Forums
- Forums
- Duggy's Reference Hangar
- USAAF / USN Library
- Boeing F2B
Boeing F2B
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
-
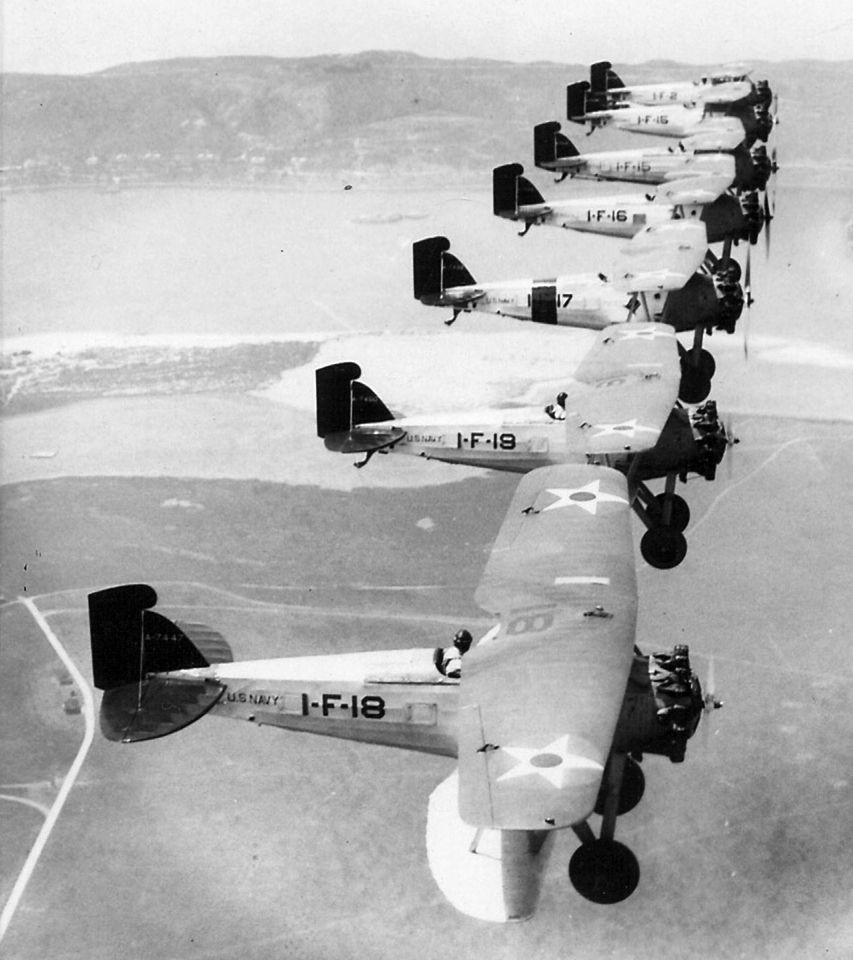
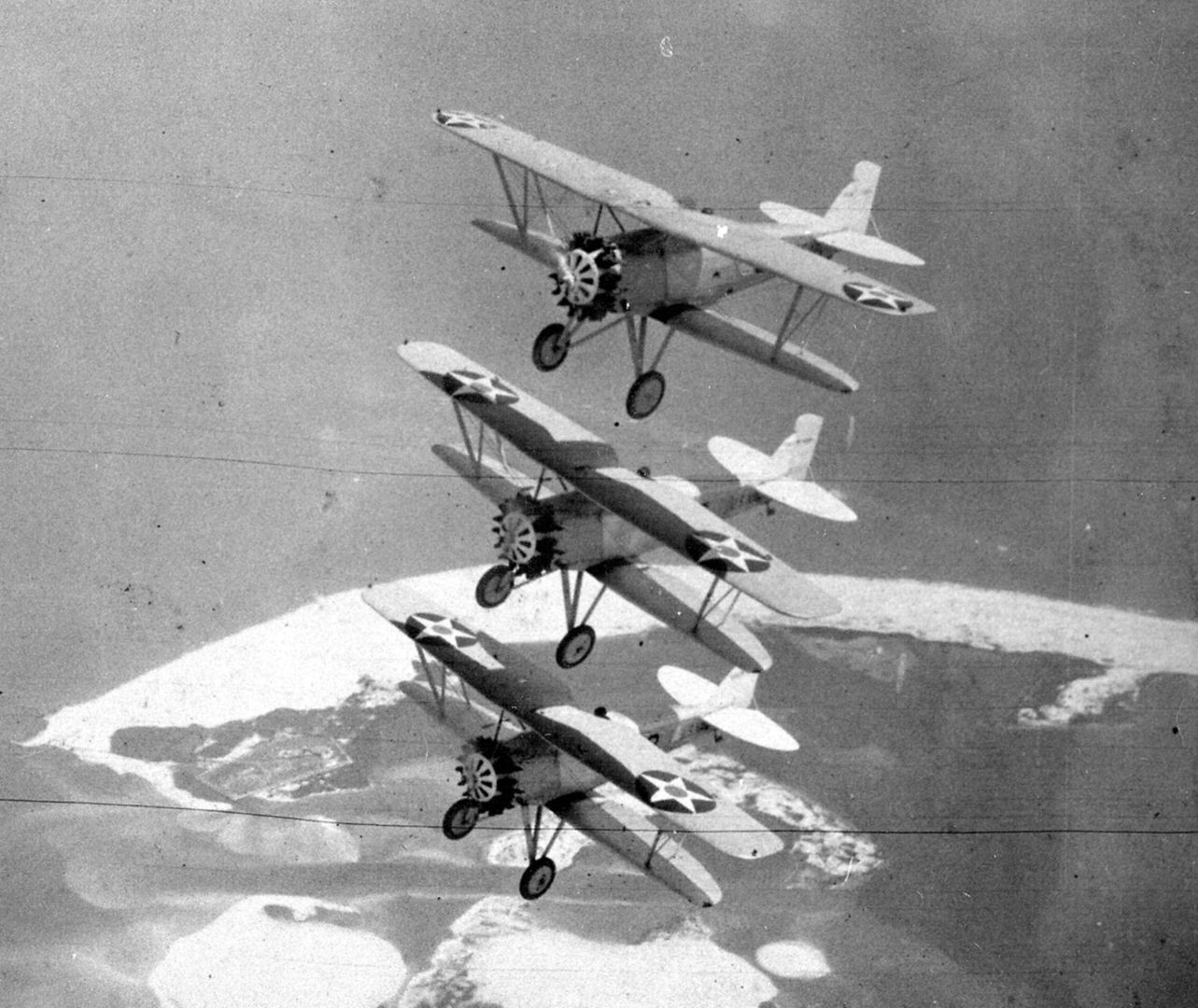
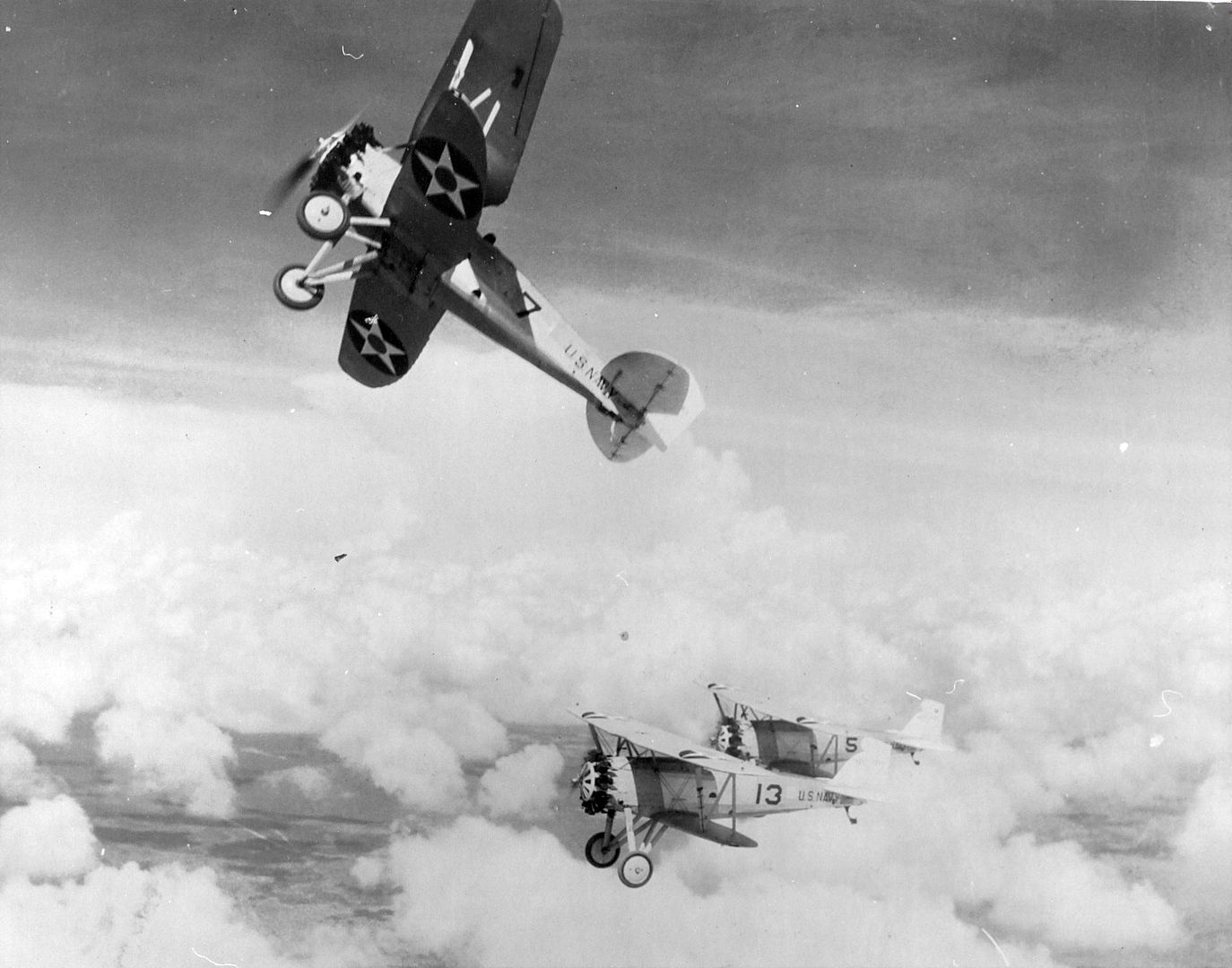
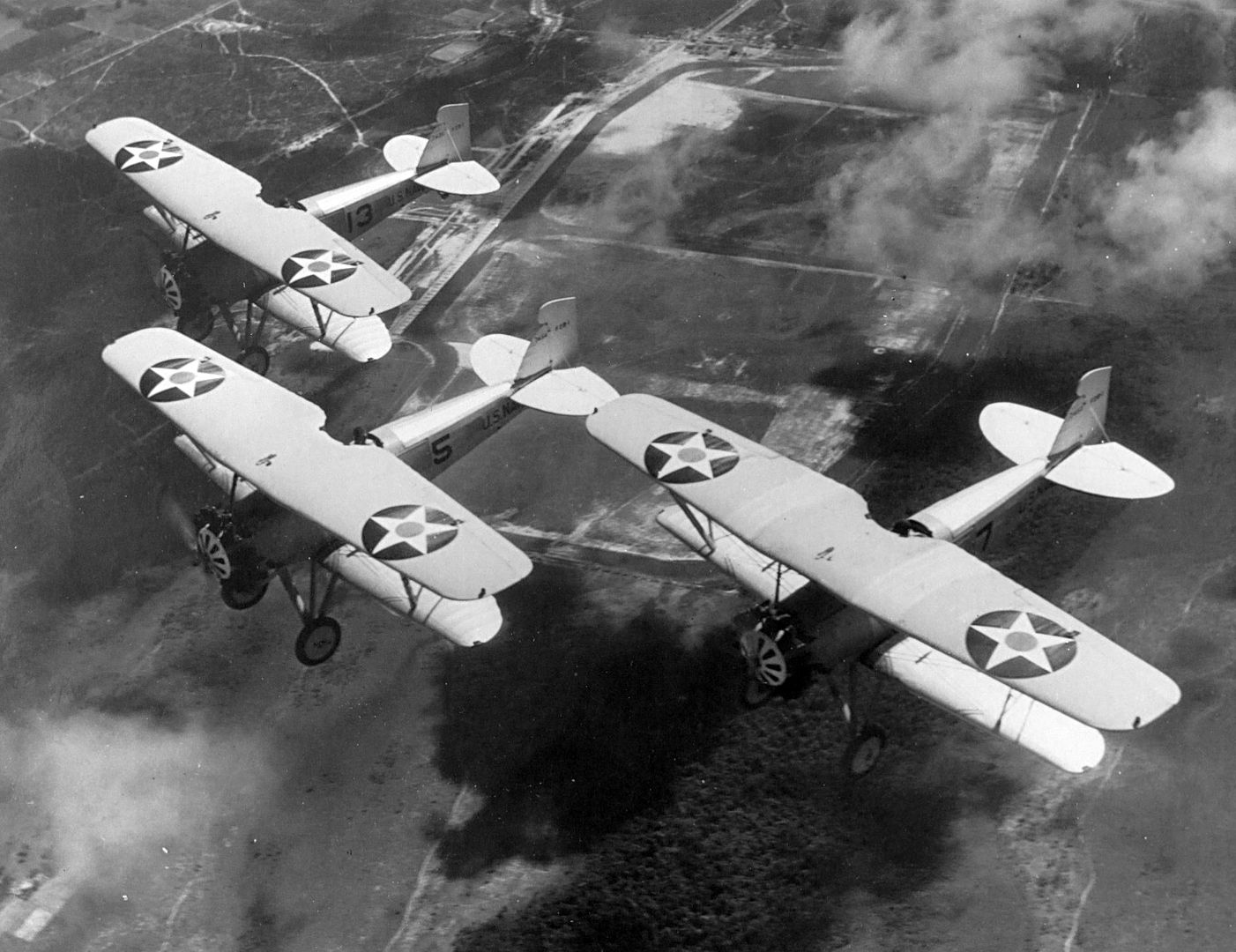
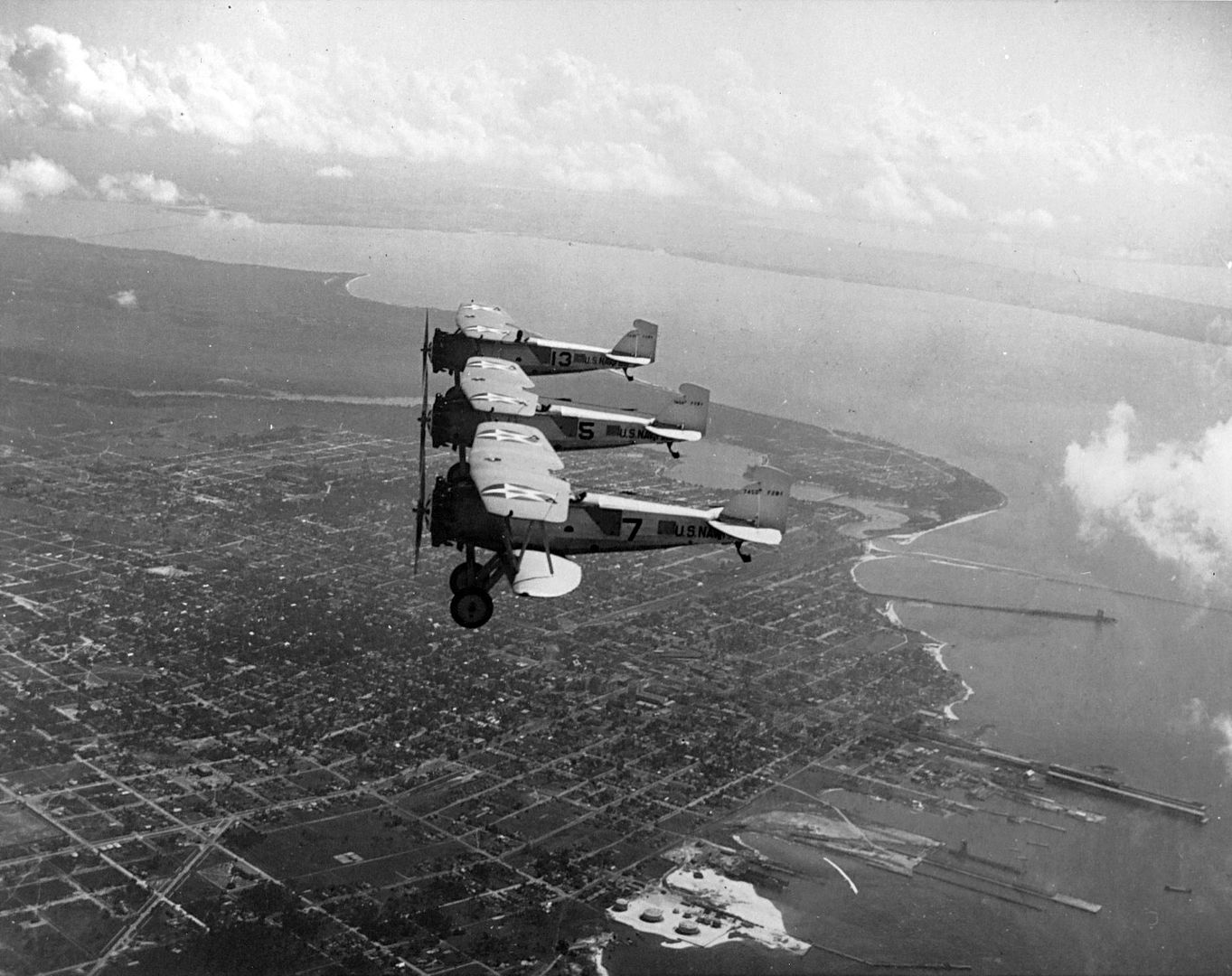
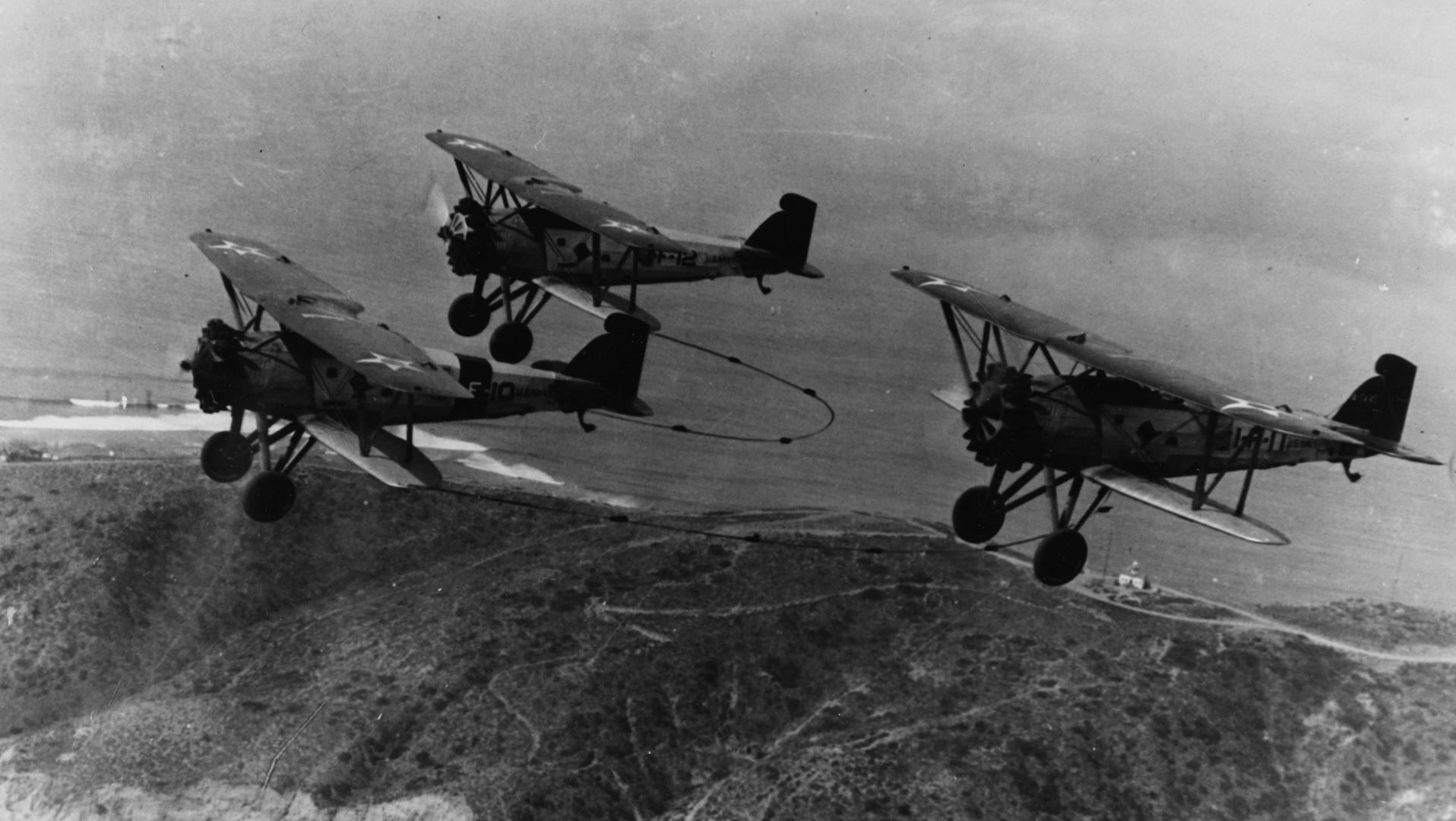
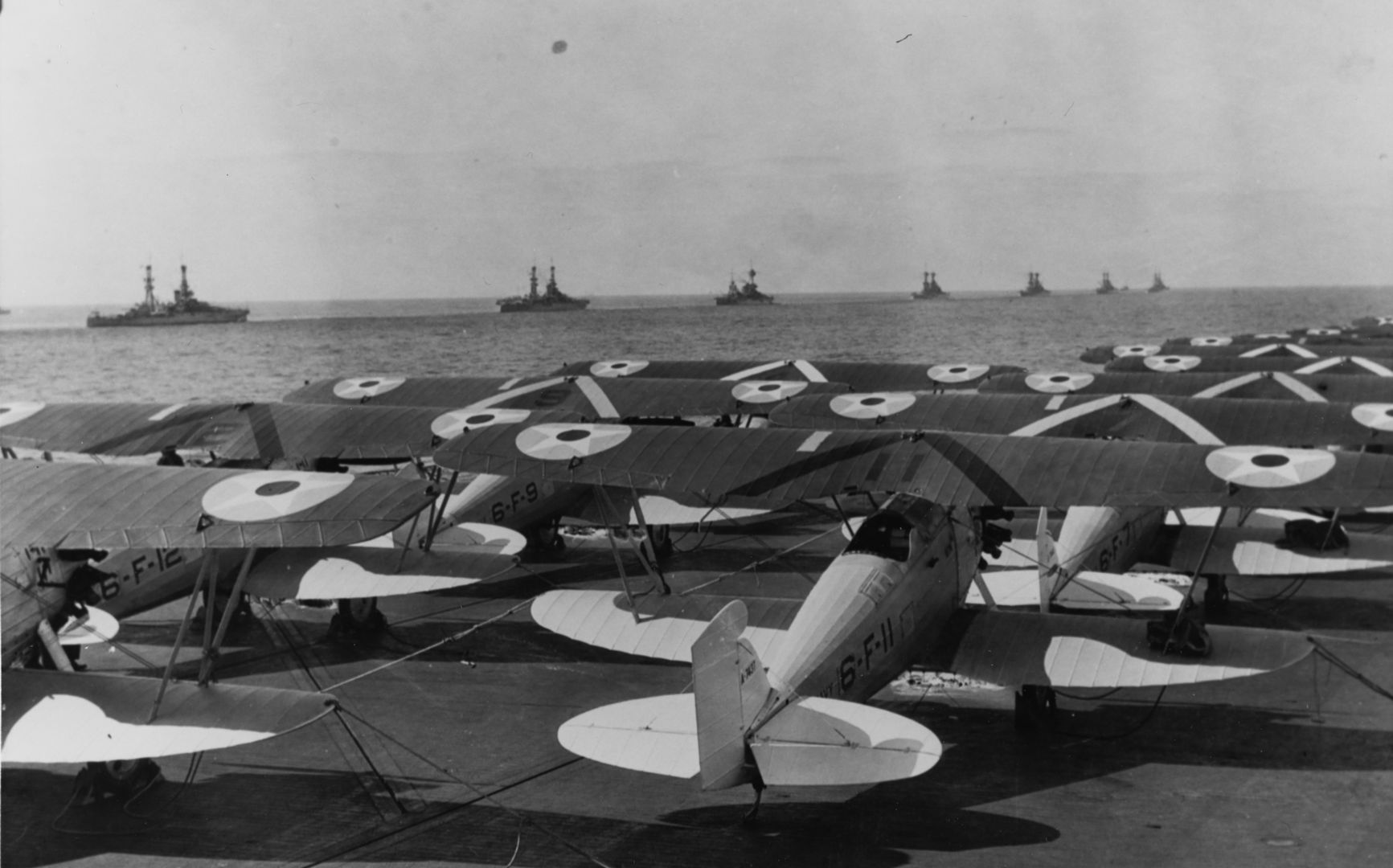
 Main AdminThe Boeing F2B biplane fighter served the United States Navy in a carrier-based fighter role. It was produced in over two dozen examples and did not see service beyond the United States. Developed from the Boeing PW-9, the F2B was a sound, dual-role fighter that provided a capable solution to the American carrier wings throughout the 1920s. This aircraft also proved the mount of choice for the U.S. Navy's "Three Sea Hawks" aerobatic team which typically tied its three F2B biplanes together for close formation flying - the group became known as the "Suicide Trio" for obvious reasons.
Main AdminThe Boeing F2B biplane fighter served the United States Navy in a carrier-based fighter role. It was produced in over two dozen examples and did not see service beyond the United States. Developed from the Boeing PW-9, the F2B was a sound, dual-role fighter that provided a capable solution to the American carrier wings throughout the 1920s. This aircraft also proved the mount of choice for the U.S. Navy's "Three Sea Hawks" aerobatic team which typically tied its three F2B biplanes together for close formation flying - the group became known as the "Suicide Trio" for obvious reasons.
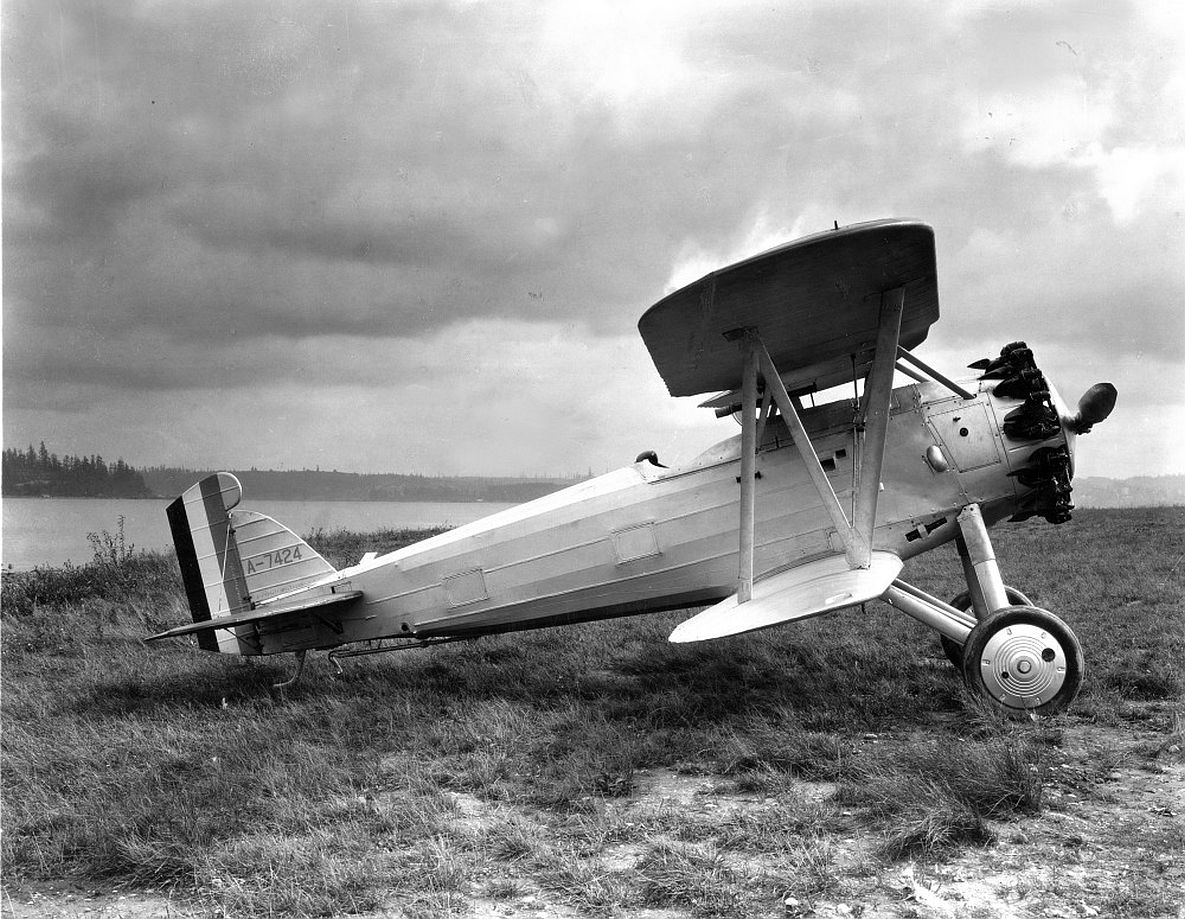
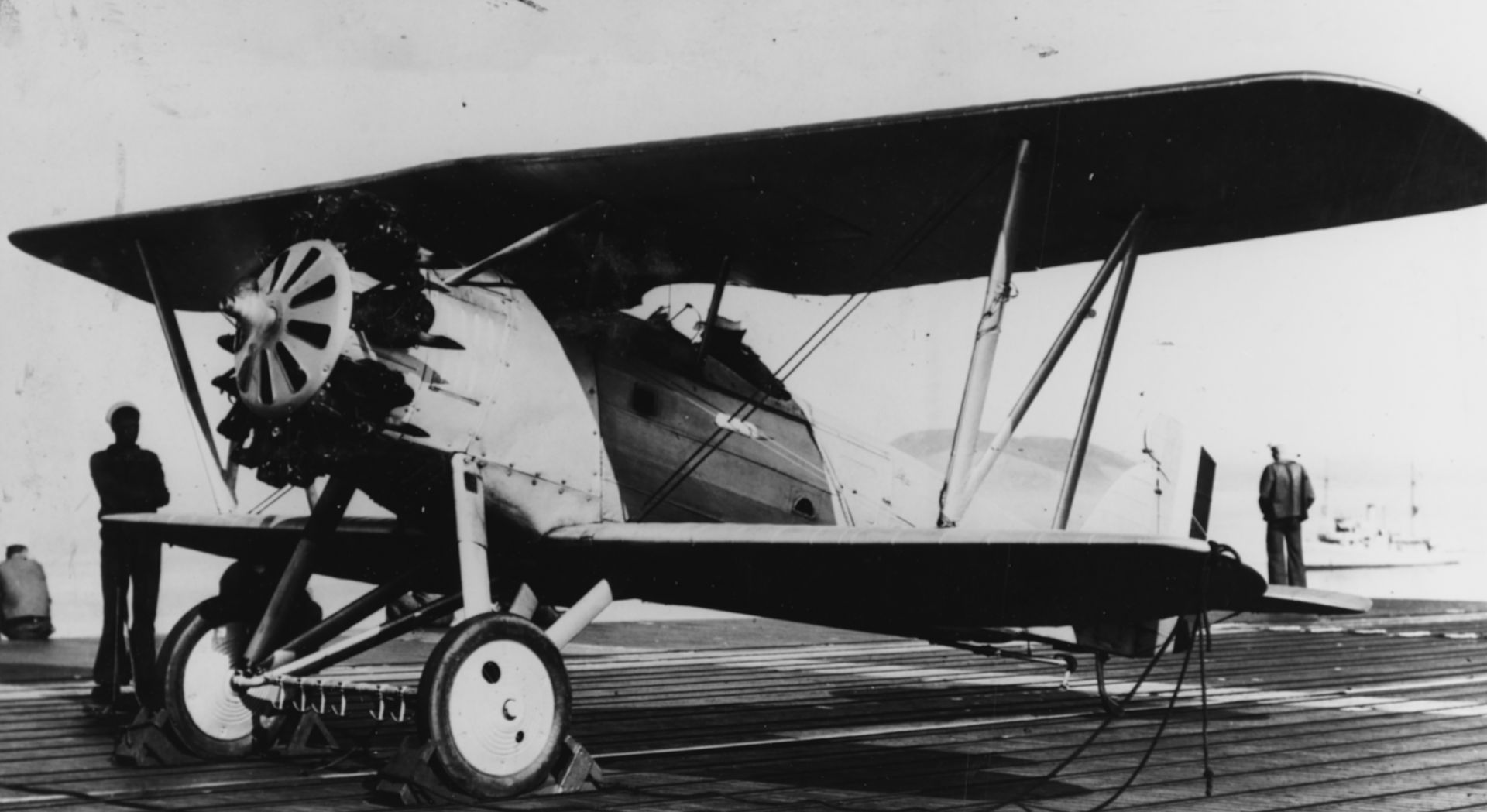
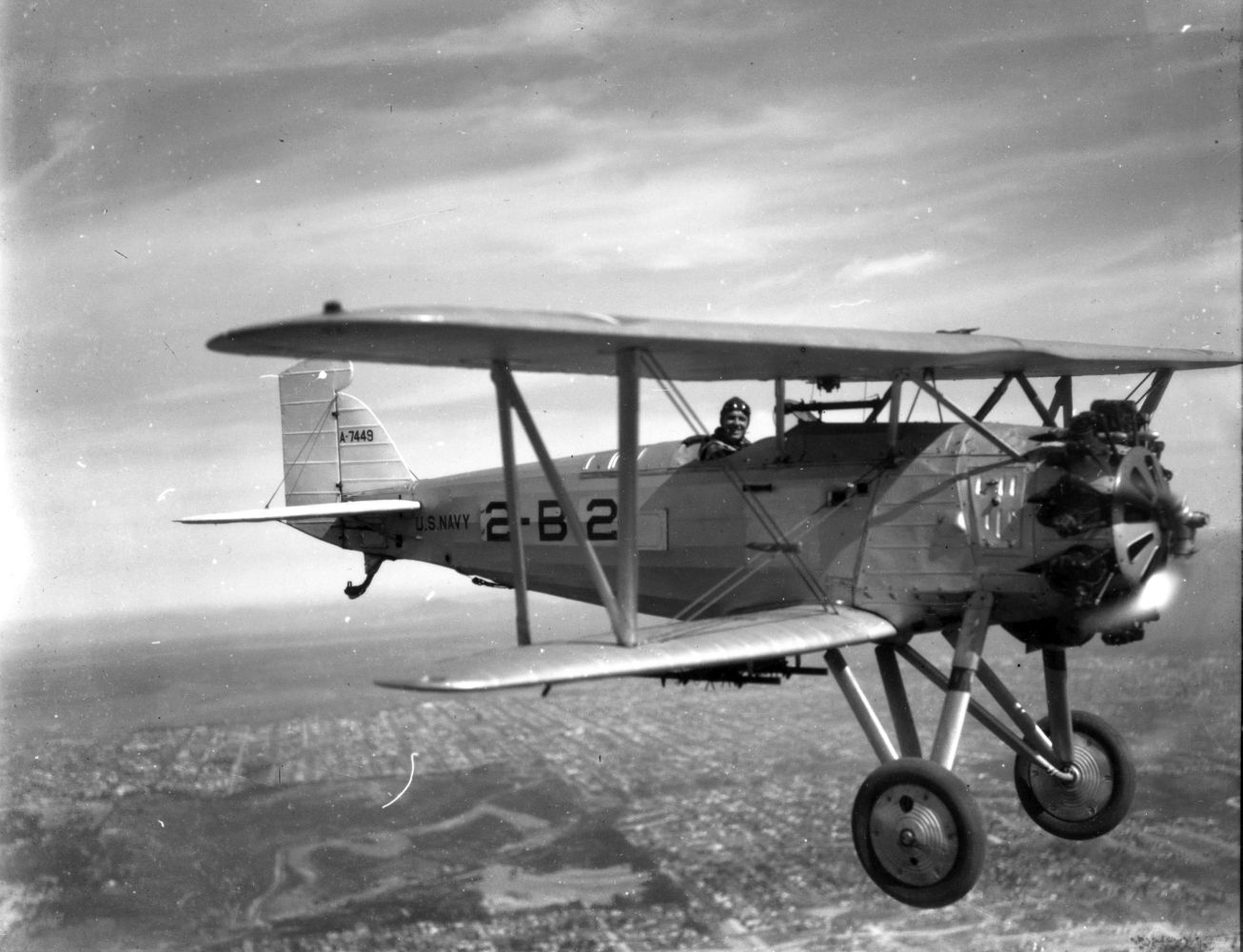
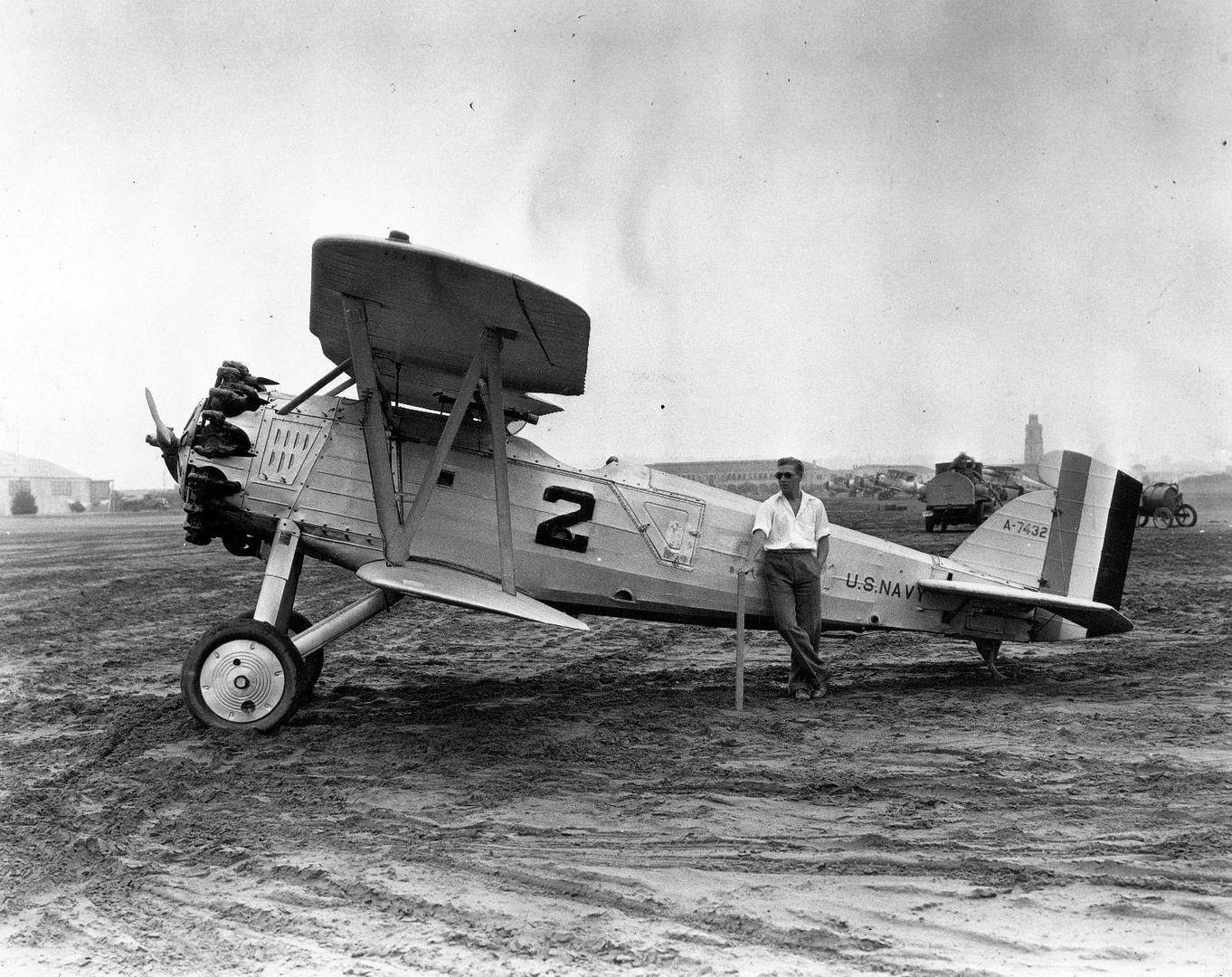
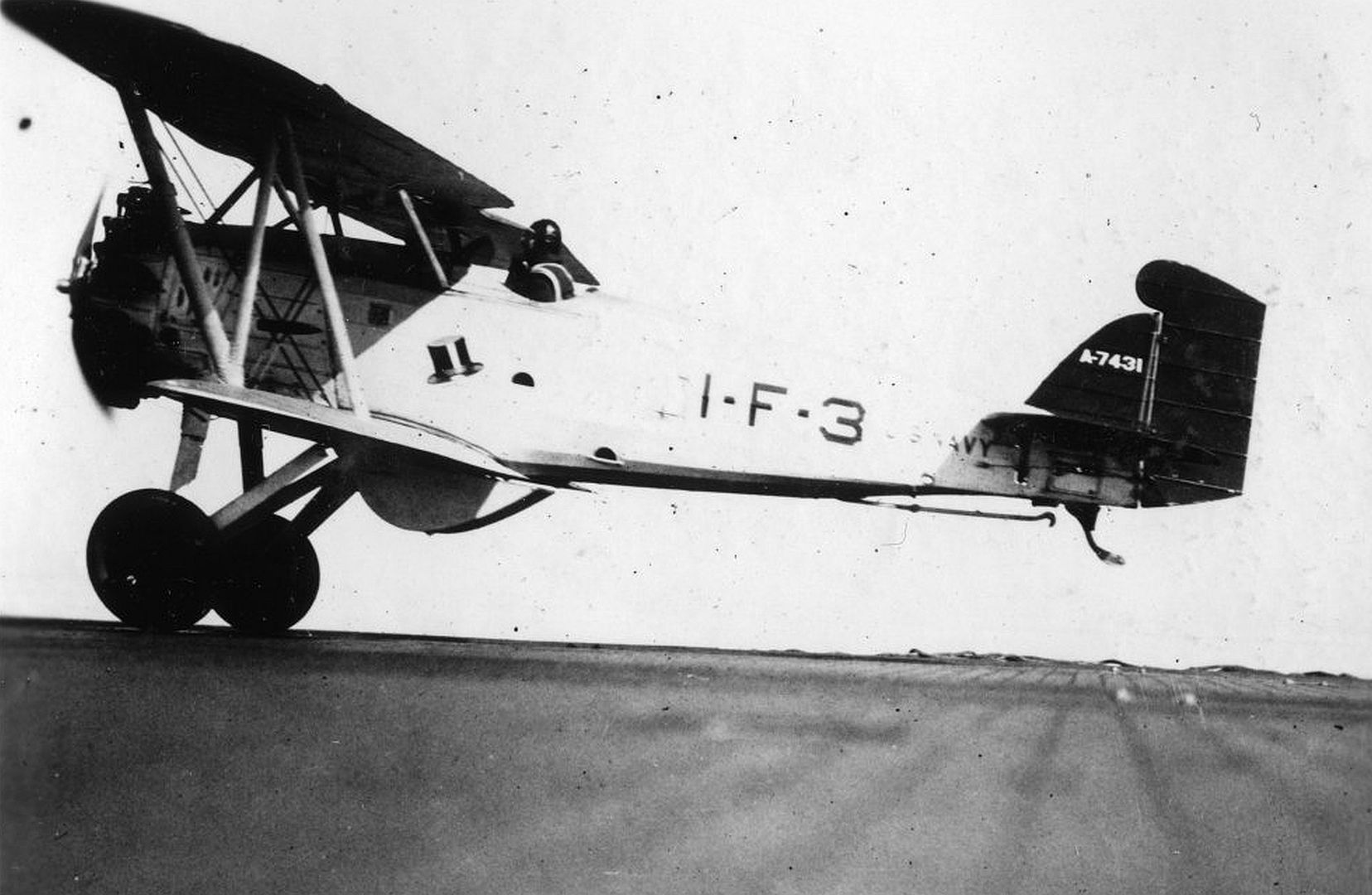
Origins of the F2B lay in testing done on a single ("one-off") experimental offshoot of the Boeing PW-9 fighter. The experiment was designated "FB-6" and known by Boeing as "Model 54". From this came the Boeing "XP-8" (Model 66) which was eventually tested (and passed on) by the U.S. Army and developed into a suitable design for the U.S. Navy. The PW-9 airframe was mated to a Pratt & Whitney R-1340-B "Wasp" series radial engine of 450 horsepower which promised the line improved performance over the original. When the U.S. Navy need arose for a new modern biplane fighter, the Model 69 arrived to fulfill just that role. The biplane wing arrangement was retained as was the twin-wheeled undercarriage with tailskid. The pilot sat under and slightly behind the upper main wing assembly in the typical open-air cockpit of the period with the engine ahead in the forward fuselage. While a spinner was added to the engine's frontal face in the prototype, this feature was dropped on the production models that followed.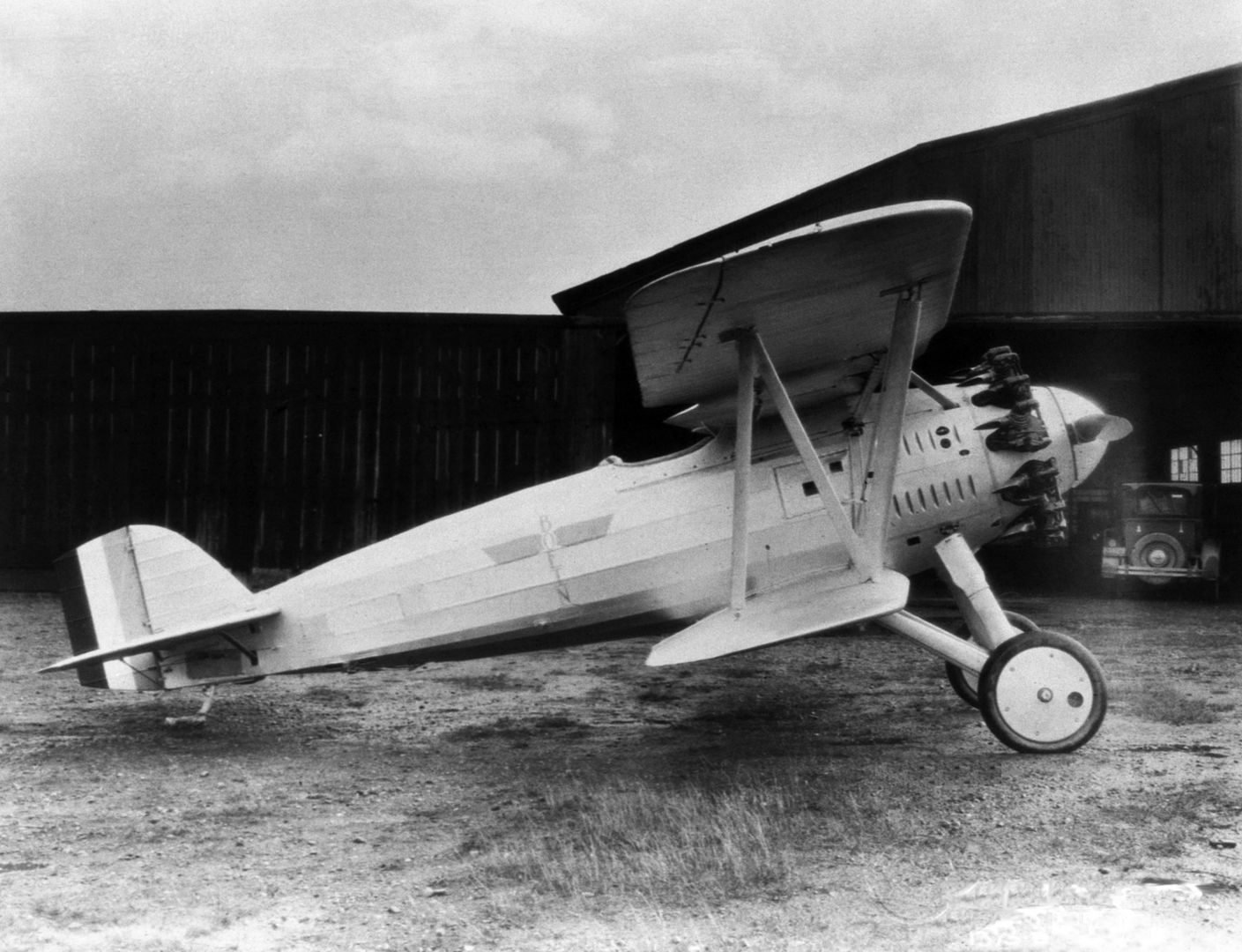
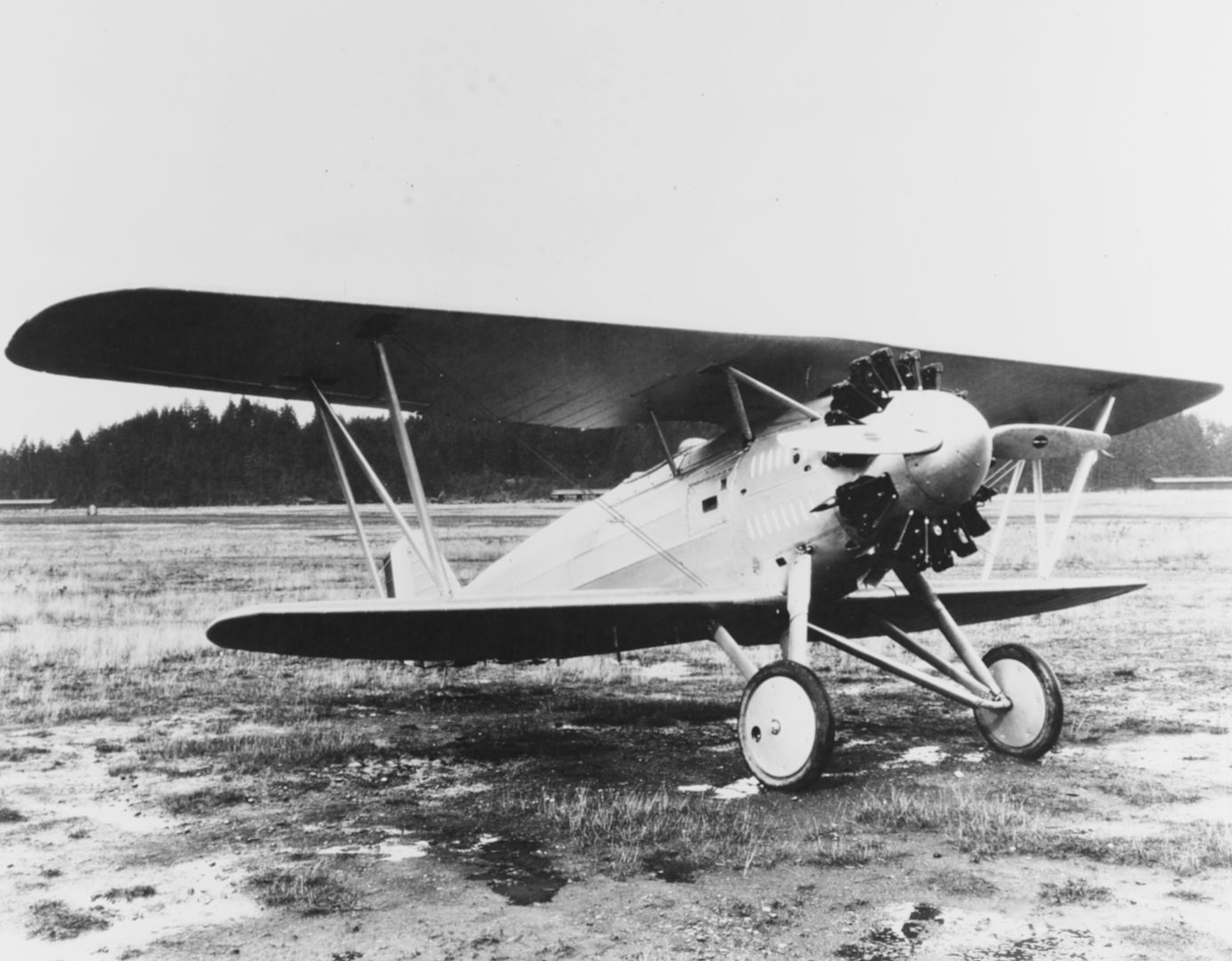
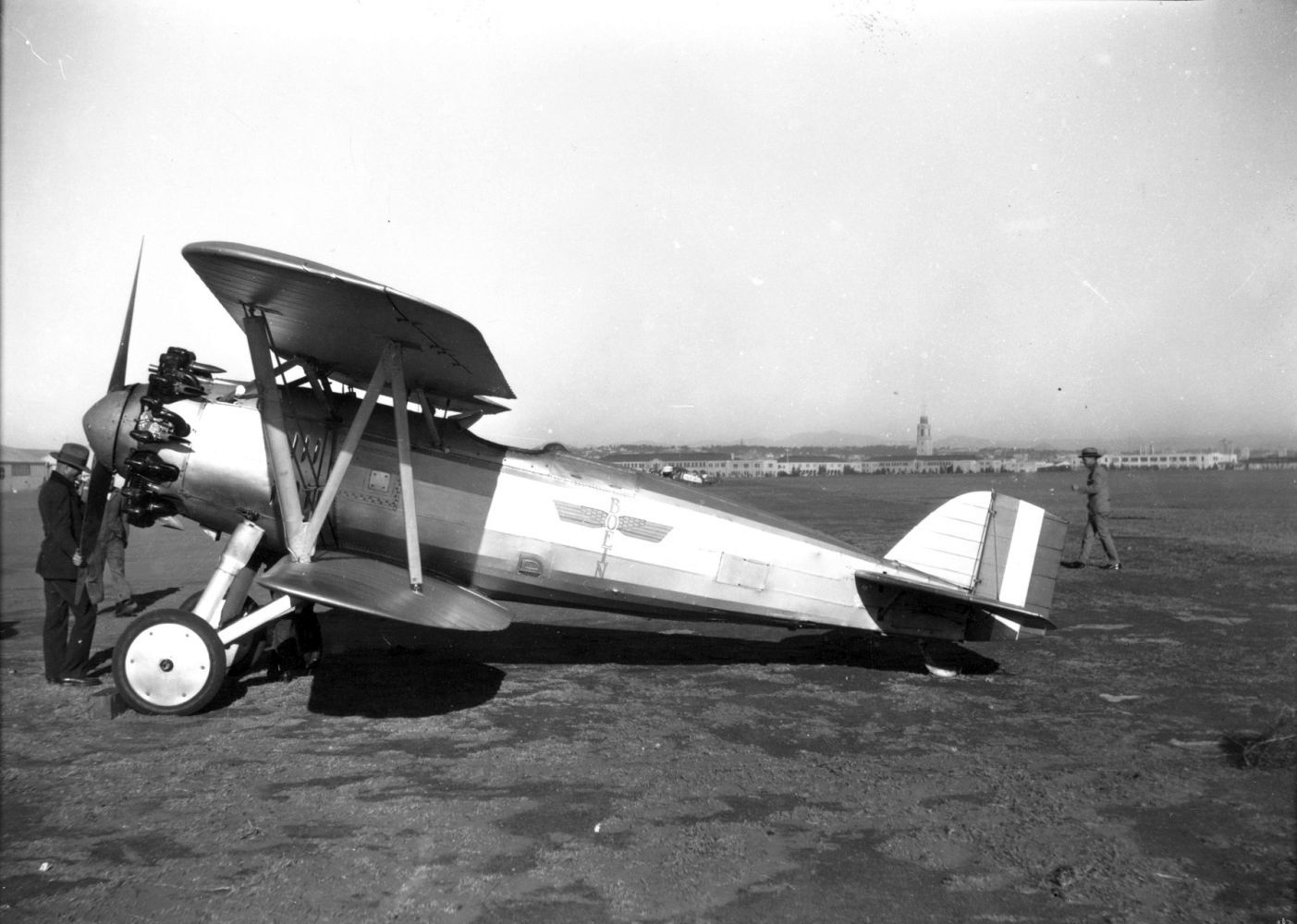


Standard armament became 2 x 0.30 caliber machine guns fitted over the engine and synchronized to fire through the spinning propeller blades though this could also be replaced by a combination 1 x .30 caliber and 1 x 0.50 caliber heavy machine gun arrangement for additional punch. The lower wing assembly was also wired for the carrying, and delivery, of conventional drop ordnance. In this fashion, the Model 69 could serve double-duty as fighter and fighter-bomber aboard U.S. carriers.
First flight of the Model 69 (as the U.S. Navy prototype "XF2B-1") was on November 3rd, 1926. Following the requisite period of testing, the aircraft was formally introduced by the U.S. Navy as the Boeing "F2B" on January 20th, 1928. The initial order was for 32 first-batch aircraft to be designation "F2B-1" and operational service began aboard the deck of the USS Saratoga (CV-3) - a soon-to-be World War 2 veteran.
In practice, the F2B was a very solid design and capable carrier-based fighter for its time, possessing the required agility and power. In the finalized configuration of the aircraft, the fighter was capable of reaching speeds near 160 miles per hour and cruised at around 130 miles per hour. Range was a handy 315 miles which was a key quality for aircraft usually called to operate far from land-bases for refueling and rearming. Its service ceiling peaked at 21,500 feet and rate-of-climb was 1,900 feet per second. Weights included 2,000lbs when empty and 2,800 under its Maximum Take-Off Weight (MTOW). The Pratt & Whitney R-1340-8 Wasp radial piston engine developed 425 horsepower, providing the necessary thrust to propel the F2B from carrier decks. Browning M2 heavy and M1919 medium machine guns made up its standard fighter armament while 5 x 25lb bombs could be slung under the lower wing section for strike sorties.
Boeing also developed the Model 69B of which two were produced and one each sent to the nations of Brazil and Japan for evaluation. However, the type was not taken up by either country. Additionally, the United States Navy did not order any more F2B fighters beyond its original stock order for 32 aircraft.
Such ended the story for this Boeing carrier-based fighter. Including the single prototype, 33 aircraft of the line were completed.
Boeing F2B-1 (Model 69)
Engine: Pratt & Whitney R-1340-B Wasp radial piston engine
Power: 425hp
Crew: 1
Span: 30ft 1in
Front view of Boeing F2B-1
Front view of Boeing F2B-1
Length: 22ft 11in
Height: 9ft 2.75in
Empty Weight: 1,989lb
Maximum Take-off Weight: 2,805lb
Gross Weight:
Maximum Speed: 158mph at sea level
Cruising Speed: 132mph
Climb rate: 1,890ft/ minute
Ceiling: 21,500ft
Range: 315 miles
Guns: Two fixed forward firing machine guns (one 0.3in and one 0.5in)
Bomb load: Five 25lb bombs on under-wing and under-fuselage racks, total 125lb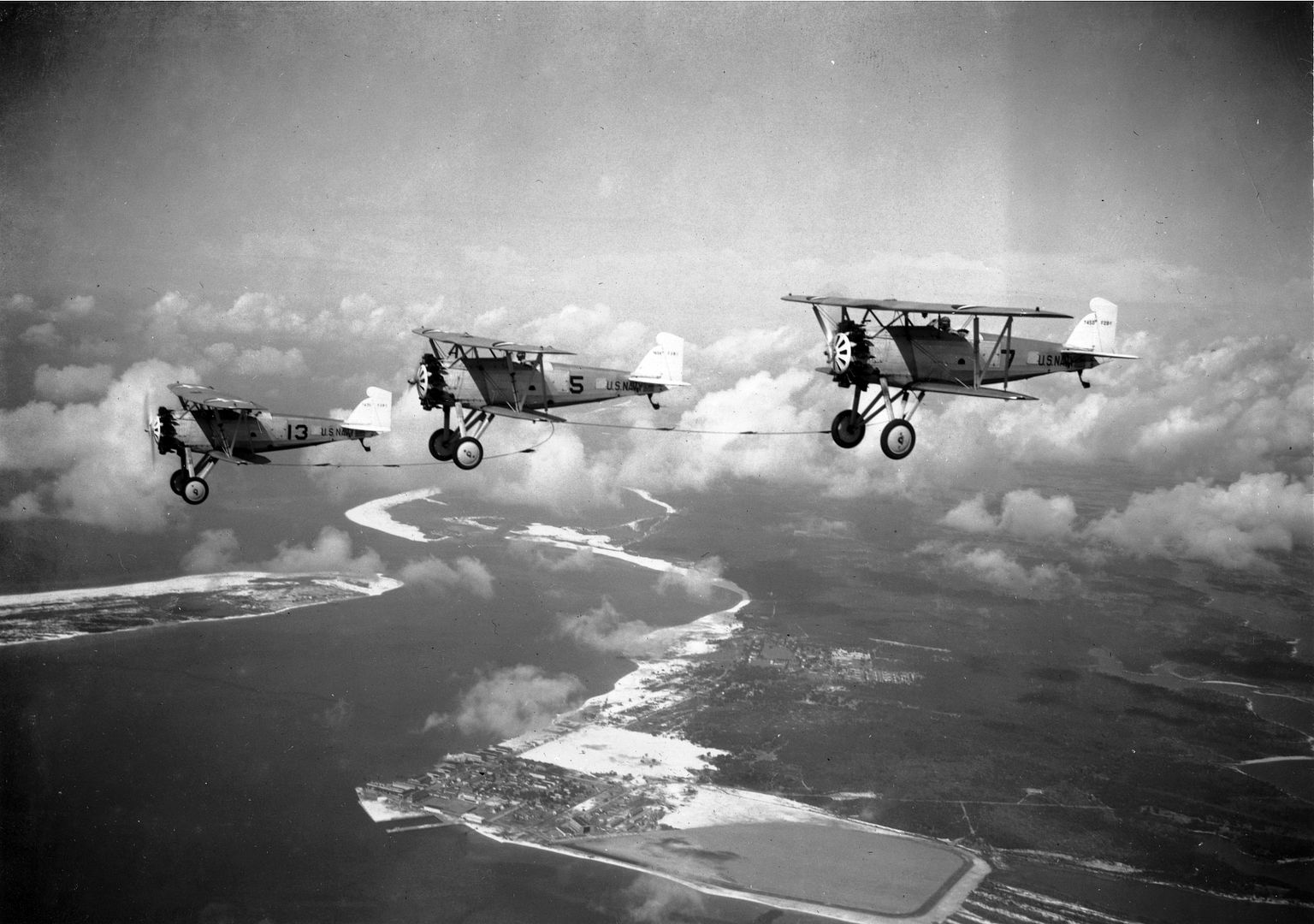



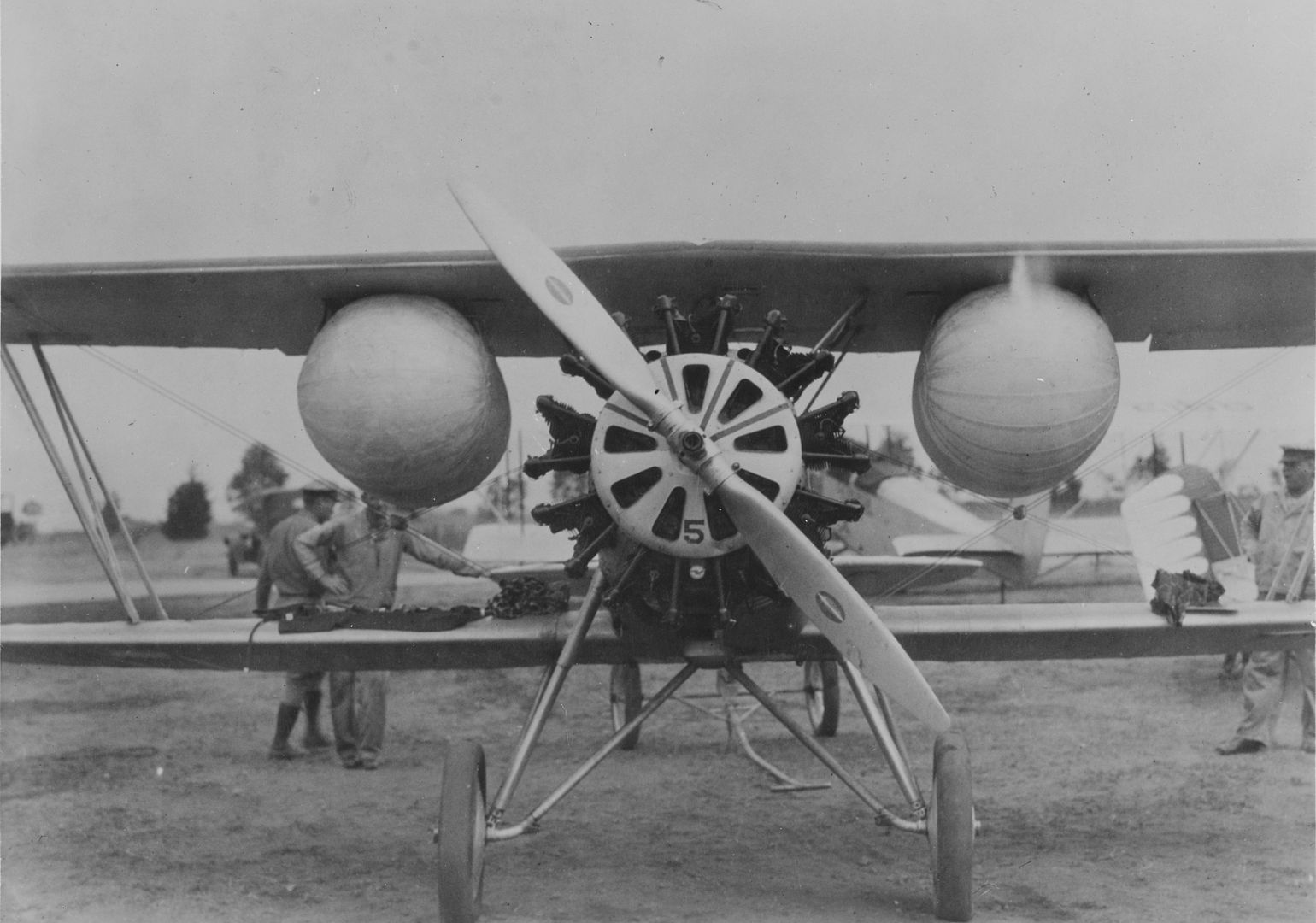










As usual right click & save as for more details.
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
