Forums
- Forums
- Duggy's Reference Hangar
- RAF Library
- Armstrong Whitworth Siskin
Armstrong Whitworth Siskin
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
-
5 years agoSun Sep 08 2019, 12:50pm
 Main AdminThe Armstrong Whitworth Siskin was a British biplane single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1920s produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. The Siskin was one of the first new RAF fighters to enter service after the First World War; it was noted for its aerobatic qualities.
Main AdminThe Armstrong Whitworth Siskin was a British biplane single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1920s produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. The Siskin was one of the first new RAF fighters to enter service after the First World War; it was noted for its aerobatic qualities.
Design and development
The design was a development of the Siddeley-Deasy S.R.2 Siskin designed by Major F. M. Green (formerly chief engineer of the Royal Aircraft Factory) of the Siddeley-Deasy Motor Car Company, to meet the requirements of RAF Specification Type 1 for a single-seat fighter powered by the promising ABC Dragonfly radial engine.
The SR.2 Siskin was a single-bay biplane of wood and fabric construction. Its wings were of unequal span and the aircraft was fitted with a distinctive fixed conventional landing gear with long oleo strut shock absorbers carrying the axle, which was connected by radius rods to a pair of V-struts situated behind the axle. The Dragonfly engine was fitted in a streamlined cowling to reduce drag, with individual cooling channels for each engine cylinder. Two Vickers machine guns were mounted in the nose decking in front of the pilot.
The Siskin first flew in May 1919, powered by a Dragonfly engine delivering 270 hp (200 kW), rather than the promised 320 hp (240 kW). Despite the expectations piled on it, the Dragonfly proved to be a disaster, far less powerful than expected and very unreliable, being prone to overheating and catastrophic vibration, that would normally cause crankshaft failure within a few hours. Despite the engine problems, the Siskin displayed good performance and handling, outmatching its Dragonfly-powered contemporaries.
In 1919, Siddeley-Deasy merged with Armstrong Whitworth, with the aviation interests becoming Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. Siddeley-Deasy had inherited the design of the RAF.8 fourteen-cylinder radial engine and its designer Sam D. Heron, and by 1920 this engine, now known as the Jaguar, had been developed sufficiently to be a possible replacement for the Dragonfly. One of the prototype Siskins was fitted with a Jaguar, flying in this form on 20 March 1921.
In 1922 Air Ministry Specification 14/22 was issued for an all-metal single-seat high performance landplane and one Jaguar-powered prototype was ordered from Armstrong Whitworth. As well as re-engining with the Jaguar, Major Green redesigned the Siskin with an all-metal structure, as the Siskin III. The change from wood to metal construction was a requirement of the Air Ministry war production plan which would use the motor car industry for aircraft production, something which would not have been possible using wood. The all-metal Siskin was the start of a general transition to metal for military aircraft to enable a rapid increase in aircraft production when required to meet wartime demand.A contract for three production aircraft was placed on 13 October 1922 with a further six ordered on 26 January 1923 including one as a prototype of a two-seat variant. The Siskin III first flew on 7 May 1923, with first deliveries to the RAF (six for evaluation) taking place in January 1924. The fighter was the first all-metal fighter in the British Royal Air Force.
Following the order from the RAF, Romania ordered 65 aircraft but they were cancelled following a crash on takeoff at Whitley Abbey, Coventry, on 18 February 1925 during acceptance tests; the Romanian pilot being killed.
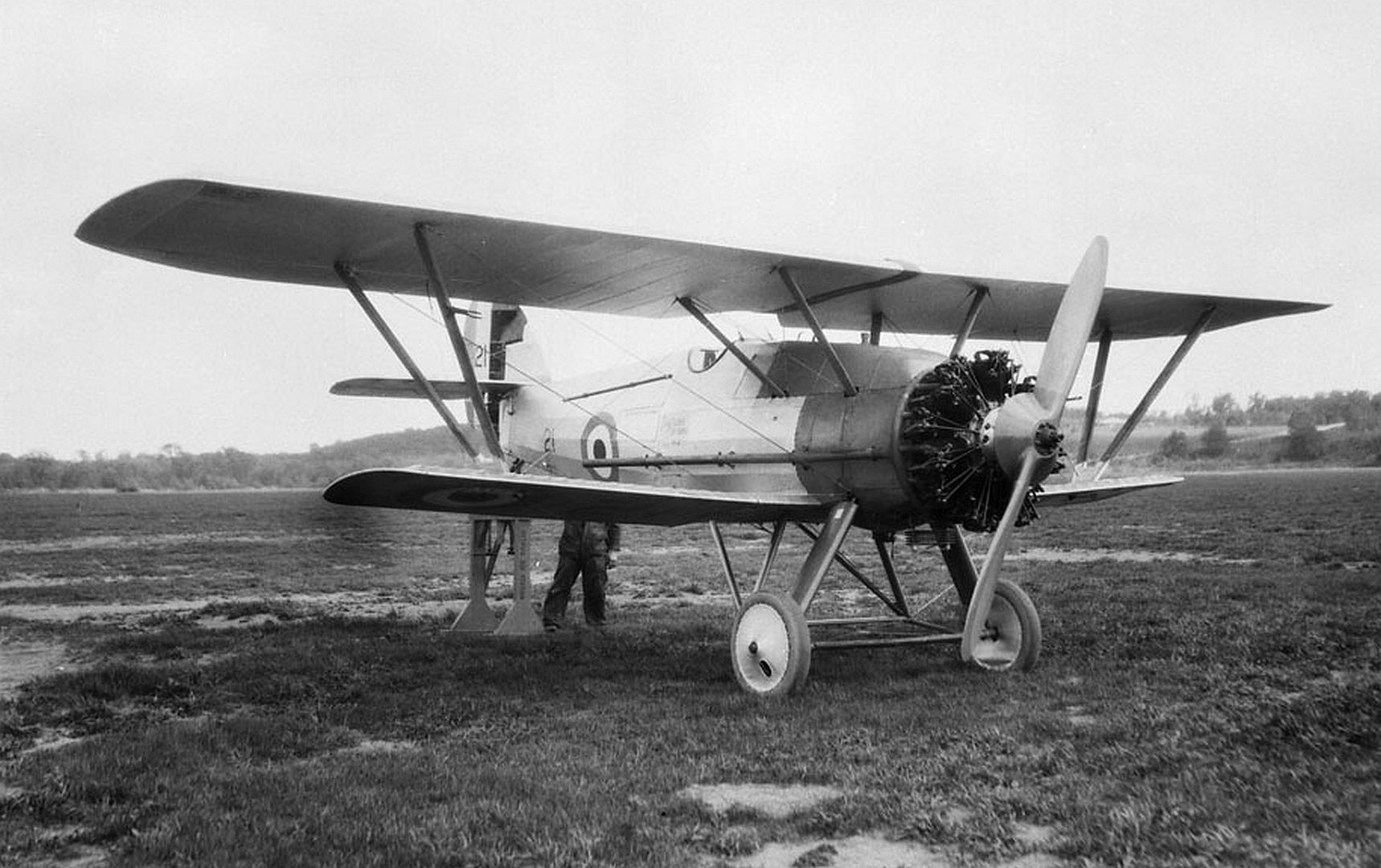
The main production version was the Siskin IIIA ordered in 1926, which originally was powered with a Jaguar IV engine, but was later re-engined with the supercharged Jaguar IVA engine. The supercharger, a novel idea at the time, had little effect on performance below 10,000 ft (3,050 m), but it greatly improved speed and climb above that height. Following an evaluation of two Siskin IIIs the Royal Canadian Air Force ordered 12 IIIAs which were delivered between 1926 and 1931.
With Armstrong-Whitworth busy building the Armstrong Whitworth Atlas some of the later Siskin IIIA production was sub-contracted out to Blackburn, Bristol, Gloster, and Vickers.
RAF Service
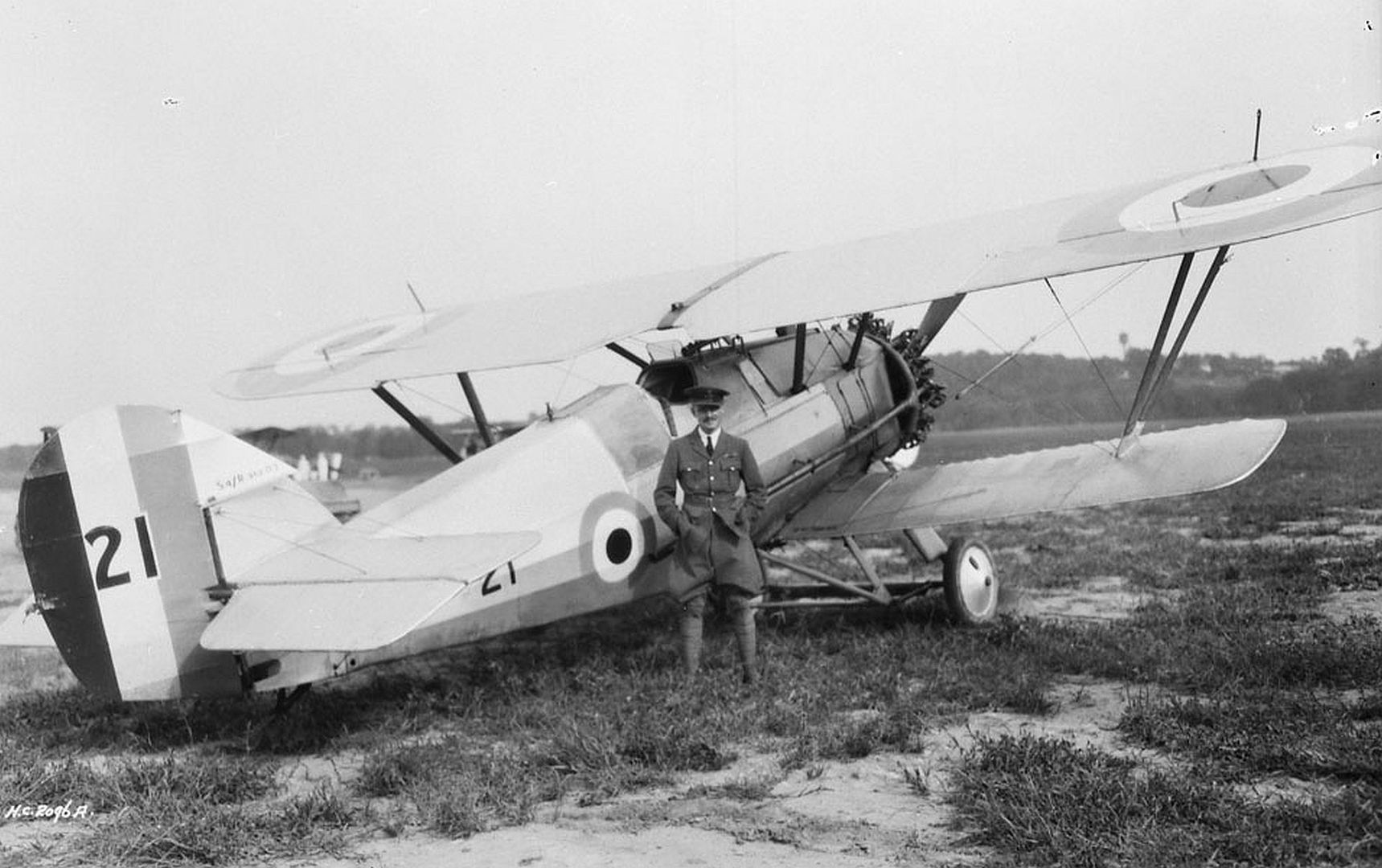
The first Siskin IIIs were delivered to No. 41 Squadron RAF at RAF Northolt in May 1924, quickly followed by No. 111 Squadron RAF. The Siskin III was popular in service, being highly manoeuvrable, although slightly underpowered. The improved Siskin IIIA was first delivered to No. 111 Squadron in September 1926. The Siskin was used by 11 RAF squadrons. The last operational RAF Siskins were replaced in October 1932 by Bristol Bulldogs.
The Siskin presented exhibitions of flying at every RAF display from 1925 to 1931.
Sweden
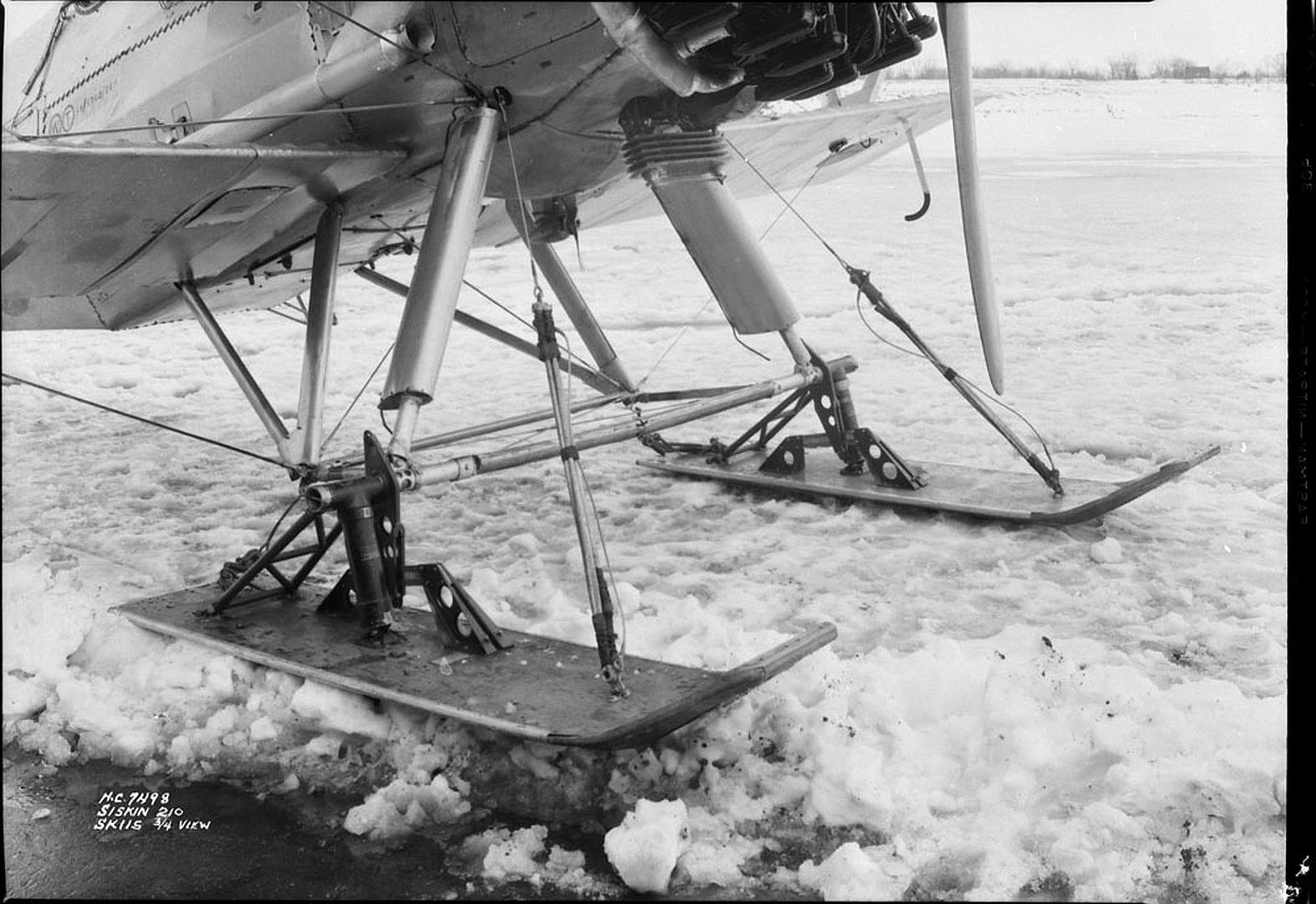
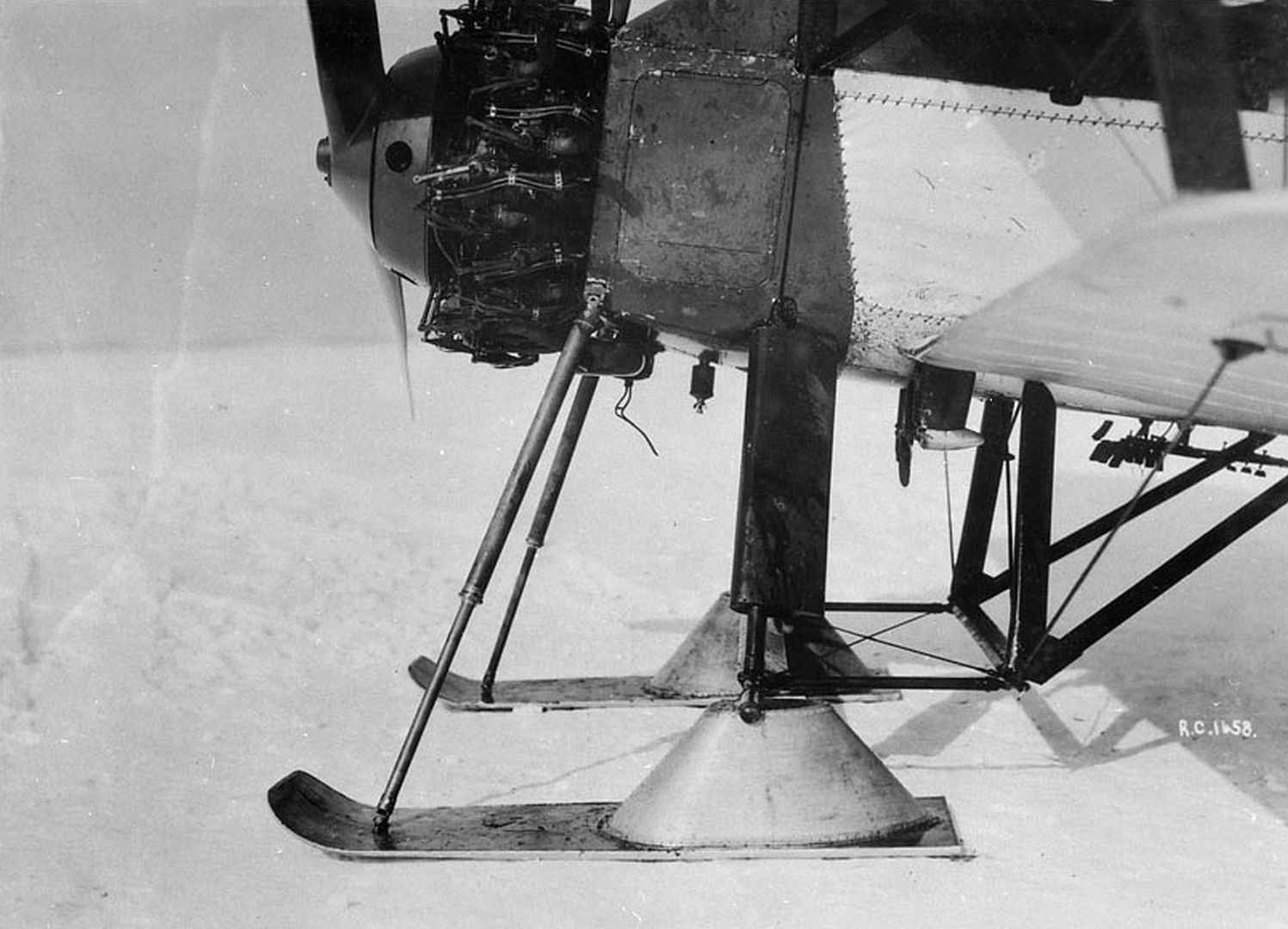
The ski-equipped second Siskin II aircraft was sold to the Royal Swedish Air Force in 1925.
Canada
Canada used the aircraft from 1926 until 1939. In 1926, the British Air Ministry sent two Siskin IIIs to Canada for testing by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) under winter flying conditions. The test pilot was Clennell H. Dickins. The Siskin was considered a modern type when it was acquired by RCAF, which eventually purchased the Mark IIIA, used to equip the Fighter Flight at Camp Borden and Trenton. In 1937, the Flight became No. I (Fighter) Squadron and was transferred from Trenton to Calgary in August 1938.
Siskin aircraft remained with this unit until the outbreak of the Second World War, eventually to be replaced by Hawker Hurricanes in 1939. The airframes were then turned over to various technical establishments for use as instructional airframes.
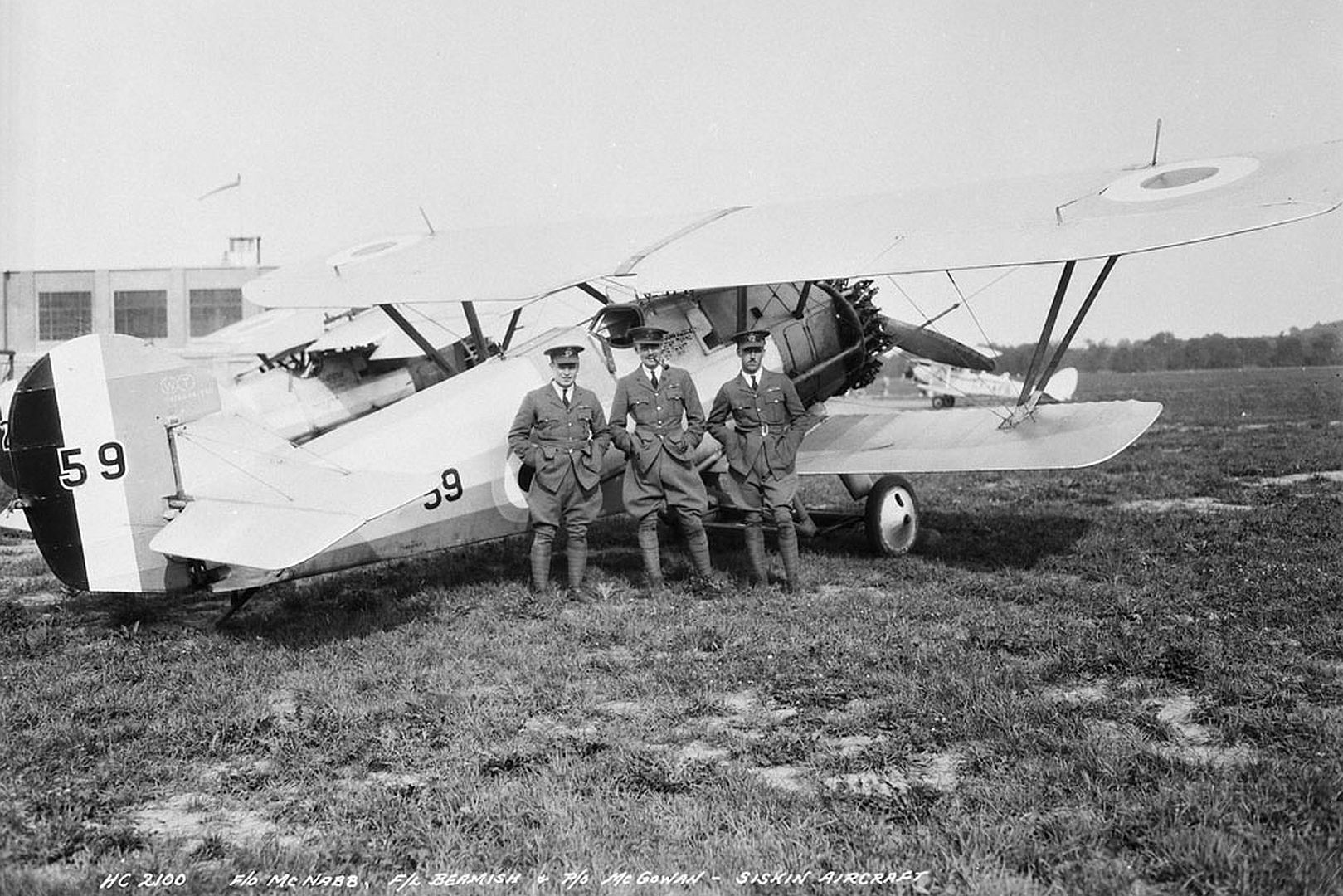
Like its RAF counterparts, in 1929, a three-plane Siskin air demonstration team was formed at Camp Borden, Ontario ? the RCAF's first official flight demonstration team. The aerobatic team put on popular solo and formation displays from coast to coast.
Air racing
The Siskin was used as a successful racing aircraft, a Siskin V flown by Flight Lieutenant Barnard winning the 1925 Kings Cup Race at a speed of more than 151 mph.
Variants
Siddeley Deasy S.R.2 Siskin ? Prototype fighter aircraft built by Siddeley-Deasy and powered by Dragonfly engine. Three built.
Siskin II ? fabric covered steel-tube fuselage and wooden wings. Two built, one two-seater and one single-seater.
Siskin III ? all-metal production version (64 built for RAF)
Siskin IIIA ? main production variant ordered in 1926 (Total 348 built, 340 for RAF, eight for RCAF)
Siskin IIIB ? prototype with improved engine. Single example converted from Siskin IIIA.
Siskin IIIDC ? two-seat dual control version (Total 53 built, 47 for RAF, two for RCAF, two for AST, two for Estonia[21]) a further 32 were converted from Siskin IIIs.
Siskin IV ? civil racing version (one built[)
Siskin V ? single-seat fighter for Romania. 65 ordered and at least 10 completed before order cancelled. Two used for racing.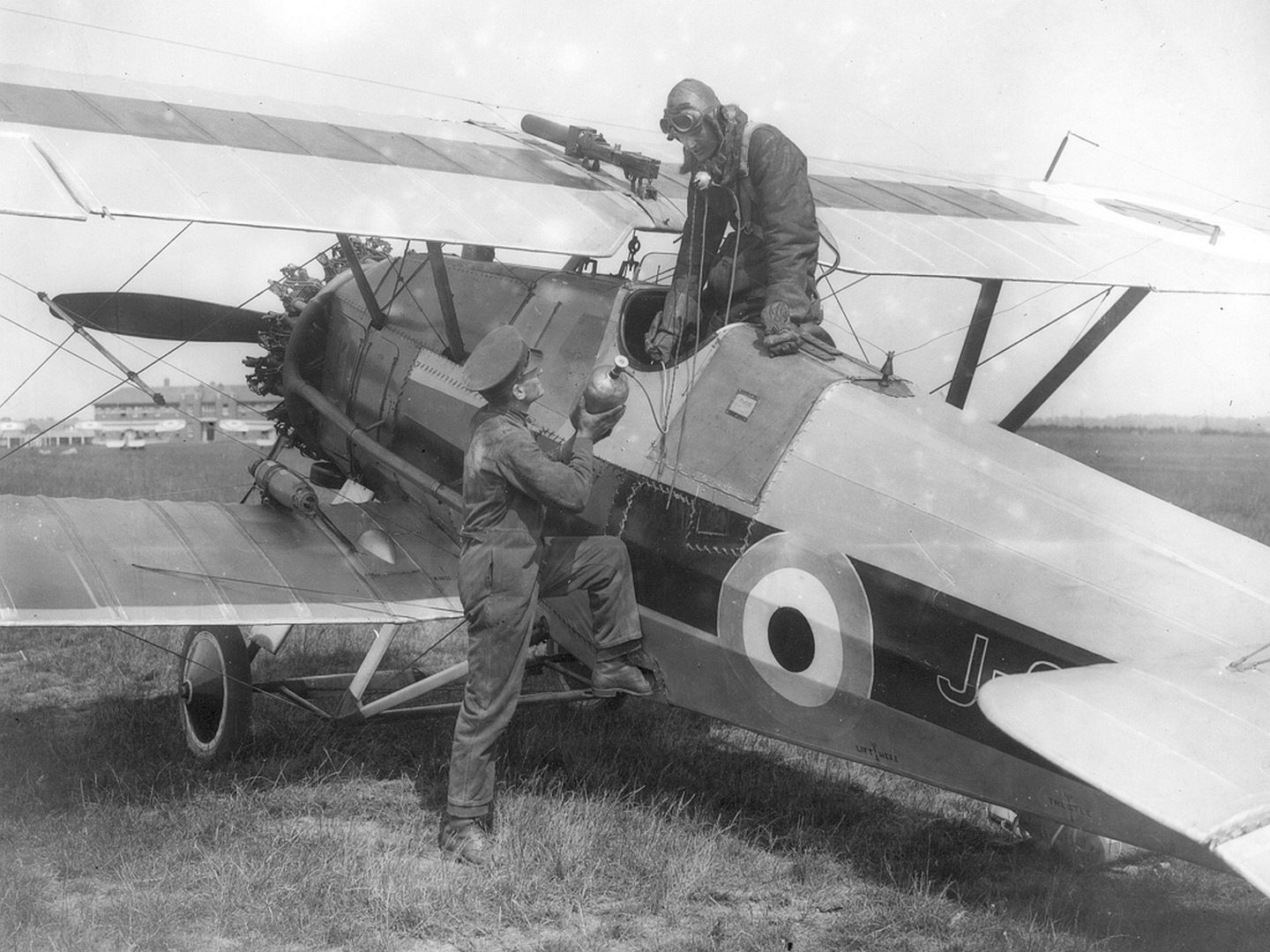
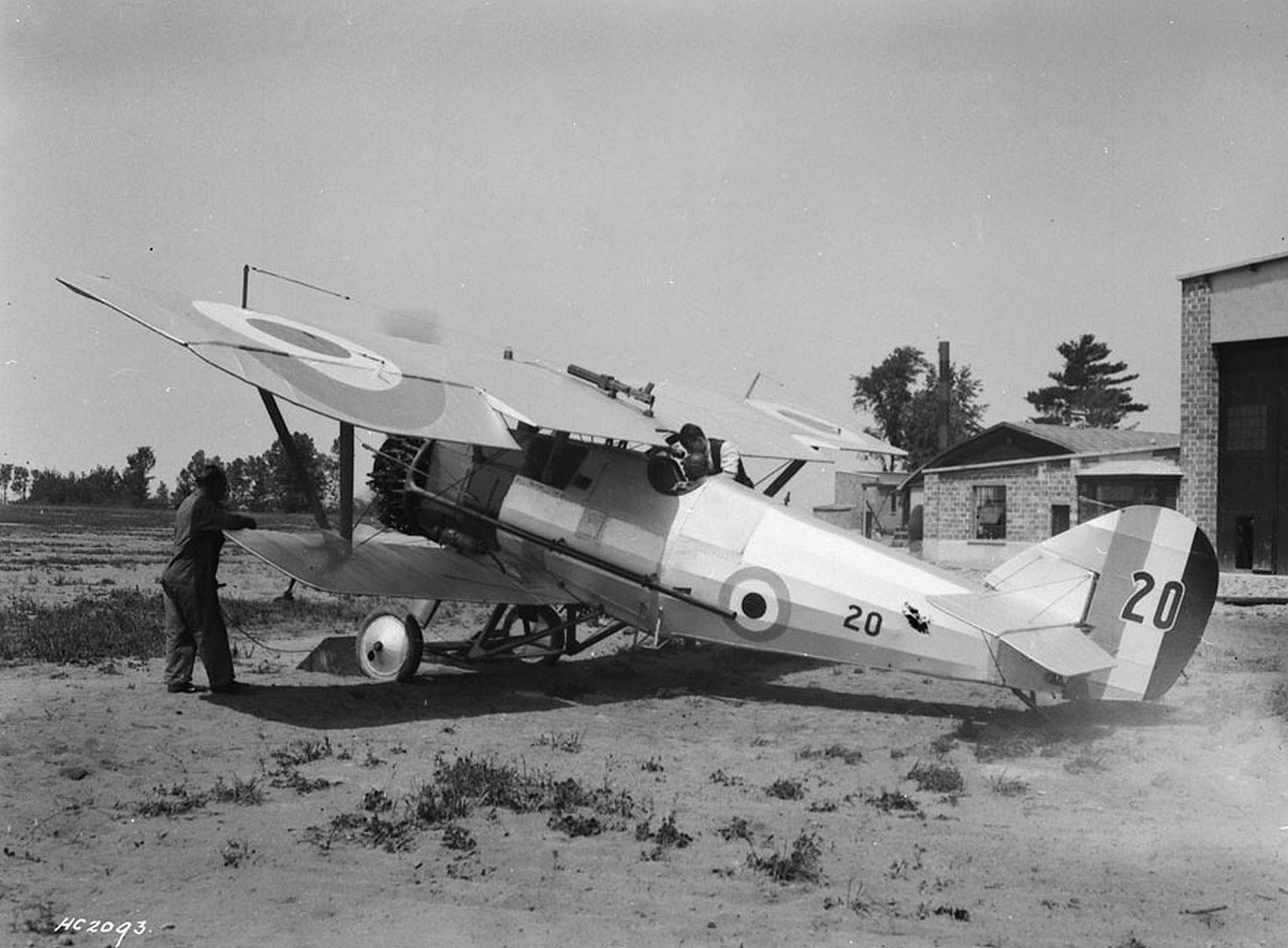
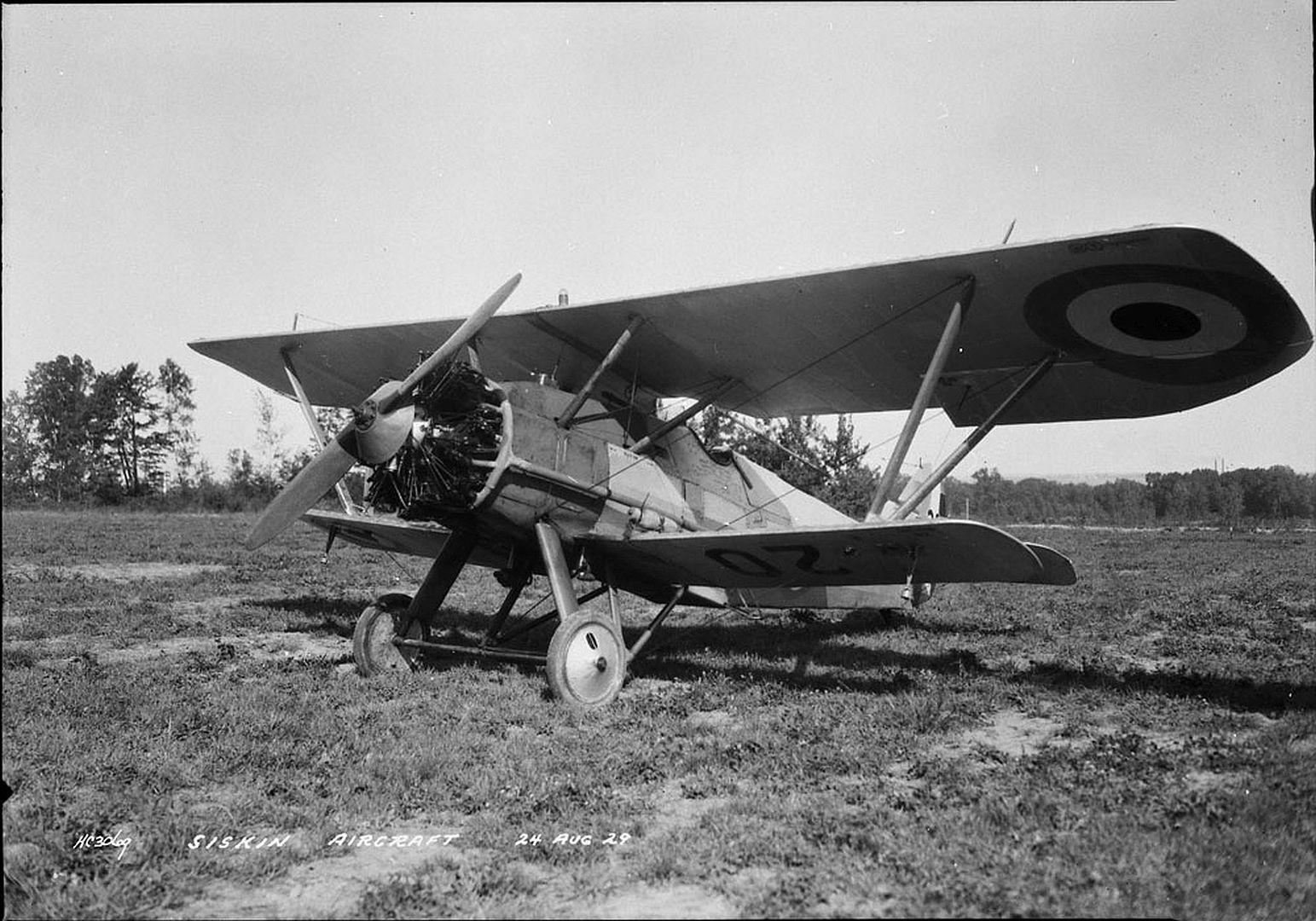
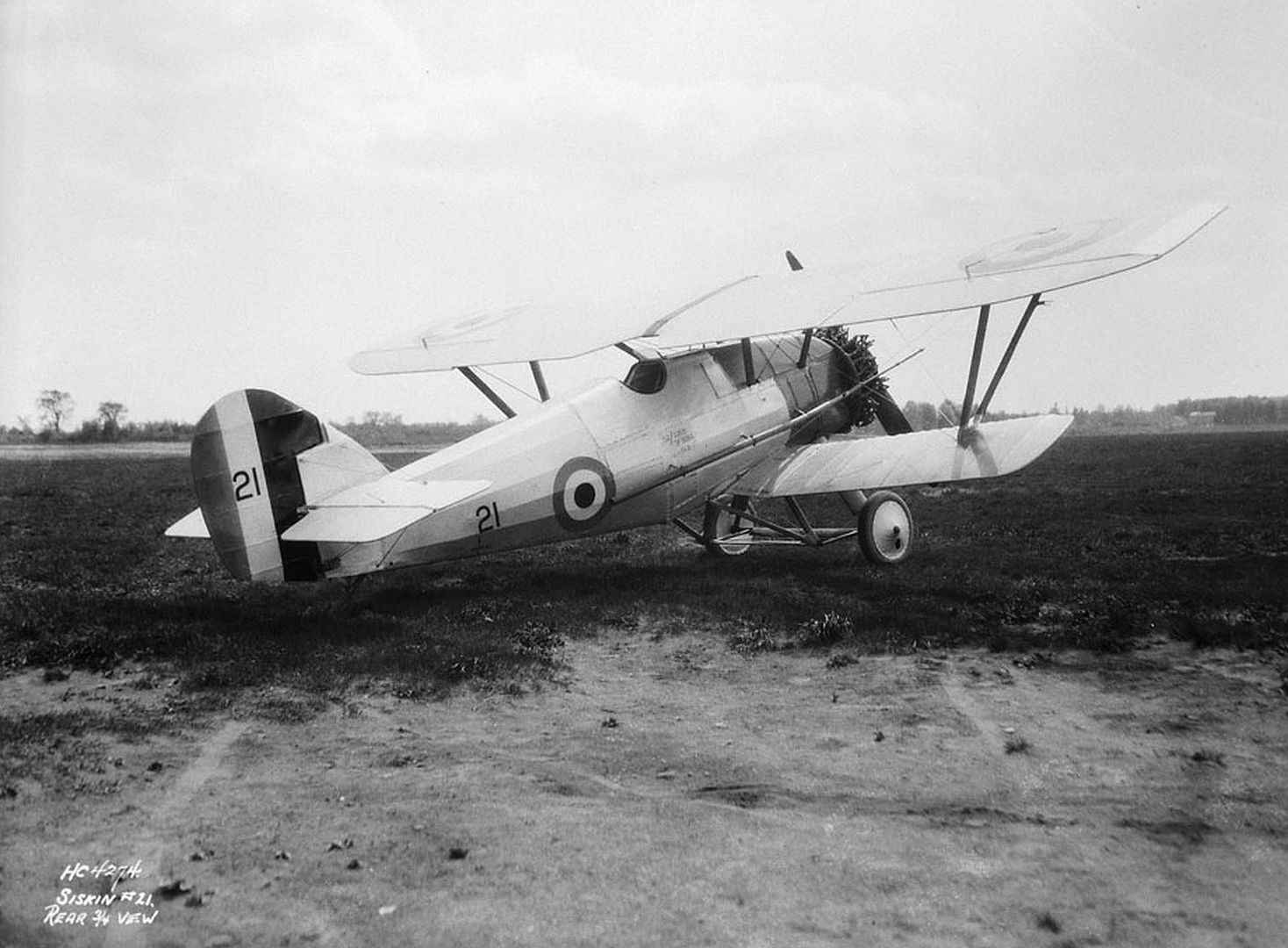
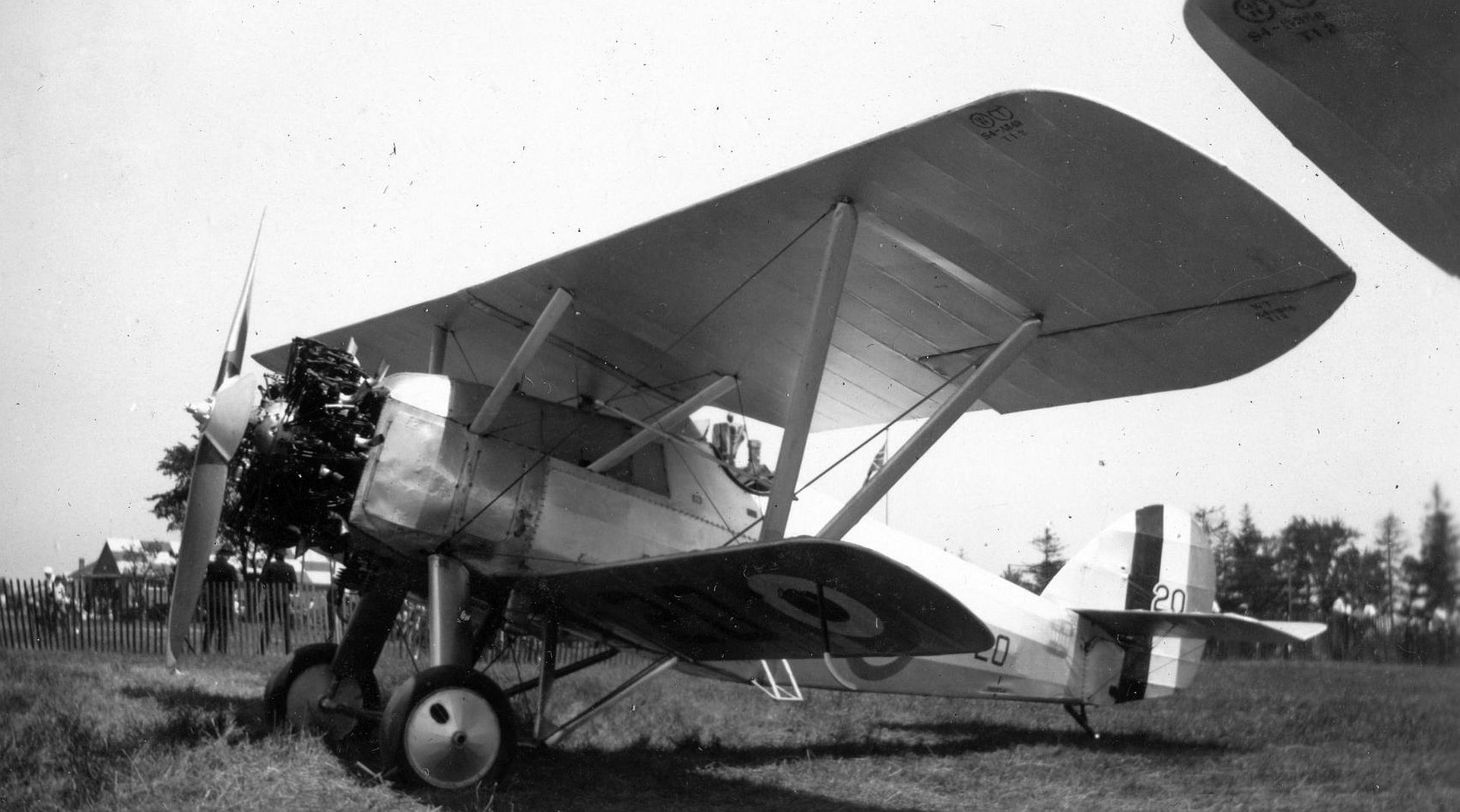
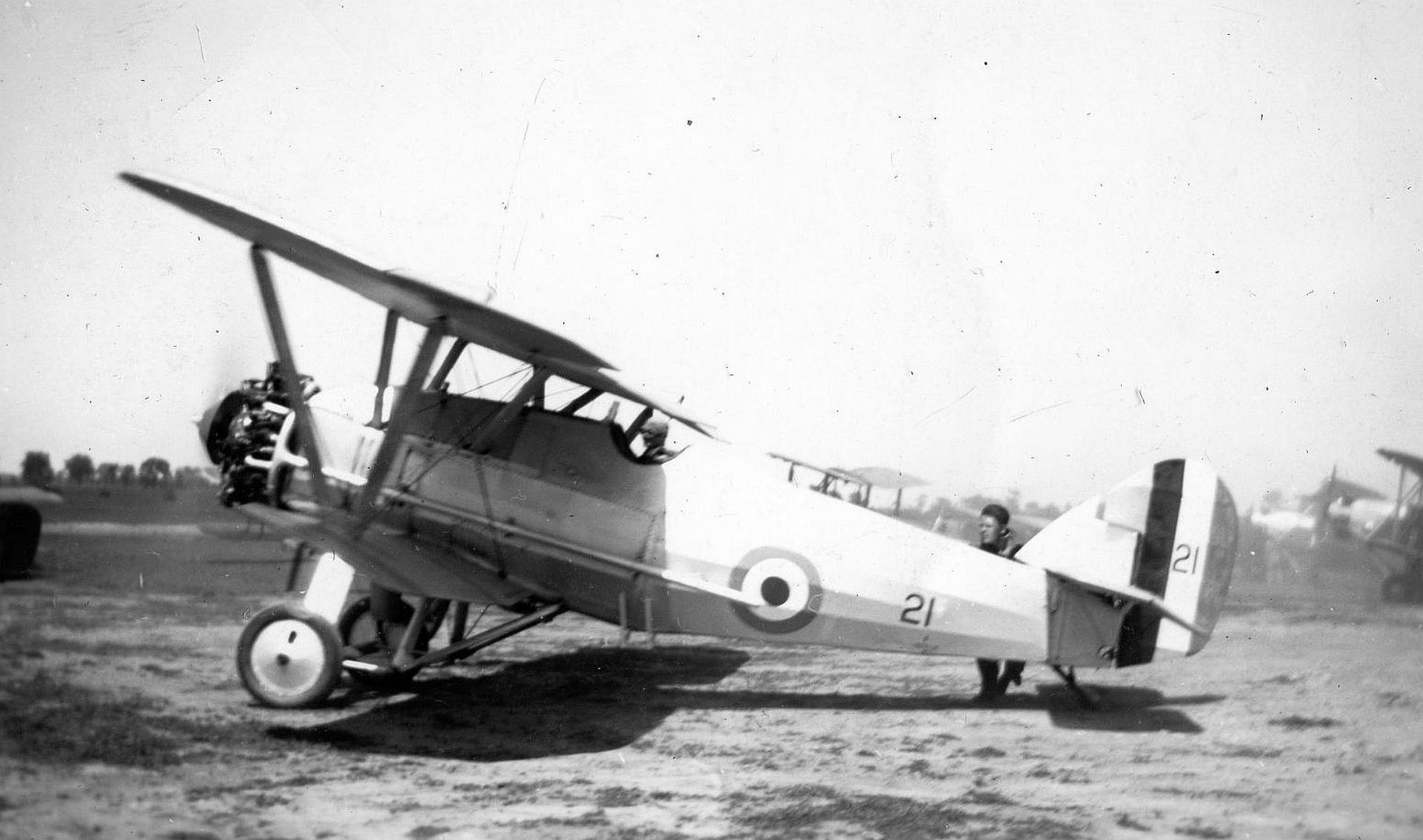
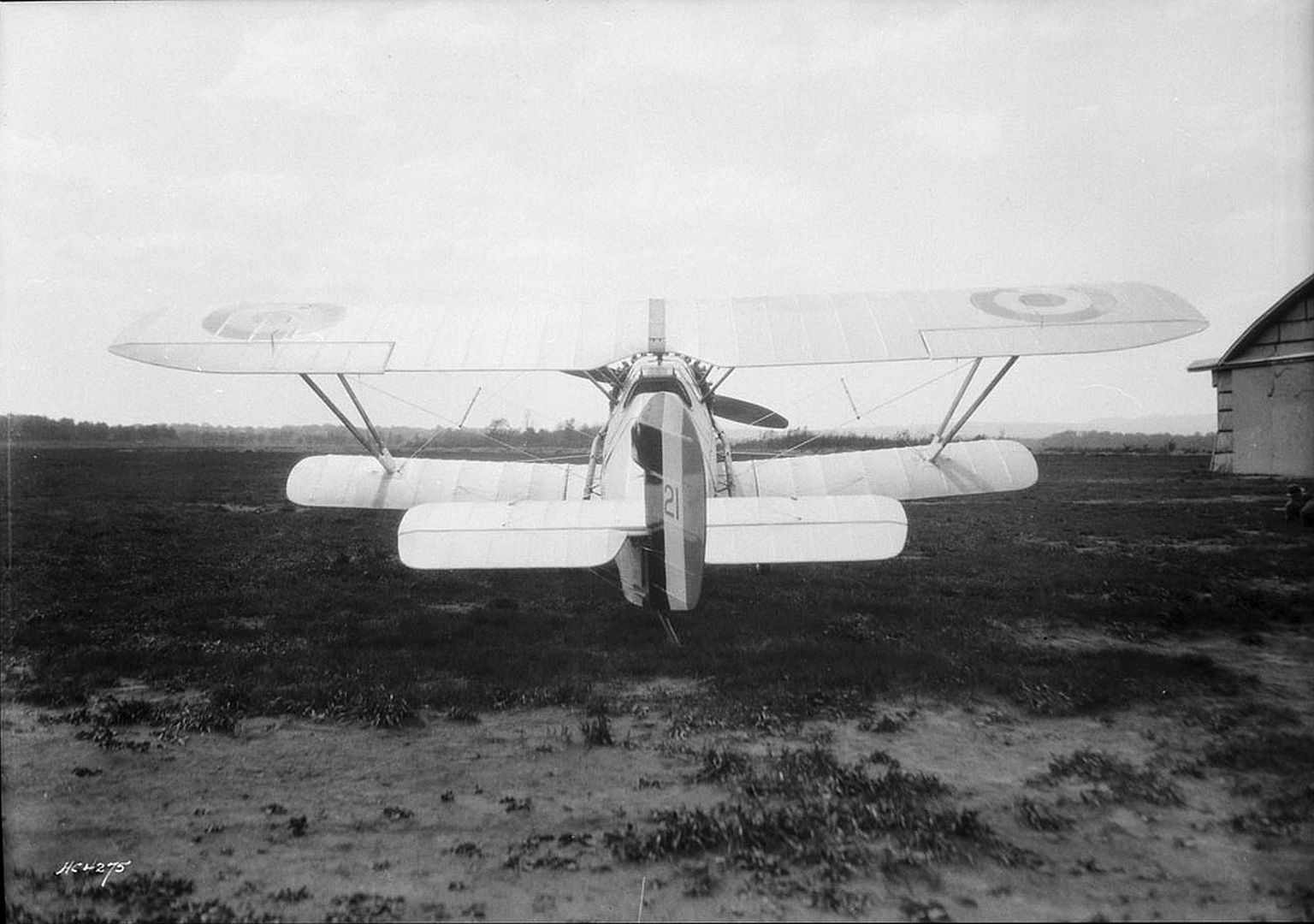
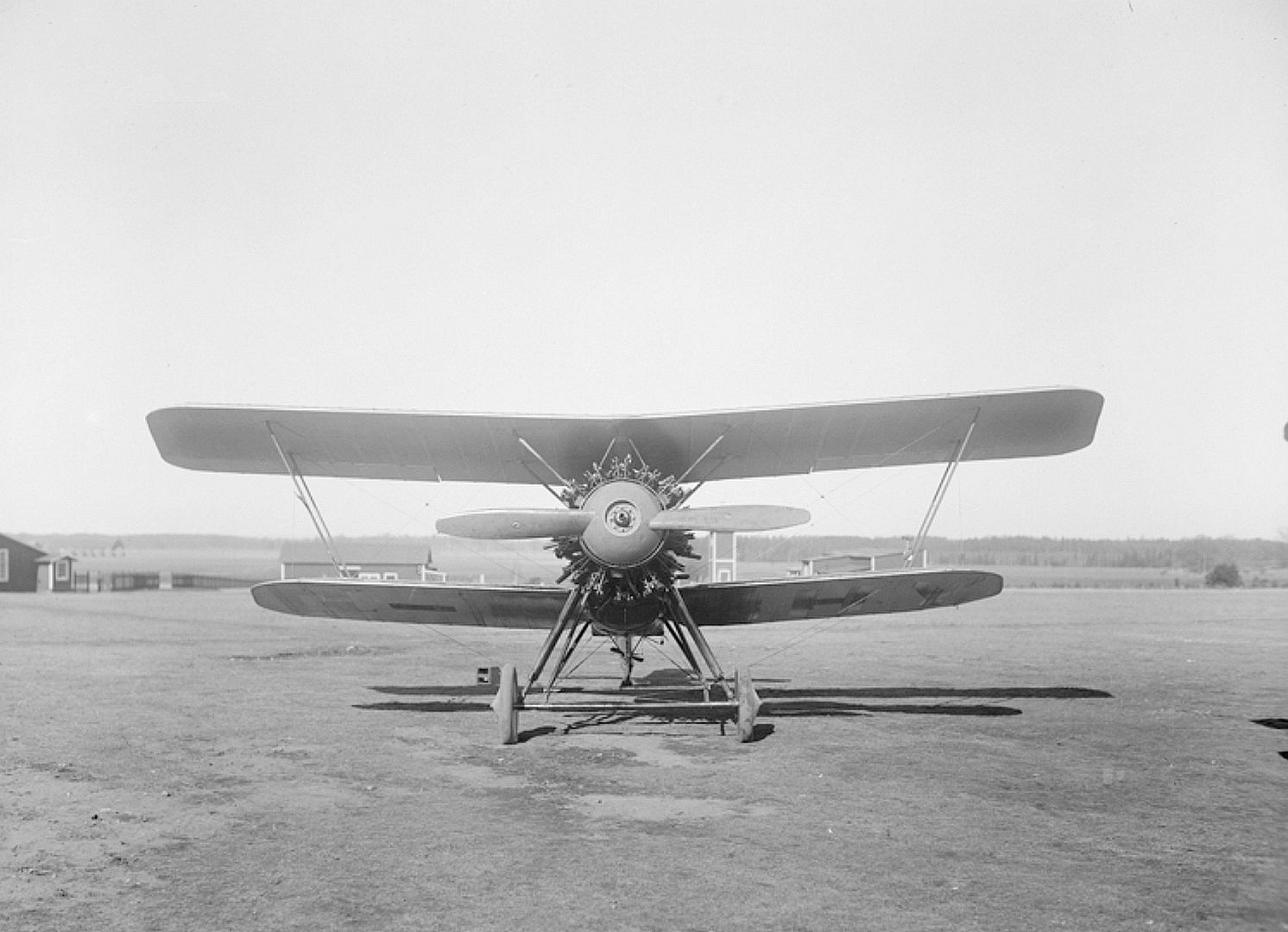
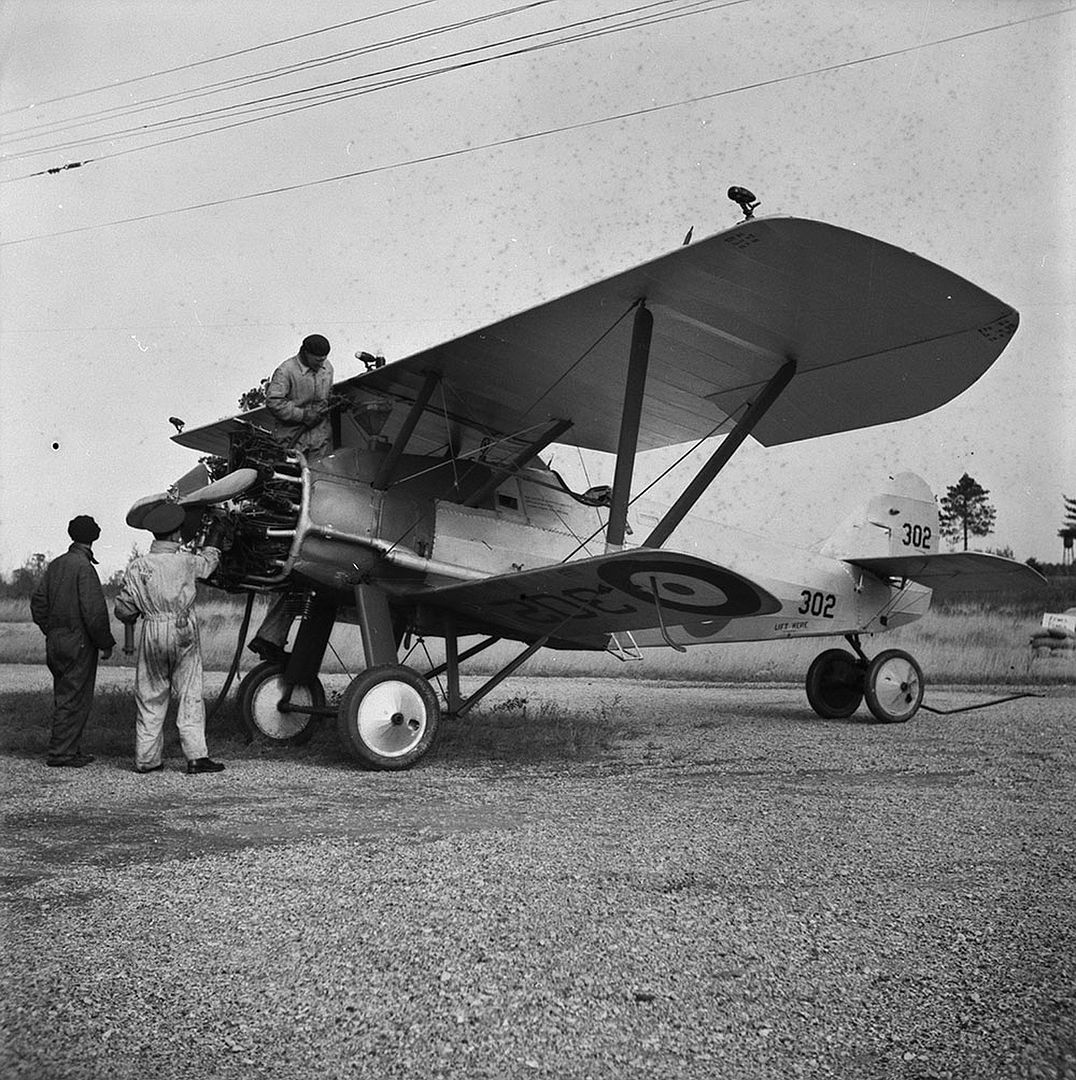
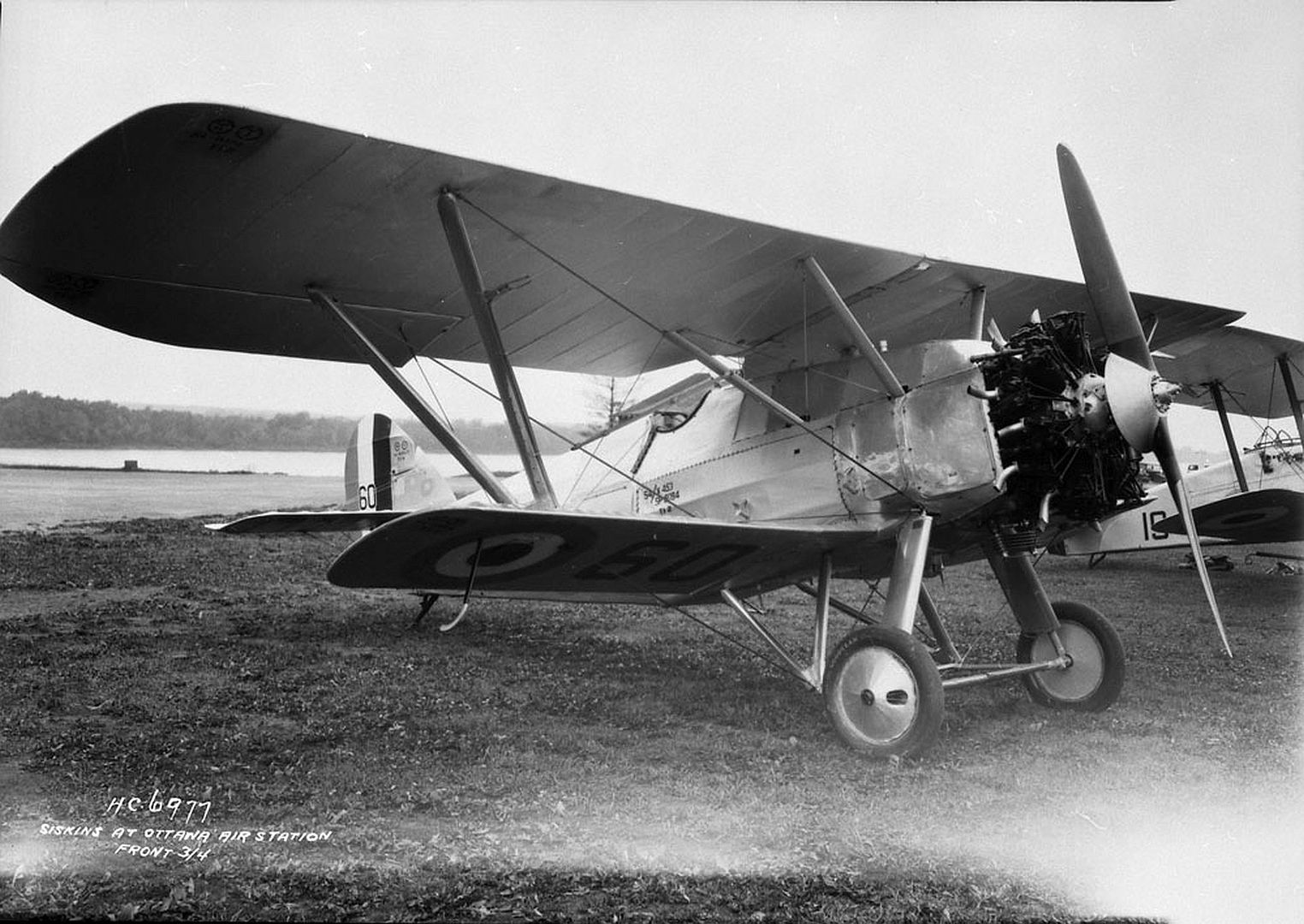
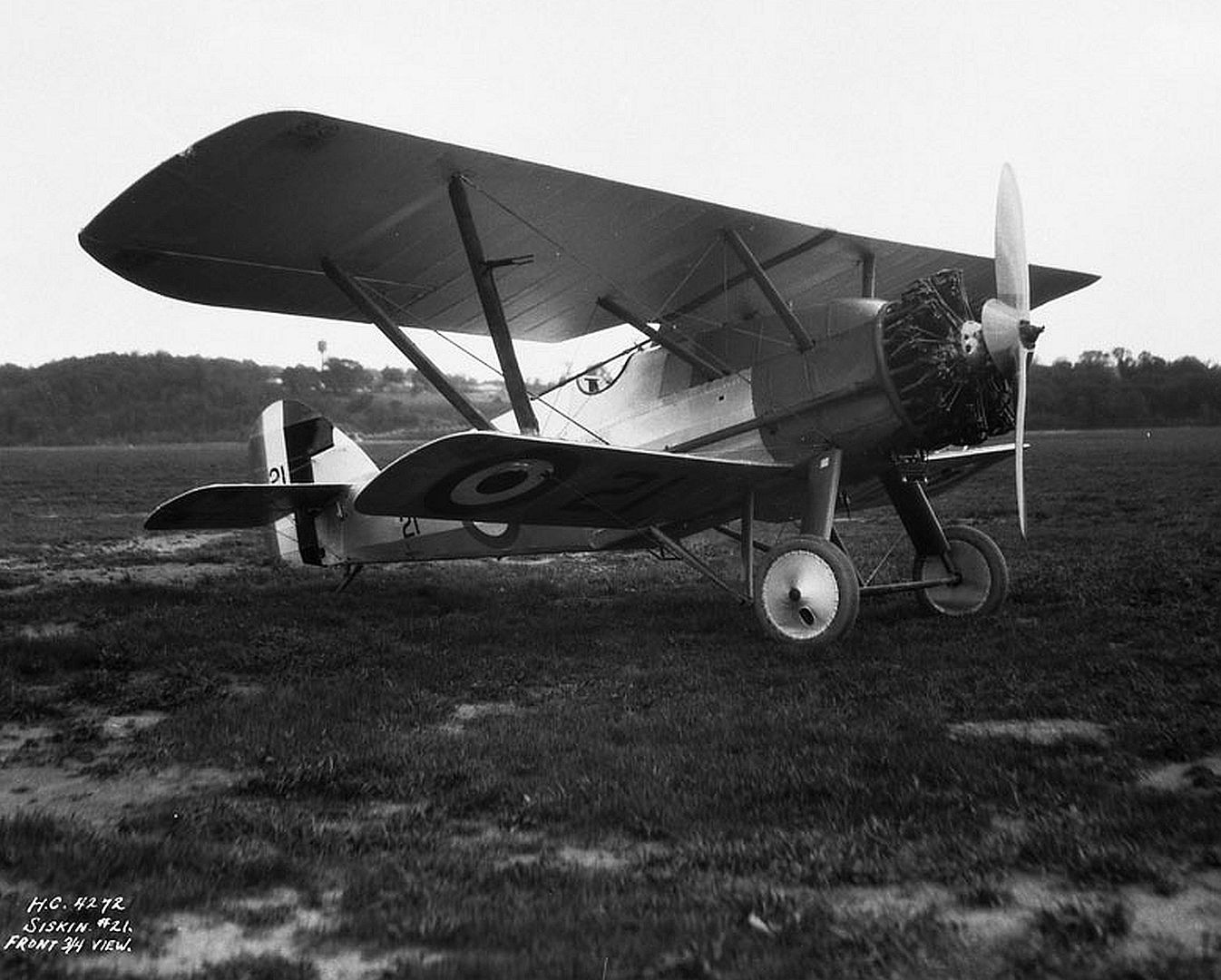
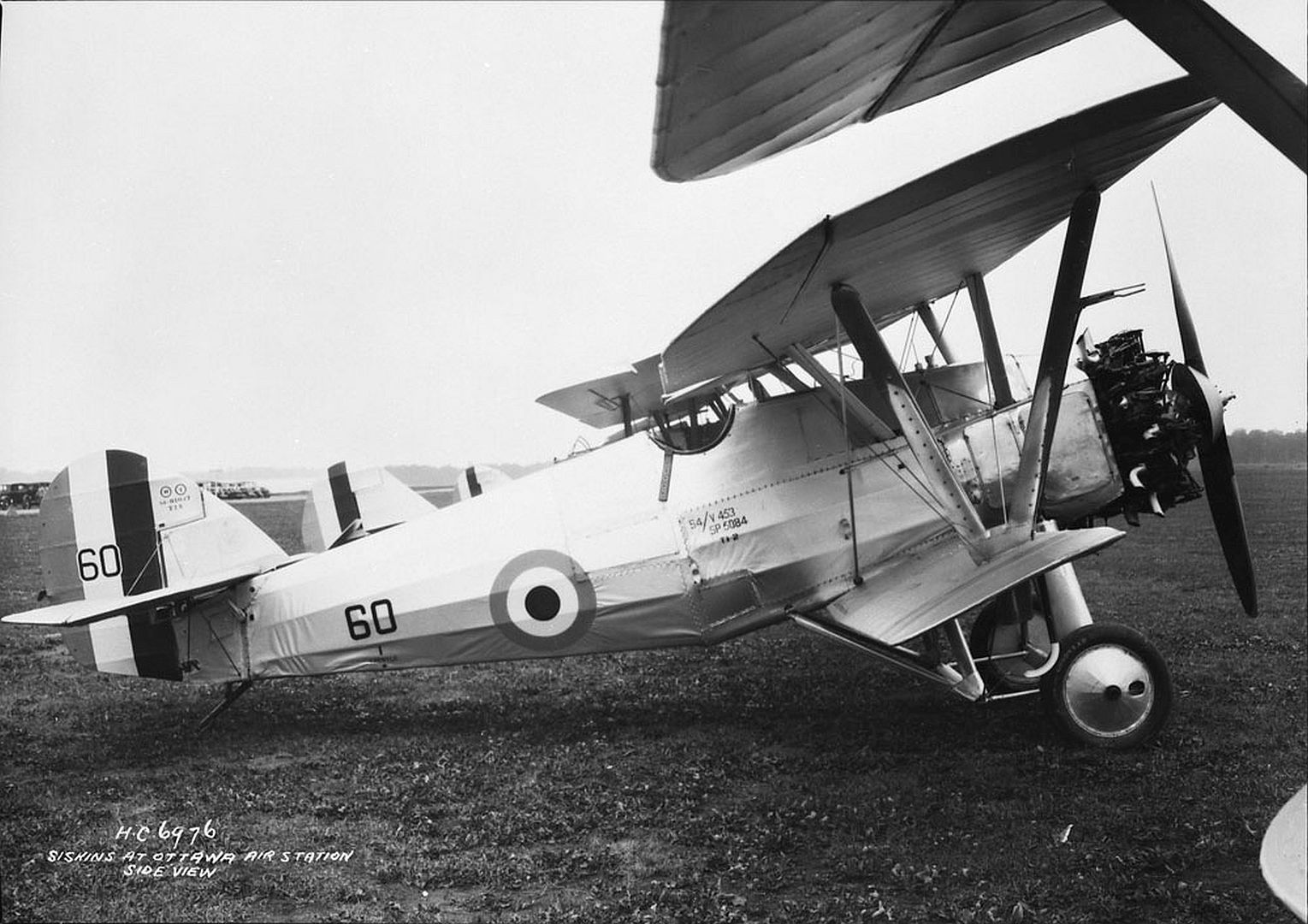
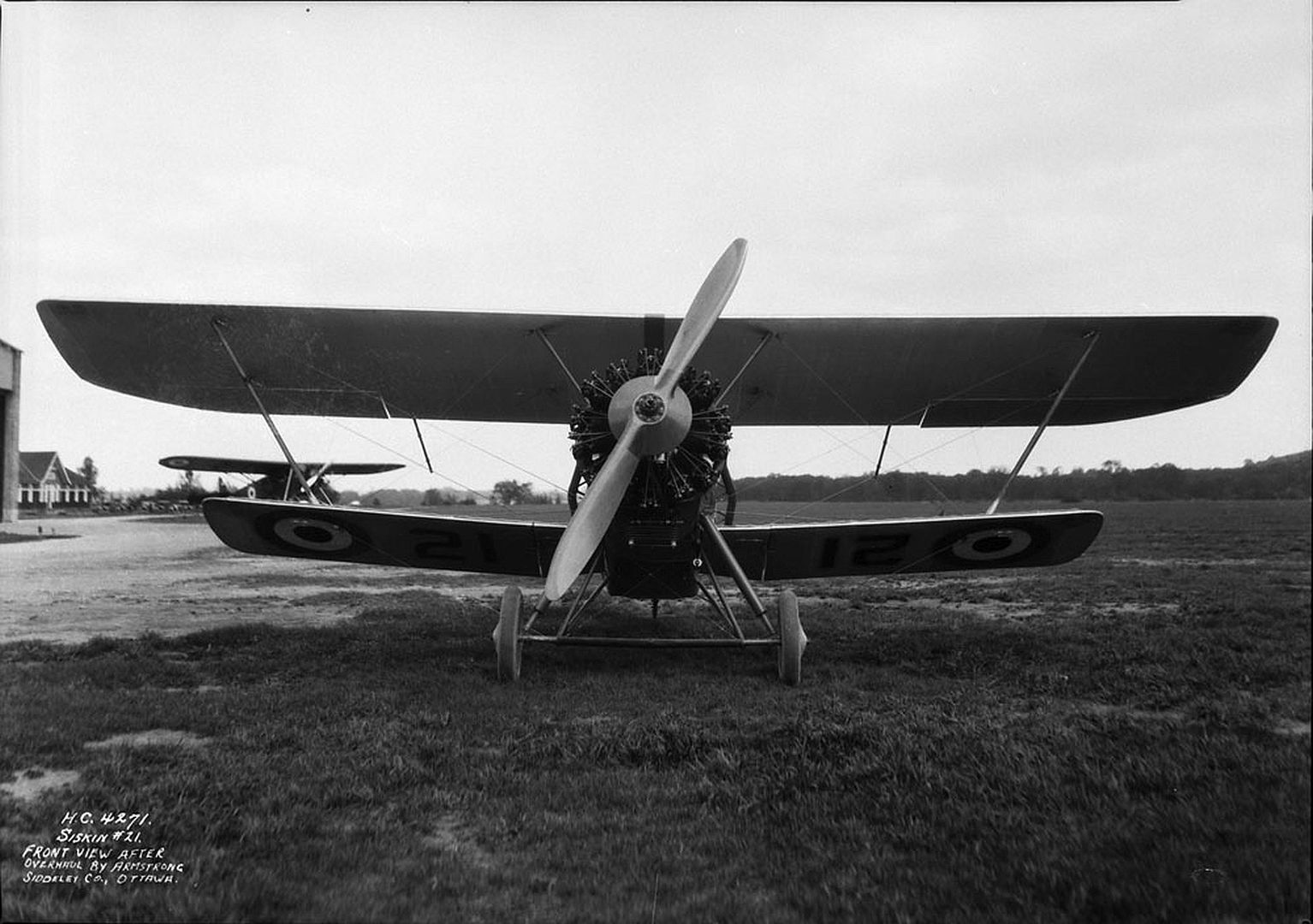
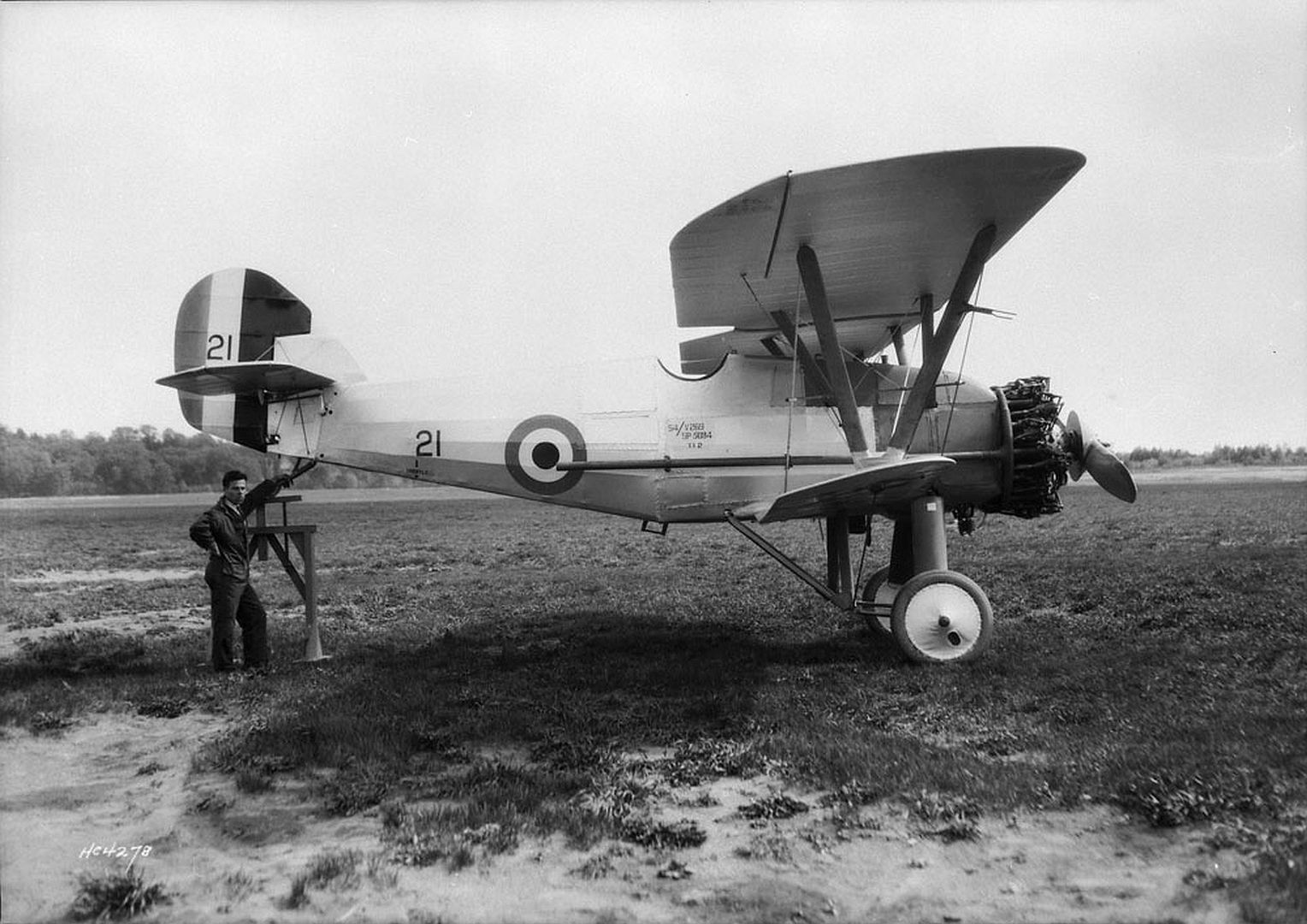
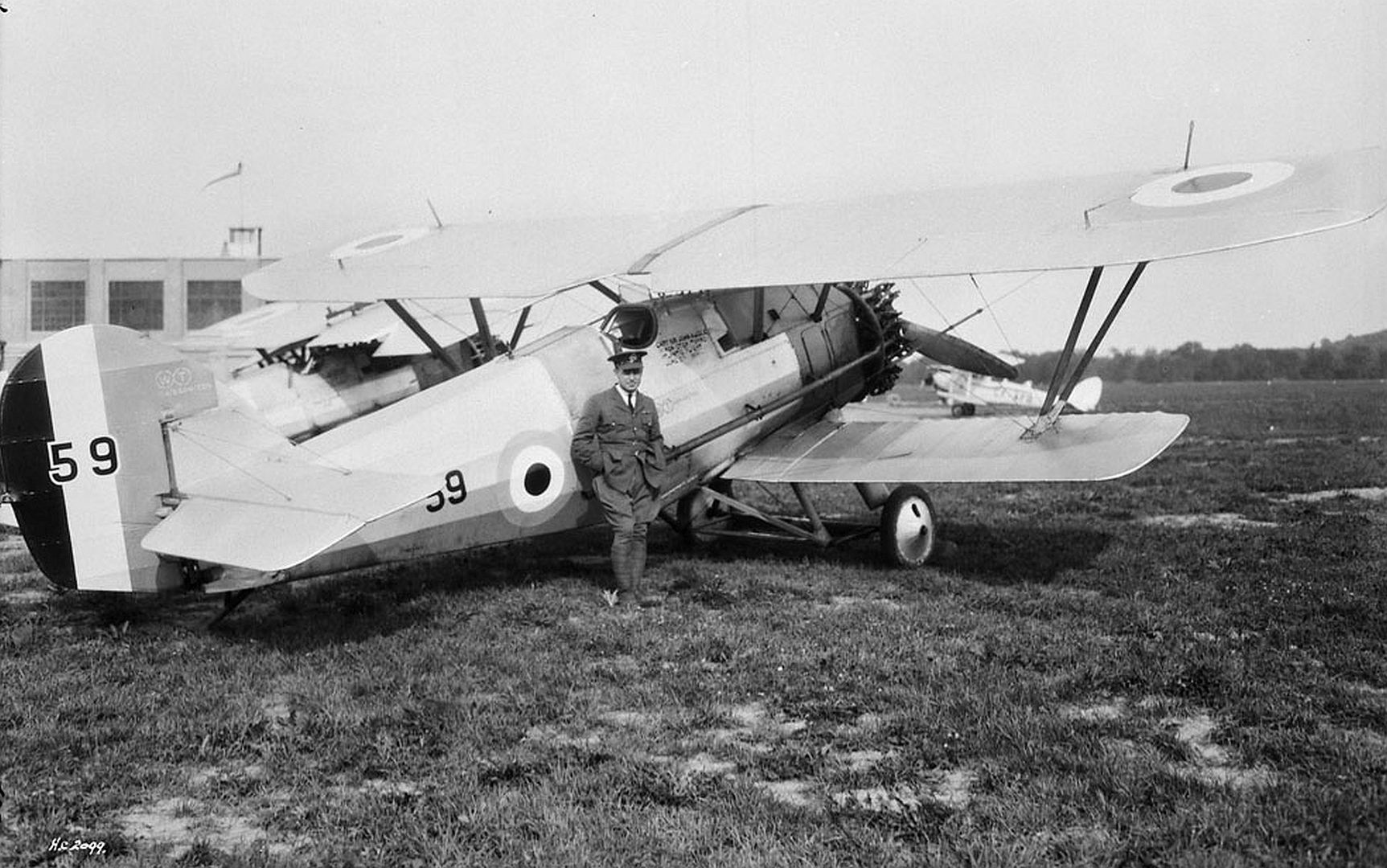
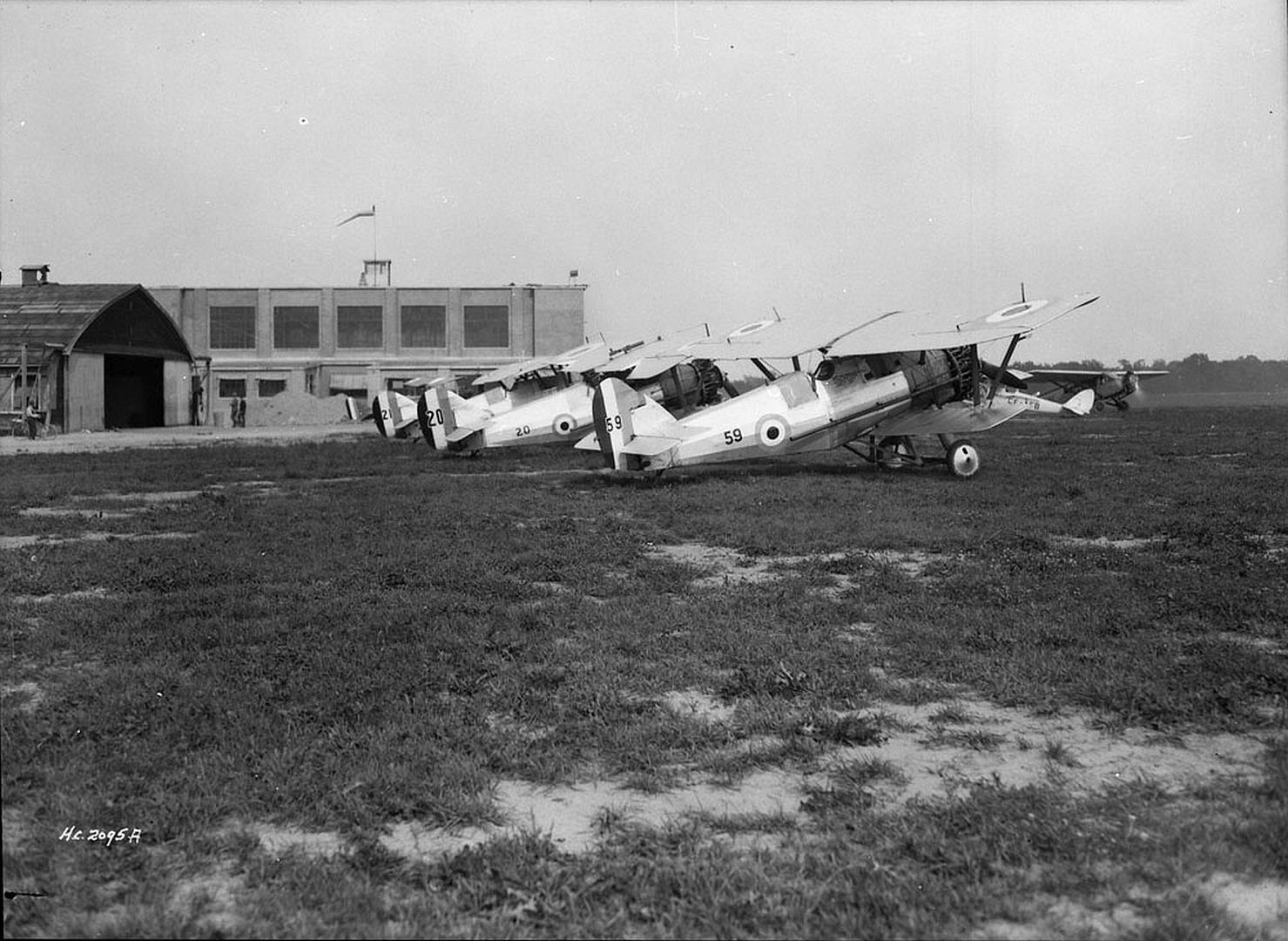
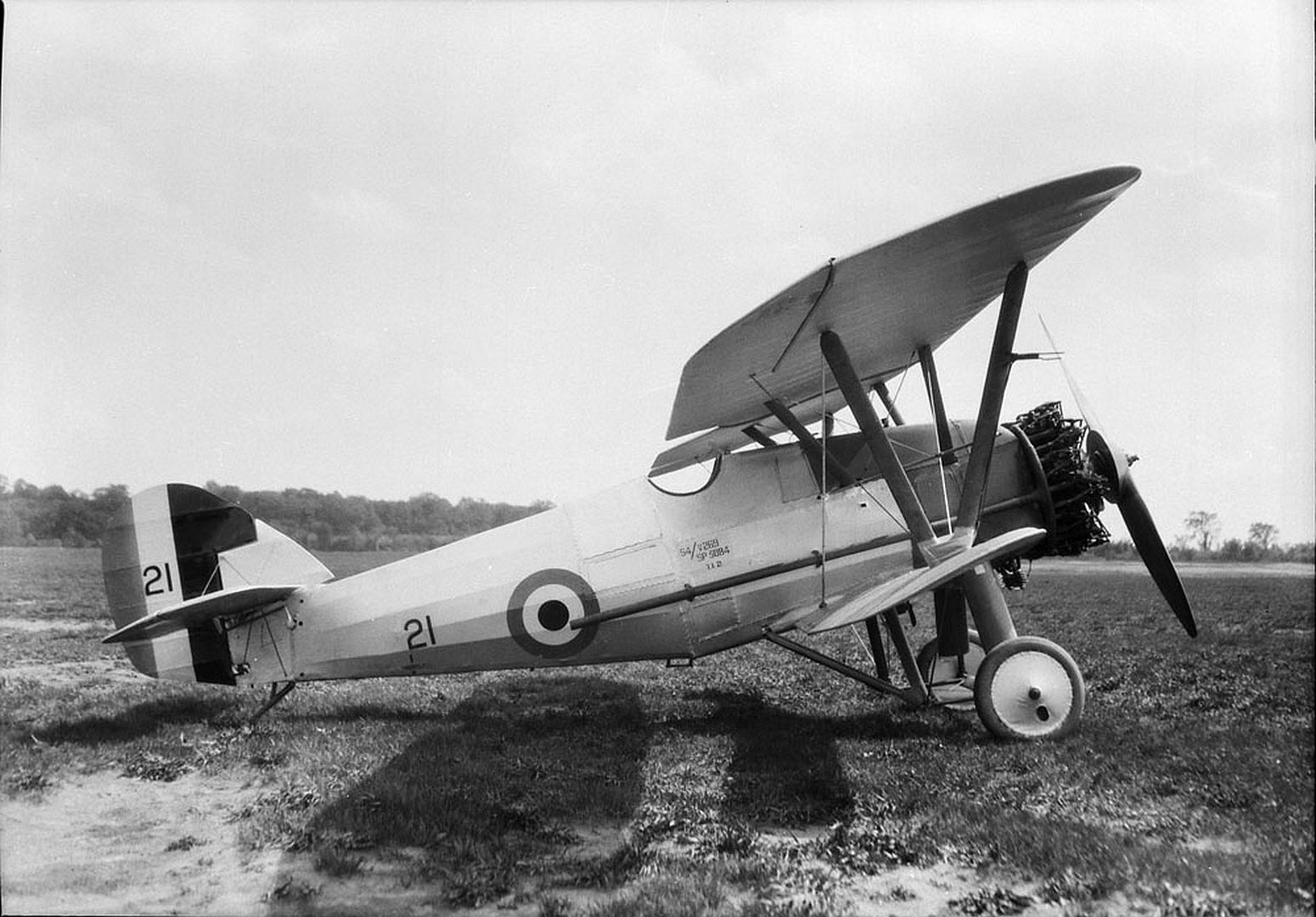
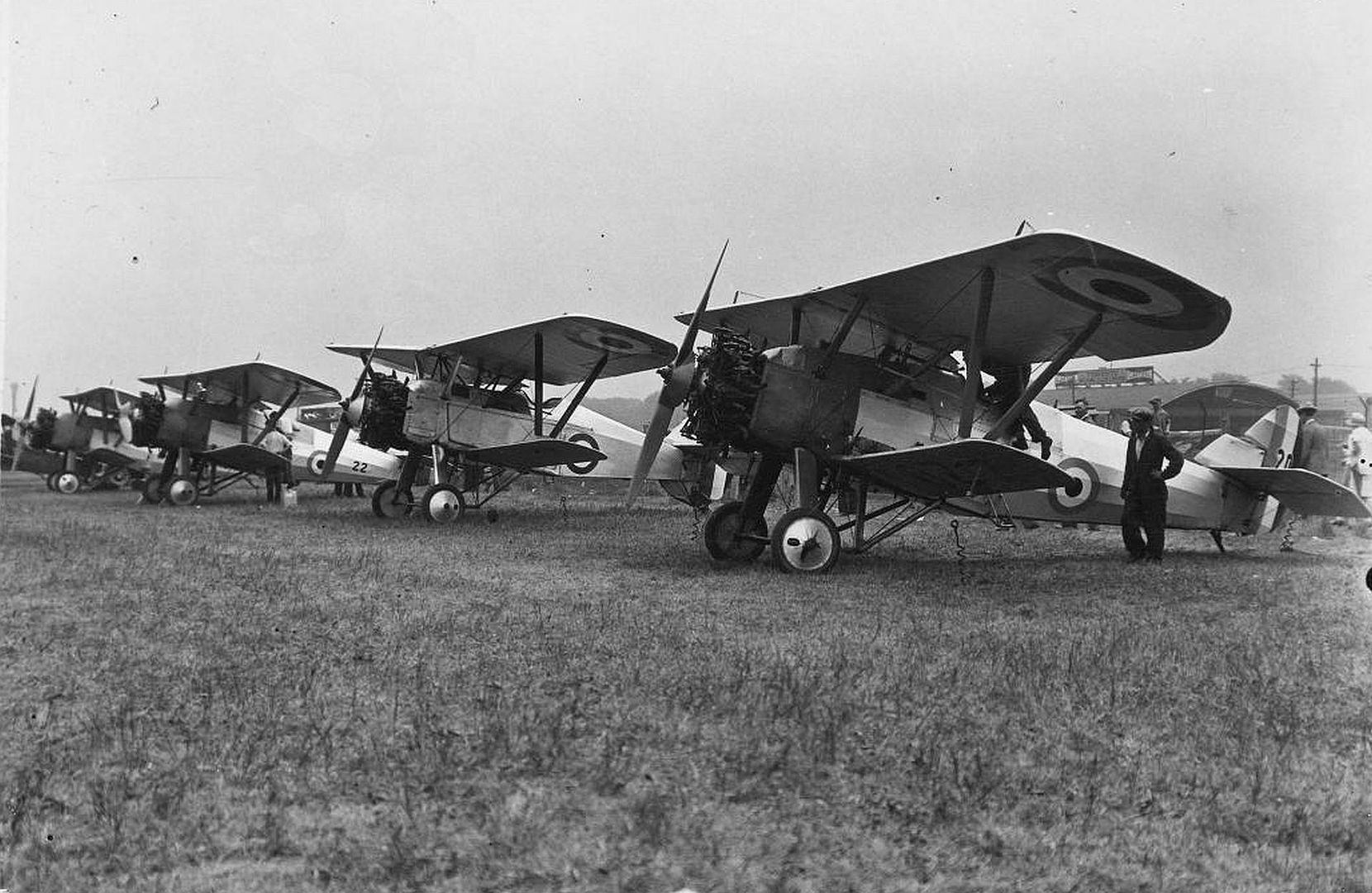
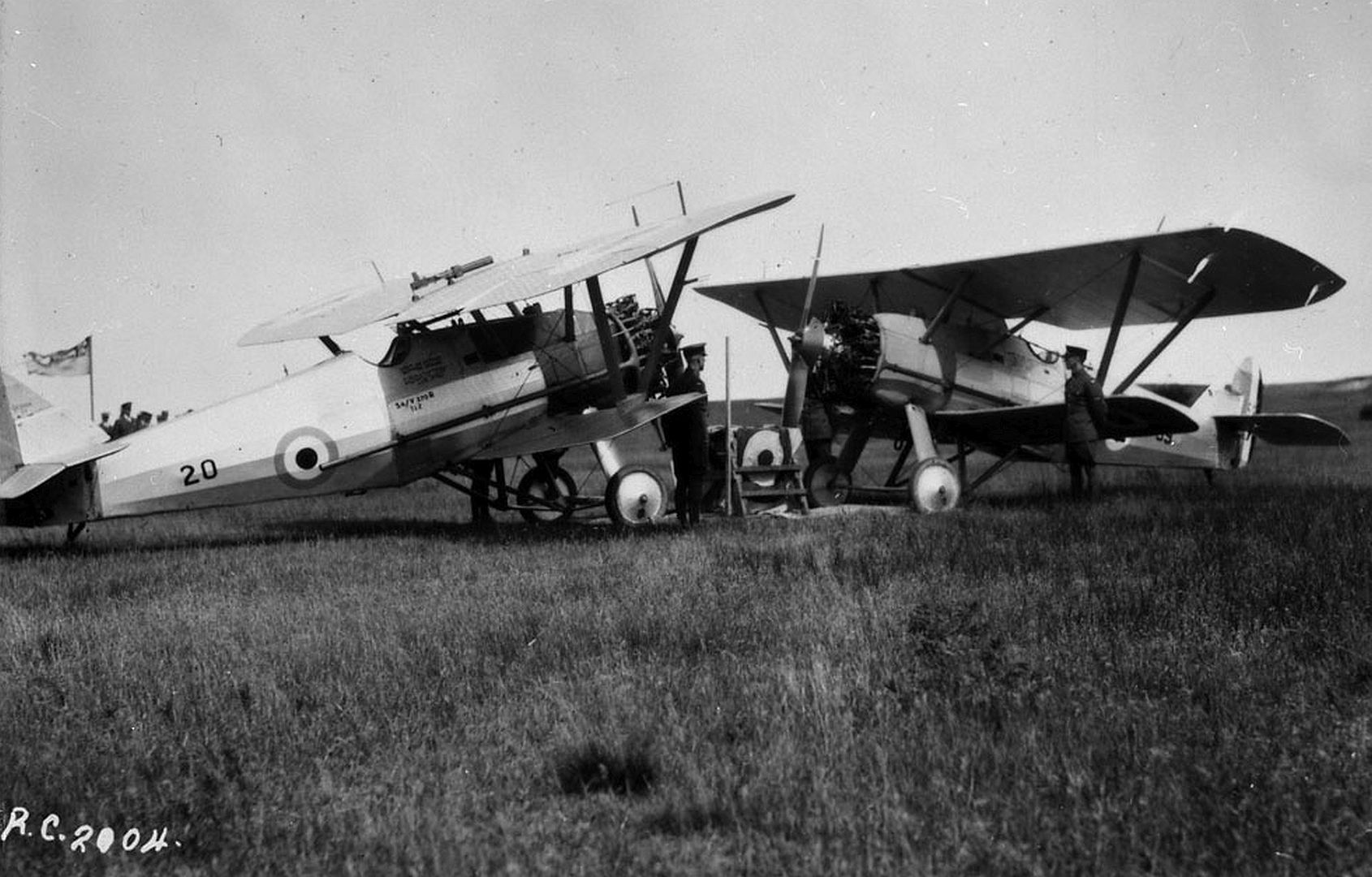
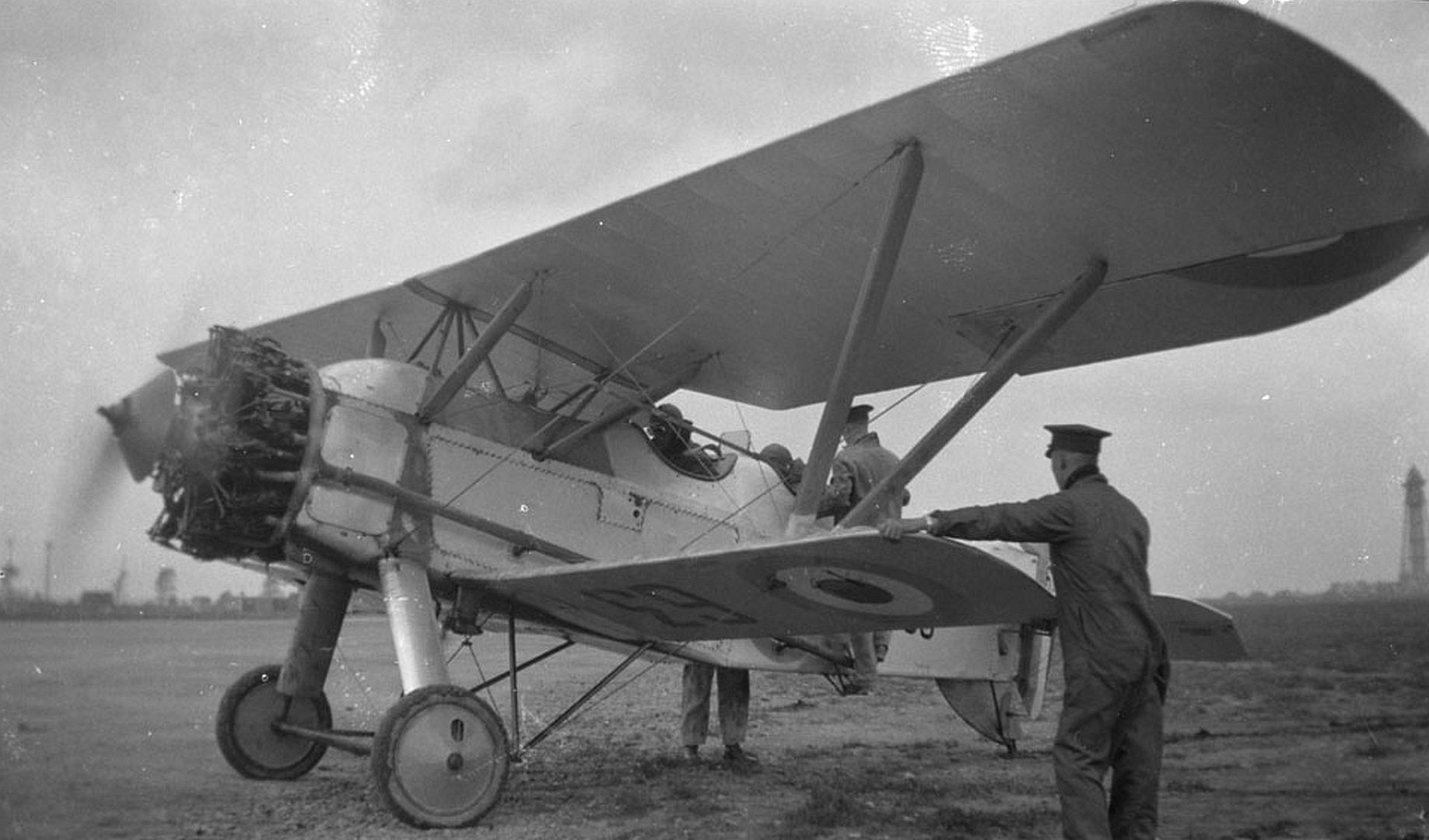
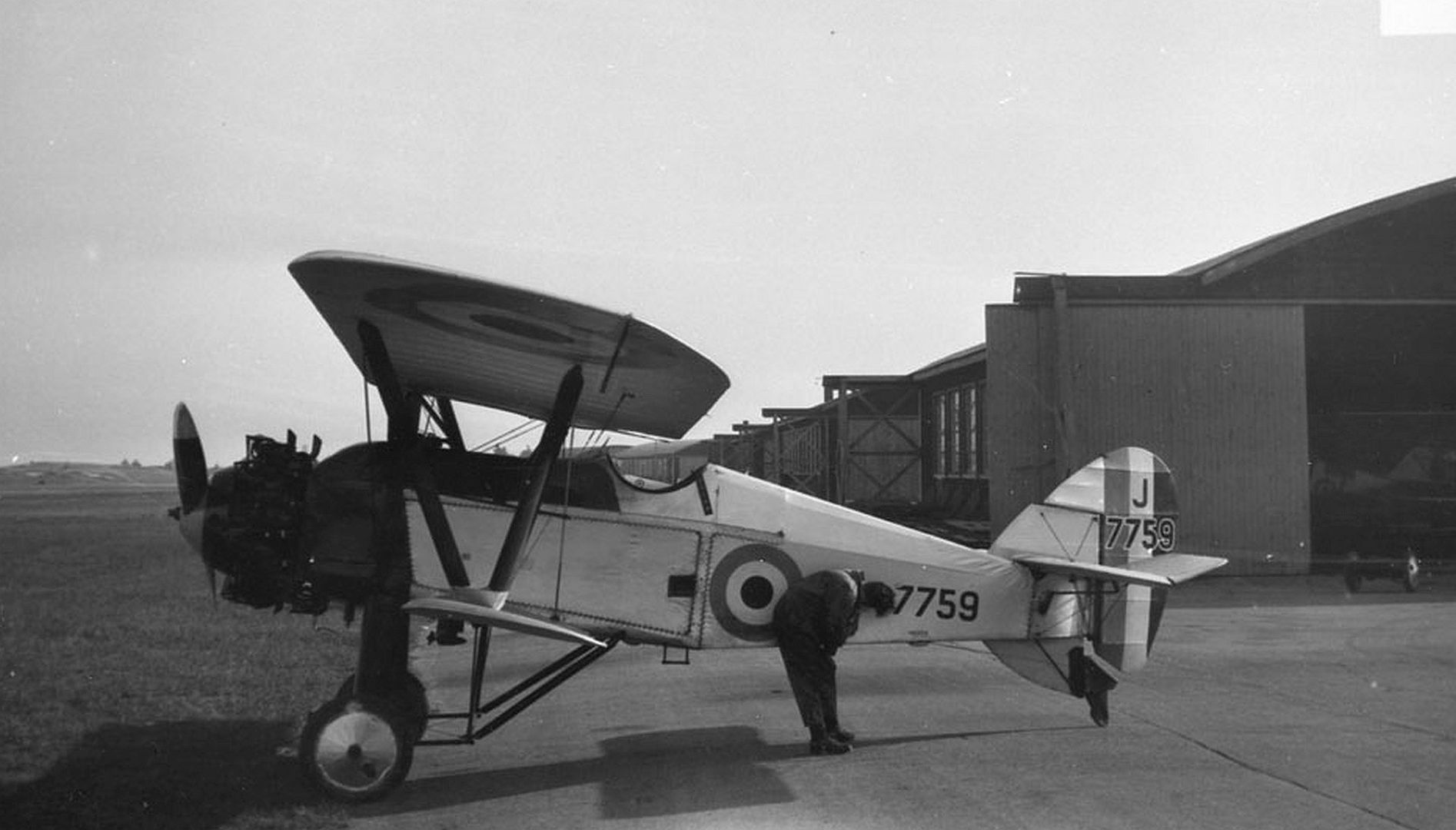
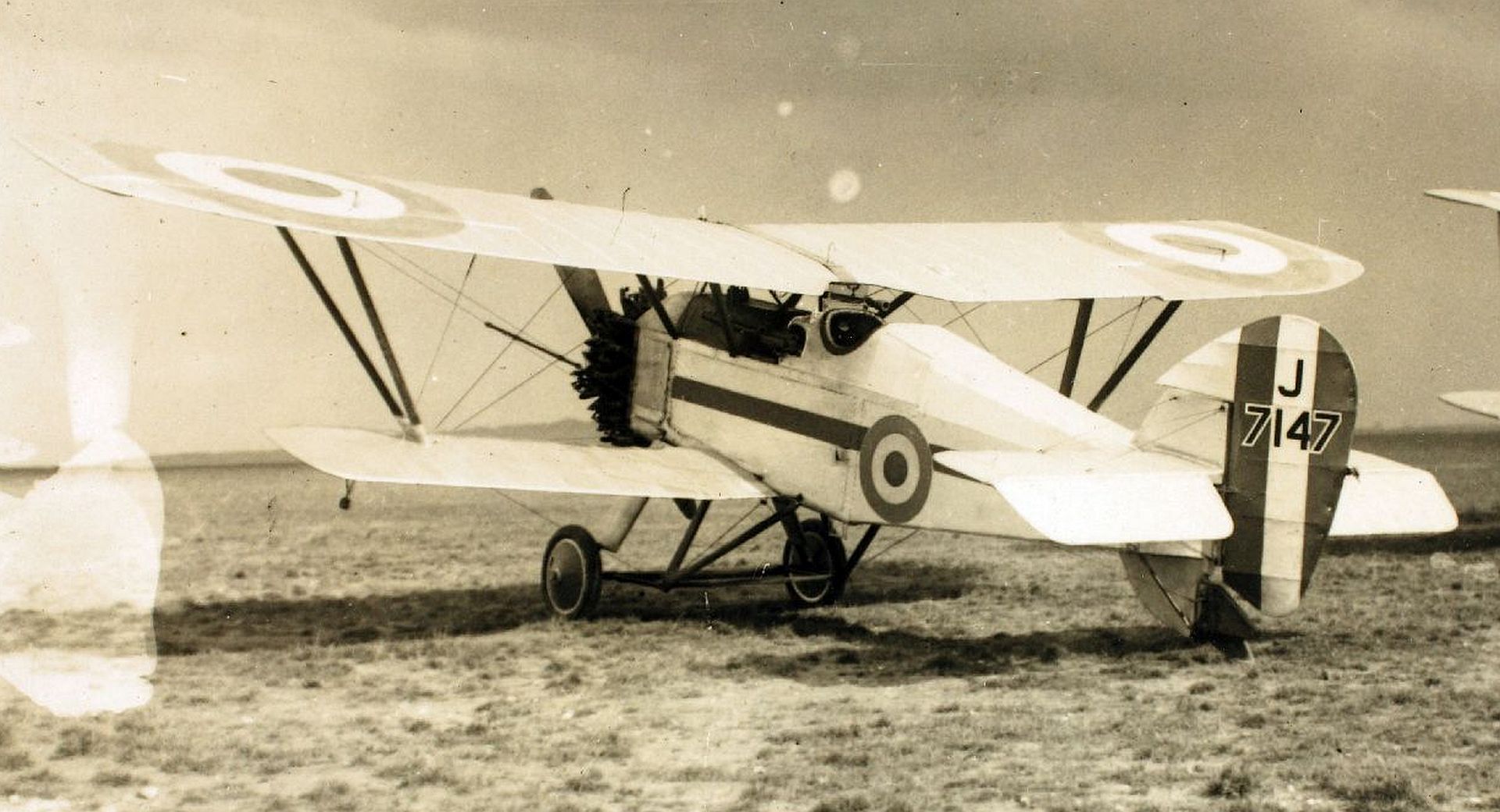
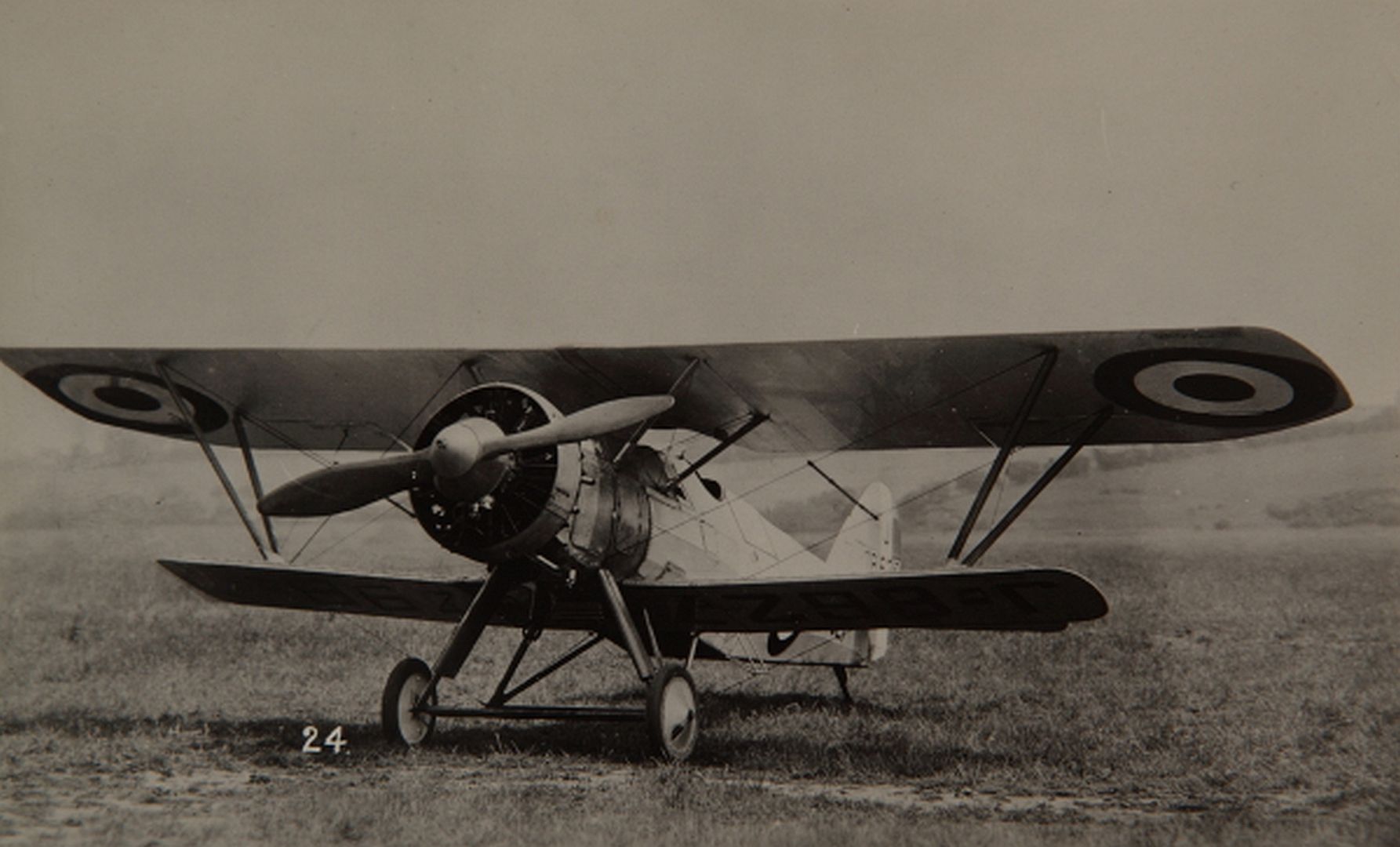



























Specifications (Siskin IIIA)
Crew: 1
Length: 25 ft 4 in (7.72 m)
Wingspan: 33 ft 2 in (10.11 m)
Height: 10 ft 2 in (3.10 m)
Wing area: 293 ft? (27.22 m?)
Empty weight: 2,061 lb (935 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 3,012 lb (1,366 kg)
Powerplant: 1 ? Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar IV radial engine, 385 hp (287 kW)
Performance
Maximum speed: 136 kn (156 mph, 251 km/h) at sea level
Range: 243 nmi[27] (280 mi, 450 km)
Service ceiling: 27,000 ft (8,230 m)
Rate of climb: 2,953 ft/min (900 m/min)
Endurance: 1 hour 12 minutes
Climb to 10,000 ft: 7 min 5 sec
Armament
2 ? 0.303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers machine guns
Provision for up to 4 ? 20 lb (9 kg) bombs under wings.
Post a reply
- Go to Previous topic
- Go to Next topic
- Go to Welcome
- Go to Introduce Yourself
- Go to General Discussion
- Go to Screenshots, Images and Videos
- Go to Off topic
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinning Tips / Tutorials
- Go to Skin Requests
- Go to IJAAF Library
- Go to Luftwaffe Library
- Go to RAF Library
- Go to USAAF / USN Library
- Go to Misc Library
- Go to The Ops Room
- Go to Made in Germany
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Juri's Air-Raid Shelter
- Go to Campaigns and Missions
- Go to Works in Progress
- Go to Skinpacks
- Go to External Projects Discussion
- Go to Books & Resources
