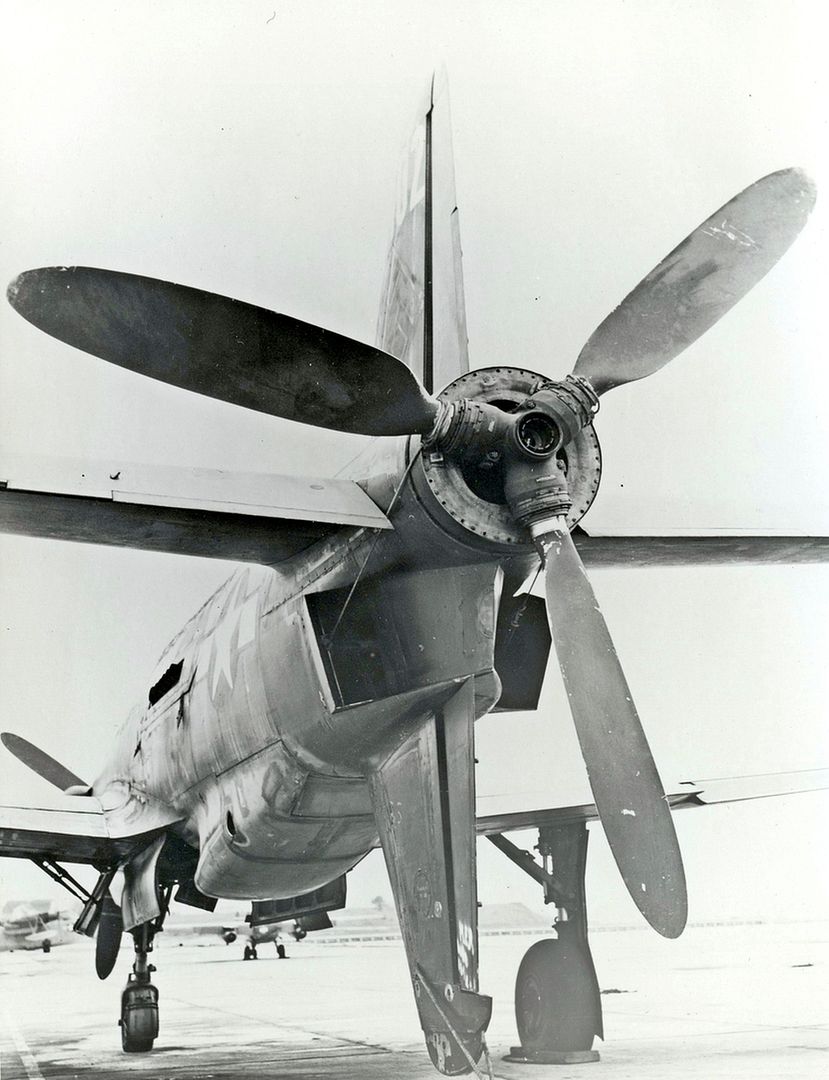
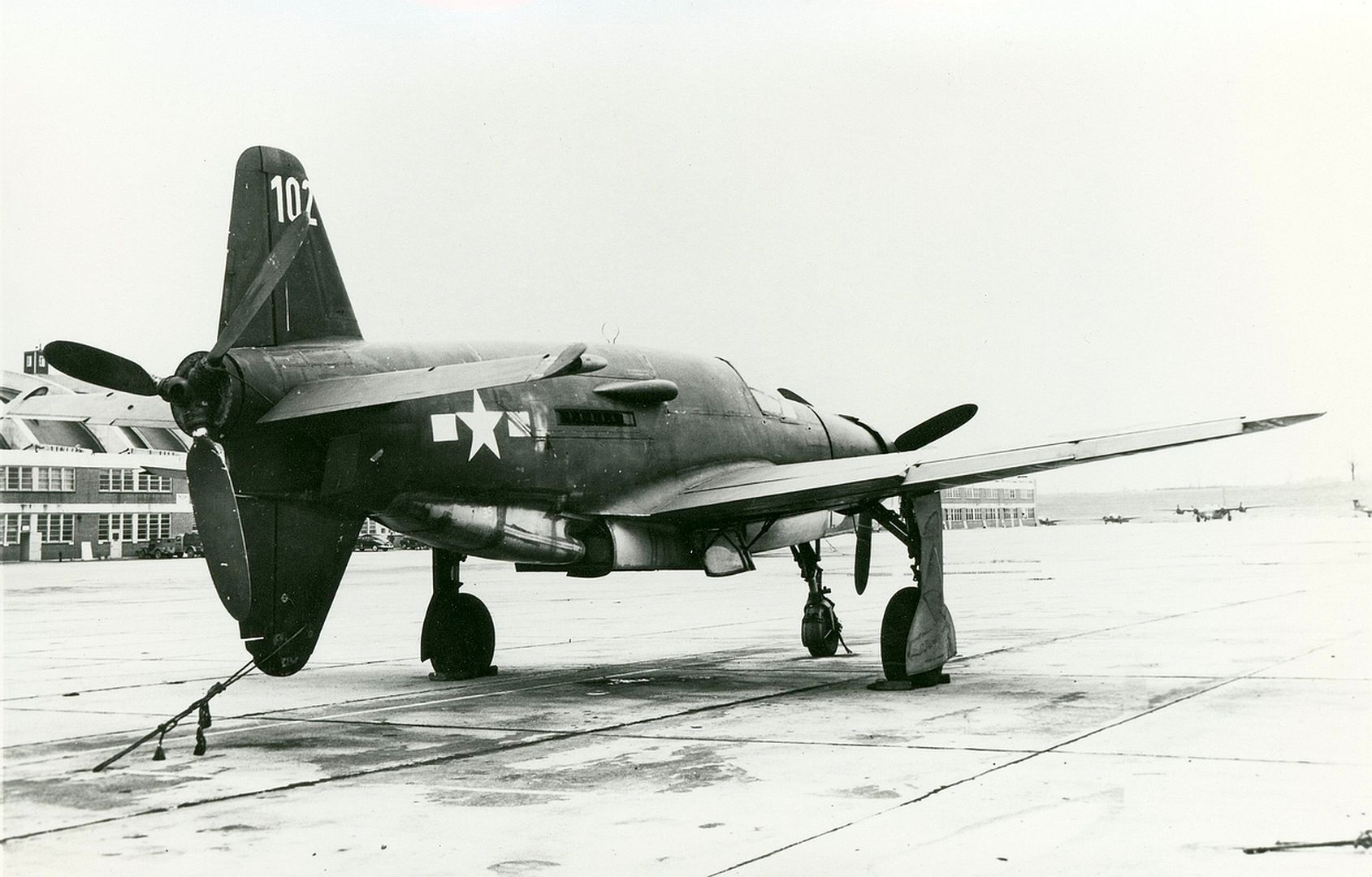










Specifications (Do 335 A-1)
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 13.85 m (45 ft 5 in)
Wingspan: 13.8 m (45 ft 3 in)
Height: 5 m (16 ft 5 in)
Wing area: 38.5 m2 (414 sq ft)
Airfoil: root: NACA 23018-630; tip: NACA 23012-635
Empty weight: 7,260 kg (16,006 lb)
Gross weight: 9,600 kg (21,164 lb)
A-6 10,085 kg (22,234 lb)
Fuel capacity: 1,230 l (320 US gal; 270 imp gal) main fuel tank (single-seat) with various extra tankage in the weapons bay and wings, depending on variant
Powerplant: 2 × Daimler-Benz DB 603E-1 V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engines, 1,342 kW (1,800 hp) each for take-off
1,417 kW (1,900 hp) at 1,800 m (5,900 ft)
Propellers: 3-bladed VDM, 3.5 m (11 ft 6 in) diameter constant-speed tractor and pusher propellers
Performance
Maximum speed: 763 km/h (474 mph, 412 kn) at 6,500 m (21,300 ft)
A-6 690 km/h (430 mph; 370 kn) at 5,300 m (17,400 ft)
Cruise speed: 685 km/h (426 mph, 370 kn) at 7,200 m (23,600 ft)
Economical cruise speed: 452 km/h (281 mph; 244 kn) at 6,000 m (20,000 ft)
Range: 1,395 km (867 mi, 753 nmi) on full internal fuel at max. continuous power
2,060 km (1,280 mi; 1,110 nmi) at economical cruise power
Service ceiling: 11,400 m (37,400 ft)
Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in 55 seconds ; 8,000 m (26,000 ft) in 14 minutes 30 seconds
Armament
Guns: 1 × engine mounted 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 103 cannon with 70 rpg plus 2 × 20 mm (0.79 in) MG 151/20 cowl-mount, synchronized autocannon with 200 rpg
Bombs: Up to 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombload in internal weapons bay and two underwing pylons
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources

